Chapter 13 - Alkenes
1/23
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
24 Terms
alkene
unsaturated hydrocarbon containing a C=C double bond comprising a pi bond and a sigma bond
general formula
CnH2n
π-bond
formed by the sideways overlap of adjacent p-orbitals above and below the bonding C atoms - creates areas of electron density
-locks carbon atoms so double bond has restricted rotation
why are π-bonds weaker than σ-bonds?
the sideways overlap of the p-orbitals has a smaller orbital overlap than the direct/head-on overlap of orbitals in the sigma bond so less energy required
why are alkenes very reactive?
the pi bond has a relatively low bonding enthalpy so it can readily break as its electrons are very exposed (high electron density)
what is the shape around the double bond?
trigonal planar = 120
stereoisomers
compounds with the same structural formula but with a different arrangement in space
Cahn-Ingold-Prelog (CIP) rules
the priority is given to atoms or groups with the highest atomic number to decide if E or Z stereoisomerism
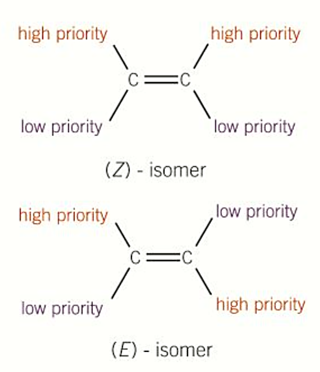
E-Z isomerism
isomers resulting from different spatial arrangements around a double bond
-what is needed: restricted rotation of groups/atoms around double bond, different groups attached to each carbon atom
-the E or Z go at the beginning of name
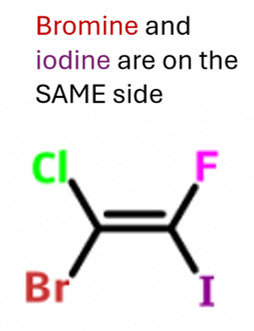
E-isomer
when the atom/group with the highest atomic number on each carbon atom are on opposite sides (Enemies)
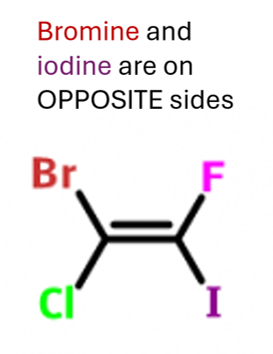
Z-isomer
when the atom/group with the highest atomic number of each carbon atom are on the same side (Zame Zide)
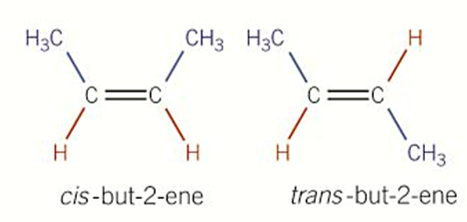
Cis-Trans Isomerism
when an atom/group attached to the carbon atom are the same
Cis-isomer = Z-isomer
Trans-isomer = E-isomer
electrophile
an electron pair acceptor
HYDROGENATION of alkenes
-reaction where hydrogen is added across double bond
-turns alkenes into alkanes
-conditions needed: temp = 150+, nickel catalyst
HYDRATION of alkenes
-reaction where steam is added across double bond
-turns alkenes into alcohols
-conditions needed: steam, high temp + pressure, acid catalyst (usually phosphoric acid)
electrophilic addition mechanism (DRAW)
.
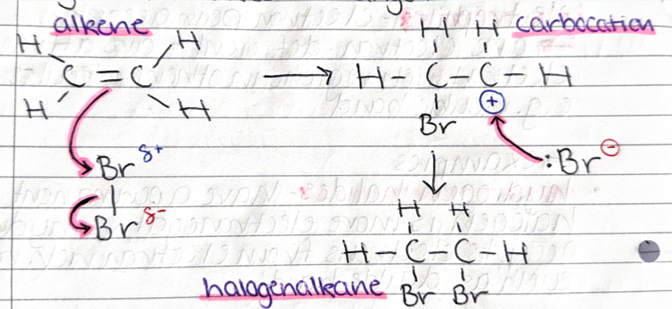
STABILITY of carbocations
electrophiles react with unsymmetrical alkenes so different products are formed with varying stability
-least to most stable = primary, secondary, tertiary

the inductive effect
when electrons from each alkyl group are pushed towards the positively charged carbon atom
-the larger the number of alkyl groups, the greater the inductive effect which causes increase in stability of carbocation
-helps to reduce positive charge of carbon atom + spreads it out
Markownikoff’s Rule
-electrophilic addition reactions with unsymmetrical alkenes will produce a major product and a minor product
-the more stable carbocation = major
-the less stable carbocation = minor
-order from minor to major = primary, secondary, tertiary
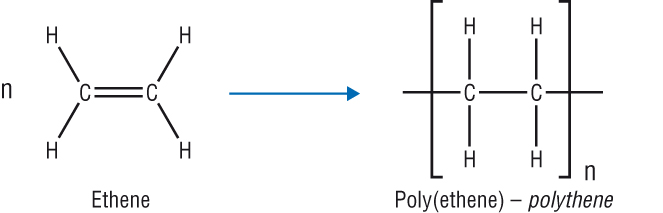
addition polymerisation
unsaturated alkenes converted into long saturated alkanes
-contains 1 monomer
general equation of addition polymerisation (DRAW)
.
DISPOSAL of polymers -3 ways
1) recycling
2) combustion for energy production
3) use as an organic feedstock
advs + disadvs of combustion
advs = energy used to produce electricity
disadvs = formation of CO2, formation of HCl or Cl2, formation of CO
bioplastics
biodegradable = broken down by microorganisms into water, carbon dioxide + biological compounds
photodegradable = bonds broken down chemically by absorbing light