Topic 6- alkenes, alkanes
1/53
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
54 Terms
Homologous series
A family of compounds with the same functional group, which differ in formula by CH2 form the next member
Functional group
An atom/ group of atoms in a molecule that is responsible for its chemical reactions
Structural formula of methyl
CH3
Structural formula of ethyl
C2H5
2 types of structural isomers
Chain isomerism (different length C chain).
Position isomers (functional group is in different positions)
What’s sterioisomerism
its the different arrangement of atoms in space.
What’s E and Z in sterioisomerism
E is Cis, Z is trans
What’s the rule for it to be a sterioisomer
Different groups must be in opposite sides of the double bond.
It can only happen in alkenes due to restricted rotation around the double bond
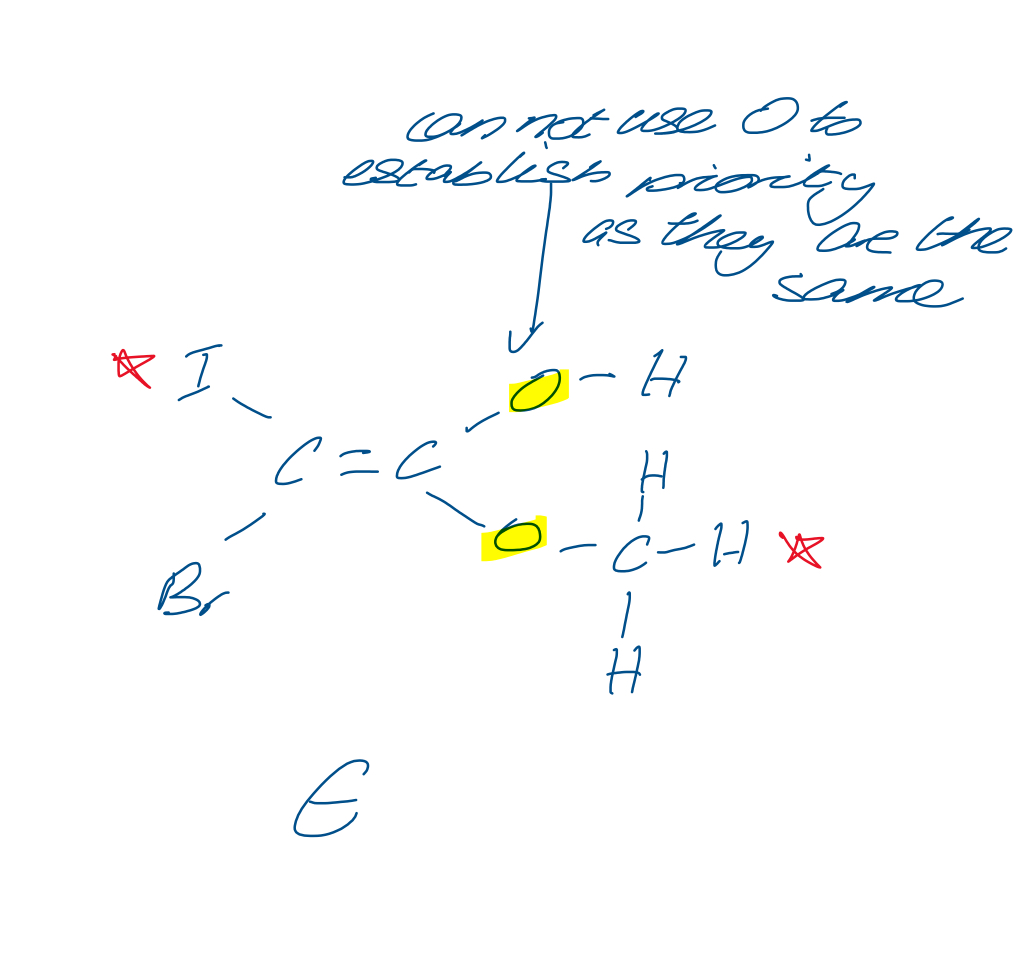
How do you assign E Z notation if all the groups are different
On the left side, see which has the higher Ar. Do the same omen the left side. Use those two to establish E or Z
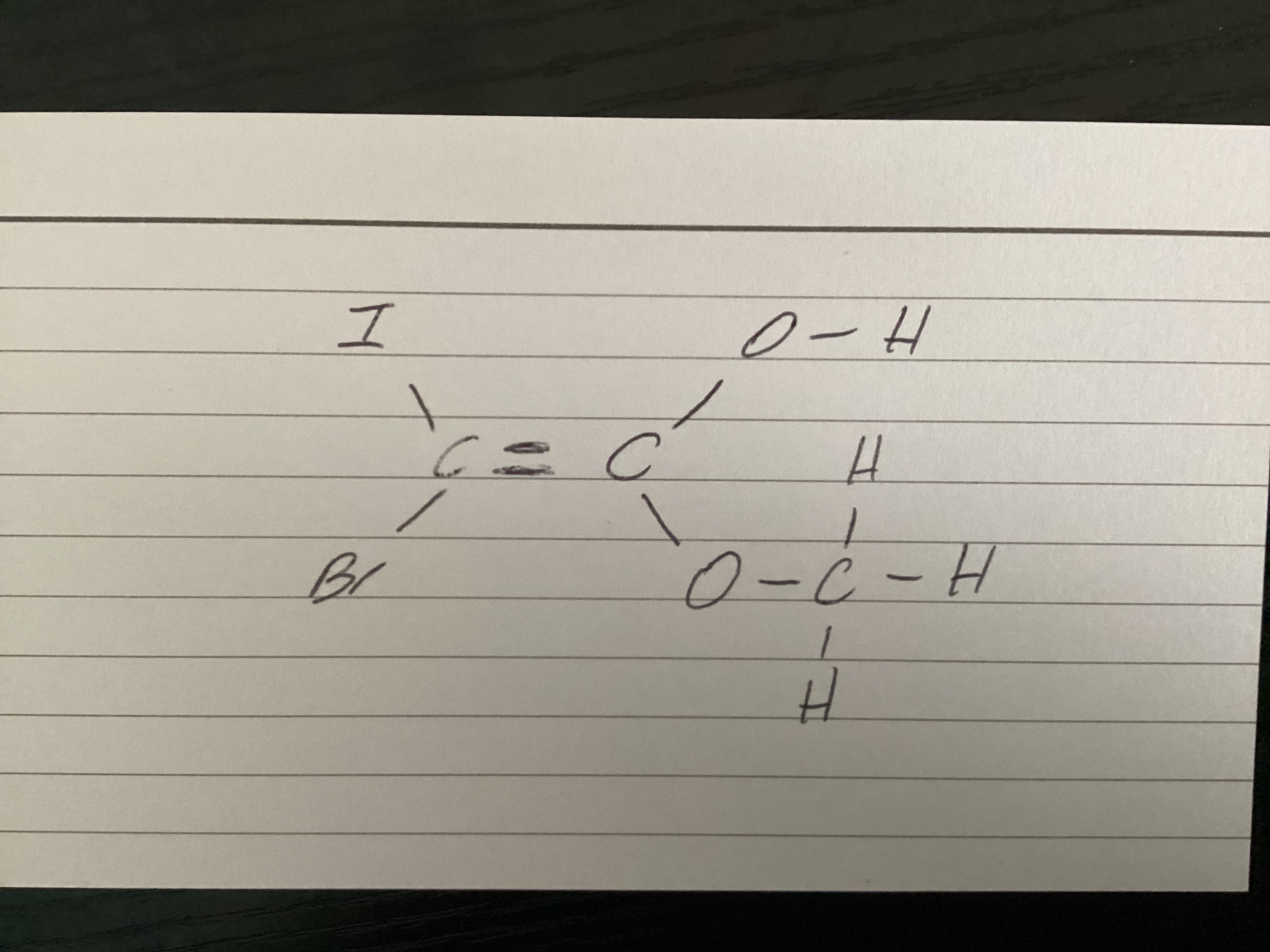
How do you assign E Z notation in this situation
What does alkanes being branched have to do with the boiling point
Lowers the boiling point as branches prevent alkane molecules from getting close together, weakening London forces (as they’re stronger the closer together)
Are alkanes polar
Not polar because C and H have similar electronegativities
Type of bonding and forces in alkanes. And reactivity
Covalent bonds called sigma bonds, only London forces. Unreactive cus of strong covalent
Why does strength of London forces increase as chain length increases
Longer chains have more electrons, and longer chain has a greater surface area so more places where London forces can form
What’s thermal cracking and why is it better that catalytic cracking
Heat + steam. Needs high pressure too
Better cus it makes a higher % of alkenes in the product.
What is catalytic cracking
Heat + catalyst
Which hydrocarbons make fuels and feedstock
Fuel = alkane.
Feedstock = alkene
What is reforming and how is it done
Changed straight chain into branched and cyclic for smoother burning in engines.
Done by heating with a platinum catalyst
Complete combustion of propane equations
C3H8(g) + 5O2(g) → 4H2O(l) + 3CO2(g)
2 incomplete combustion of propane equations
C3H8 + 4O2 → 2CO(g) + 4H2O(g) + CO2(g),
C3H8 + 4O2 → C(s) + 2CO2 + 4H2O
Problems with things released from incomplete combustion of alkanes
C - black smoke or soot.
CO- carbon monoxide interferes with uptake of O2 by red blood cells.
HC- unturned hydrocarbons appear as smoke and cause lung irritation and global dimming
All reactions in the oxidisation of sulfur
S(s) + O2(g) → SO2 (g).
2SO2(g) + O2 → 2SO3(g).
SO2 + H2O → H2SO3 (sulphurous acid).
SO3 + H2O → H2SO4 (sulphuric acid)
What is an acidic oxide
And oxide that has the properties of an acid e.g. SO2 and SO3
All reactions in the oxidation of nitrogen
N2(g) + O2(g) → 2NO(g).
2NO(g) + O2(g) → 2NO2(g).
2NO2 + H2O → HNO2 + HNO3
three catalysts in catalytic converters and what three pollutants they remove
Platinum, rhodium, and palladium = catalysts.
HC, CO, NOx = pollutants.
They don’t work properly when cold so pollutants are released in the initial few minutes of a car starting
3 catalytic converter reactions
2CO + O2 → 2CO2,
HC + O2 → CO2 + H2O,
2NO + CO → N2 + 2CO2
What’s biodiesel
Made form vegetable oils mixed with ordinary diesel
What’s bioethanol
Made by fermentation of sugars by yeast. Them distillation to concentrate the ethanol.
Now bacteria is used for fermentation as it gives a higher % of ethanol
Factors to consider when choosing biofuels
Land use, yield, manufacture/ transport, carbon neutrality
What’s a free radical
Any species with an unpaired electron
What’s homolytic fission
Both species formed from the breakup are the same (Cl• and Cl•)
Things needed for the chlorination of methane
at room temp = no traction.
With heat = chloromethane.
At room temp with UV light = chloromethane (photochemical chlorination of methane)
describe the mechanism for the reaction between butane and bromine that forms the products given in the equation bellow:
C4H10 + Br2 → C4H9Br + HBr
Initiation:
Br2 → 2Br•.
Propagation:
C4H10 + Br• → HBr + •C4H9.
Br2 + •C4H9Br + Br•.
Termination:
•C4H9 + Br• → C4H9Br.
•C4H9 + •C4H9 → C8H18.
Br• + Br• → Br2
Why do pi bonds make alkenes more reactive
Bond enthalpy is more in sigma than pi due to pi bonds being from sideways overlap, which is easier to break than the direct overlap in sigma.
There’s a pair of electrons in the sigma bind and a pair in pi. Therefore, the double bond is a region of high electron density, making them highly reactive molecules.
The electrons in the pi blonds are held more weakly and are more unusable to attach and the bond being broken. Pi bonds are weaker than sigma doe to where the shared electrons are found.
Why do addition reactions occurs to alkenes
The pi bond is open to attack and the addition of other species
What are the 5 additions reactions of alkenes
Hydrogenation of alkenes,
Halogenation,
Hydration,
Addition of hydrogen halides,
Oxidation to diols
conditions needed for the hydrogenation of alkenes
150°, nickel catalyst
How is hydrogenation used to make margarine
Hydrogenating vegetable oil.
This prowess increases the melting point making it more solid.
Unsaturated to saturated by breaking double bonds to add hydrogen.
Conditions needed for the halogenation of alkenes
There aren’t any
Conditions needed for the hydration of alkenes
phosphoric acid (H3PO4),
300°c,
60atm
Conditions needed for the addition of hydrogen halides to alkenes
There aren’t any
Conditions needed for the oxidation of alkenes to diols
Potassium manganate(VII) (oxidising agent).
Dilute sulphuric acid (for acidic conditions)
What’s a diol
Contains 2 hydroxyl (OH) groups
What happens when you oxidise an alkene to diols
Potassium manganate (VII) changes from purple to colourless
What’s heterolytic fission
When a covalent bond breaks with both electrons going towards one atom
What’s an Electrophile
electron deficient species (positive ions/ molecules) and can accept an electron pair from electron rich species.
E.g. carbocations and carbonyl compounds
What’s a nucleophile
electron rich species that donates electron pairs to electron deficient species.
e.g. include carbanions, water , ammonia, cyanide ion etc
What’s markownikoff’s rule
When a hydrogen halide reacts with an asymmetric alkene, the H atom of the hydrogen halide is more likely to bond to the C which is attached to the greater number of H atoms
Which is the most stable of 3° 2° 1° carbocations
Most 3° > 2° > 1° least stable
Why does the more stable carbocation give the major product
The positive charge of carbocation can be spread over more atoms, making it more stable, so can exist for a longer amount of time, because alkyl groups are electron releasing
Conditions needed for the addition reactions of alkenes
High temperature and pressure
Polymer of ethane
Poly(ethene)
Why do addition polymers exist in the environment for a long time
Difficult to break down cus they’re unreactive cus their bonds are non polar and relatively strong
ways to fix polymer waste
Recycle, reuse, incineration for energy, chemical feedstock (breaking into H and CO