IB Psychology: Hormones, Neurotransmission, Parts of the Brain & Brain Functions
1/82
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
83 Terms
What are hormones?
Class of chemicals that affect behaviour
How are hormones released?
Secreted by glands in the endocrine system
Where are hormones released into?
Bloodstream
How do hormones work?
they alter the operations of target cells by changing the types, quantities, or activities of important enzymes and structural proteins
Difference between hormones and neurotransmitters
hormones are not released by the terminal buttons of a neuron; instead, they are secreted by glands in the endocrine system
whereas neurons in the brain as a neurotransmitter
Hormones are released directly into the bloodstream; as a result, they take longer to produce changes in behaviour than neurotransmitters.
pineal gland
secretes melatonin
pituitary gland
The endocrine system's most influential gland. Under the influence of the hypothalamus, the pituitary regulates growth and controls other endocrine glands.
Hypothalamus
A neural structure lying below the thalamus; it directs several maintenance activities (eating, drinking, body temperature), helps govern the endocrine system via the pituitary gland, and is linked to emotion and reward.
fight or flight response
an emotional and physiological reaction to an emergency that increases readiness for action
sympathetic nervous system
the division of the autonomic nervous system that arouses the body, mobilizing its energy in stressful situations
parasympathetic nervous system
the division of the autonomic nervous system that calms the body, conserving its energy
adrenal glands
a pair of endocrine glands that sit just above the kidneys and secrete hormones (epinephrine and norepinephrine) that help arouse the body in times of stress.
Adrenaline
A hormone released into the bloodstream in response to physical or mental stress
Kiecolt-Glaser et al
investigated the effect of stress on wound healing and demonstrated that high levels of cortisol supress
Neurotransmission
The process by which these messages are sent.
Action potential
The electrical impulse that travels along the body of the neuron.
Neurotransmitters
A neurotransmitter is a chemical messenger that carries signals between neurons. Neurotransmitters are released from the terminal buttons at the end of an axon after the action potential has sent an electrical charge down the neuron. The neurotransmitter then crosses the synaptic gap to reach the receptor site on another neuron.
Reuptake
The reabsorption of a neurotransmitter by the terminal buttons of the pre-synaptic neuron after it has performed its function of transmitting a neural impulses. This prevents further activity of the neurotransmitter. Prozac is an SSRI - that is, a selective serotonin reuptake inhibitor, allowing more serotonin to remain in the synaptic gap.
Excitatory function:
These types of neurotransmitters increase the likelihood that the neuron will fire an action potential. It is also when a drug attaches to a receptor site for a neuron and activates the neuron as if the neurotransmitter was sending a message.
Inhibitory function:
When a neurotransmitter decreases the likelihood that the neuron will fire an action potential. It may also be when a drug attaches to a receptor site for a neurotransmitter and blocks the transmission across the synapse. For example, scopolamine does this to acetylcholine receptors.
Acetylcholine
The most common neurotransmitter. Acetylcholine receptor sites are found in the hippocampus. It appears that acetylcholine plays a key role in memory consolidation from STM to LTM.
Dopamine
A neurotransmitter that helps control the brain's reward and pleasure centers. Dopamine also helps regulate emotional responses. Dopamine deficiency results in Parkinson's Disease, and people with a lower number of dopamine receptor sites may be more prone to addiction.
Norepinephrine
Arousal and alertness. Increased norepinephrine produces feelings of exhilaration, excessive energy, sleeplessness and loss of appetite
Serotonin
A neurotransmitter that works to regulate mood, appetite, and sleep. Low levels of serotonin have been linked to Clinical Unipolar depression and high levels of aggression. High levels of serotonin have been linked to hallucinations.
Synaptic Cleft
the space between the presynaptic and postsynaptic neurons
Reuptake
A process in which neurotransmitters are sponged up from the synaptic cleft by the presynaptic membrane.
Cell body
includes a nucleus which contains the genetic material of the cell.
Dendrites
branch like structures come from the cell body and carry nerve impulses from neighbouring neurons towards the cell body
Myelin Sheath
fatty layer which protects the axon and speeds up electrical transmission of the impulse.
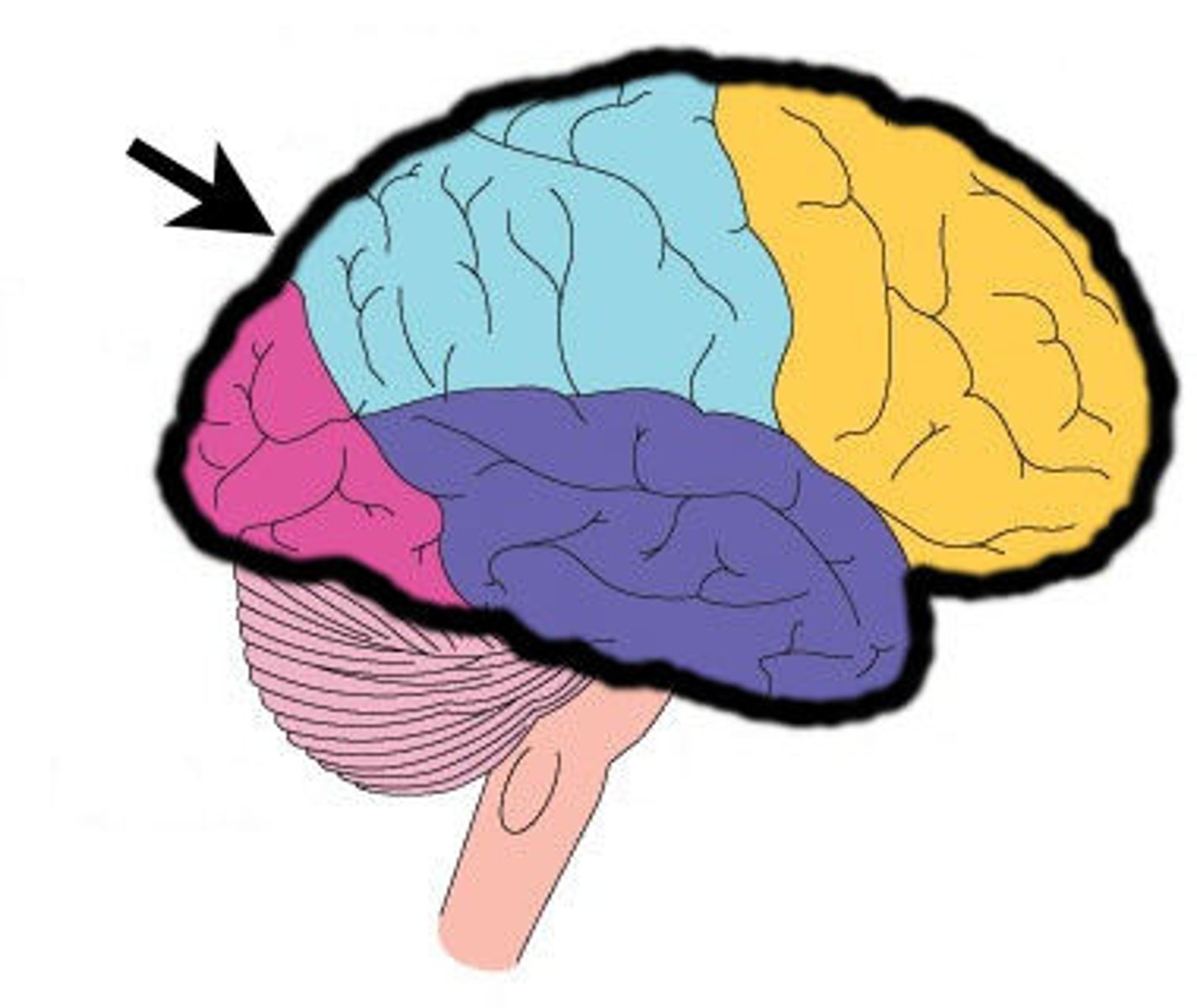
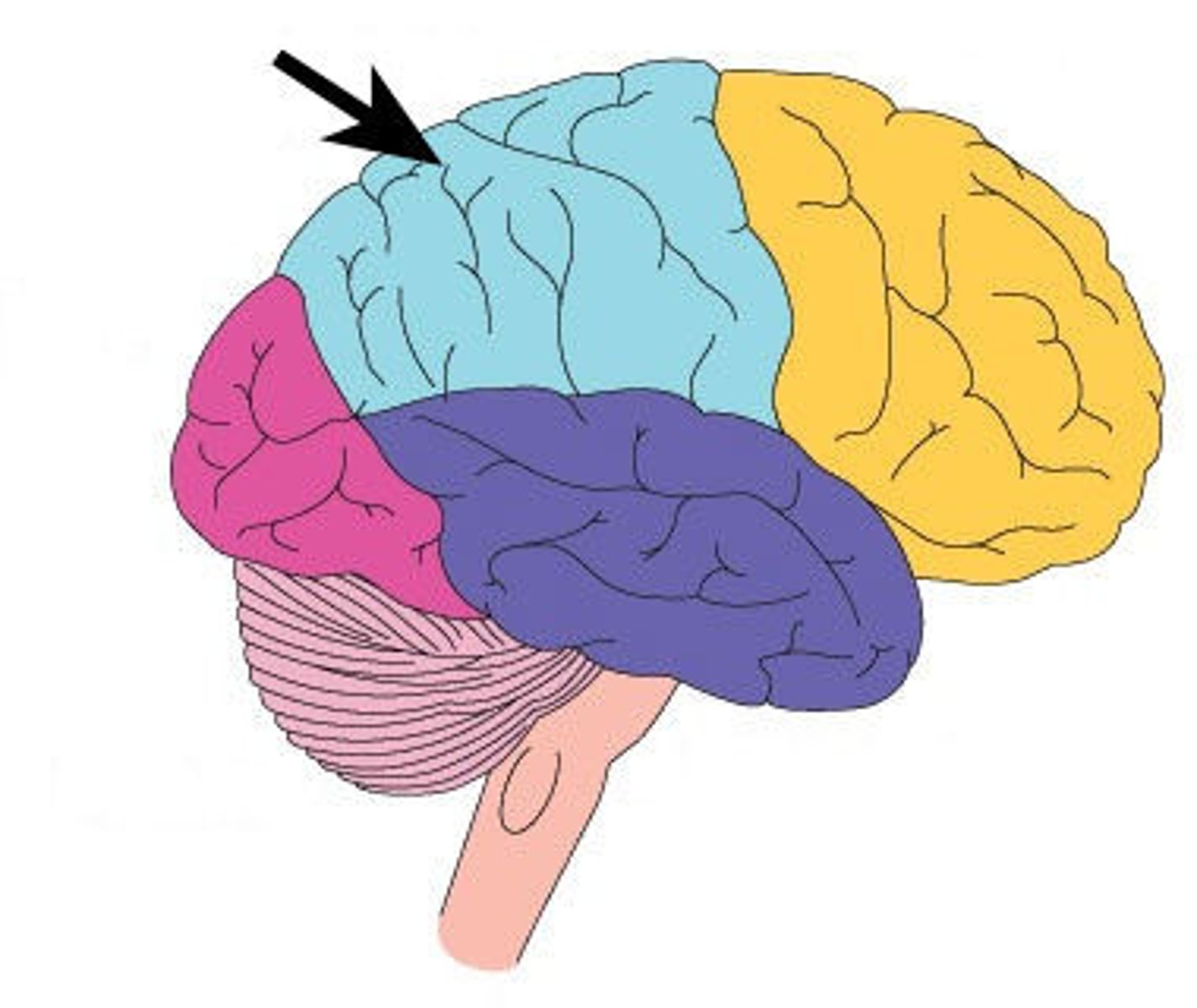
Frontal Lobe
Responsible for problem-solving, reasoning, and motor skills.
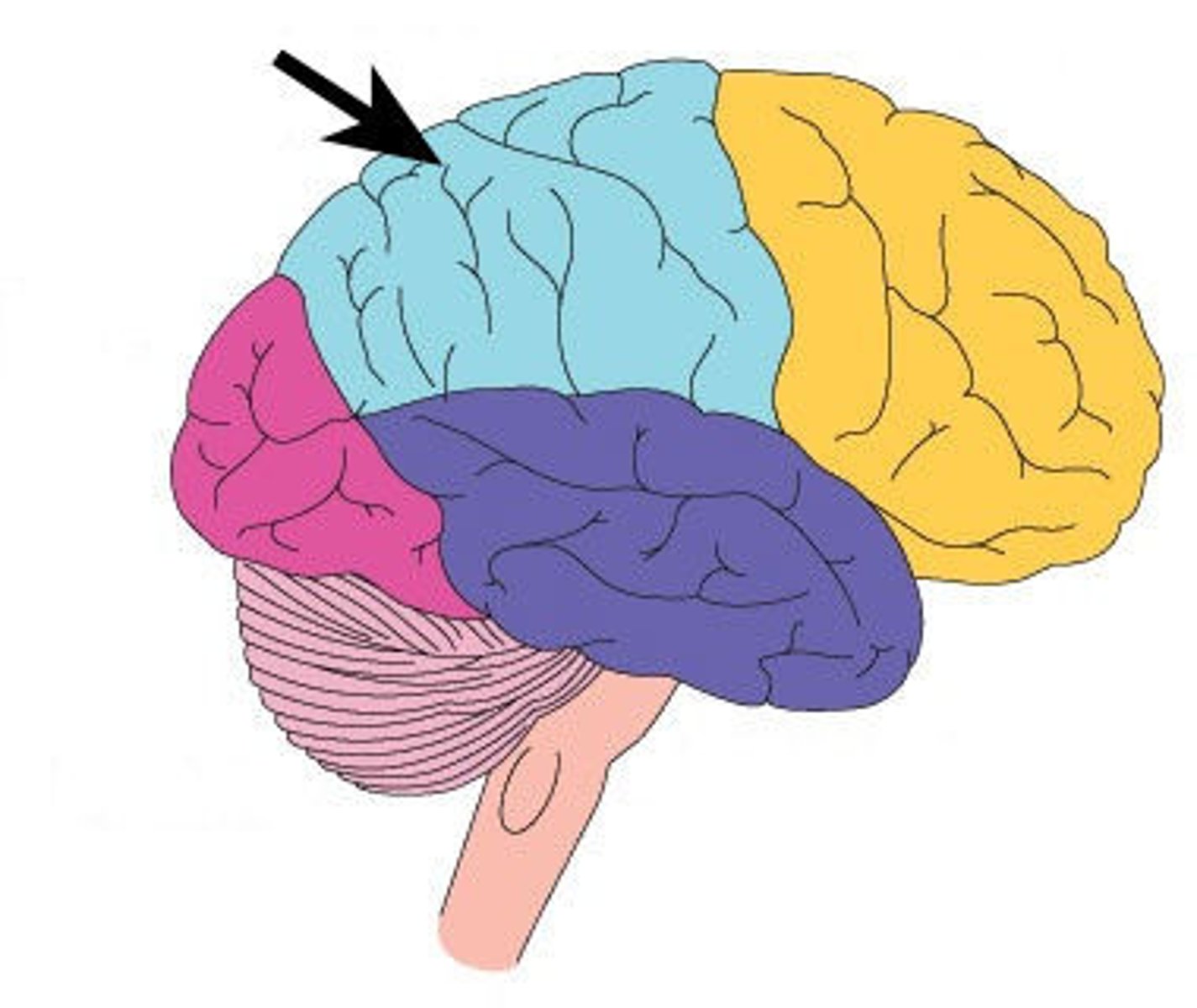
Parietal Lobe
Contains the area where bodily sensations occur, such as touch and pain.
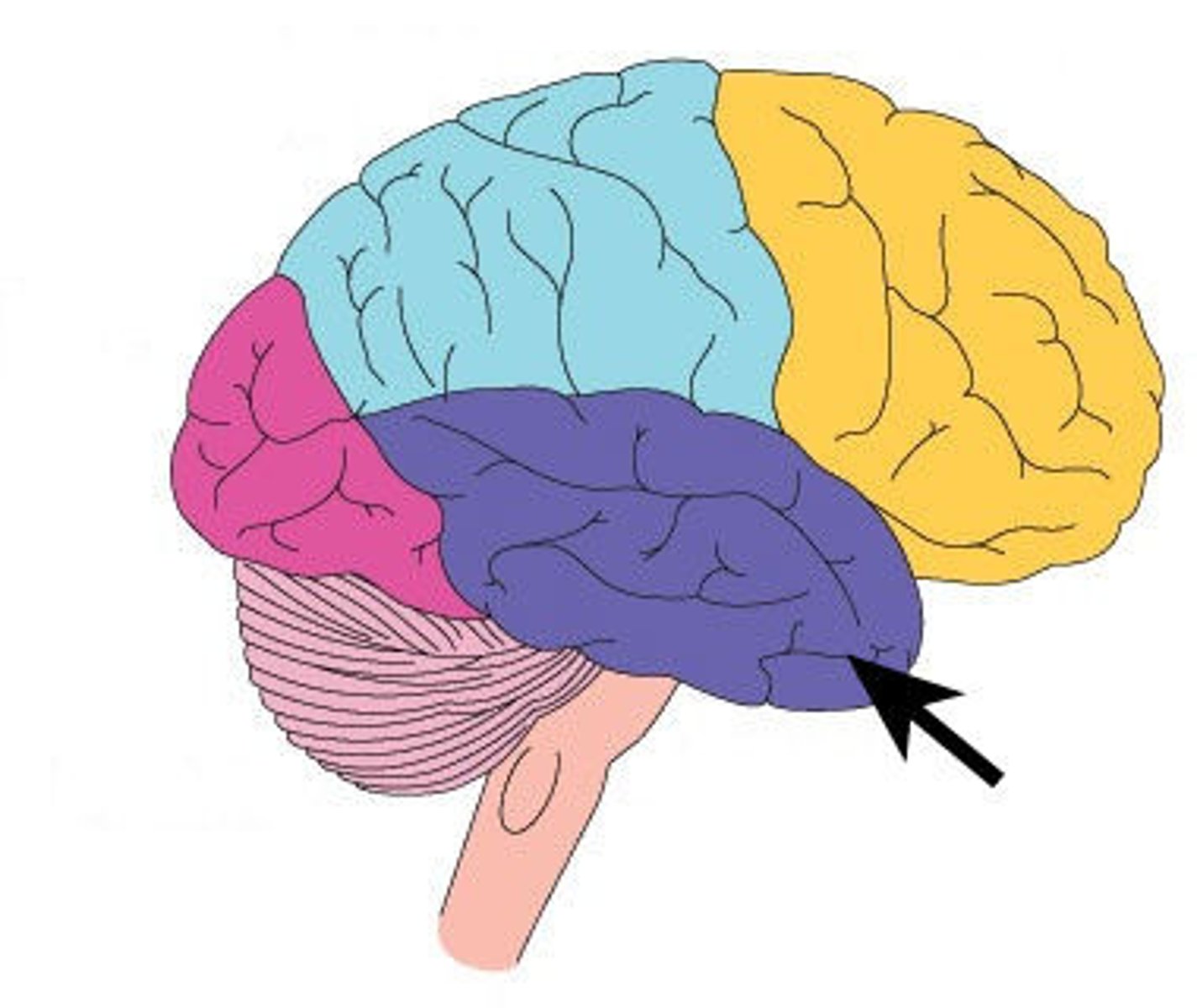
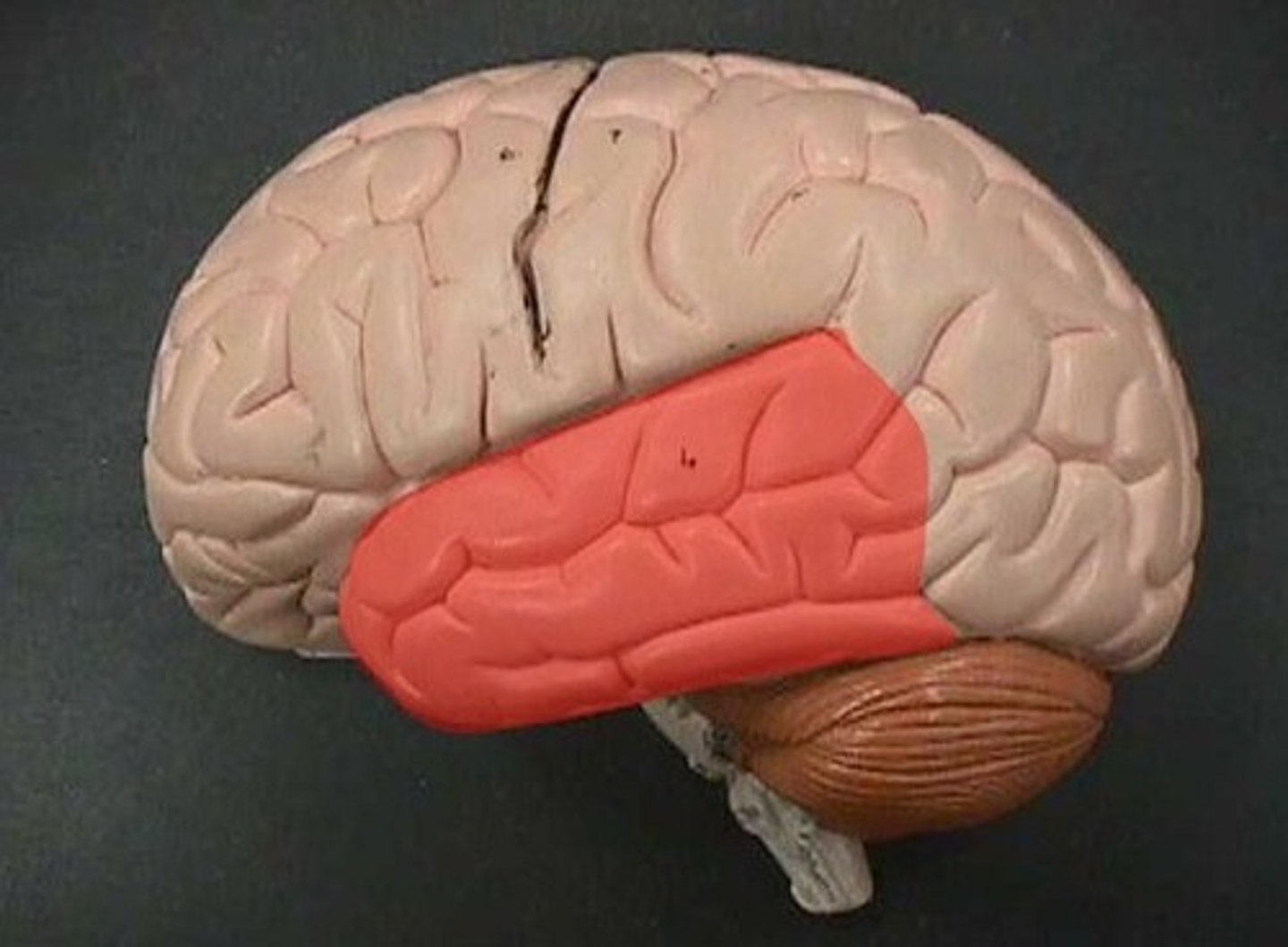
Temporal Lobe
Contains areas important to hearing and understanding speech.
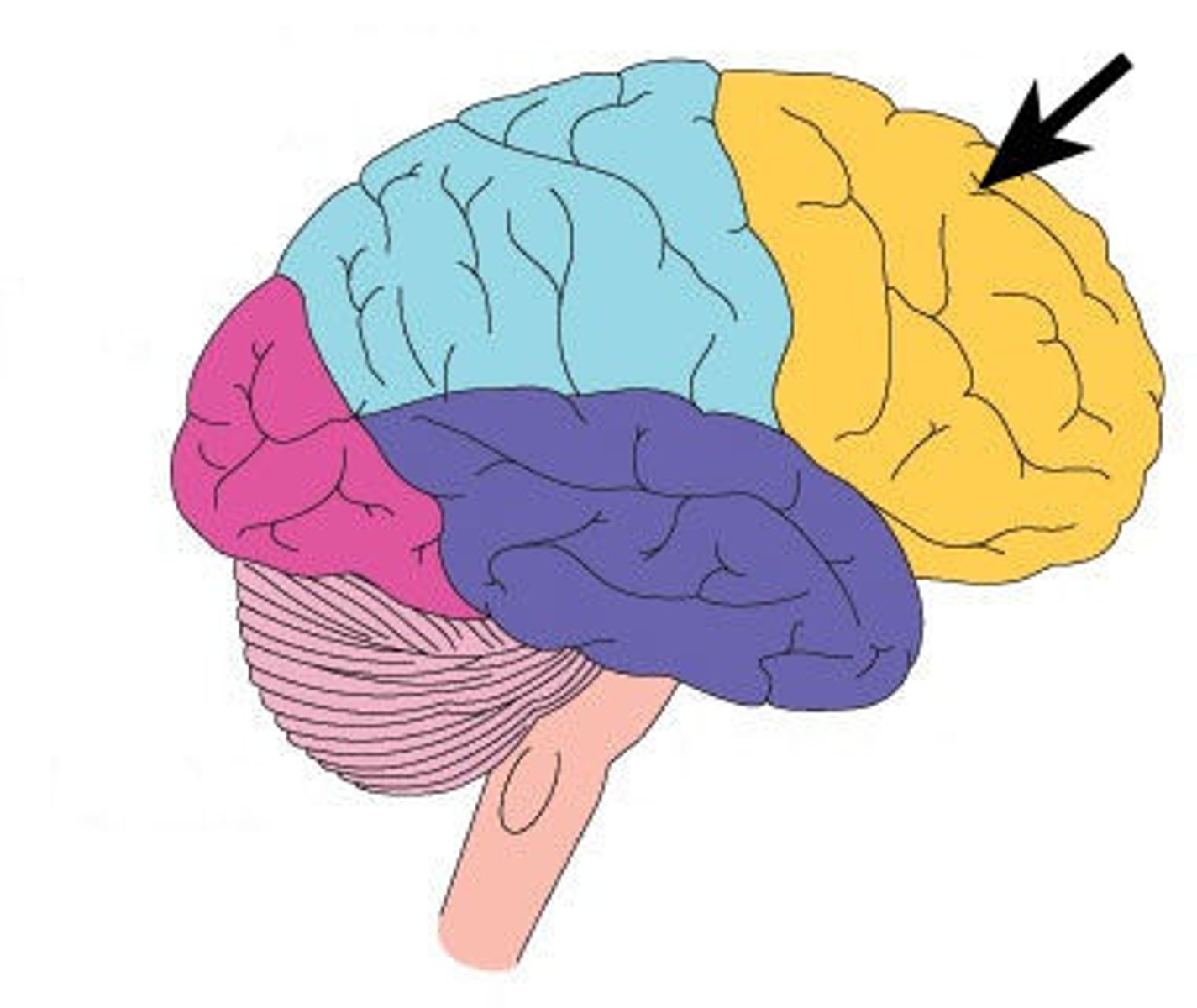
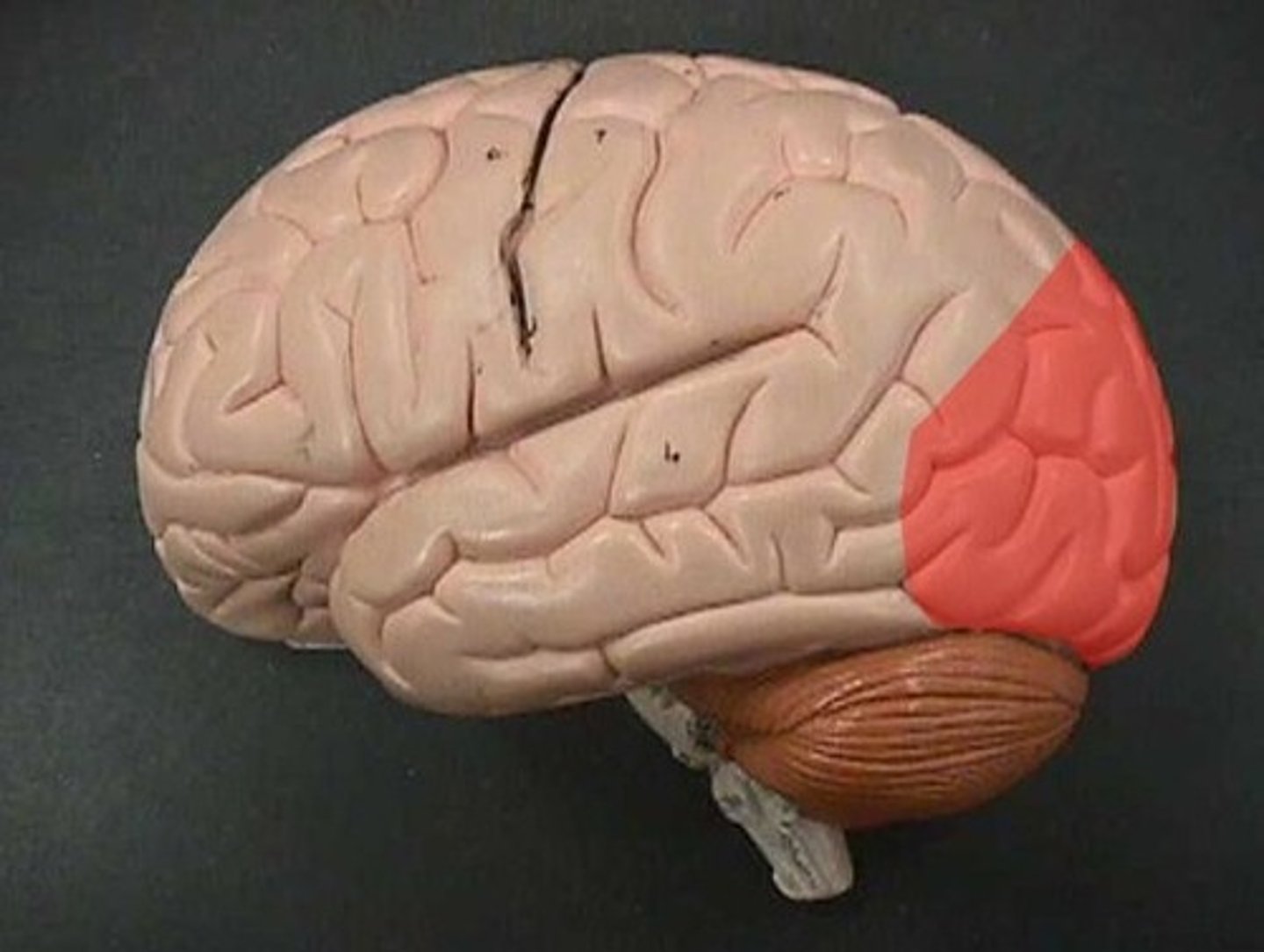
Occipital Lobe
Contains areas important to vision.
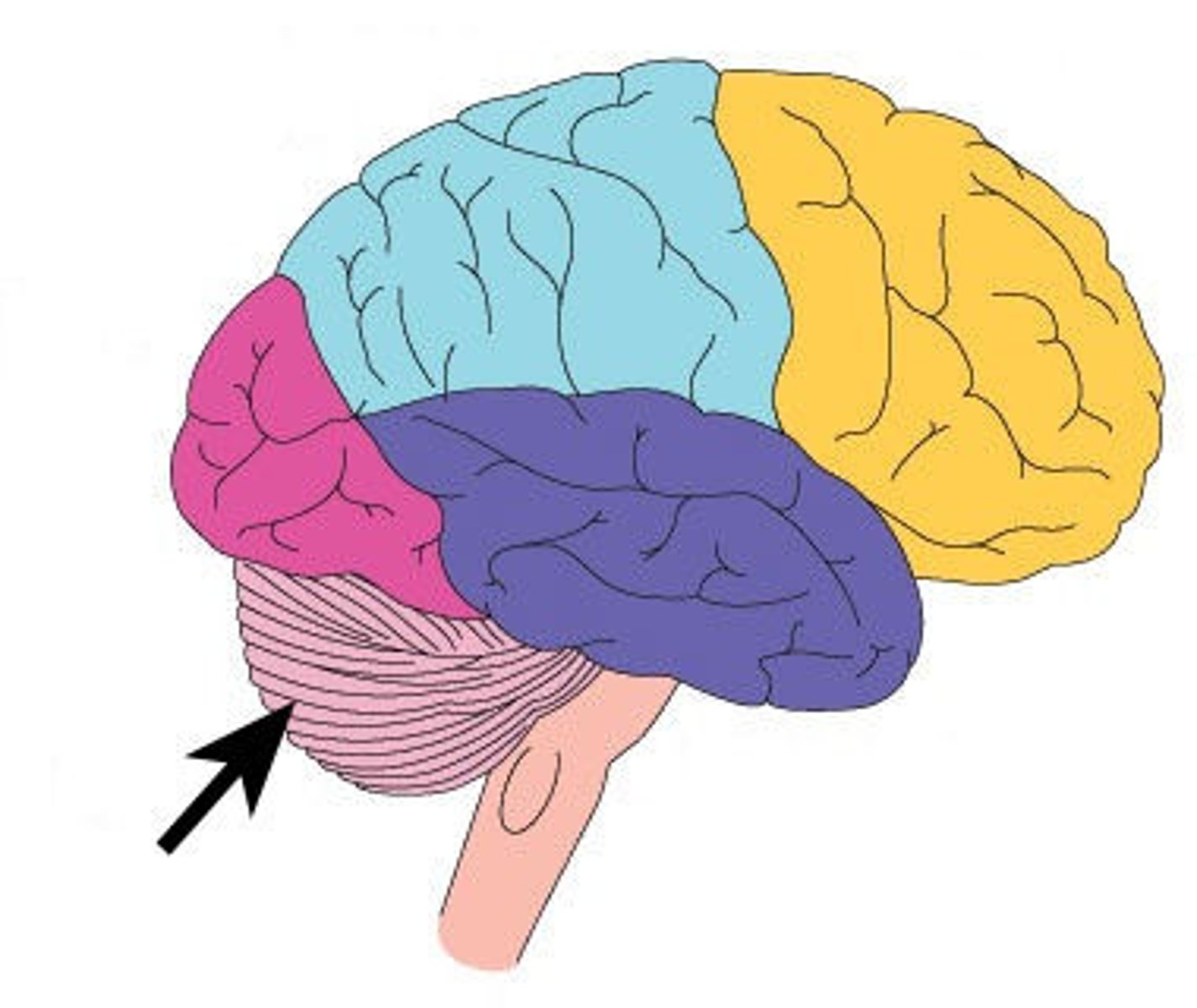
Cerebellum
Control of finely coordinated movements. Coordination center, and balance.
Cerebrum
Higher level brain functions; thoughts, emotions, memory, reasoning, language, and processing of sensory information.
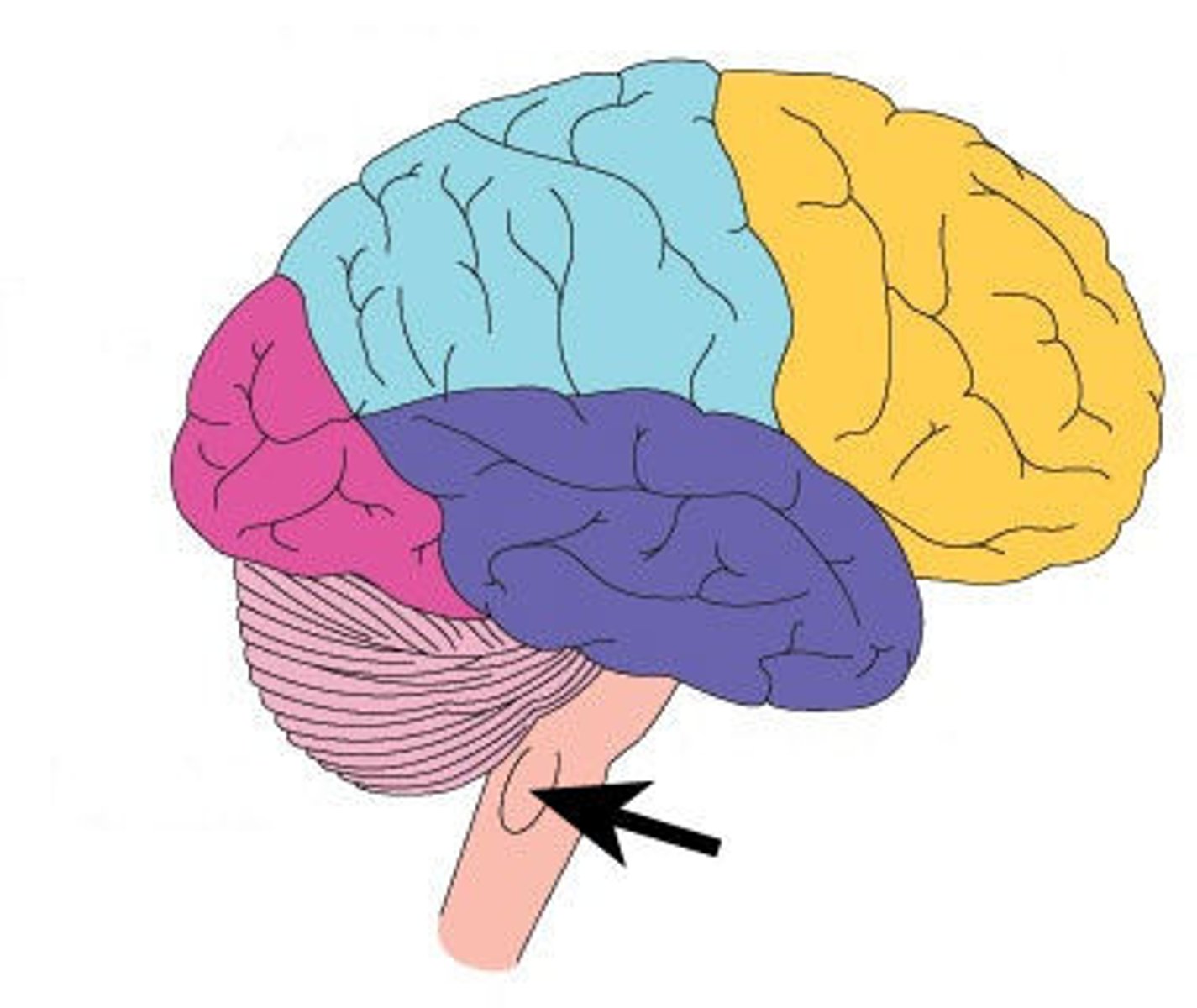
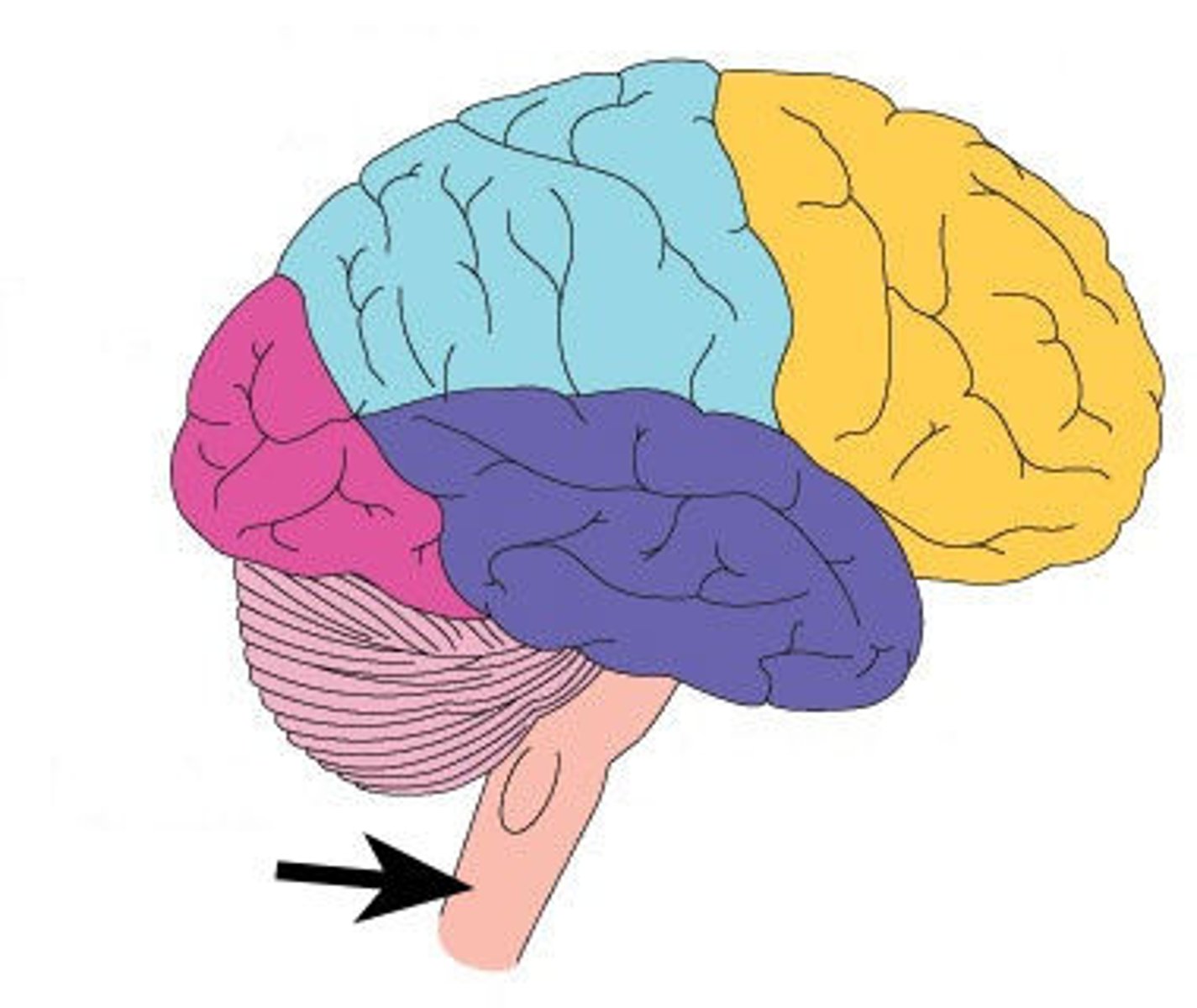
Brain Stem
Connection to spinal cord. Filters information flow between peripheral nervous system and the rest of the brain.
Cerebellum
Cerebrum
Frontal Lobe
Medulla Oblongata
Occipital Lobe
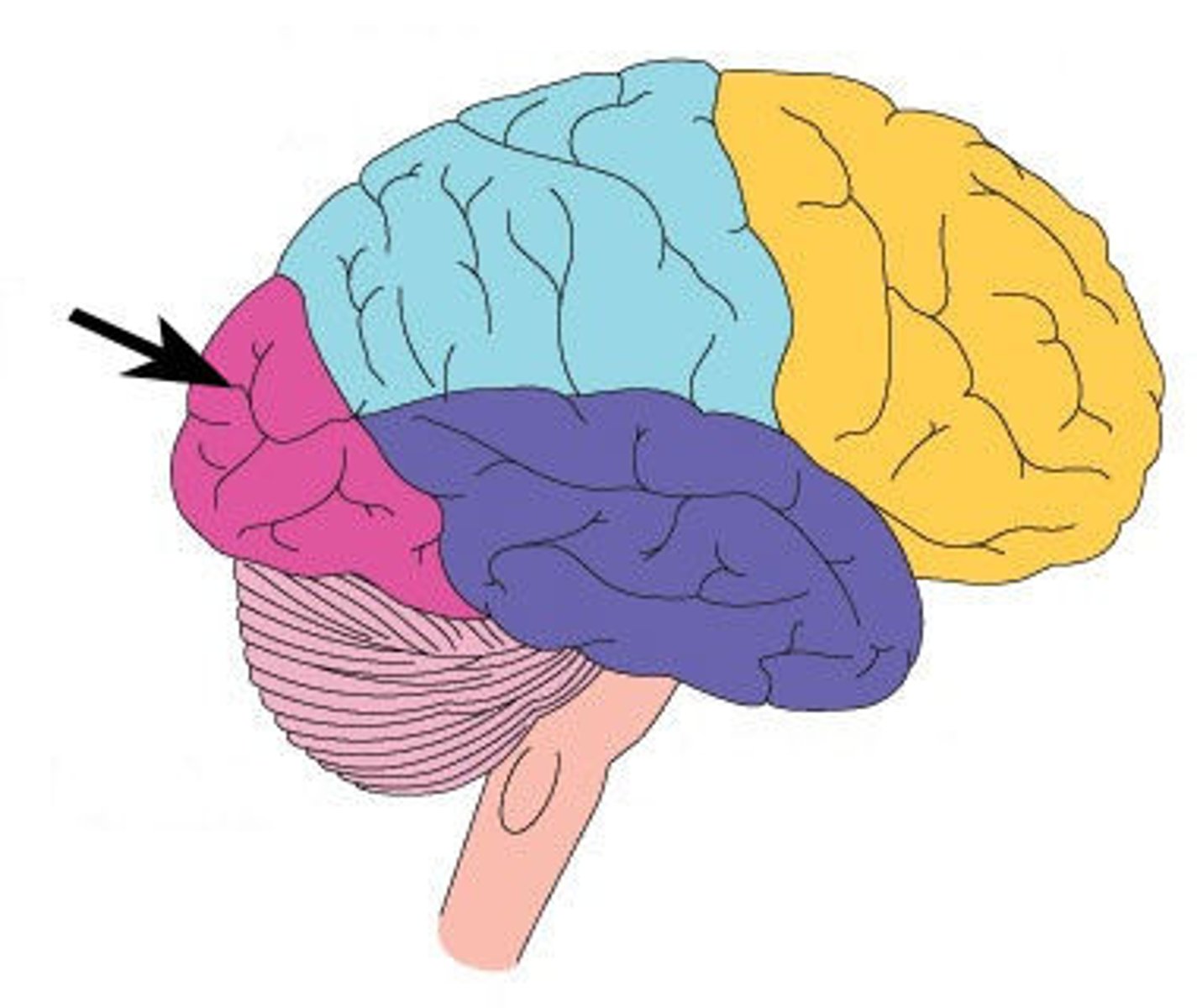
Parietal Lobe
Brain Stem
temporal Lobe
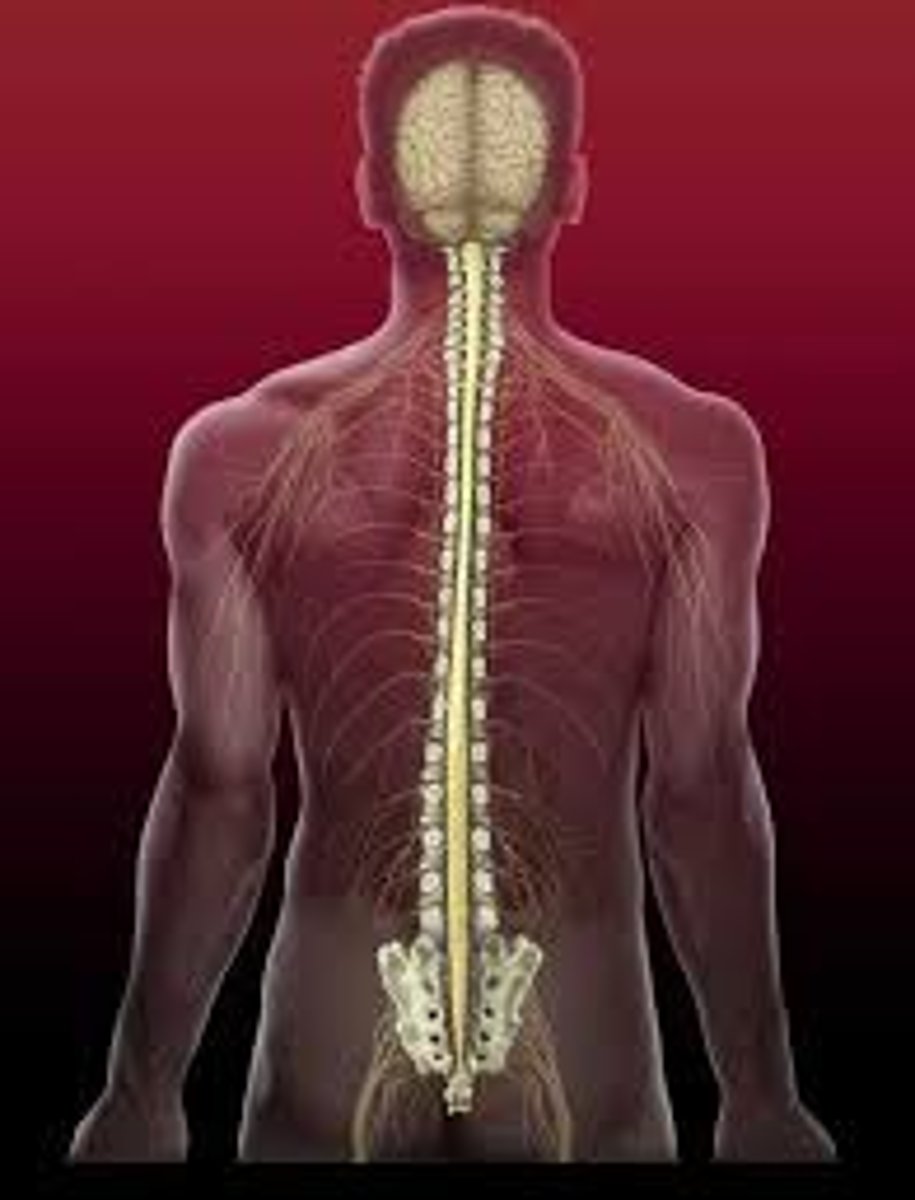
Spinal Cord
Sends signals between brain and rest of body
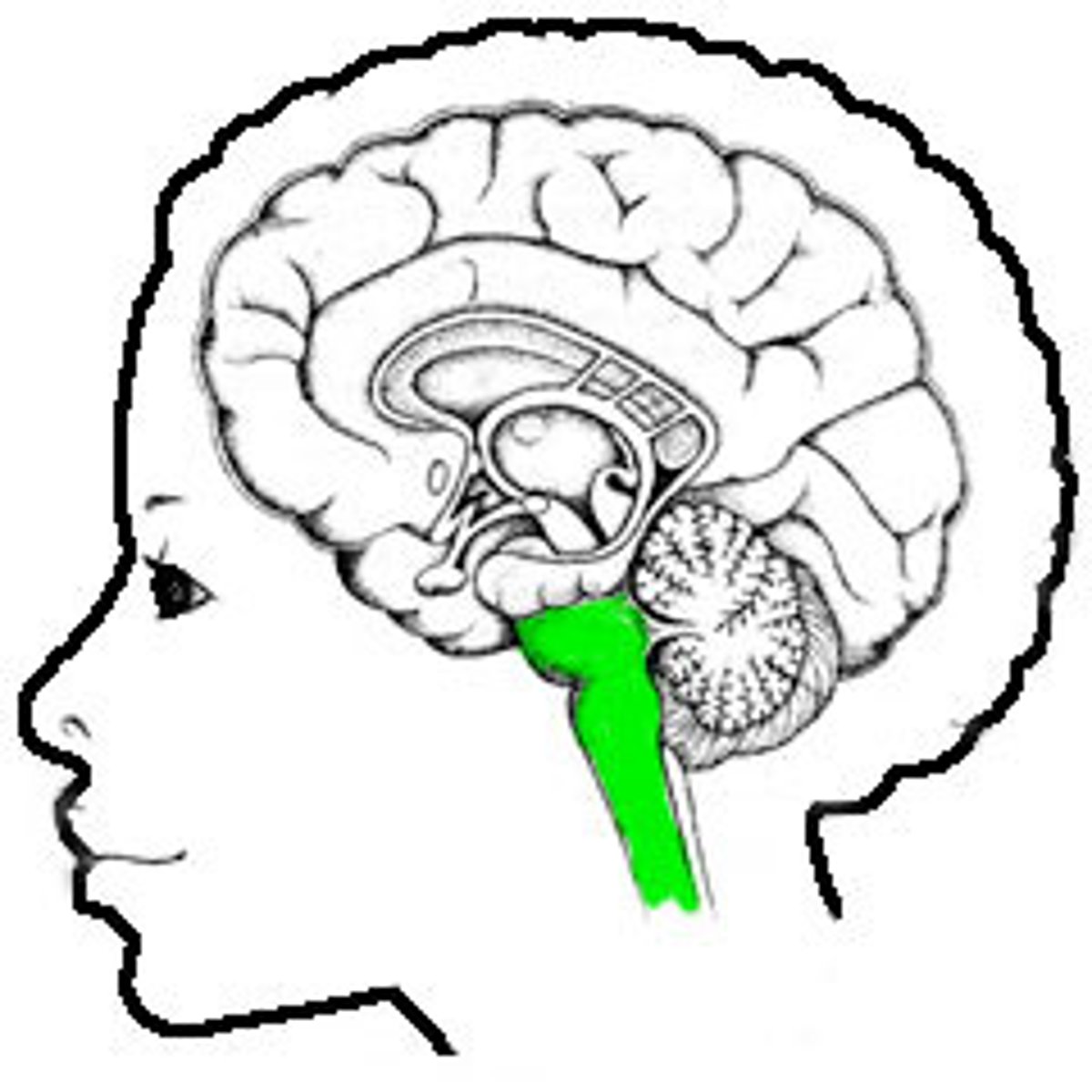
Brain Stem
Oldest part of the brain, responsible for survival functions (e.g. breathing, heart beat, etc.); includes medulla and pons; aka "the lizard brain"
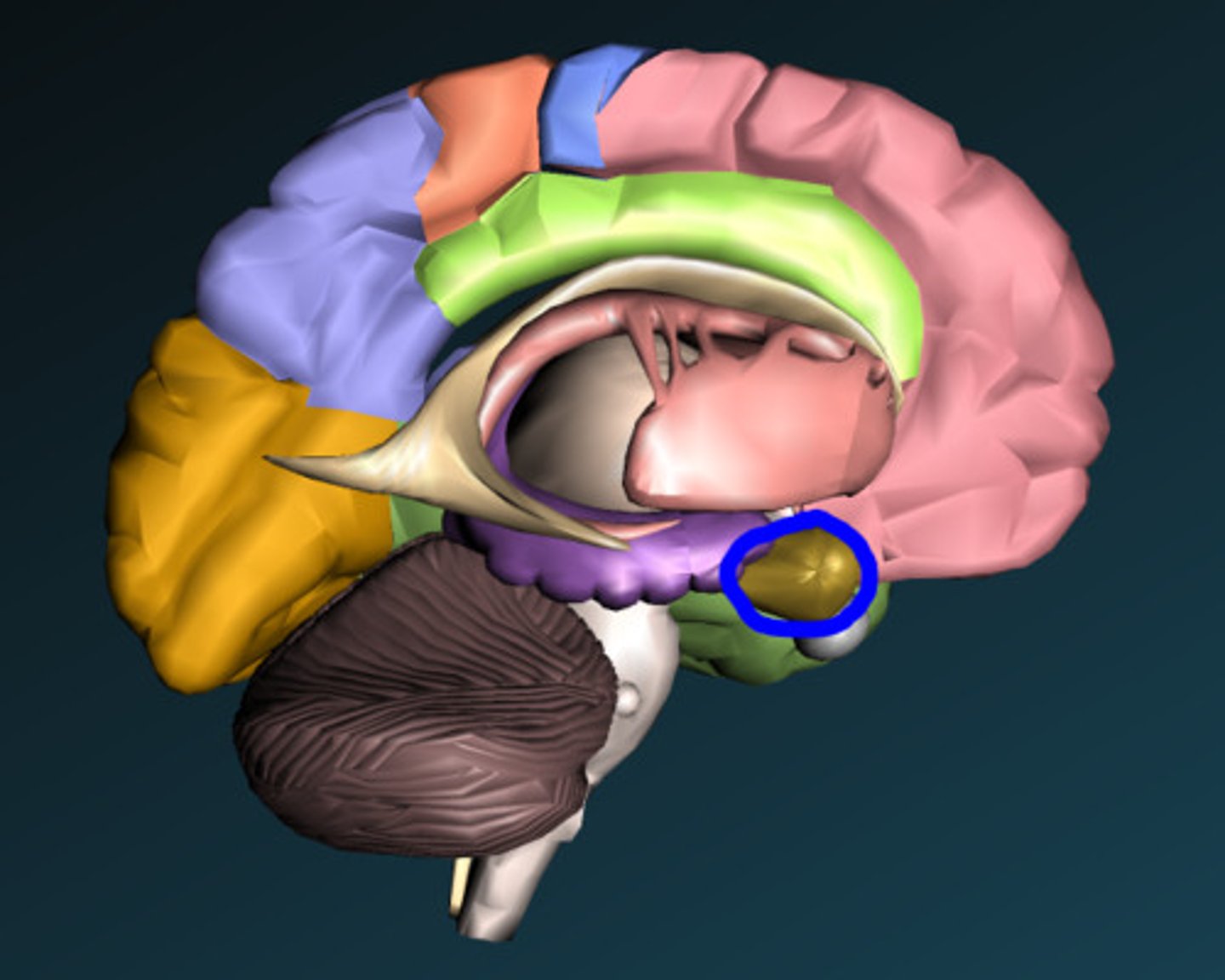
Amygdala
Fight or flight, emotional center, anger or fear
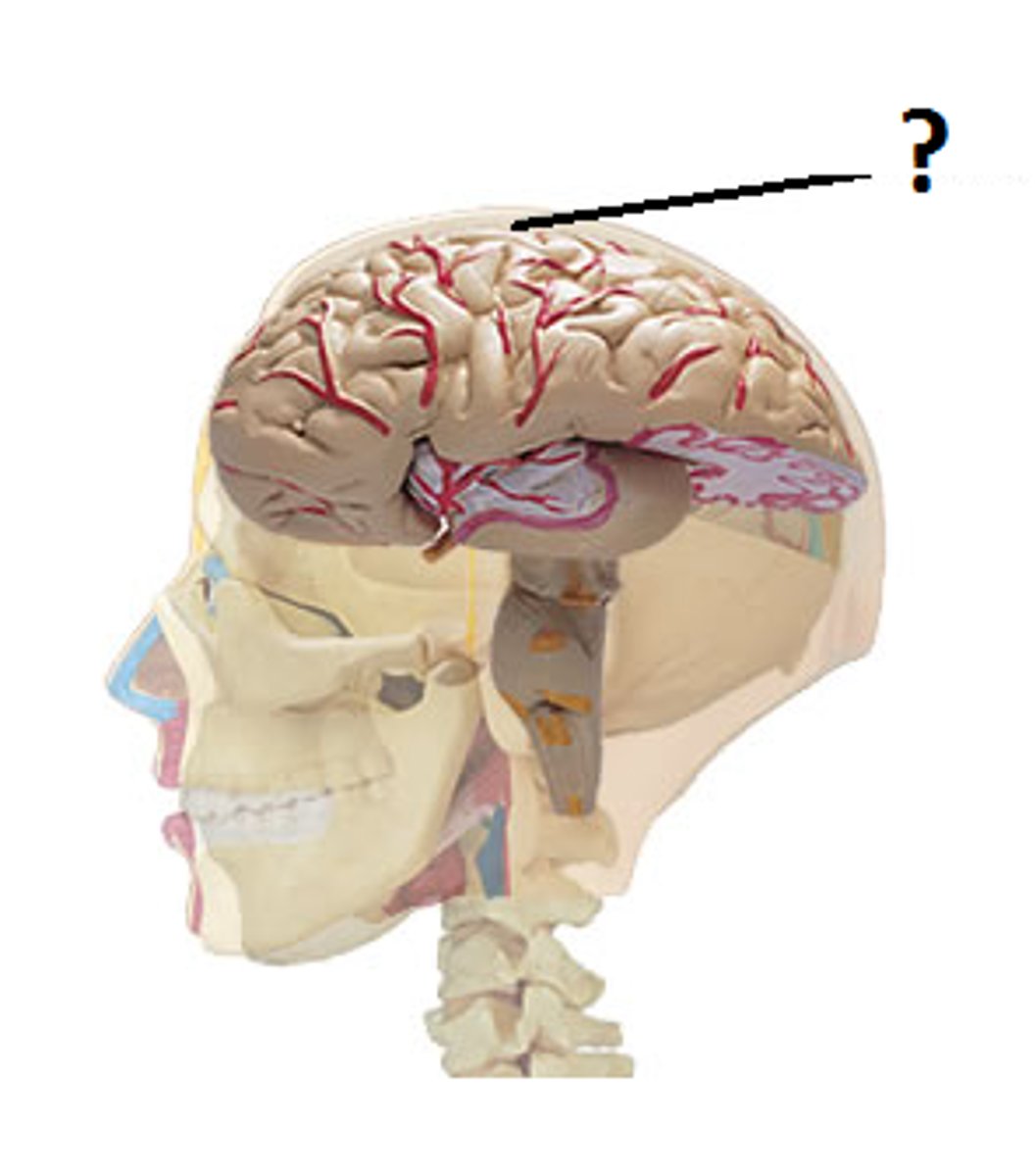
Cerebrum
Information processing, outer layer of brain.
Lobes of the cerebrum
Occipital, Temporal, Parietal, Frontal
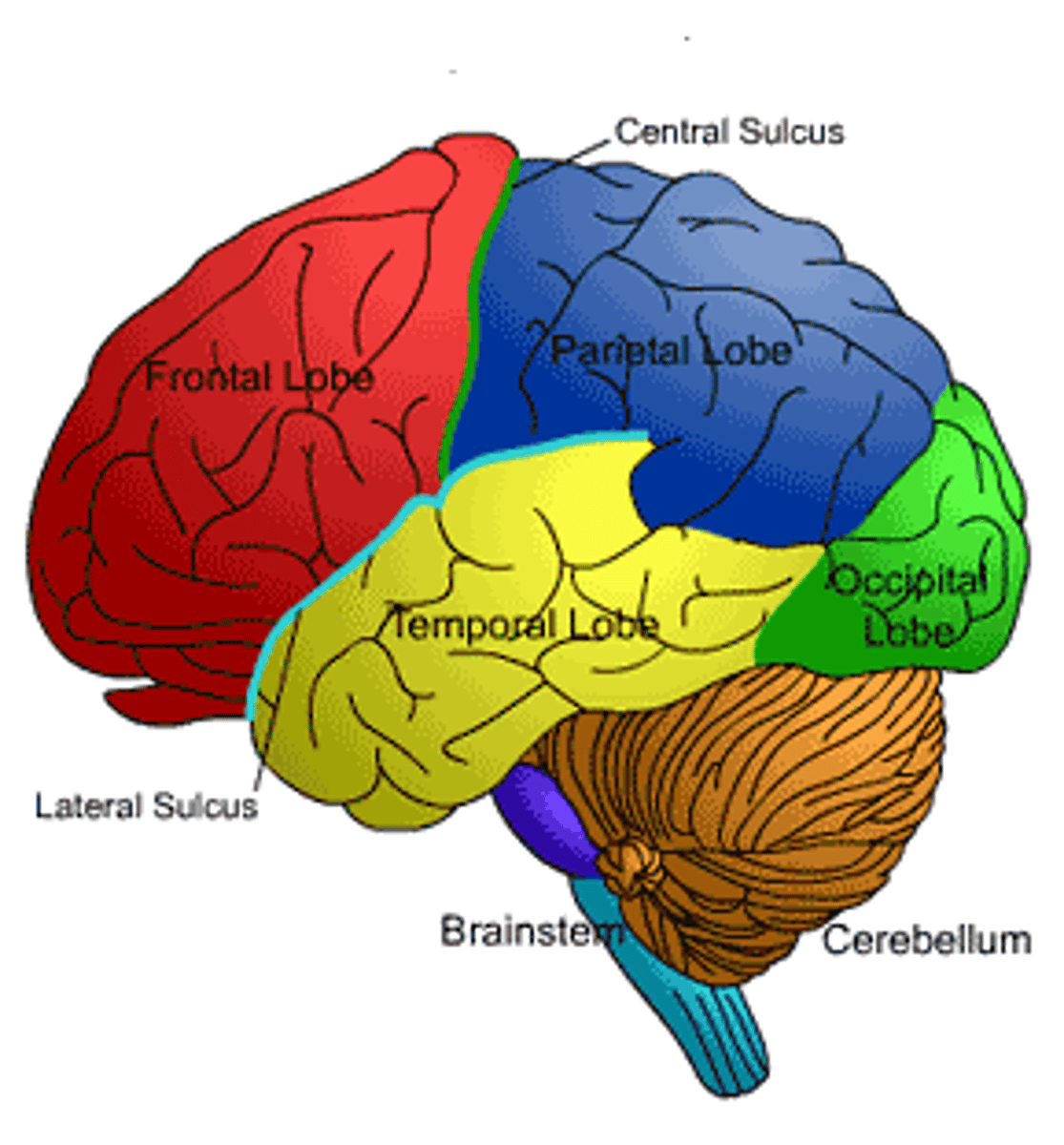
Occipital Lobe
Visual Perception
Temporal Lobe
Hearing
Parietal Lobe
Mainly made up of "association areas" for perception and sensation (includes sensory cortex)
Frontal Lobe
Responsible for planning, personality, judgement, voluntary movement (motor cortex)
Visual Agnosia
when an affected person is able to copy/draw things that they cannot recognize. Individuals afflicted with the associative type often cannot identify, describe or mimic functions of items, though perception is intact, since images of objects can be copied or drawn.
Synthasthesia
mingling of the senses due to cross-wiring in the brain.
HM
A man that suffered from epilepsy and seizures so bad that it hindered his life. Brain surgery to fix seizures removed most of his hippocampus and then he suffered from amnesia and had an inability to form new memories. His condition proved localization of function in the brain.
phantom limbs/pain
amputees often feel the amputated limb as if it is still there and sometimes feel pain in the missing limb
Prosopagnosia
inability to recognize faces - associated with damage to the boundary between the brain's occipital and temporal lobes, a region better known as the fusiform face area.
Phineas Gage
railroad worker who survived a severe brain injury that dramatically changed his personality and behavior; case played a role in the development of the understanding of the localization of brain function
dendrite
the bushy, branching extensions of a neuron that receive messages and conduct impulses toward the cell body
neuron
a nerve cell; the basic building block of the nervous system
neurotransmitter
chemical used by a neuron to transmit an impulse across a synapse to another cell
synaptic transmission
The relaying of information across the synapse by means of chemical neurotransmitters.
action potential
a neural impulse; a brief electrical charge that travels down an axon
terminal buttons
Small knobs at the end of axons that secrete chemicals called neurotransmitters
receptor sites
holes in the surface of the dendrites or certain cells of the muscles and glands, which are shaped to fit only certain neurotransmitters
excitatory neurotransmitters
chemicals released from the terminal buttons of a neuron that excite the next neuron into firing
inhibitory neurotransmitters
chemicals released from the terminal buttons of a neuron that inhibit the next neuron from firing
Agonists
drugs which mimic the activity of neurotransmitters
antagonist
chemicals that counteract a neurotransmitter, preventing a signal from being passed further
reuptake
A process in which neurotransmitters are sponged up from the synaptic cleft by the presynaptic membrane.
Axon
A threadlike extension of a neuron that carries nerve impulses away from the cell body.
synapse
the junction between the axon tip of the sending neuron and the dendrite or cell body of the receiving neuron
dendrites
a neuron's bushy, branching extensions that receive messages and conduct impulses toward the cell body
acetylcholine
enables muscle action, learning, and memory
dopamine
A neurotransmitter associated with movement, attention and learning and the brain's pleasure and reward system.
serotonin
A neurotransmitter that affects hunger,sleep, arousal, and mood.
Norepinephrine
A neurotransmitter involved in arousal, as well as in learning and mood regulation
Kasamatsu and Hirai (1999)
Researched how the neurotransmitter serotonin can affect behavior by studying how sensory deprivation affects the brain. Studied monks who went on a pilgrimage. Found higher levels of serotonin in the brain when the monks began to talk about hallucinations.
Antonova et al
researched the role of acetylcholine in spatial memory in humans. Did this by injecting male participants with placebo or scopolamine and placing them in a virtual reality game to try and find a pole. Those in the experimental group took longer. Scopolamine is an antagonist and blocks the effect of Acetylcholine and hence this supports the role of Ach in spatial memory.
Caspi et al (2003)
Longitudinal study on possible role of gene 5-HTT in depression. Found that participants with a mutation of the gene were more likely to become depressed than those with the normal gene.
Martinez and Kesner
Three groups of rats were put into a maze: one with scopolamine to decrease levels of acetylcholine, one with nothing (control group) and another with physostigmine to increase acetylcholine levels. They found that the group with higher acetylcholine levels ran through the maze much faster and made less errors than the other two. They concluded that acetylcholine is linked to memory.
Scopolamine
antagonistic drug that blocks the receptors receiving Acetylcholine and hence the function of Acetylcholine.