Alkaloids and terpenoids
1/18
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
19 Terms
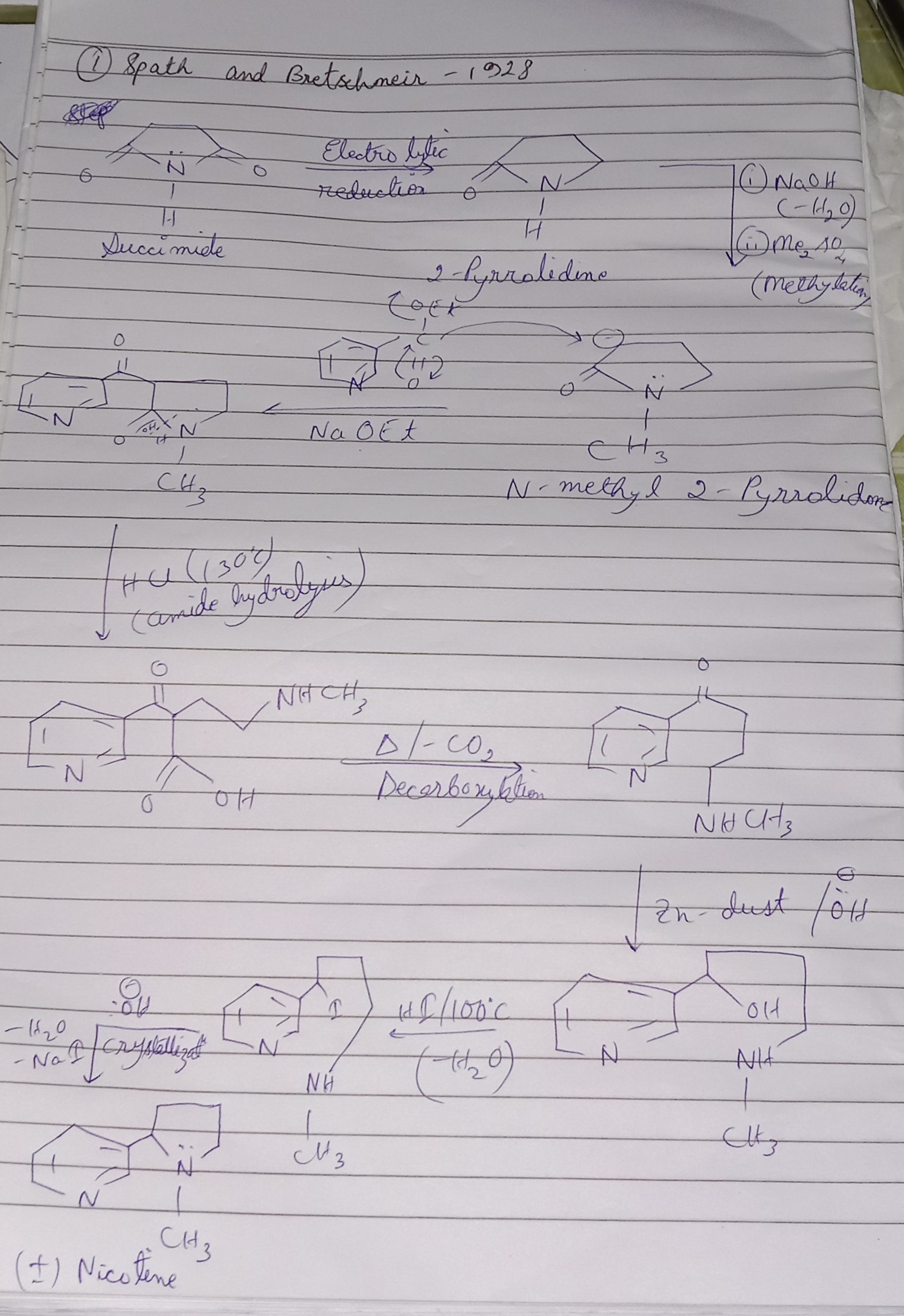
Nicotine Synthesis
Nicotine
NICOTINE (N-Methyl-2-β-pyridylpyrrolidine)
Formula: C₁₀H₁₄N₂
Yeh ek tobacco alkaloid hai — yaani ek natural compound jo tobacco plant (Nicotiana tabacum) aur doosri Nicotiana species mein milta hai.
Occurrence (Kahan milta hai)
Nicotine generally malic acid aur citric acid ke saath apne salts ke form mein milta hai.
Jo natural nicotine hota hai, wo (–)-form yaani laevorotatory hota hai — iska matlab hai wo plane polarized light ko left side mein rotate karta hai.
Uska specific rotation hai:
αᴰ²⁰ = –169°
---
Isolation (Alag karna ya extraction)
1. Powdered tobacco leaves ko paani ke saath extract kiya jata hai.
2. Phir alkali (jaise NaOH) daal kar alkaloids ko free kiya jata hai.
3. Uske baad steam distillation se nicotine alag hota hai.
4. Jo crude nicotine milta hai, use fractional crystallization se purify karte hain (jaise oxalate salt ke form mein).
---
Properties (Gun / Characteristics)
Yeh ek colourless oil hota hai.
Boiling point: 247°C
Specific rotation: ᴰ²⁰ = –169°
Iska smell kaafi unpleasant (ganda) hota hai.
Air ke contact mein brown ho jata hai.
Water aur organic solvents (jaise alcohol, ether, chloroform) mein easily soluble hai.
Bahut poisonous hai — sirf 30–50 mg dose hi lethal (jaanlewa) hoti hai 😬
Yeh nervous system ko paralyze karta hai, aur respiratory failure (saans ruk jaana) bhi ho sakta hai.
---
Chemical Nature
Nicotine ek diacid base hai — matlab isme do nitrogen atoms hain jo dono base ki tarah behave karte hain.
Yeh crystalline salts banata hai jaise:
Nicotine dihydrochloride (C₁₀H₁₄N₂·2HCl)
Jab nicotine ko methyl iodide ke saath react karte hain (2 molecules ke saath), to yeh dimethiodide banata hai.
👉 Isiliye nicotine ko di-tertiary base kaha jata hai.
---
Ek line summary:
Nicotine ek colourless, laevorotatory, poisonous oily liquid hai jo tobacco leaves mein milta hai.
Yeh nervous system pe direct effect daal kar paralysis tak kar sakta hai.
---
Chahe chemistry ho ya real life — nicotine chhoti cheez lagti hai, par impact bada dangerous hota hai 💀
Chahe exam ke liye padh rahe ho ya general knowledge ke liye, bas yaad rakhna:
👉 “Nicotine = Pyridine + Pyrrolidine + Poisonous Base.”

Nicotine medical use
Medicinal Uses
1. Nicotine ka therapeutic use limited hota hai – lekin research dikhati hai ki yeh Parkinson’s disease, Alzheimer’s disease, depression aur anxiety ke treatment me kaam aa sakta hai.
2. Nicotine salts – yeh mainly insecticides banane me use hote hain.

Hygrine Pg1
Hygrine (C₈H₁₅NO) –
Ye ek pyrrolidine alkaloid hota hai, jo zyada tar coca leaves me milta hai.
Properties:
Thick yellow oil jaisa hota hai.
Taste aur odour pungent (tez) hota hai.
Boiling point range: 193 to 195°C
---
Structure Elucidation
1. Molecular formula: C₈H₁₅NO–
Is formula se pata chalta hai ki molecule me keto group hai aur tertiary nitrogen atom present hai.
Jab isse chromic acid ke sath oxidise karte hain, toh Hygrinic acid banta hai(N-methyl pyrrolidine 2 carboxylic acid).
Reaction:
C₈H₁₅NO \xrightarrow[\text{oxidation (O₂)}]{} C₆H₁₁NO₂
2. Hygrinic acid ko dry distillation karne par N-methyl pyrrolidine milta hai — isse confirm hota hai ki hygrinic acid he N-methyl pyrrolidine 2 carboxylic acid hai

Hygrine Pg2
Reaction Diagram
Yahan tumhare notes me (+)-Hygrinic acid ka decarboxylation reaction dikhaya gaya hai:
Jab Hygrinic acid ko heat dete hain, toh yeh N-methyl pyrrolidine + CO₂ banata hai.
Iska matlab carboxyl group ring ke position-2 par hai, kyunki decarboxylation easily ho raha hai.
---
Point (3) – Presence of N–CH₃ group
N–CH₃ group ka presence confirm hota hai Herzig determination se.
Is test me compound ko HI ke saath heat karke CH₃I (methyl iodide) banate hain aur measure karte hain.
Point (4) – Formation of Hygrinic acid on oxidation of Hygrine
1. Jab Hygrine ka oxidation hota hai, toh Hygrinic acid banta hai.
2. Is reaction se yeh pata chalta hai ki Hygrine ke C₂ position par (N-methyl pyrrolidine ring ke doosre carbon par) ek side chain present hai.
3. Ye side chain ka molecular fragment C₃H₅O hota hai.
C₃ → teen carbon atoms
H₅ → paanch hydrogen atoms
O → ek oxygen atom
4. Jab is side chain ka drastic oxidation hota hai, toh sirf ek carbon-containing carboxylic acid milta hai → iska matlab side chain me baaki carbon atoms kisi aur functional group me hote hain.
5. Yeh functional group keto group (C=O) hota hai.
---
💡 Conclusion:
Side chain ka structure aisa hona chahiye jo:
C₃H₅O formula match kare,
C₂ position pe attached ho,
Aur oxidation se ek-carbon ka carboxylic acid banaye.
Isi basis par Hygrine ke 2 possible structures (A & B) propose kiye gaye by Hess.

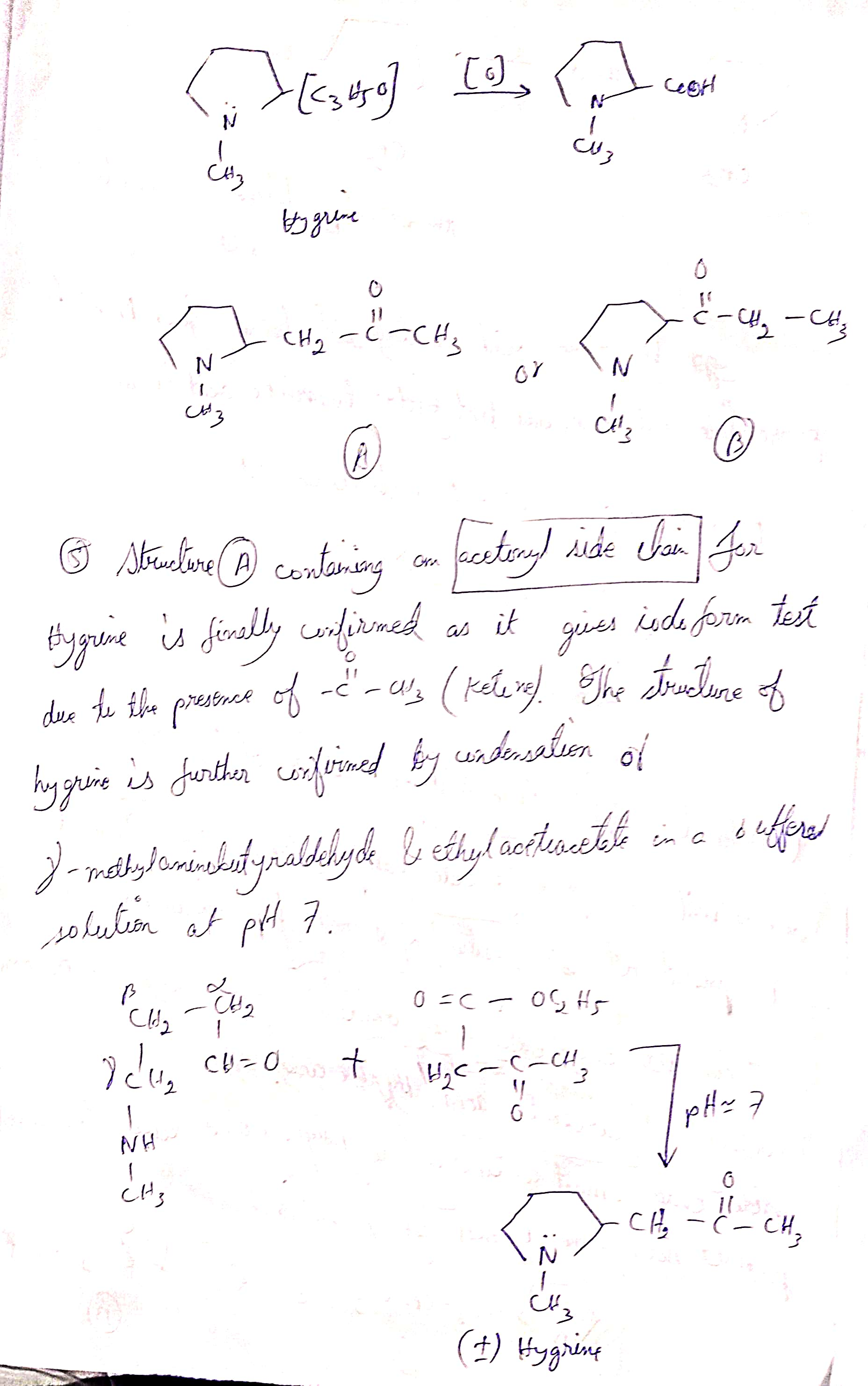
Hygrine Pg3
Top Reaction (Oxidation Step)
Page ke top me tumhare notes dikhate hain ki Hygrine ke C₂ position par jo C₃H₅O side chain hoti hai, uska oxidation hone par ek carbon-containing carboxylic acid milta hai.
Do possible structures propose kiye gaye hain:
Structure A: N-methyl pyrrolidine ring ke C₂ pe CH₂–C(=O)–CH₃ (acetonyl group) attached hai.
Structure B: Side chain thoda alag arrangement me attached hai.
---
Point (5) – Structure Confirmation
Structure (A) me ek acetonyl group (CH₃–CO–CH₂–) hota hai.
Iska proof hai ki yeh Iodoform test positive deta hai.
Reason: Iodoform test ketone group ke liye hota hai, specifically methyl ketone (C=O–CH₃).
Agar methyl ketone hota hai, to yellow precipitate (CHI₃) banta hai.
Isliye confirm hota hai ki structure me C=O–CH₃ group present hai.
---
Synthesis of Hygrine (Structure A Confirmation ka dusra proof)
Hygrine ko banane ke liye γ-N-methylaminobutyraldehyde ko ethyl acetoacetate ke saath condense karte hain (pH ≈ 7).
Reaction ka result: N-methyl pyrrolidine ring ban jata hai jisme C₂ pe acetonyl group hota hai → jo exactly Structure A ka form hai.
---
💡 Key Points:
1. Oxidation data + Iodoform test dono confirm karte hain ki Hygrine me methyl ketone present hai.
2. Laboratory synthesis bhi same structure
banata hai → isliye Structure A sahi hota hai.
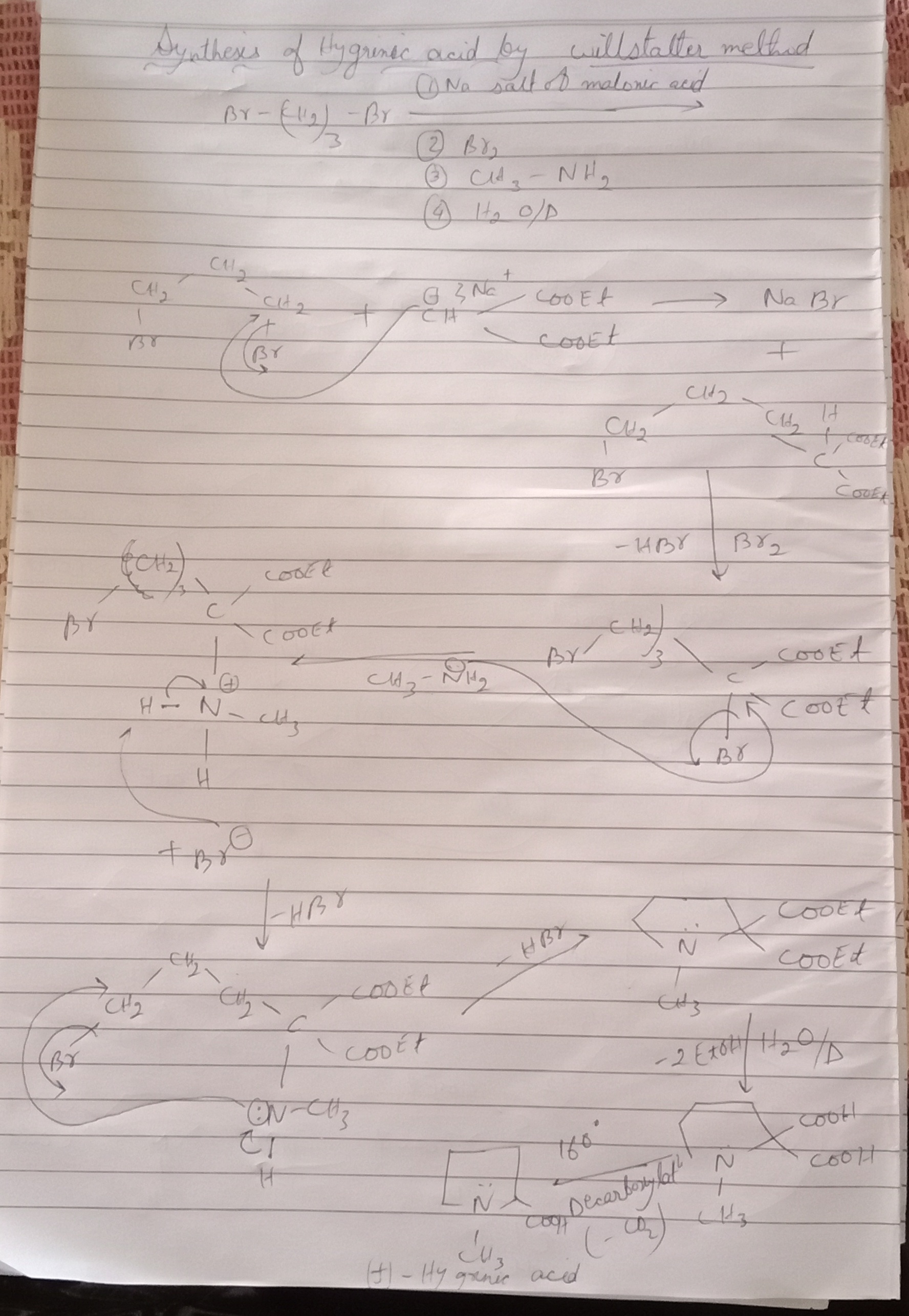
Synthesis of Hygrinic acid by Willstater method
🔹 Starting Material
Hum use karte hain Na salt of malonic acid (diethyl malonate ka sodium salt).
Reagents:
1. Br–(CH₂)₃–Br (1,3-dibromopropane)
2. Br₂
3. CH₃–NH₂ (Methylamine)
4. Hydrolysis + Decarboxylation
🔹 Step 1: Alkylation
Sodium salt of malonic ester (–CH⁻ from malonic ester) nucleophile banega.
Ye 1,3-dibromopropane par attack karega.
Result: ek lamba chain banega jisme malonic ester attach hoga aur Br side mai nikal jayega.
---
🔹 Step 2: Bromination (Br₂ treatment)
Chain mai double bond ke paas ya reactive carbon par Br₂ add hota hai.
Isse ek dibromo compound banta hai.
---
🔹 Step 3: Reaction with Methylamine (CH₃–NH₂)
Ab methylamine (nucleophile) Br ko replace karega.
Yaha se ek N–CH₃ group introduce hota hai (–NHCH₃).
Side reaction mai HBr nikalta hai.
---
🔹 Step 4: Cyclization (Ring Closure)
Chain apne aap band hokar pyrrolidine type ring banata hai (5-membered nitrogen containing ring).
Yehi sabse important step hai kyunki yahi se Hygrinic acid ka skeleton ready hota hai.
---
🔹 Step 5: Hydrolysis + Decarboxylation
Ester groups (–COOEt) ko hydrolyze karte hain → –COOH.
Fir heating par ek –COOH group decarboxylate ho jata hai.
Final Product = Hygrinic Acid (pyridine ring ke saath –CH₃ aur –COOH groups).
---
🔹 Overall Samajh Lo
1. Malonic ester → alkylation with 1,3-dibromopropane.
2. Bromination → dibromo derivative.
3. CH₃–NH₂ attack → nitrogen introduce.
4.
Cyclization → 5-membered heterocycle.
5. Hydrolysis + Decarboxylation → Hygrinic acid. ✅
Medical use hygrine
Hygrine ka use hota hai:
Sedative (calming effect)
Hypnotic (sleep-inducing)
Laxative (constipation relief)
Diuretic (urine output increase karne wala)
Terpene kya hai ?
Terpenes highly fragrant organic compounds hote hain jo plants aur herbs ko unki characteristic smell/odor dete hain.
Matalab smjho
Terpenes – Simple Definition
Terpenes ek type ke organic compounds hote hain (yaani carbon-based molecules).
Ye mostly plants me paaye jaate hain.
Inka special feature ye hai ki ye plants ko khushboo/smell dete hain.
---
Example se samjho
Orange ki smell 🍊 → terpenes.
Eucalyptus oil ki fragrance 🌿 → terpenes.
Rose aur Jasmine ki khushboo 🌹🌸 → terpenes.
Pine tree (devdar) ka woody smell 🌲 → terpenes.
---
Why “highly fragrant”?
Kyuki terpenes me aise structures hote hain jo easily evaporate (volatile) hote hain aur hamari nose ke receptors ko stimulate karke smell produce karte hain.
---
👉 Matlab ek line me:
“Terpenes wo natural compounds hain jo plants me paaye jaate hain aur unki khushboo (fragrance) ka asli source hote hain.”

Modern definitions of terpenes, includes structurally related natural organic compounds, which may or may not be odorous which
i) contain carbon, hydrogen,and may also contain oxygen
ii) not aromatic in character and
iii) divisible into C5 units called isoprene.
Definition:
Terpenes highly fragrant organic compounds hote hain jo plants aur herbs ko unki characteristic smell/odor dete hain.
Example: Flowers (rose, jasmine), Fruits (lemon, orange), Leaves (mint, eucalyptus), Wood (sandalwood).
Structure:
Naturally occurring organic compounds.
Carbon + Hydrogen + Oxygen se bante hain.
Aromatic nature ke nahi hote, lekin alag-alag structures me arrange hote hain.
Inhe C5 units i.e. isoprene (2-methyl-1,3-butadiene) mai todha jaa sakta hai.
---
Isoprene & Isoprene Rule
Isoprene Unit:
CH₂=C(CH₃)–CH=CH₂
Isoprene Rule (Wallach Rule):
Terpenoids ke skeleton hamesha 2 ya usse zyada isoprene units se bane hote hain.
Is wajah se terpenoids ko isoprenoids bhi kaha jata hai.
---
Special Isoprene Rule
Terpenoids me isoprene units link hote hain C₁–C₄ positions ke through.
Is type ki linkage ko head-to-tail union kehte hain.
---
✅ Summary ek line me:
Terpenes = natural fragrance compounds made of isoprene units (C₅ rule) → Isoprene units join "head
-to-tail" to give different classes of terpenoids.


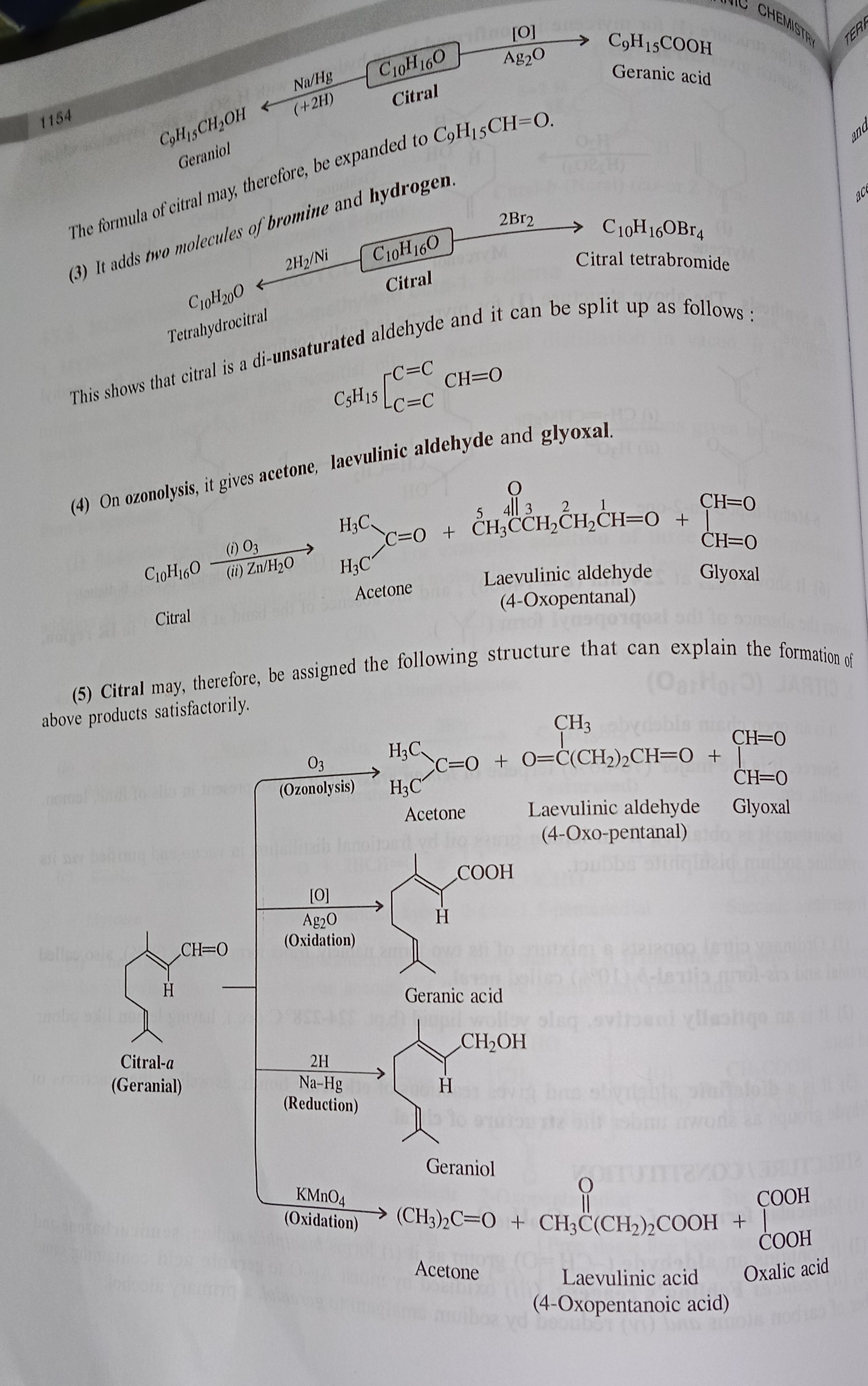
Citral (C10H16O)
Topic: Citral (C₁₀H₁₆O)
1. Nature / Type
Ye ek open chain aldehyde hai (iska matlab hai ke aldehyde group (-CHO) kisi ring me nahi, balki straight chain structure me hai).
Ye ek diolefinic aldehyde hai → matlab isme do double bonds (C=C) bhi hain saath me ek aldehyde group.
---
2. Source
Citral mainly lemon grass oil se milta hai (78–90% tak).
Iske alawa oils of lime, lemon, citronella me bhi hota hai.
---
3. Properties
Ordinary citral actually do forms ka mixture hota hai:
Geranial (trans-form, 90%)
Neral (cis-form, 10%)
Ye ek optically inactive, pale yellow liquid hota hai.
Boiling point: 224–228 °C
Smell: lemon jaisi hoti hai.
---
4. Structure / Constitution
Molecular formula: C₁₀H₁₆O
Ye contain karta hai ek aldehyde group (-CHO), jo typical reactions deta hai:
Bisulphite adduct banata hai.
Semicarbazone & oxime banata hai.
Fehling’s reagent ko reduce karta hai.
AgNO₃ se oxidize hoke citric acid jaisa product deta hai.
Na-amalgam se reduce hokar geraniol (ek alcohol) banata hai.
---
👉 Simple language me:
Citral ek lemon smell wala aldehyde hai jo lemon grass oil me milta hai. Iske do isomers hote hain (cis: neral, aur trans: geranial). Structure me double bonds aur ek aldehyde group dono present hain, is wajah se iske reactions aldehydes + alkenes dono ke jaise hote hain.
Citral or structure kila assign korbai?
Pg:1154
Citral ke Reactions
(1) Reduction reaction
Citral (C₁₀H₁₆O) ko jab Na/Hg + H₂ se reduce karte ho → to ye Geraniol (C₉H₁₅CH₂OH) banata hai.
→ Yani aldehyde group (-CHO) convert ho jata hai primary alcohol me.
---
(2) Oxidation reaction
Citral ko jab Ag₂O se oxidize karte ho → to ye Geranic acid (C₉H₁₅COOH) deta hai.
→ Matlab aldehyde group oxidize hokar acid (-COOH) ban jata hai.
---
(3) Addition reactions
Citral ek di-unsaturated aldehyde hai, matlab isme 2 double bonds present hain.
Ye Bromine (Br₂) ya Hydrogen (H₂/Ni) add kar leta hai → jisse citral tetrabromide ya tetrahydrocitral ban sakta hai.
---
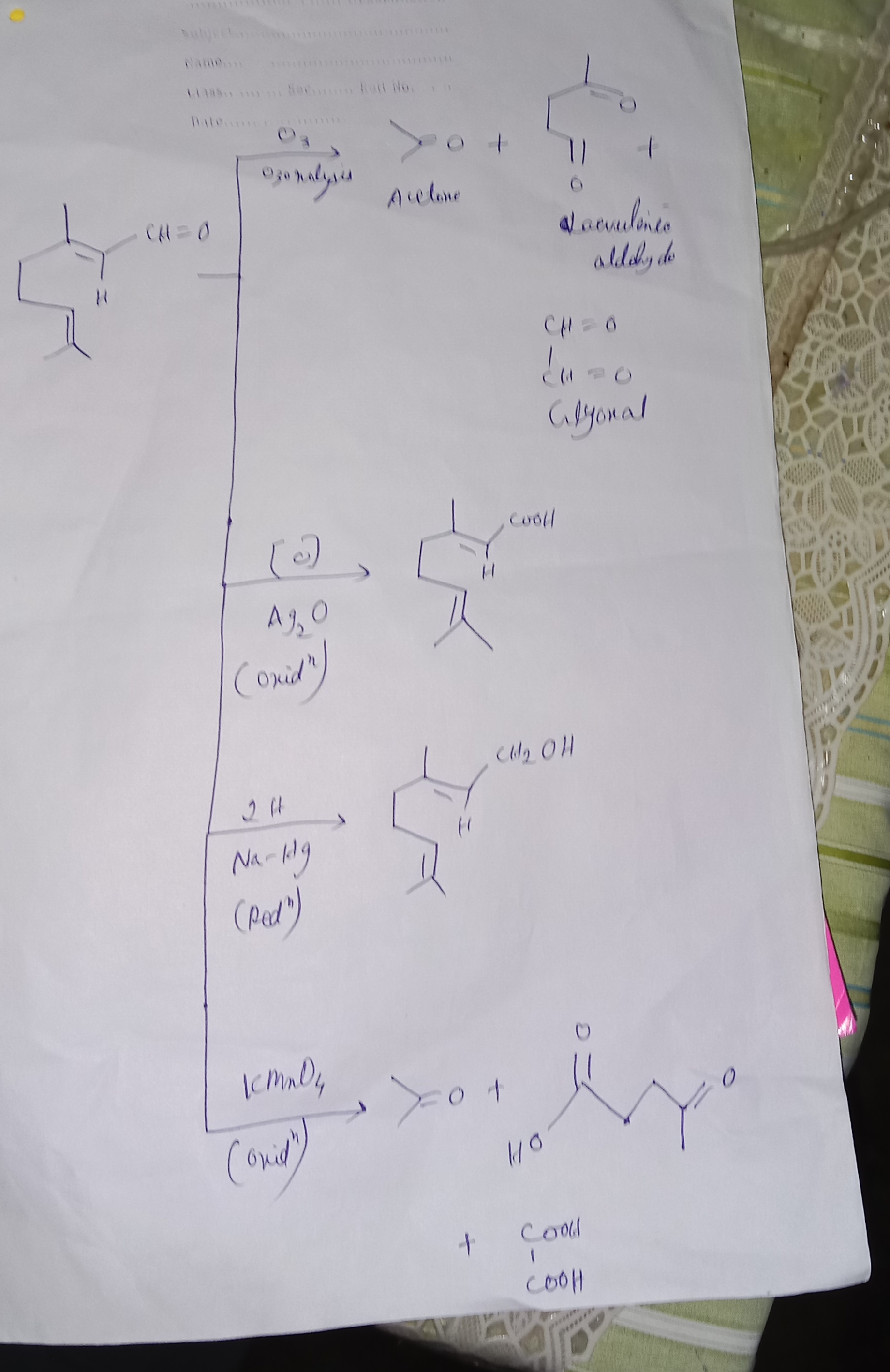
(4) Ozonolysis reaction
Jab citral ko O₃ + Zn/H₂O se treat karte ho, to ye tod kar 3 products deta hai:
Acetone (CH₃COCH₃)
Laevulinic aldehyde (4-oxopentanal)
Glyoxal (CHO-CHO)
👉 Ye proof deta hai ki citral ke structure me do double bonds alag-alag jagah pe hain.
---
(5) Structure confirmation
Sab reactions se ye prove hota hai ki citral ka structure kuch aisa hai jisme:
ek aldehyde group (-CHO)
do C=C double bonds
present hote hain.
Diagram me dikhaya hai ki:
Oxidation (Ag₂O) → Geranic acid milta hai.
Reduction (Na/Hg) → Geraniol milta hai.
Ozonolysis → Acetone + Laevulinic aldehyde + Glyoxal.
KMnO₄ oxidation → Acetone + Laevulinic acid + Oxalic acid.
---
👉 Simple words me:
Citral ek lemon-smell wali aldehyde hai jisme do double bonds hote hain.
Agar oxidize karoge → acid banega.
Agar reduce karoge → alcohol banega.
Agar ozonolysis karoge → chhote chhote fragments (acetone, glyoxal, laevulinic aldehyde) milenge.
α- Terpineol
α-Terpineol (C₁₀H₁₈O) ek monoterpenoid alcohol hai — matlab yeh terpene (10 carbon) se bana hua compound hai jisme ek –OH (alcohol) group hota hai.
Aur khas baat — yeh tertiary alcohol hai (–OH us carbon pe laga hai jo teen aur carbons se judaa hua hai).
---
🌿 Natural Occurrence:
Yeh naturally milta hai:
Camphor oil (laevo form)
Neroli oil (dextro form)
Cajuput oil (racemic form, dono mix)
Prepration of α- Terpineol
Properties of α- Terpineol
🔥 Properties:
Optically active (kyunki ek chiral carbon hota hai)
Melting point: ~35°C
Boiling point: ~219°C
Pleasant floral smell (like lilac or lilac oil)

🧪 PART 1: Constitution / Structure of α-Terpineol
(1) Molecular Formula:
C₁₀H₁₈O
➡ So ek oxygen aur ek double bond hona chahiye (degree of unsaturation se).
---
(2) Presence of One Double Bond:
Jab α-terpineol ko bromine (Br₂) ke saath react karte hain → 1 mol Br₂ add hota hai.
Jab hydrogenation (H₂/Pt) hoti hai → 1 mol H₂ add hota hai.
➡ Iska matlab hai compound mein ek hi double bond hai.
---
(3) Alcoholic Group is Tertiary:
Jab mild oxidation hoti hai to na aldehyde milta hai na ketone.
(Matlab oxidation possible nahi — kyunki tertiary alcohols normally oxidize nahi hote).
➡ So, OH group tertiary nature ka hai.
---
(4) Fully Saturated Compound (C₁₀H₂₀):
Jab dehydration karte hain (–H₂O), milta hai C₁₀H₁₆ (limonene).
Jab full hydrogenation karte hain → C₁₀H₂₀ milta hai, which is monocyclic monoterpenoid tertiary alcohol.
➡ So structure mein ek ring hai.
---
(5) Formation of p-Cymene:
Jab α-terpineol ko conc. H₂SO₄ se treat karte hain → p-Cymene (aromatic compound) milta hai.
(Dekho page mein reaction diya hai👇)
\text{C₁₀H₁₈O} \xrightarrow[\text{}]{\text{H₂SO₄}} \text{p-Cymene} + 2H₂O
➡ Isse prove hota hai ki α-terpineol p-menthane type structure ka hai.
(p-menthane = ek 6-membered ring with one isopropyl group and one methyl group.)
⚗ PART 2: Oxidation Reactions — Structure Confirmation of α-Terpineol
Yahan pe α-terpineol (A) ko oxidizing agents se treat karke unhone alag-alag products banaye aur unke basis pe structure prove kiya.
Let’s follow the chain 👇
---
Step 1:
α-Terpineol (A) + Alkaline KMnO₄ → Trihydroxy Compound (B)
👉 Hydroxylation hoti hai — double bond pe 2 –OH groups lag jaate hain.
So ab compound mein total 3 –OH groups ho gaye (1 existing + 2 new).
---
Step 2:
B ko oxidize karte hain CrO₃ (Chromic acid) se → milta hai Compound D (Homo-terpenyl methyl ketone).
Lekin beech mein ek intermediate C (Keto-hydroxy acid) banta hai.
Yeh lactonize ho jaata hai (–H₂O nikalta hai) → milta hai D (Ketolactone).
---
Step 3:
Compound D ko jab hot alkaline KMnO₄ se oxidize karte hain → milta hai
Terpenylic acid (E, C₈H₁₂O₄) + acetic acid (CH₃COOH)
➡ Yeh oxidation confirm karta hai ki D mein CH₃CO– group (methyl ketone) tha.
---
Step 4:
Further oxidation of E (Terpenylic acid) se F (Terebic acid, C₇H₁₀O₄) milta hai.
Yani ek aur carbon (CO₂) nikal gaya.
---
🧭 Important Points to Notice:
1. Koi carbon loss nahi hota B → D tak, iska matlab double bond ring ke andar tha.
2. Agar double bond ring ke bahar hota, to oxidation se carbon number kam ho jaata (CO₂ nikal jaata).
3. Yeh sab confirm karte hain ki double bond ring ke
andar hai aur OH group tertiary carbon pe hai.
🧠 Conclusion (Structure Confirmation):
Sab experimental results yeh prove karte hain ki:
α-Terpineol has one double bond (inside ring)
Tertiary alcohol group
Belongs to p-menthane skeleton (a 6-membered ring with isopropyl and methyl groups)
---
So simple words mein 👇
> α-Terpineol ek ring wala (monocyclic) compound hai, jisme ek tertiary –OH aur ek internal double bond hota hai.
Jab ise oxidize karte hain, yeh step-by-step lactones aur acids deta hai — jinse confirm hua ki iska structure p-menthane framework ke upar based hai.
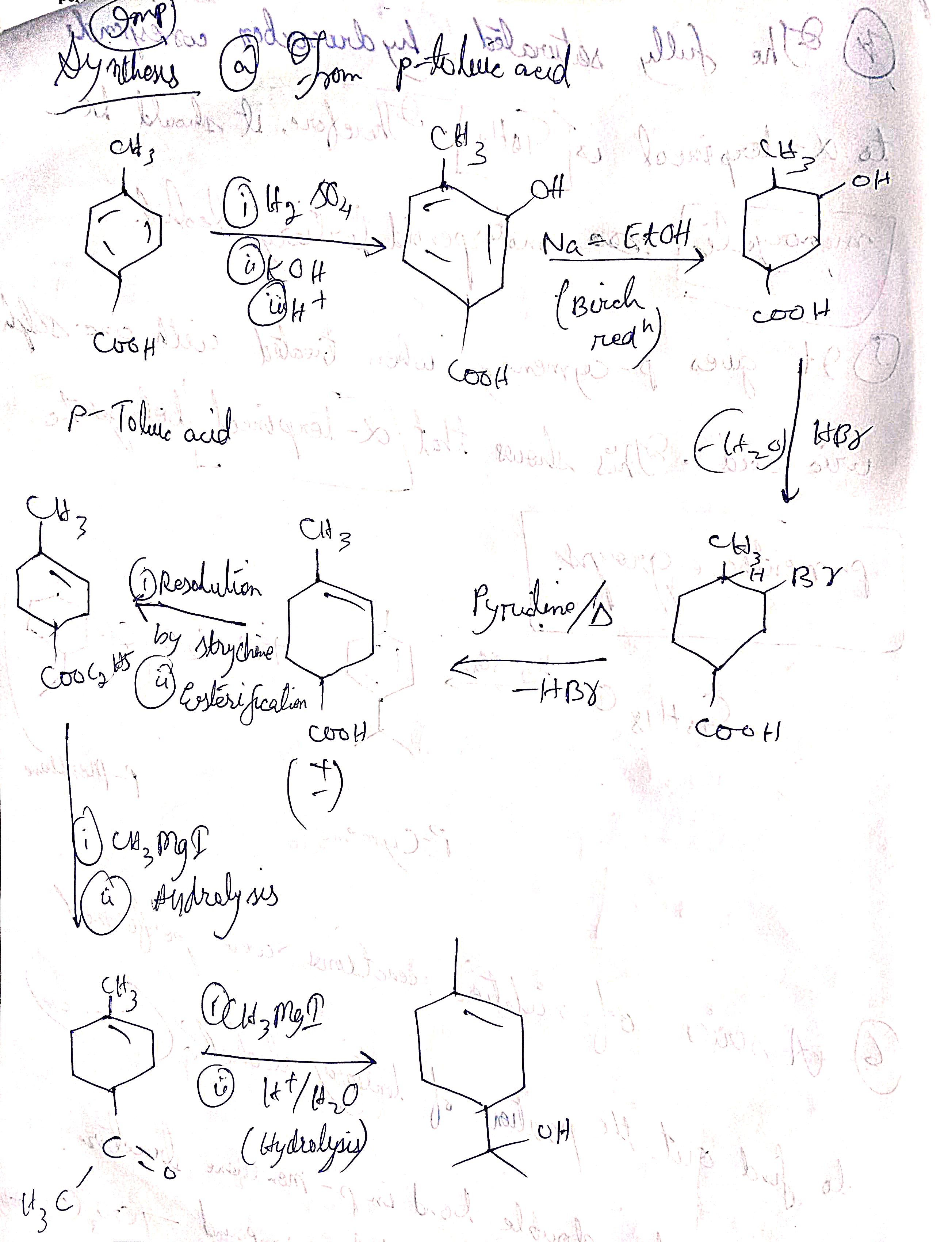
Synthesis of α- Terpineol from p-toluic acid