Adult Echo 2 Final
1/106
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
107 Terms
A connective tissue disorder that often affects the elderly causes swelling and loss of mobility in the body's joints.
rheumatoid arthritis
Non primary cardiac tumors are how many more times as likely to occur than primary cardiac tumors?
20 times
Amyloidosis involves improperly folded _________ that infiltrate the myocardium.
proteins
Secondary metastatic tumors, frequently travel:
To the pericardium, myocardium and then to the endocardium
From the IVC to the right atrium and then to the right ventricle
From the pulmonary veins into the left atrium
All of the above
All of the Above
A skin lesion that develops in late stage AIDS infections is called
Kaposi's sarcoma
A dumb-bell shaped configuration of the inter-atrial septum often mistaken as cardiac mass is associated with:
Lipomatous hypertrophy
A common cardiomyopathy that develops in patients with chronic HIV infections is:
Dilated cardiomyopathy
Kawasaki's disease is an inflammatory illness that affects children. A cardiac manifestation of Kawasaki's disease is:
Dilated coronary arteries
Dilated ventricular chambers
Cardiac thrombus formation
Mitral regurgitation
Dilated coronary arteries
The most common primary malignant intracardiac tumor in adults is which of the following?
Myxoma
Papillary fibroelastoma
Angiosarcoma
Fibroma
Angiosarcoma
A cardiac manifestation of carcinoid is
Restricted TV leaflet motion
Restricted MV leaflet motion
PHTN
Aortic stenosis
Restricted TV leaflet motion
A well-encapsulated, small tumor composed of fat cells is named____________.
Lipoma
The following is true of rhabdomyomas:
Found in the ventricular walls
Most common cardiac tumor in children
Often obstruct the conduction pathways in the myocardium
All of the above
All of the above
The improper retention and storage of iron particles in the body is called:
Hemochromatosis
An arteritis that presents with intimal thickening of the aorta and it's major branches is called:
Takayasu’s Arteritis
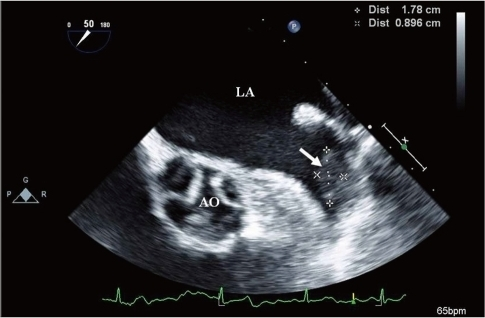
The TEE image of the left atrial appendage revealed:
A LAA clot
Normal velocity in the LAA?
>4m/s
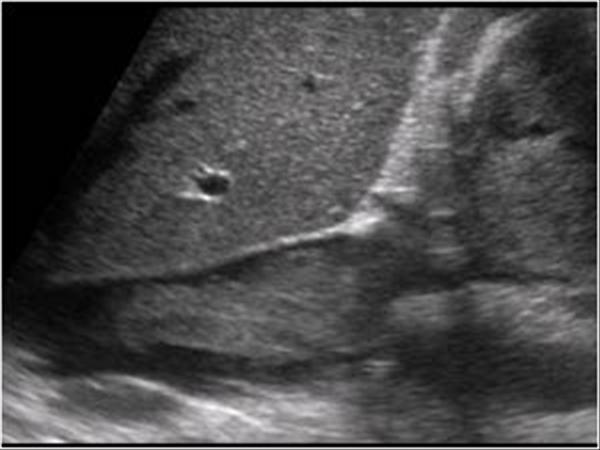
The mass in the IVC on the image above is most likely consistent with which of the following diagnoses?
Rhabdomyosarcoma
Myxoma
Infiltrative renal cell carcinoma
Angiosarcoma
Infiltrative renal cell carcinoma
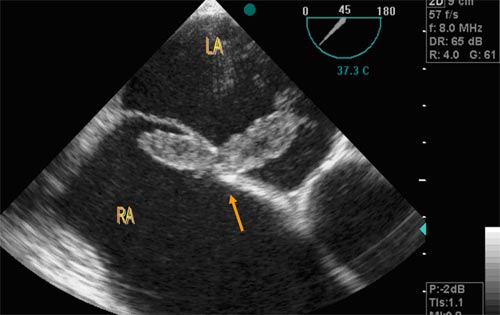
A patient is referred to the echo lab because of symptoms of TIA's. The patient had an echo previously which showed a small patent foramen ovale. A TEE is performed and reveals the above diagnosis.
Normal inter-atrial septum
Catheter protruding through the intra-atrial septum
A large clot lodged in the patent foramen ovale
An ASD closure device
A large clot lodged in the patent foramen ovale
In cases of secondary metastatic tumors in the heart, a common echocardiographic finding is
Pericardial effusion
Well-circumscribed mass with definitive borders
Thickening of the interatrial borders
Cystic space in the pericardium
Pericardial effusion
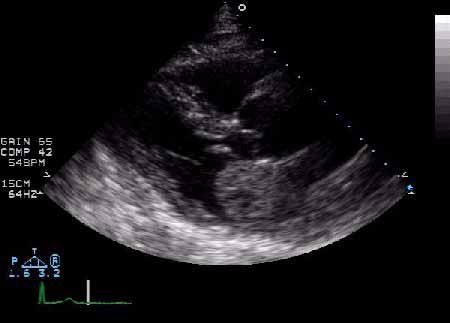
The image above demonstrates a benign primary cardiac tumor. The most likely diagnosis is which of the following?
right atrial myxoma
left atrial myxoma
right atrial hemangioma
left atrial hemangioma
left atrial myxoma
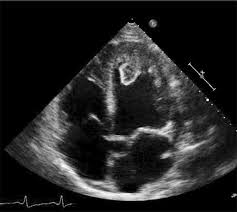
This was taken on a patient who has been diagnosed with postpartum cardiomyopathy and who currently has an ejection fraction of 20%. What is the most likely diagnosis?
left atrial myxoma
left mitral valve vegetation
left ventricular thrombus
right atrial myxoma
left ventricular thrombus
Most common benign cardiac Tumor:
Myxoma
Most common malignant cardiac tumor:
Angiosarcoma
Traits of Papillary Fibroelastomas:
Primary benign cardiac tumor
common on valves (AoV) & papillary muscles
Usually on arterial side of AoV
Small, mobile, pedunculated
May appear like Lambl’s excrescences
Largest concern is embolism
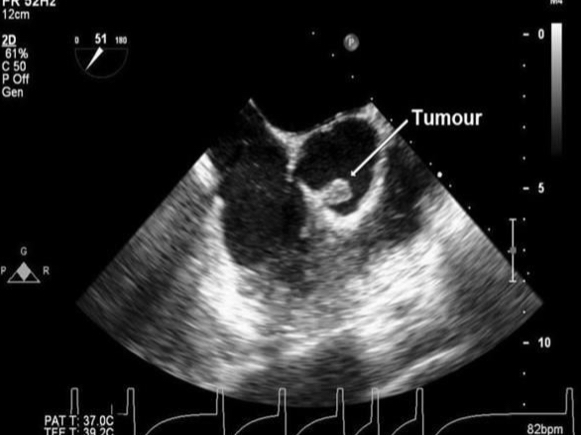
Traits of Fibromas
primary benign cardiac tumor
Bulky, made of fibrin tissue
Embedded in the myocardium of any chamber
Usually ventricular
Makes it difficult to remove, typically leads to transplant
Usually intramural
Usually solitary
Age range: 2 - 5
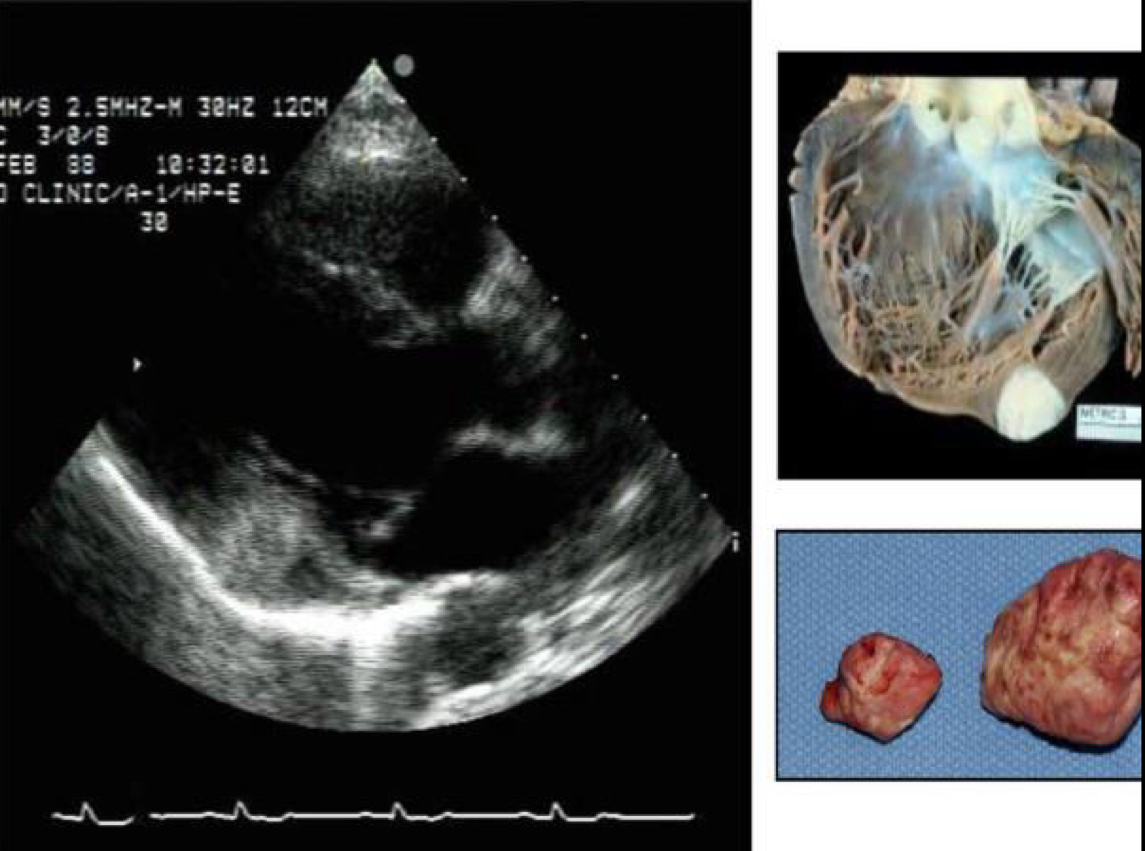
Angiosarcomas mostly occur in which cardiac chamber?
RA
Common primary benign cardiac tumors:
Myxoma
papillary fibroelastoma
Lipoma
Rhabdomyoma
Fibroma
Primary malignant cardiac tumors
angiosarcoma
Rhabdomyosarcoma
Other (rare) ones: fibrosarcoma, lymphoma, sarcoma, mesothelioma
Where is cardiac thrombus most often located?
LV
LAA
IVC/RA
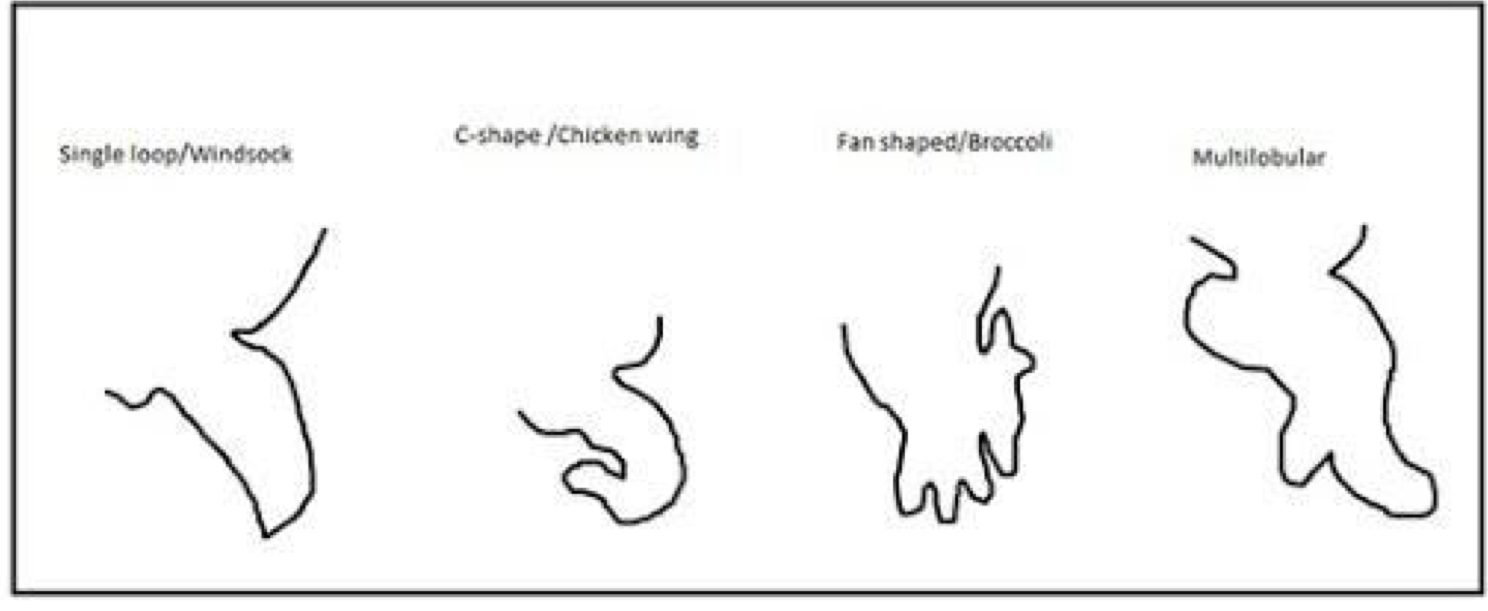
Different LAA shapes:
Treatments for cardiac thrombus:
anti-coagulation
NOAC/DOAC: apixiban
Heparin
Thrombolysis
EKOS: Ultrasound assisted catheter-delivered thrombolysis. Thrombus “opens up” d/t ultrasound and allows more medication into the thrombus
Oral
Thrombectomy
Angiovac
Surgical
What are some indications to use EKOS?
When should it be turned off/not used?
most commonly used for pulmonary embolisms
Can be used for critical DVTs
MUST be turned off during echocardiograms
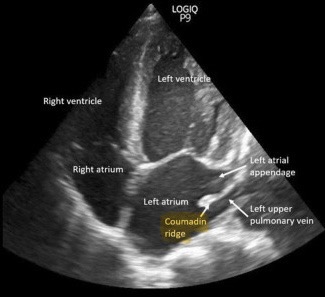
What is the Ridge of Coumadin?
a part of the left atrium that lies between the left atrial appendage
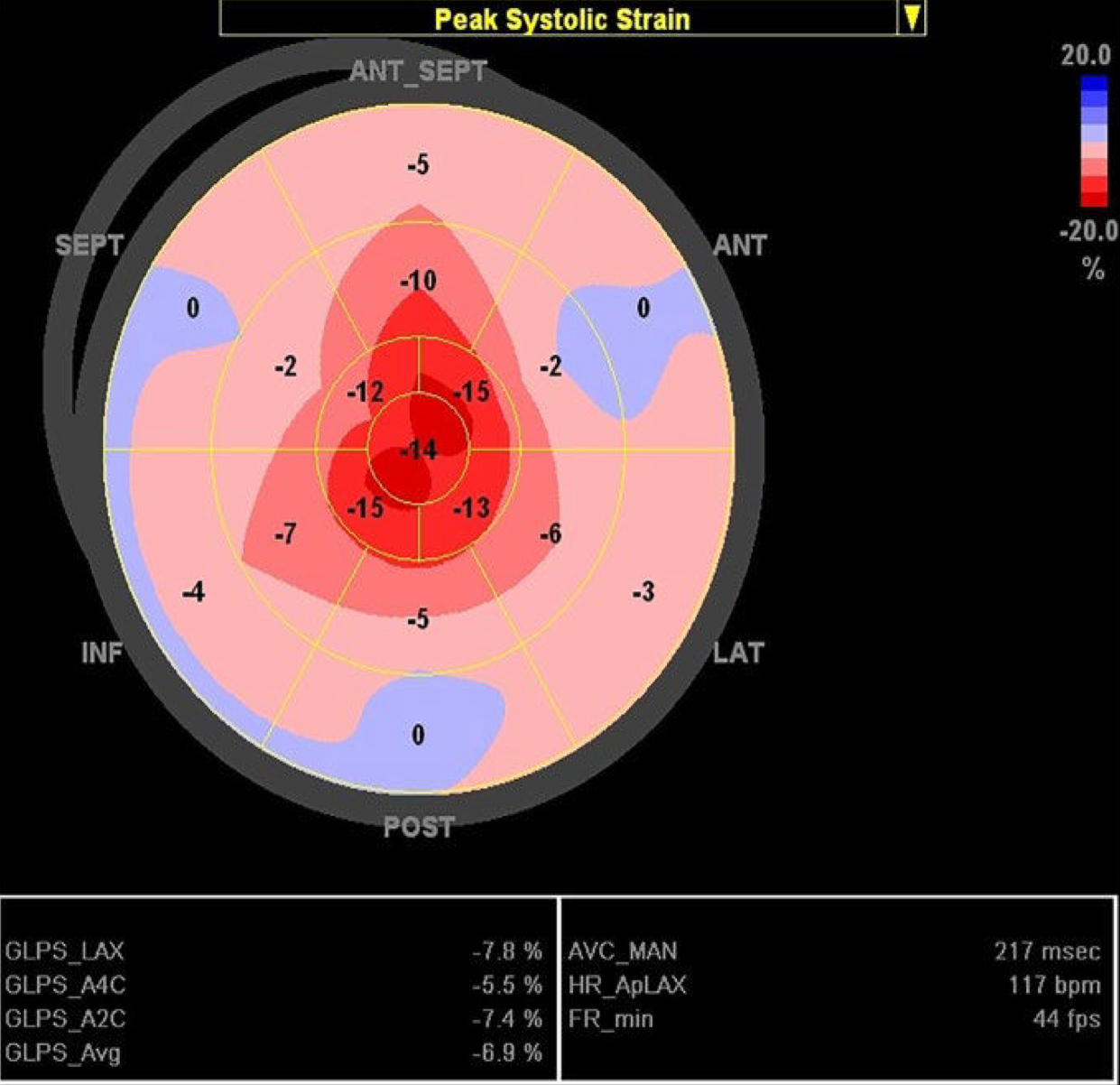
Echo features of amyloidosis:
Ground Glass, Granular, “Sparkling” myocardium
Apical Sparing (strain pattern)
Ventricular hypertrophy
Atrial Dilatation
Pericardial/pleural effusion
Diastolic Dysfunction
thickened valves w/ regurgitation
thickened IAS
thickened papillary muscles
What is the typical strain pattern for amyloidosis? Is it specific for this disease?
Apical Sparing: a preservation of contractility in the apical segments, with a decrease in the basal & mid segments
It is NOT specific for amyloidosis
Traits of Myxomas
Primary benign cardiac tumor
Usually pedunculated on/near the IAS
Most common in the LA
Gelatinous Texture
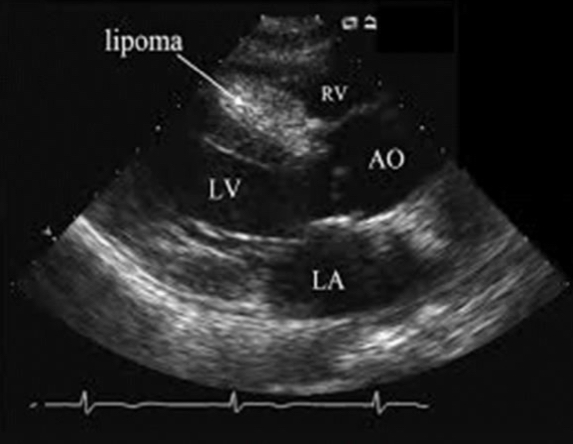
Traits of Lipomas
Primary benign cardiac tumor
Encapsulated
Most commonly in LV, RA, or IAS
Can occur in any heart layer
Mostly sessile (NOT pedunculated/attached by a stalk)
Typically asymptomatic
Traits of Hemangiomas
primary & benign
comprised of blood vessels & tissue
Most commonly in the ventricles
What disease is associated with rhabdomyomas?
tuberous sclerosis
Rhabomyomas are most commonly found in which age group?
in children
Traits of Rhabdomyomas
primary benign cardiac tumor
Most common tumor in children
Yellowish-gray color
made of muscle cells
Invades ventricular myocardium
May cause arrhythmias
Associated w/ tuberous sclerosis
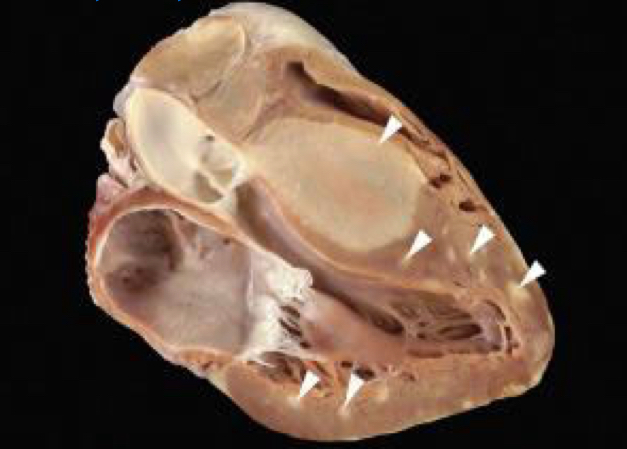
Traits of Angiosarcomas
primary malignant cardiac tumor
Most common primary malignant tumor
Mostly occur in the RA
Large, mural mass
May extend into the pericardium
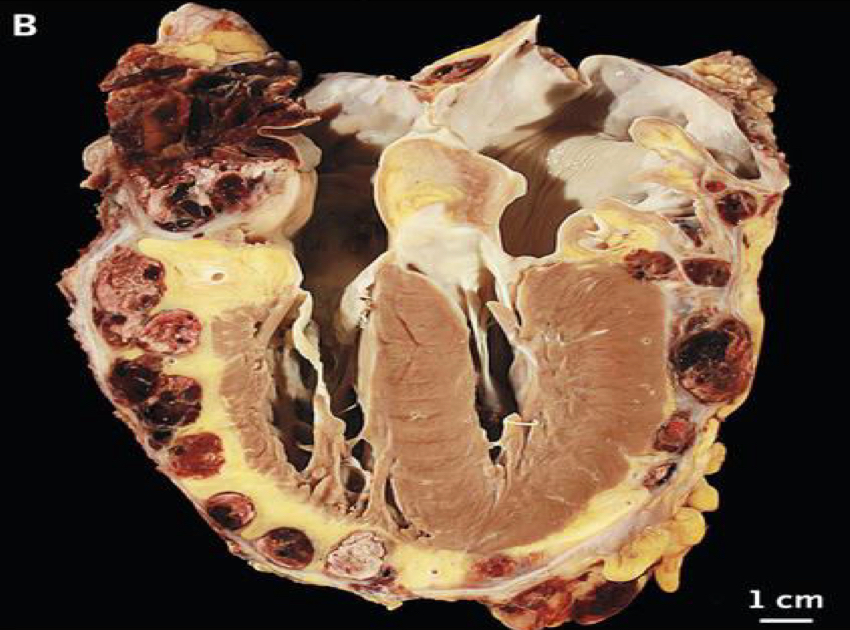
Traits of Carcinoid tumors
secondary & malignant
often originate in the digestive system
metastasize to the liver & releases serotonin
Mostly affects right heart valves
Traits of rhabdomyosarcomas
primary & malignant
often embedded in ventricular myocardium
Traits of Osteosarcomas (in the heart)
Secondary & Malignant
originates in bone
rarely mets to the heart
Traits of Fibrosarcomas
Primary & malignant
infiltrates the entire heart
Traits of melanoma (in the heart)
secondary & malignant
skin cancer
commonly mets to the brain and heart
Traits of Lymphoma (in the heart)
secondary & malignant
commonly in the RA
assocaited with pericardial effusion
Traits of squamous cell carcinoma (in the heart)
secondary & malignant
typically originates int he lungs
can travel via the pulmonary veins or pericardium
Connective tissue disorder caused by a defect in the synthesis of collagen causing loose joints, hyper-elastic skin and easily damaged blood vessels—there are treatments but no cure.
Ehler’s-Danlos
A rare neuro-developmental disorder characterized by a distinctive, "elfin" facial appearance along with a low nasal bridge,an unusually cheerful demeanor and ease with strangers. Cardiovascular problems include: supravalvular AS, hypercalcemia
William’s Syndrome
Also known as brittle bone disease. Abnormal collagen formation
Osteogenesis imperfecta
An inherited disease of the nervous system: Heart disorders include atrial fibrillation, tachycardia and hypertrophic cardiomyopathy
Friedrich' ataxia
An inherited disease of the nervous system: Heart disorders include atrial fibrillation, tachycardia and hypertrophic cardiomyopathy
Friedrich' ataxia
Enlargment of the RV as a response to increased resistance or high blood pressure in the lungs.
Results in pulmonary hypertension, RVH, RV dilatation
Cor Pulmonale
A genetic disorder of the connective tissues. Heart disorders include MVP and dilated aorta
Marfan’s Syndrome
A set of four cardiac defects: Supravalvular mitral membrane, parachute mitral valve, subaortic stenosis and coarctation of the aorta.
Shone’s complex
The reversal of any congenital shunt from left to right to right to
left secondary to PHTN. It is a cyanotic heart defect consisting of VSD,
dextroposition of the aorta, pulmonary hypertension and RVH
Eisenmenger’s Syndrome
It is a very rare congenital heart disease with a partial or total loss of the myocardial muscle in the RV
Uhl’s
A disorder marked by the deposition of amyloid in various organs and tissues of the body. It may be associated with a chronic disease, such as rheumatoid arthritis, TB, or multiple myeloma
Amyloidosis
A disease in which eosinophils accumulate in the lung in response
to a parasitic infection. Cardiac damage caused by the damaging effects
of eosinophil granule proteins is known as Loeffler endocarditis
Loeffler’s
Hereditary disease which causes an overload of iron in the body
Hemochromatosis
A disease in which abnormal collections of chronic inflammatory
cells (granulomas) form as nodules in multiple organs. Cause is
unknown
Sarcoidosis
Tumor of the adrenal gland affecting heart rate and blood pressure
Pheochromocytoma
A rare multi-system genetic disease that causes non-malignant
tumors to grow in the brain and on other vital organs such as the
kidneys, heart, eyes, lungs and skin
Tuberous sclerosis
A form of pericarditis that is also known as the post-myocardial
infarction syndrome. It occurs 6-8 weeks after an infarction and is
characterized by chest pain and pericardial effusion
Dressler’s
A relatively common autosomal dominant congenital disorder considered to by a type of dwarfism. Heart disorders: PS, ASD, HOCM
Noonan’s
Chromosomal abnormality in which all or part of the sex chromosomes are absent. Cardiac problems include: Biscupid AV, coarctation of the aorta and anomolous venous drainage.
Turner’s Syndrome
Also known as "aortic arch syndrome" is a form of large vessel granulomatous vasculitis and massive intimal fibrosis. Mainly affects the aorta and pulmonary arteries.
Takayasu's arteritis
A congenital malformation of the tricuspid valve in which one,
two or all three leaflets are displaced downward from the annulus with
RV atrialization
Ebstein’s Anomaly
A disease characterized by a persistently elevated eosinophil count with involvement of the heart, nervous system or bone marrow. Causes endomyocardial fibrosis
Hypereosinophilia
A form of congenital heart disease consisting of an ASD and
mitral stenosis
Lutembacker’s
Abnormal accumulation of glycolipids in blood vessels, tissues and various organs causing impaired function
Fabry’s
Type of nonischemic cardiomyopathy that involves primarily the RV. It is characterized by hypokinetic areas involving the free wall of the RV, with fibrofatty replacement of the RV myocardium with associated arrhythmias.
Arrhythomogenic RV dysplasia
Parasite which can lead to cardiomyopathy
Chagas
A disease which damages muscle and nerve cells throughout the body. It is caused by an accumulation of glycogen. Can result in LVH, tumor like appearance of the papillary muscles and poor global ventricular systolic function
Pompe's
A genetic disorder that leads to abnormal blood vessel formation in the skin, mucous membranes, lungs, liver and brain. Also associated with pulmonary arteriovenous fistulas
Osler-Weber-Rendu
A chronic form of spondylitis in males marked by arrhythogenic RV dysplasia caused by abnormal protein formation.
Ankylosing spondylitis
A form of nonbacterial endocarditis that is seen in systemic lupus erythematosus.
Libman-Sack's
An autoimmune condition that develops in response to an
infection in another part of the body. Inflammatory arthritis
Reiter's
Congenital heart defect which is classically understood to involve four anatomical abnormalities. It is the most common cyanotic heart defect and the most common cause of blue baby syndrome—consists of PS, VSD, deviation of the aorta, RVH
Tetralogy of Fallot
Autoimmume disease where the body's immune system becomes
hyperactive and attacks normal, healthy tissue. Resulting symptoms
include inflammation, swelling, damage to joints, skin, kidneys, blood,
heart and lungs.
Lupus
A 34 year old man with lymphoma presents with a 3 week history of decreased exercise tolerance. Physical exam reveals a diaphoretic man with a BP of 90/60, HR of 120 and respiratory rate of 24/min. Lungs are clear, heart sounds are distant. Echo reveals a large, circumferential pericardial effusion with RV diastolic collapse. The most appropriate next step in treating this patient is which of the following?
Evaluate for RA systolic collapse
Record Doppler filling velocities with a respirometer
Insert a Swan-Ganz catheter
Perform a pericardiocentesis
Evaluate for RA systolic collapse
Etiological possibilities for the development of constrictive pericarditis include which of the following?
cardiac surgery
viral
bacterial
all of the above
all of the above
When evaluating a patient for cardiac tamponade, the echo helps determine the size, location and hemodynamic effects of the pericardial effusion on the heart. Cardiac tamponade is a diagnosis made by which of the following?
Cardiac catheterization
Electrocardiogram
Tamponade is a clinical diagnosis
Thoracotomy
Tamponade is a clinical diagnosis
Classic clinical signs and symptoms of constrictive pericarditis include which of the following?
pericardial knock
murmur
none of the above
Ewart's Sign
pericardial knock
the physiologic severity of a pericardial effusion largely depends on which of the following?
volume and rate of fluid accumulation
volume and presence or absence of loculations in the fluid
rate of accumulation and fluid composition
fluid composition
volume and rate of fluid accumulation
A small posterior echo-free space is detected during the systolic phase only by M-mode/2D echo. This is considered a:
Cardiac tamponade
Normal finding
Moderate pericardial effusion
Large pericardial effusion
Normal finding
In order to be considered full blown tamponade physiology, which of the following must be present?
right ventricular systolic collapse and right atrial diastolic collapse
right ventricular diastolic collapse and right atrial systolic collapse
left atrial systolic collapse and right ventricular diastolic collapse
left ventricular collapse and right atrial collapse throughout systole and diastole
right ventricular diastolic collapse and right atrial systolic collapse
A 10 mmHg decrease in systemic blood pressure with inspiration associated with cardiac tamponade is referred to as which of the following?
Beck's triad
precordium
orthostatic hypotension
pulsus paradoxus
pulsus paradoxus
What are the components of Beck’s Triad?
hypotension
JVD
Muffled heart sounds
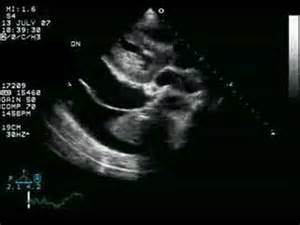
What diagnosis can be made from this echo image?
Normal parasternal long axis
Pericardial effusion
Pericardial and pleural effusion
Pleural effusion
A 45-year old female presents to her doctor with complaints of increasing dyspnea on exertion for three months. Her physical exam reveals jugular venous distention, ascites and a pericardial knock. What is the most likely diagnosis?
Constrictive pericarditis
Constrictive pericarditis is best defined as which of the following?
a condition in which a pericardial effusion results in tamponade physiology
a condition in which the patient develops an outflow tract obstruction
a condition in which the pericardium becomes thickened and fibrotic
none of the above
a condition in which the pericardium becomes thickened and fibrotic
(T/F) The best way to differentiate constrictive pericarditis from restrictive cardiomyopathy is by determining if respiratory variation is present.
True
Which of the following does not present the possibility for development of constrictive pericarditis?
cardiac surgery
Viral infection
Bacterial infection
Aortic dissection
aortic dissection
Pulsed-wave Doppler evidence of cardiac tamponade includes:
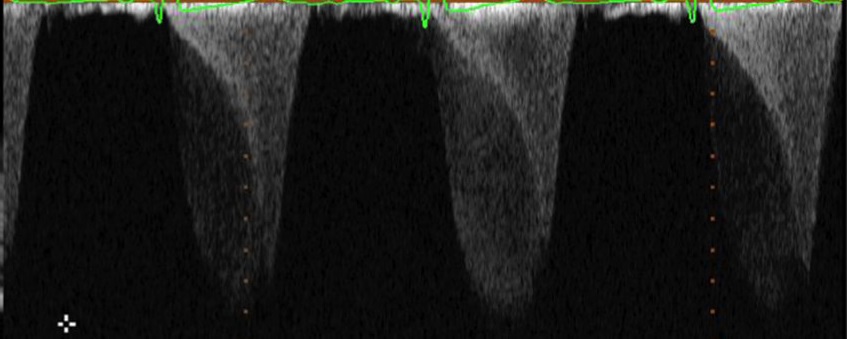
A 45 year old patient comes to the lab as a referral from his doctor. He has had elevated blood pressure that has not responded to traditional medications. When performing his echo, you attempt to CW the MV to evaluate for any MR. You get the resulting waveform. What do we see here?