Natural Selection
1/27
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
28 Terms
Natural selection- def
Process by which fitter individuals who r better adapted to the environment survive and pass on the advantageous alleles/genes to future generations.
Main driving force of evolution: “survival of the fittest”.
Process of natural selection
Some individuals in a pop- hv a phenotype- aids their survival in presence of selection pressure- r best adapted to survive and breed.
Those that survive- reproduce + pass on advantageous alleles to their offspring- process repeats over many gens- frequency of advantageous allele increases. Those who don’t hv the advantageous allele r less likely to survive + pass on their alleles
Evolution
A change in the frequency of alleles in a gene pools over time as a result of natural selection. A change in the adaptive features of a pop over time as the result of natural selection.
Adaptation
Process by which pops become more suited to their environment over many gens.
Selection pressure
An environmental factor which affects the change of survival of an organism
Environmental factors- def
A feature of the environment of an organism that affects its survival.
Environmental factors
Abiotic/ biotic
Can limit pop size by decreasing the rate of pop growth whenever a pop reaches a certain size.
Pop limitation
Comp for food
Comp for reproductive mate
Supply of water
Temp
Comp for food
Limited supply of prey for predators- many carnivores will be hunting the same prey. If an animal cant hunt/feed- dies
Comp for reproductive mate (lions)
Female lions often outnumber male lions in app. Males compete w each other to mate w females.
During the contest- male lion could be injured/ killed. Male loses- cant pass on his alleles to any offspring
Supply of water
Arid/dry areas- water sources can be far from each other. Can die of dehydration if water sources dries up
Temp
Extreme heat- overheat + die. Can prevent animals from hunting during the day for long periods- less likely to get food
Types of selection
Environmental factors that affect the chance of survival of an organism. A selection pressure determines which traits are successful.
Stablising, directional, disruptive
Selection pressure
An environmental factors that affects the chances of survival of an organism. Increase chance of sample alleles being passed on to the next gen
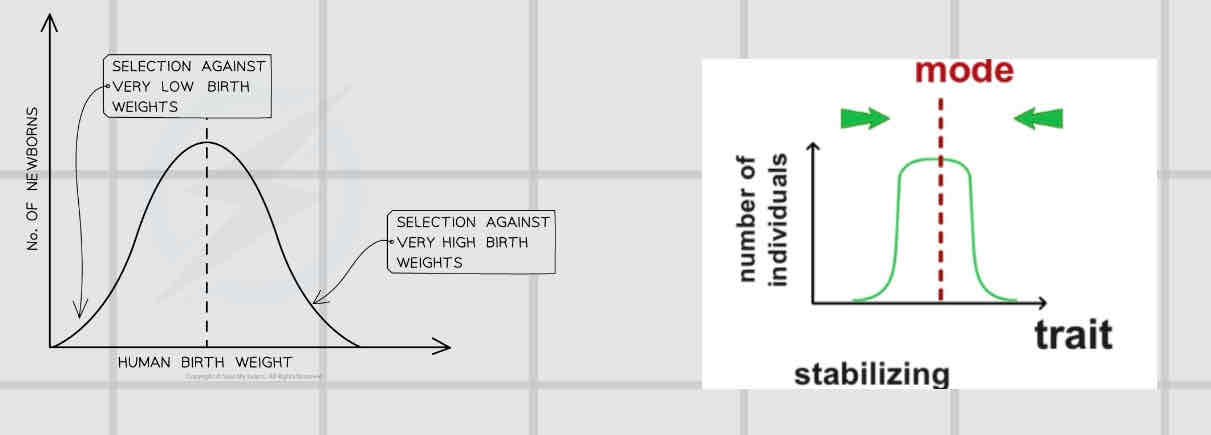
Stabilising
Keeps allele frequencies constant over generations. Changes if there is a change in the environment
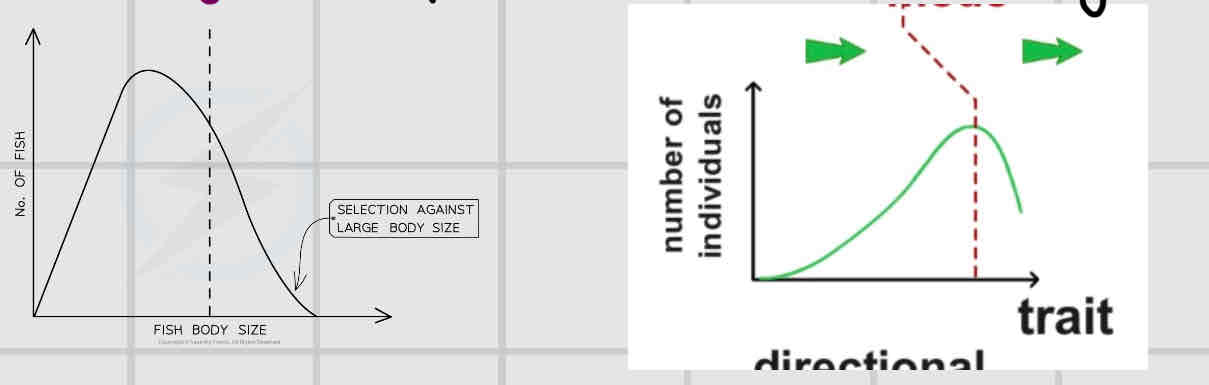
Directional
Produces a gradual change in allele frequencies over several gens. This occurs when there is a change in the environment which can lead to certain alleles becoming advantageous.
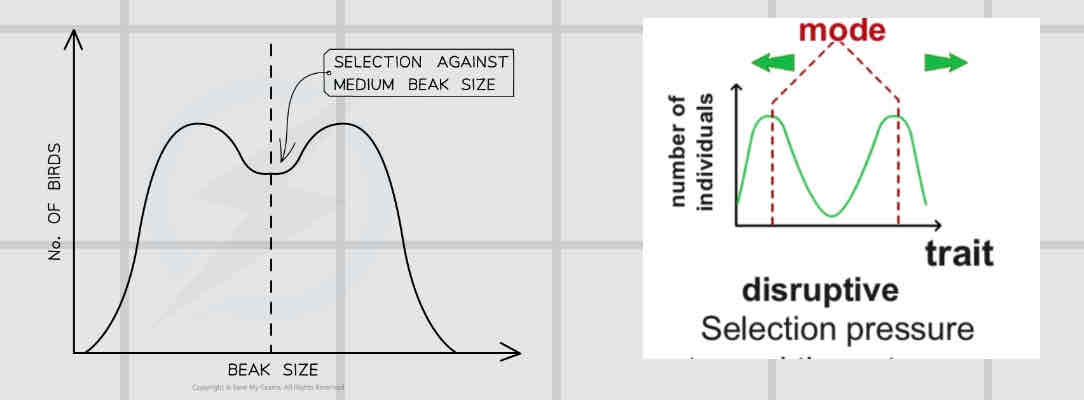
Disruptive
Maintains high frequencies of 2 diff sets of alleles.
Bimodal distribution
Both extremes r selected for/ favoured
It maintains polymorphism.
polymorphism.- continued existence of 2 or more distinct phenotypes in the species.
Occurs in an environment which shows variation.
Changes in allele frequencies
Caused by evolution. Selective pressure decreases the likelihood that certain individuals w specific alleles survive to reproductive age- prevents alleles being passed on.
Genetic drift
Directional selection
Founder + bottleneck effect
Genetic drift- def
A change in allele frequencies due to random sampling/ chance
Alleles can be passed on/ lost purely by chance
Not due to natural selection
Genetic drift- explanation
Small pop- chance can affect what alleles r passed on.
Meiosis- haploid gametes- half of the alleles passed on- results from RANDOM FERTILISATION.
Most likely to have when a small no. Of individuals r separated from the rest of a large population.
Only some of the organisms of each generation reproduce
Founder effect- def
When a few individuals from an existing pop relocate to an isolated area which results in a small pop breeding together and a small gene pool
Reduction in a gene pool compared w the main pops of a species, resulting in only 2/3 individuals who start of a new pop.
Founder effect- explain
A few individuals from a pop start of a new pop w a diff allele frequency that the OG pop.
Decrease in genetic diversity
Only some alleles from parent pop will be present.
More susceptible to effects of genetic drift as pop is v small.
Only part of the gene pool is present in this small pop
Alleles in the new pop may be present at different frequencies or can be missing all together
Evolution of the new pop may take a different direction than the original parent pop
Bottleneck effect- def
No. Of species fall to a v low level resulting in a loss of a large no. Of alleles + a reduction in the gene pool of the species.
Bottleneck effect explanation
Decrease in genetic diversity in the pop as alleles r lost.
Surviving pop end up breeding w close relatives- decrease in gene pool.
Hardy-Weinberg Principle- def
States that: allele frequencies remain constant from gen to gen based on these assumptions:
Pop is large. No selective pressures against on of the genotypes, no migration, mating is random, sexual reproduction, no mutations.
Hardy-Weinberg Principle- explain
Allows calc of allele frequencies.
Used to see if directional selection is acting on a pop.
Use it to determine the ratios of diff genotypes in a pop + using chi-squared test to compare them against those expected.
Frequencies r represented as proportions of the pop
Calc of H-W Principle.
p= frequency of dominant allele
q= frequency of recessive allele
p² + q² + 2pq= 1
p²= homozygous dominant= p*p
q²= homozygous recessive= q*q
2pq= chance of individual being heterozygous. Inherited dominant allele from father and recessive from mother= p*q= pq or vice versa= q*p= q-
Antibiotic resistance- process
Random mutation occurs. Selection pressure i.e antibiotics. An allele produced in a bacterium which gives it resistance to the effects of antibiotics- phenotype of resistance is displayed immediately. Those w adv allele hv a selective adv hence survive + reproduce. Pass on allele to their offspring. Frequency of allele increases.