Receptor Ligands
1/17
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
18 Terms
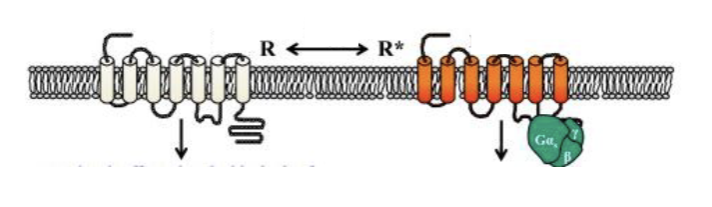
What is the two state receptor model?
R → inactive receptor
R* → active receptor
What is the basal state?
receptors in cell with NO ligands present
How do active receptors differ from inactive receptors?
active binds the G protein
inactive does not
What is the distribution of active and inactive receptors with no ligand present?
~5% are active
inactive receptors are more energetically favorable
What happens if a ligand that is an agonist binds to the receptor?
agonist has preferential affinity for the active state of receptor
more L = more [R*L]
What happens if a ligand that is an antagonist binds to the receptor?
preferential affinity for INACTIVE receptors
called an inverse agonist
What happens if a ligand that is a partial agonist binds to the receptor?
binds BOTH active + inactive receptors
more active bound
only some inactive bound
What determines the affinity of a ligand for a target?
# of bonds
strength of bonds
What is the equilibrium dissociation constant (kD)?
measure of affinity
lower the # → higher affinity
1 um =
1000 nM
1 mM =
1000 uM
How do agonists, partial agonists, neutral antagonists and inverse agonists differ in their affinity for various receptor conformations?
partial agonists → higher affinity for active
T/F: In a partial agonist, the ligand will NEVER get 100% of active receptors?
TRUE
The dissociation constant (KD) is a measure of a drug’s:
a. selectivity
b. efficacy
c. activity
d. none of these answer choices are correct
D
measure of AFFINITY
_____________ displays both agonistic and antagonistic effects. In the presence of a ___________, a partial agonist will act as a(n) _____________.
a. Partial agonist, inverse agonist, full agonist
b. Inverse agonist, full agonist, antagonist
c. Full agonist, neutral antagonist, partial agonist
d. Partial agonist, full agonist, antagonist
D
A drug has a Kd = 3nM for its active form and a Kd =600 nM for the inactive form. Does this drug have greater affinity for the inactive or active receptor? And what type of agonist is it?
a. Inactive; partial agonist
b. Inactive; inverse agonist
c. Active; partial agonist
d. Active; inverse agonist
C
lower Kd = higher affinity
partial Ag bc it has affinity for both forms, but still more active than inactive
The ED50 is a measure of the _____ of a drug. It’s the dose of the drug that produces a desired response in ___ of the population.
potency, 50%
Drug A and B both bind to the same receptor. Drug A has a Kd of 0.3 nM and Drug B has a Kd of 0.2 mM. Which of the following is true?
a. Drug B has a higher affinity than Drug A
b. Drug A has higher selectivity than Drug B
c. Drug A has lower affinity than Drug B
d. Drug A has higher affinity than Drug B
e. More information is needed
D
0.2 mM → 200,000 nM
****lower Kd = higher affinity
0.3 nM > 200,000 nM