AP Biology Enzymes
1/52
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
53 Terms
Metabolism
all chemical reactions in an organism
metabolic pathways
series of chemical reactions that either build complex molecules or break down complex molecules
steps of substances being broken down
substrate->intermediate->product
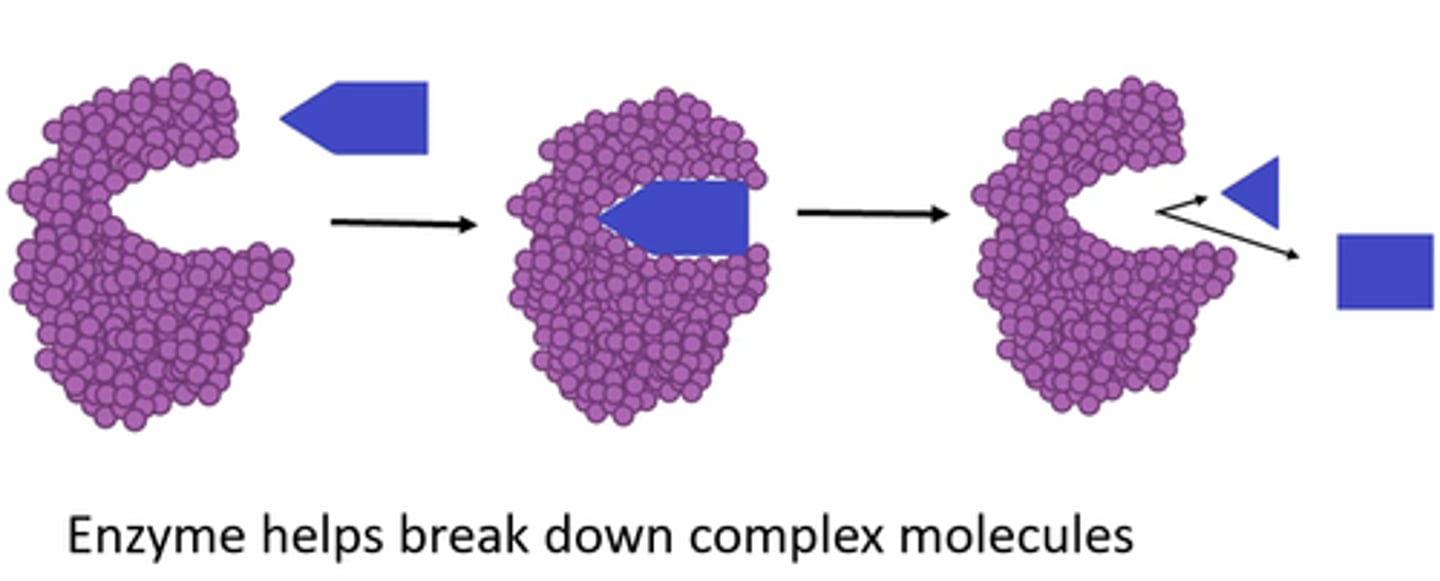
catabolic metabolic pathway
pathways that RELEASE energy by BREAKING DOWN complex molecules into simpler compounds
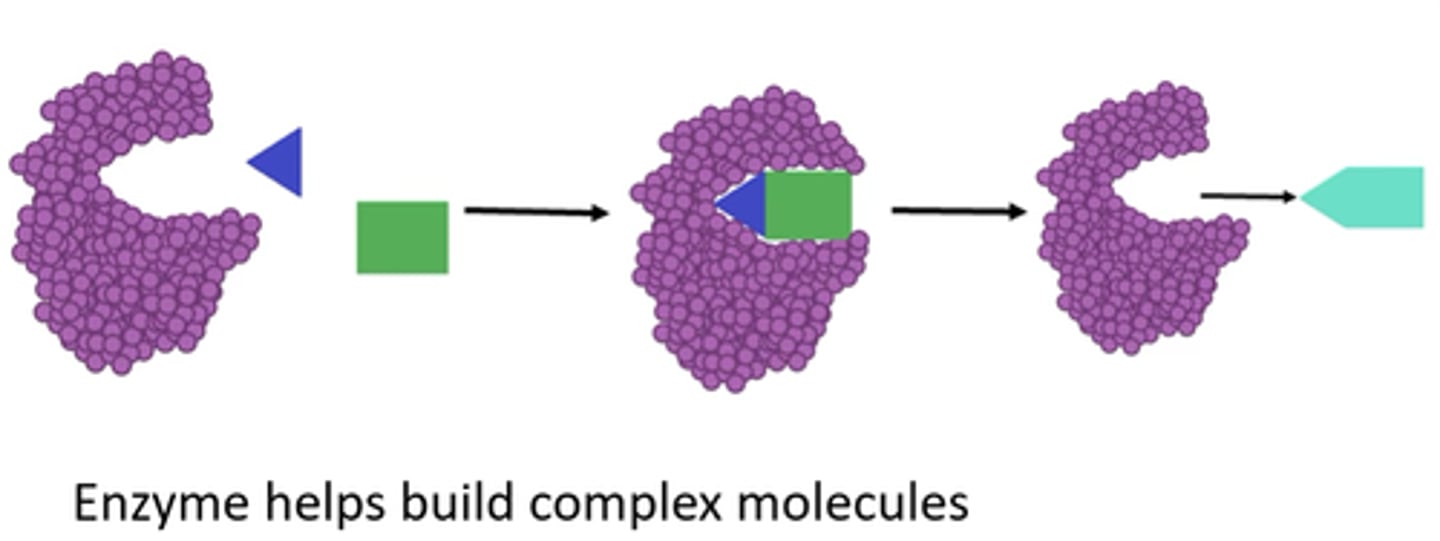
anabolic pathways
CONSUME energy to BUILD complicated molecules from simpler compounds
energy
-the ability to do work
-organisms need energy to survive and function
loss of energy flow result
death
kinetic energy
-energy associated with motion
thermal energy
energy associated with movement of atoms or molecules (kinetic)
Potential energy
stored energy
chemical energy
potential energy available for release in a chemical reaction (potential)
thermodynamics
-study of energy transformations in matter
-apply to universe as a whole
1st law of thermodynamics
-energy cannot be created or destroyed
-can be transferred or transformed
1st law example: think...
-chemical (potential energy) stored in nut transformed into kinetic energy for squirrel to climb tree
2nd law of thermodynamics
-energy transformation increases entrophy (disorder) of the universe
-during energy transfers/transformations some energy is unstable and lost as heat
-basically using energy= release heat
2nd law example
as squirrel climbs tree, energy is released as heat
free energy
-scientists use to determine the likelihood of reactions in organisms, or if the reaction is energetically favorable
-free energy of reactions determine if reaction occurs spontaneously
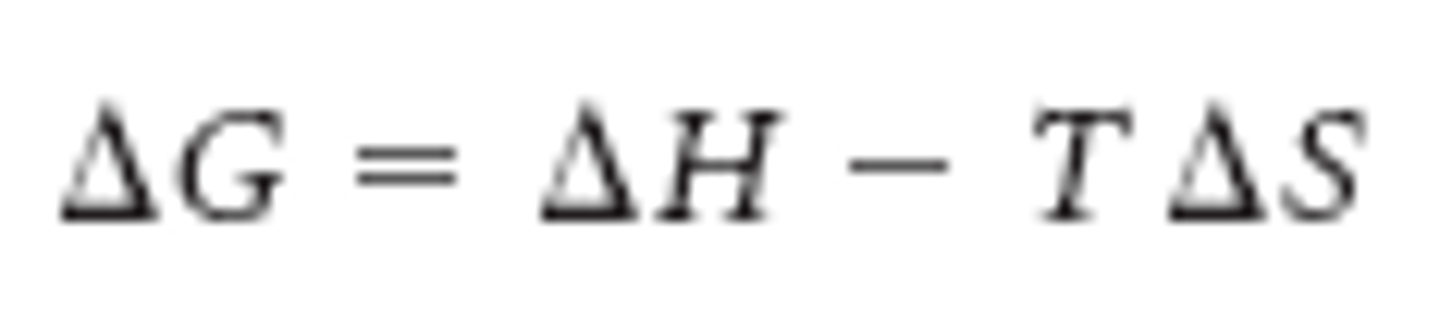
exergonic or endergonic determination
-based on how the free energy changes
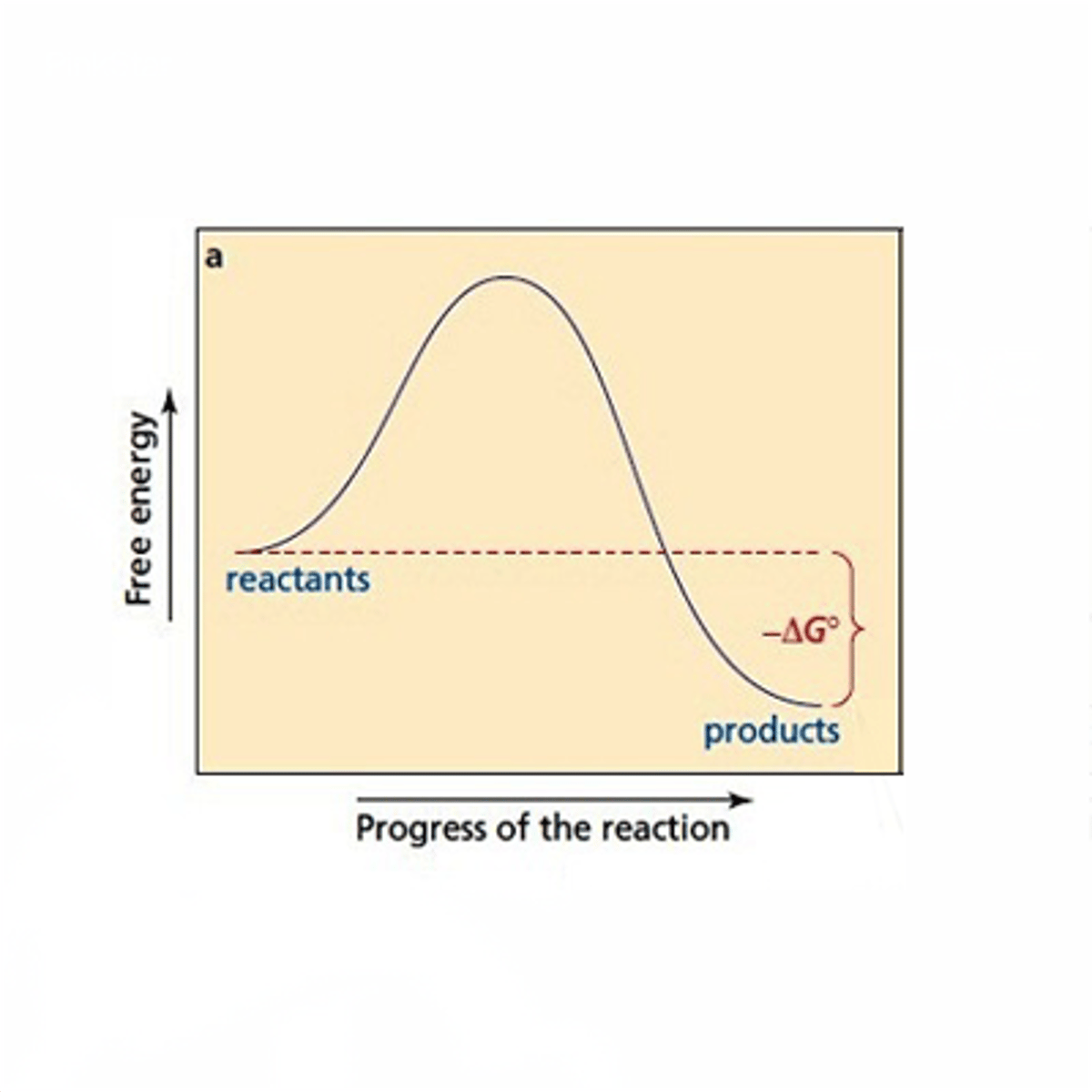
exergonic reactions
-reactions that release energy
-ex. cellular respiration
-spontaneous
endergonic reactions
-reactions that absorb energy
-ex. photosynthesis
-not spontaneous

living cells have what?
- constant flow of materials in and out of membrane
-cells not a equilibrium
cell work types:
mechanical, transport, chemical
Mechanical cell work
- movement
-ex. cilia, movement of chromosomes, contraction of muscle cells
-not really plants however- mostly animal cells
transport cell work
-pumping substances across membranes against spontaneous movement (concentration gradient)
chemical cell work
- synthesis of molecules
-ex. building polymers from monomers
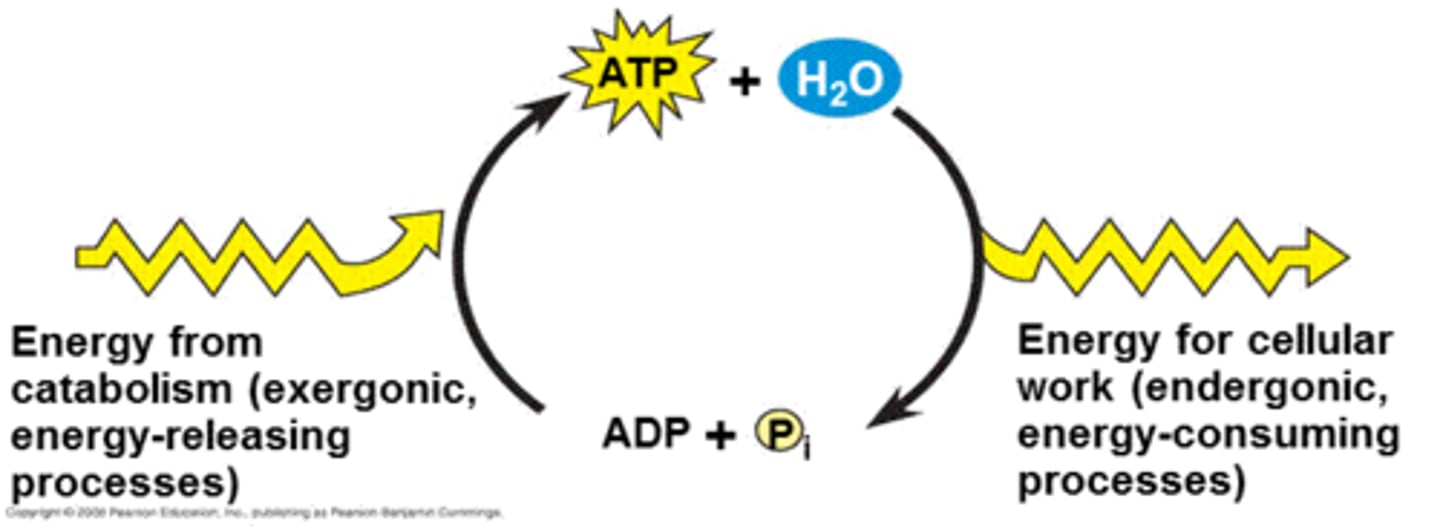
ATP
- adenosine triphosphate: molecule used as source of energy to perform work
-ATP couples exergonic reactions to endergonic reactions to power cellar work
Organisms energy through ATP
- obtain energy by breaking bond between 2nd and 3rd phosphate via hydrolysis
- ATP->ADP
Phosphorylation
released phosphate moves to another molecule to give energy
ATP Cycle
rate of metabolic reactions
-laws of thermodynamics tell spontaneous or not, but not rate
-some spontaneous reactions move too slowly to use
-enzymes catalyze
enzymes
-macromolecules that catalyze (speed up) reactions by lowering initial energy
- are not consumed by reaction
-type of protein (can denature)
-enzyme names end in -ase
enzyme reactant
- act on reactant called substrate
active site
- area for substrate to bind
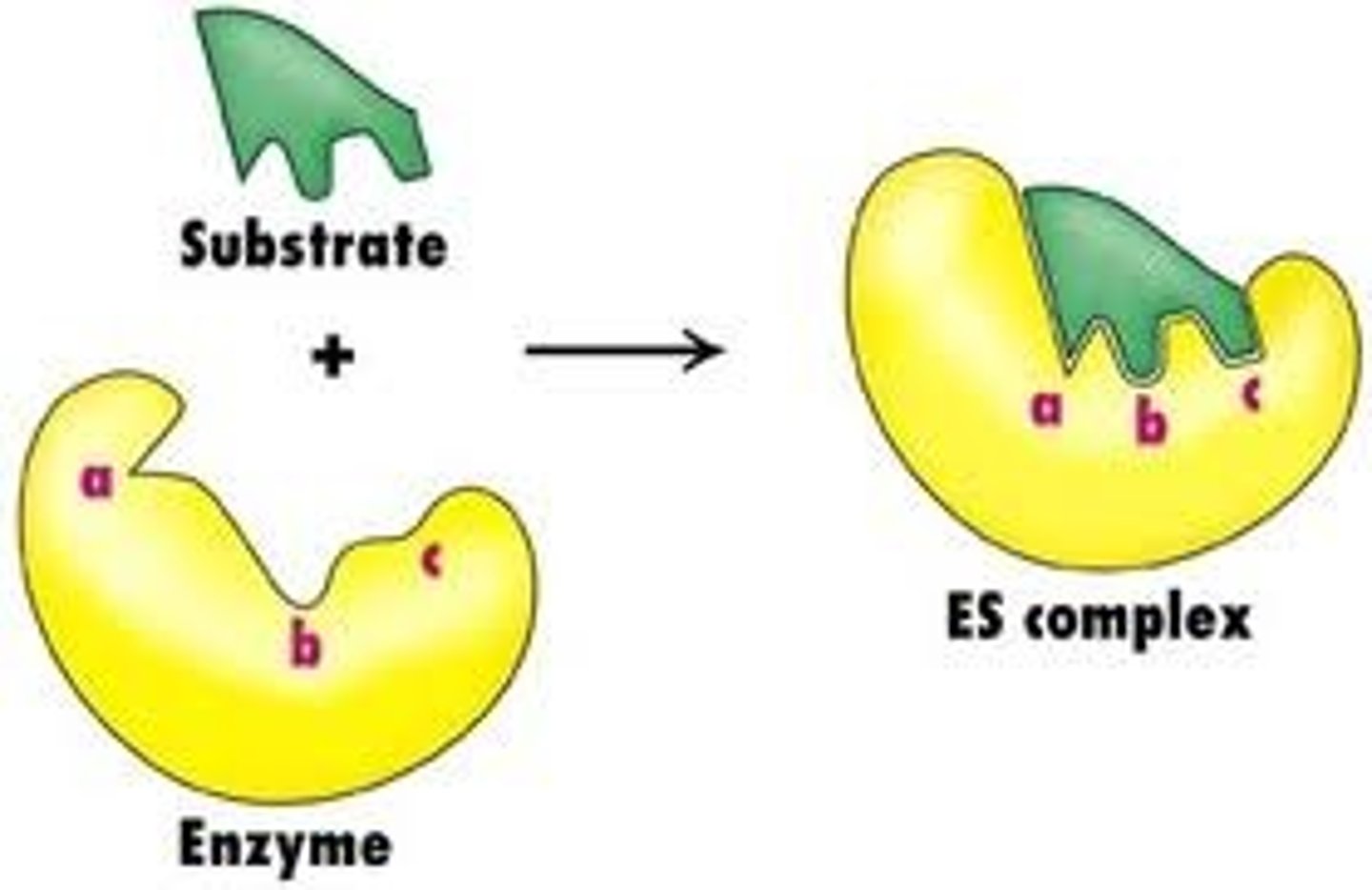
enzyme substrate complex
- substrates held in active site by weak interactions
-substrates converted to products
-products released
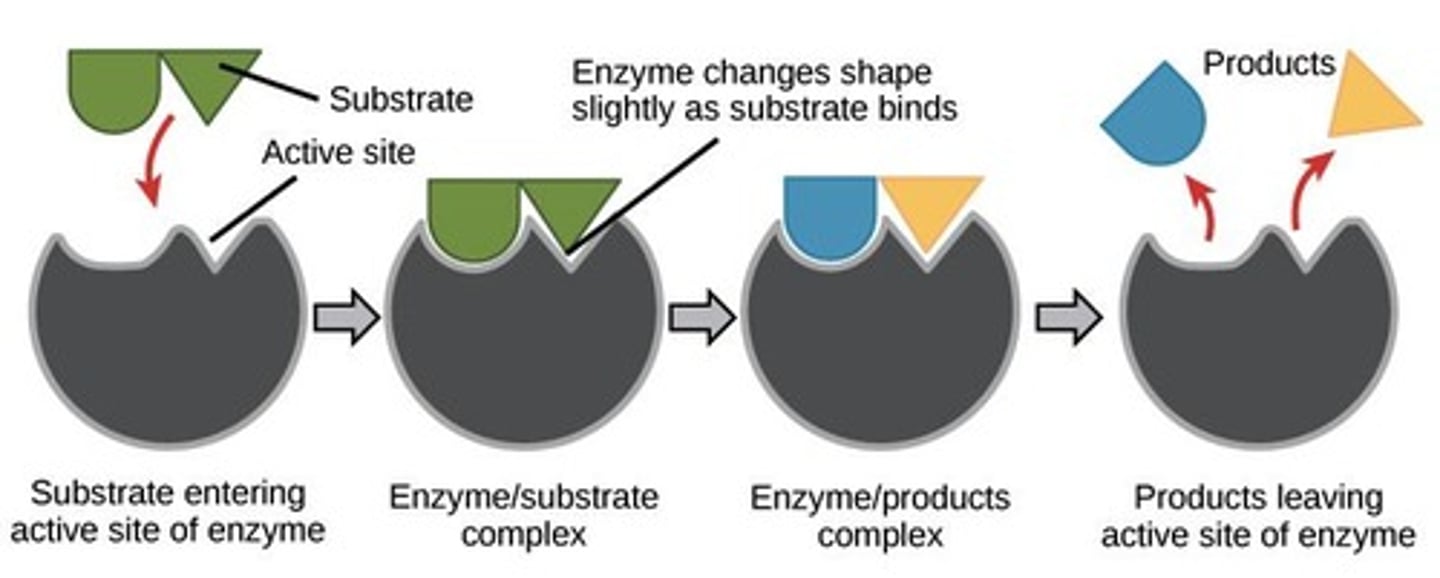
induced fit
enzymes will change the shape of their active site to allow the substrate to bond better
enzyme catabolism
enzyme anabolism
effects on enzymes
- are proteins-> 3D shape can be affected (denatured) by:
-temperature
-ph (likes basic)
-chemicals
shape change=
FUNCTION CHANGE
Optimal Conditions
-conditions that allow enzymes to function optimally
- increases with temp (at a certain point, will denature)
-function best at specific ph (to far outside can break H bonds, changing shape)
Enzyme cofactors
- non-protein molecules that assist enzyme function
-inorganic cofactors= metals
-can be bound loosely or tightly
holoenzyme
-enzyme with cofactor attached
coenzymes
- organic cofactors
-ex. vitamins
enzyme inhibitors
- reduce activity of specific enzymes
-inhibition can be permanent or reversible
permanent and reversible inhibitors
- permanent: inhibitor binds with covalent bonds
-ex. toxins and poisons
-reversible: inhibitor binds with weak interactions
competitive inhibitors
-reduce enzyme activity by blocking substrates to active sites
- can be reversed with increased substrate concentrations
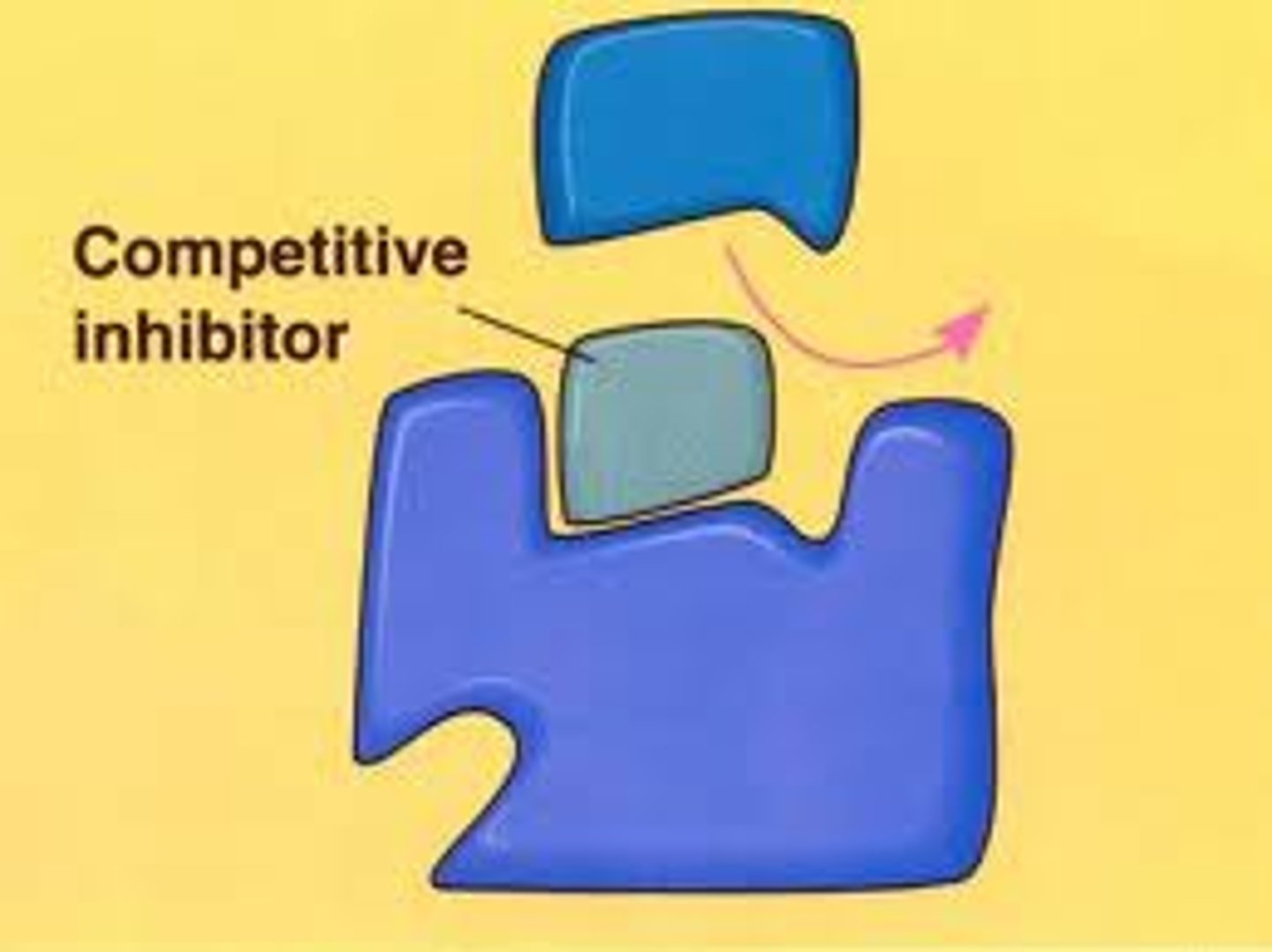

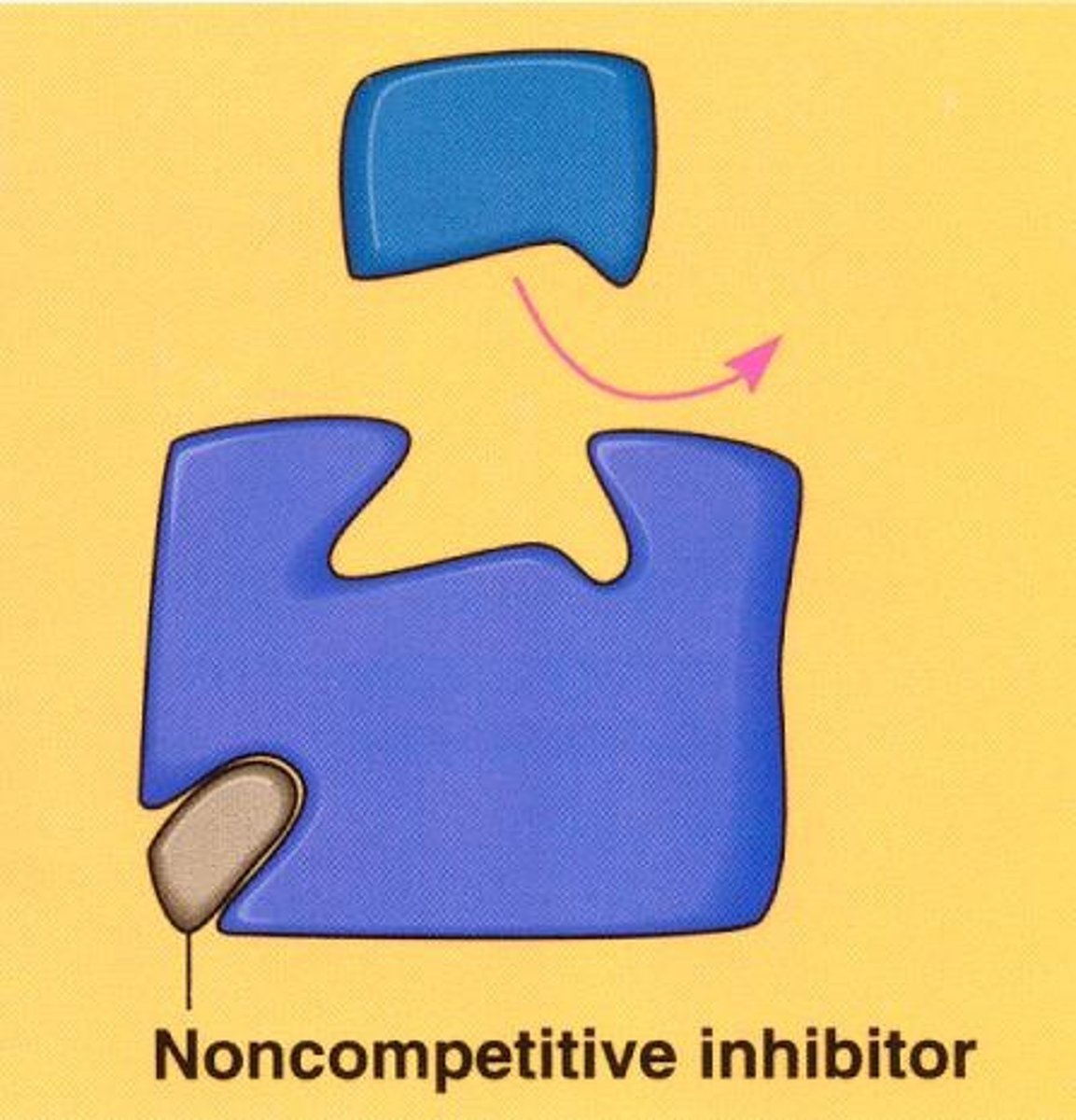
noncompetitive inhibitors
- bind to an area other than the active site (allosteric site) which changes the sahpe of the active site
-type of allosteric inhibition
regulation by cell
- must be able to regulate metabolic pathways
-control when and where enzymes active
-switch genes that code fro enzymes on or off
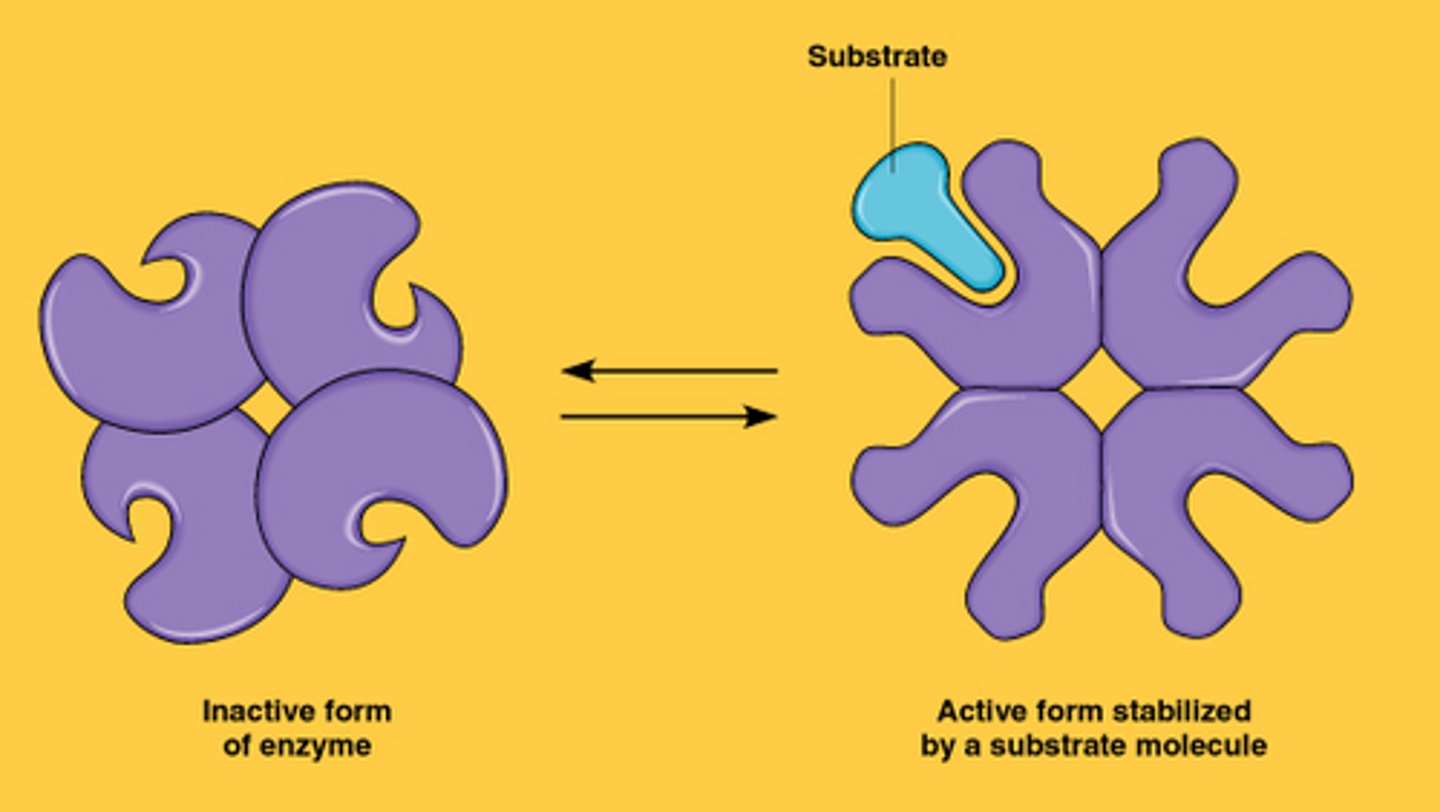
allosteric regulation
- allosteric enzymes have 2 binding sites
- 1 active site
-1 allosteric site (regulatory site other than active)
allosteric regulation how
- molecules bond to allosteric site- changes shape and function of active site
- may result in inhibition (by inhibitor) or stimulation (by activator) of the enzymes activity
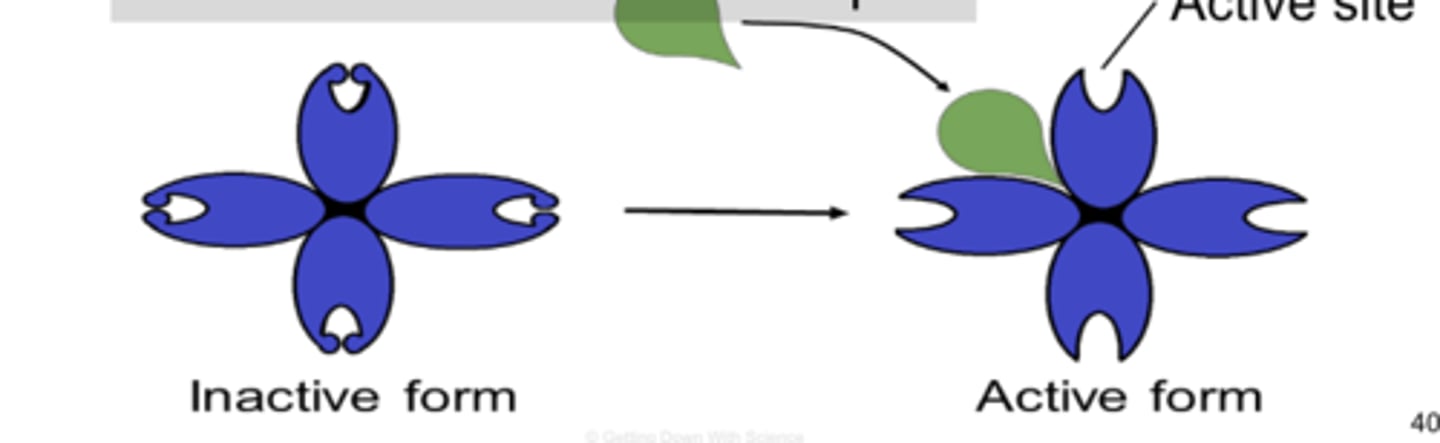
allosteric activator
-substrate binds to allosteric site and stabilizes the shape of the enzyme so that the active sites remain open
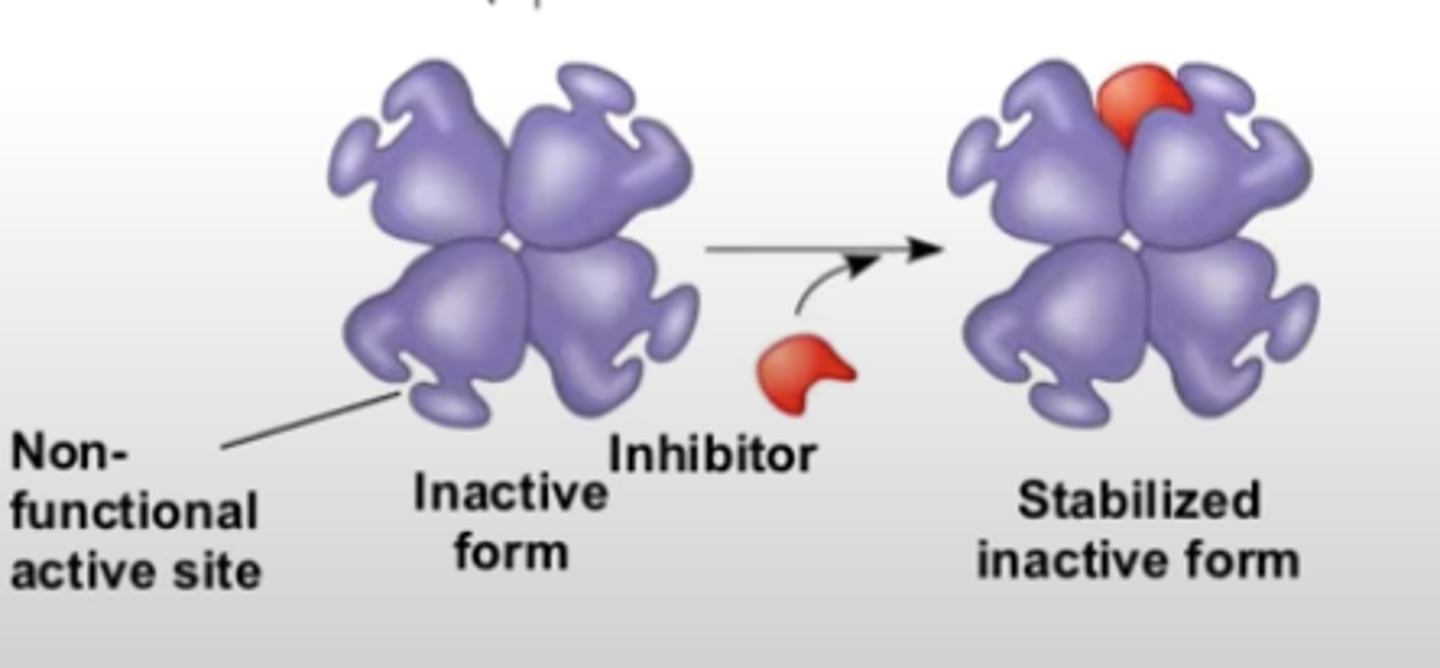
Allosteric inhibitor
substrate binds to allosteric site and stabilizes the enzyme shape so that the active sites are closed (inactive form)
cooperativity
substrate binds to one active site (on an enzyme with more than one active site) which stabilizes the active form
-considered allosteric regulation since binding at one site changes the. shape of other sites