Molecular Cell Biology Test 2
1/273
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
274 Terms
How does systemic lupus erythematosus affect the body?
causes the body to produce antibodies to multiple vital proteins (such as PCNA), disrupting their function and damaging cell function
symptoms of systemic lupus erythematosus
inflammation throughout body, tissue damage, fatigue, frequent fevers, joint pain
what testing system is used for diagnosis of systemic lupus erythematosus?
ELISA
What does ELISA stand for
enzyme linked immunosorbent assay
How does ELISA work?
create grid of wells, each lined with different protein commonly attacked by the lupus
sample blood of patient, place into wells
If the blood carries antibodies for that protein, it will stick to the walls
Use secondary antibody for protein antibody
Secondary protein carries HRP (horseradish peroxidase) which will convert TMB into a blue coloured substrate
Therefore, if blue appears in the well, then there were antibodies for that protein present
Who was the leading voice for the Central Dogma theory?
Francis Crick
Transcription expresses…
genes
What direction does RNA polymerase read template strand?
3’-5’
What direction does RNA polymerase synthesize RNA?
5’-3’
Which strand of DNA is the template strand?
The strand read by RNA polymerase to synthesize a complimentary strand of RNA
Which strand of DNA is the coding strand?
The strand NOT read by RNA polymerase, instead it matches up base-wise with the synthesized RNA strand
the strand of mRNA produced is base-wise the same as the….
coding strand
What is different between DNA nucleotide and RNA nucleotide
They have different sugars (ribose for RNA, deoxyribose for DNA)
They have 1 different base each (DNA = Thymine, RNA = Uracil)
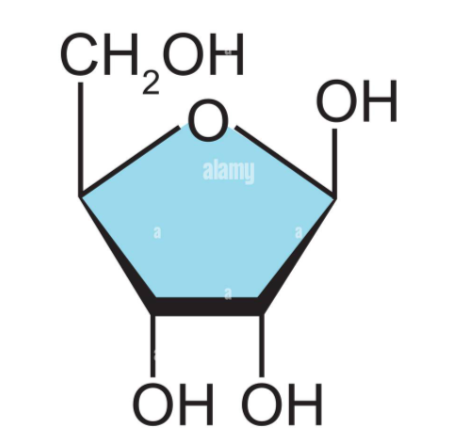
What sugar is this?
Ribose
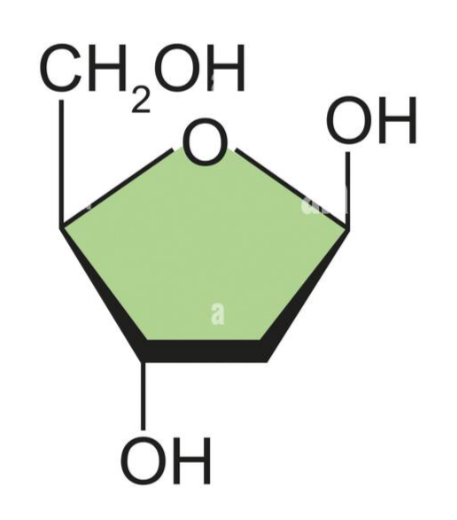
What base is this?
Deoxyribose
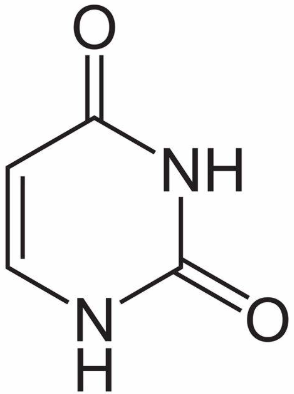
What base is this?
Uracil
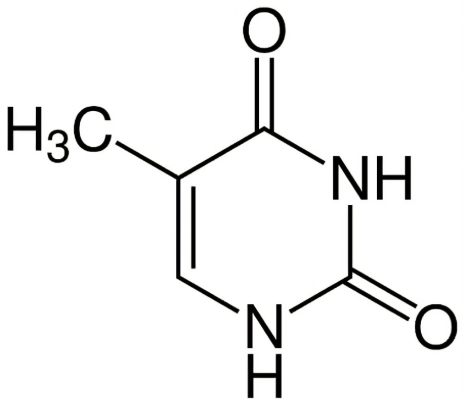
What base is this?
Thymine
What is the purpose of mRNA
codes for proteins
what percentage of all RNA in a cell is mRNA
2%
What is the purpose of rRNA
acts as the RNA component of ribosomes, never translated
what is the purpose of tRNA
acts as an adapter between mRNA and protein formation, carries AAs
who theorized existence of tRNA before it was actually discovered
Francis Crick
what is the purpose of miRNA
controls the expression of genes
size of miRNA
<22 bases in length
What is the purpose of lncRNA
regulates gene expression
what is the purpose of other types of RNA found in cells
also aids in expression of genes
how long is lncRNA
200+ bases
RNA polymerase is ____-dependant
DNA
does RNA polymerase require helicase to open the helix?
No, it does not
what is the function of RNA polymerase
binds to DNA, opens up double helix, begins synthesis by reading template strand
RNA polymerase acts as both a _____
catalyst and denaturing agent
Types of RNA polymerase
RNA poly I
RNA poly II
RNA poly III
Purpose of RNA poly I
transcribes and initiates rRNA transcript
Purpose of RNA poly II
transcribes protein coding transcripts (mRNA) and miRNA
purpose of RNA poly III
transcribes tRNA transcripts and some rRNA
What is the promoter sequence of DNA
region which is never transcribed, acts as site where RNA poly can bind and initiate transcription
What number is assigned to the site of initiation of transcription
+1
where are the promoter sequences in prokaryotes?
-35 (TTGA box) and -10 (TATA box)
Sequence of nucleotides at -35 (P)
TTGACA
Sequence of nucleotides at -10 (P)
TATAAT
Are the promoter sequences the same for every organism?
No, but the ones used are the most common and applicable sequences
What allows RNA poly to bind to DNA in prokaryotes
sigma factor protein
how does the sigma factor protein work? (P)
acts as guide for RNA poly to find where to start transcription and bind to DNA
How does transcription initiation in Eukaryotes differ from P?
multiple proteins bind to TATA box to encourage transcription
general transcription factors
Used by all genes being transcribed, no specificity
Specific transcription factors
used by specialized cells to produce certain proteins, uses specific factors which bind to pull GTFs in
Types of GFPs
TFIID → TBP, TAF
TFIIB
TFIIF
TFIIE
TFIIH
Purpose of TFIID factor
first to bind to DNA, causes distortion that allows TFIIB to bind
Purpose of TBP factor
binds to TATA box,
Purpose of TAF factor
associates with TBP at TATA box, helps in initiation
Purpose of TFIIB factor
binds to DNA after TFIID to bring RNA pol to it
Purpose of TFIIF factor
assists in binding RNA poly to promoter site
TFIIE factor purpose
aids in forming initiation complex and in elongation process
TFIIH factor purpose
opens double helix at start site, also phosphorylates RNA pol II to release all other TFs and allow it to bind to DNA
what sequence is found at -35 (E)?
G/C G/C G/A CGCC (TFIIB)
what sequence is found at -10 (E)?
T A T A A T A A/T, TFIID subunit
what is an example of a specific transcription factor
MYoD
How does MYoD work?
acts as regulatory protein, binds to Ebox sequence due to high affinity near promoter
Ebox sequence
CANNTG
MYoD is ______
muscle-specific
MyoD is a _____ transcription regulator
Master
MyoD is expressed inly in ______ cells
muscle
the Ebox is found in
muscles cells, is specific
what would be the conseqence of no MyoD in an individual
no muscle cells would be produced, whih would result in no muscular tissue within that individual
what happens to cells who do not normally express MyoD when they are forced to express it
they transition into muscle cells → they begin producing muscular proteins and sequences, which transforms the cell
What is the phenomenon called when a cell is forced to express a different phenotype than expected or originally coded for (ex. forced MyoD expression in a non-muscle cell)
Transdifferentiation
how can a cell be forced into Transdifferentiation using MyoD?
attaching a sequence that codes for MyoD with a strong promoter that is recognized by the cells, such as CMV (viral promoter)
Transdifferentaition into neural cells
Done using NeuroD, will transform cell into neuron using overexpression of particular proteins
How would you determine a stretch of DNA is part of a promoter without knowing sequence of promoter?
know that promoter is upstream of gene sequence
use sequence for GFP to test immediately of gene is working
being damaging suspected region of bases, test if GFP is produced
Once part is damaged and no GFP is produced, the promoter region can be identified
Promoter bashing
damaging suspected promoter regions to identify where specifically boxes lay
truncation
process in promoter bashing where end sequences are chopped off to see if transcription is inhibited or not
nucleic acid hybridization
specific transcript identification process that uses labeled mRNA probes complimentary to target to identify
How are RNA probes made for hybridization?
all RNA is isolated in organism
RNA is converted into cDNA using reverse transcriptase; cDNA is amplified using PCR to produce multiple double stranded copies
T7 promoter is added, T7 RNA Polymerase binds to it and produces ssRNA → fluorochrome or gold particle is added to produced RNA for detection
using nucleic acid hybridization and northern blotting
process involving production of cDNA using reverse transcriptase to bind to mRNA, cDNA is then electrophoresed and northern blotted → used to identify quantities of RNA types present in an organism
does reverse transcriptase need a primer?
yes
what is PCR
polymerase chain reaction, allows for large volume of replication to occur
what is pcna
Proliferating cell nuclear antigen → type of protein
is DNA or RNA more stable?
DNA is more stable
Northern blotting
process of electrophoresis on RNA molecules to separate by size, which are blotted onto a membrane sheet → into saline solution containing RNA probes, which hybridize with matching strands
Then, glowing is tested for and the target sequences are identified and excised from the paper
is northern blotting sensitive?
it is moderately sensitive, and needs lots of material or the results will not be as accurate
what does RT-PCR stand for
reverse transcription based polymerase chain reaction
what is RT PCR
start with RNA
Reverse transcribe into cDNA with primer
use PCR to amplify cDNA, which can then be electrophoresed
is RT PCR sensitive
it is extremely sensitive; any changes get amplified
densiometery
using band thickness from electrophoresis to determine quantity
what does ISH stand for
In situ hybridization
what is ISH
way of identifying locations of mRNA produciton inside tissue
How does ISH work
use RNA probes which match with specific mRNA inside organism and wash across tissue → test visualization and detect probes in bonded in tissue
What are the three main kinds of modifications done to mRNA in eukaryotes
5’ capping, 3’ poly a tail addition, RNA splicing
what is 5’ capping
the addition of methyl guanosine cap to 5’ end of mRNA, protects molecule from degradation and helps in recognition of molecule
Does ISH have good resolution
It has a high resolution and is very quick
what is 3’ polyadenylation
addition of 50-200 A bases to 3’ end of mRNA, prevents RNA from degradation and increases survival
what enzyme adds adenine to 3’ tail
polyA-polymerase
does poly A polymerase need a template?
No, as it does not need to read one to add the tail
What is the name of the untranslated regions at the 5’ and 3’ ends of mRNA
5’ UTR and 3’ UTR
when does RNA processing occur
During transcription
what enzyme does the RNA processing
RNA polymerase II
how does RNA processing occur during transcription
C terminal tail of RNA poly II carries enzymes that signal for modification to occur when released, also carries phosphate groups to phosphorylate to allow enzymes to bind
How to determine consensus sequences that represent splice sites using bioinformatics
lay out sequence of full DNA, then sequence of spliced DNA (mRNA is published as DNA sequence)
Remove matching segments, left with introns
Find similarities between starting/ending sequences
What are the consensus sequences for intron splicing
GUXXX at 5’ end, AG at 3’ end. However, it is more complicated than just these bases (these can occur in exons and not cause splicing)
what base does Y refer to in sequences
any pyrimidine