uplearn resistivity
1/19
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
20 Terms
When describing a thermistor, NTC stands for...
Negative temperature coefficient
Is a thermistor an insulator, semiconductor, or conductor??
Semiconductor
Select the correct graph for an NTC thermistor
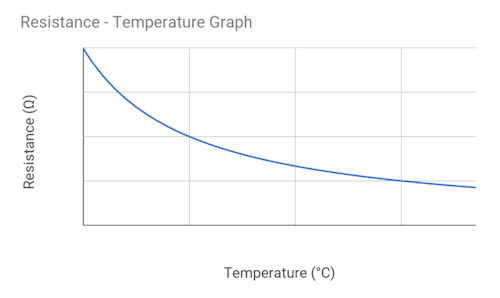
When the temperature of an NTC thermistor increases what happens to free charge carriers and resistance...
The number density of free charge carriers increases and the resistance decreases
uses of thermistors:
The resistance of a thermistor changes in response to temperature.
∙ ∙ The uses of a thermistor are therefore those related to sensing temperature changes.
∙ ∙ Good examples include heat alarms and kettles
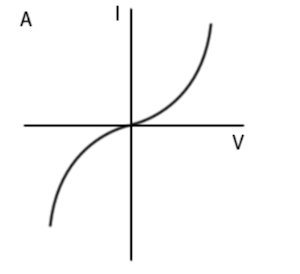
Select the correct I-V graph for an NTC thermistor
As the length of a section of wire increases, its resistance ...
Increases because the charge carriers have to travel through more resistive material
relationship between resistance and length of wire…
directly proportional
As the cross-sectional area of a piece of wire increases, its resistance…
Decreases
because the movement of the charge carriers becomes less impeded, which means that resistance decreases
The resistance of a section of wire relationship with its crossectional area…
inversely proportional
The resistivity of a component depends on...
what material it is made from
The units of resistivity are:
ohm metre
The definition of 1Ωm is...
A material has resistivity of 1Ω when a cubic metre of material has a resistance of 1Ω
Provided that the temperature is constant, resistivity...
is a constant for each material
Several measurements are taken during this experiment. Which of the following is the independent variable??
Length of wire
Which of the following plots should be used to represent that data graphically??
Length of wire on x-axis, resistance of the wire on the y-axis
Thermistor (Negative Temperature Coefficient or NTC Thermistor)
An electrical component that has a resistance that decreases as the temperature increases
Resistivity
A property of a material, measured in Ω m. ρ = RA/l where ρ = resistivity (in Ohm.metres (Ω⋅m)), R = resistance (in Ohms), A = area (in m2) and l = length of wire (in m).
A material has resistivity of 1 Ω m when a cubic metre of material has a resistance of 1 Ω
A wire has a resistivity of 0.005 Ωm. What would the resistivity be if the length of the wire was doubled and the diameter was halved
length and diameter don’t have any effect on resistivity
Which one of these factors would cause the resistivity of a wire to change??
Increasing the temperature