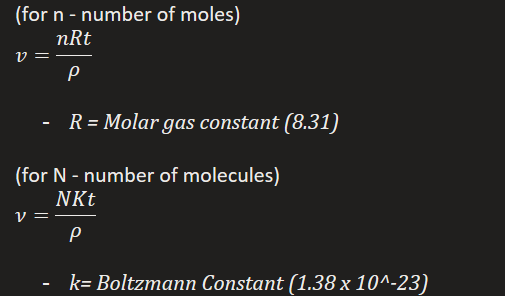Physics - Thermodynamics
1/23
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
24 Terms
What does the First Law of Thermodynamics state?
Internal energy increases when either: Heat increases OR work done to object increases.
What is Internal Energy
Internal energy is the sum of the randomly distributed potential and kinetic energies in a body.
What do you need to remember when something changes states of matter?
Potential energy changes but kinetic energy remain the same.
Give type of Kinetic Energies.
1 - Translational
2 - Rotational
3 - Vibrational
What is potential energy caused by in substances?
The mutual attractive forces between molecules.
Negative Electrostatic Potential
e.g. Solid → High Negative Electrostatic Force
Liquid → Small Negative Electrostatic Force
Gas → Zero Electrostatic force
Outline differences between potential and kinetic energy
Potential Energy | Kinetic Energy |
Due to position of molecules | Due to vibration or motion of molecules |
Independent of temperature | Contingent on temperature |
| Also called thermal energy |
Give the worded internal energy formula.
Change in internal energy = Energy supplied by heating + Energy supplied by work done to it.
What is Temperature?
The measure of kinetic energies of particles in a substance.
When and how is kinetic energy transferred between systems.
When Temperatures are different + Convection, Conduction, & Radiation
What is the boiling point of water?
100°C
Water and steam co-exist in thermodynamic equilibrium
Only when Atmospheric pressure is = 1
Smallest possible temperature?
Absolute zero. 0K = -273°C
Difference between Heat & Temperature?
1 - Heat is transfer of thermal energy between two objects due to difference in temperature.
2 - Temperature is the average kinetic energy of all particles within body.
Temperature Equation?
T = P/V
What is Avogadro’s Law?
Volume is directly proportional to Number of molecules/ number of moles.
What is Boyle’s Law?
Volume is inversely proportional to Pressure.
What is Charles’ Law?
Volume is directly proportional to T.
What is pressure Law?
Temperature is directly proportional to Pressure
What is assumed when using the Ideal Gas Laws?
That all other variables of gas are constant.
What is Atmospheric Pressure equal to?
Atmospheric pressure = 1.01 x 10^5
Define an Ideal Gas.
Theoretical gas that obeys all laws at all temperatures and pressures.
Write out the assumptions made for an Ideal Gas…
Mutual attractive forces between molecules are negligible
All collisions are elastic
Volume of molecules is negligible
Molecules move in random motion
Define an Isothermal Change.
Any change while temperature is constant.
Define Isobaric change?
Any change where pressure is constant.
Work done = pressure x change in volume
Give the ideal gas equation.
(for n - number of moles)
R = Molar gas constant (8.31)
(for N - number of molecules)
k= Boltzmann Constant (1.38 x 10^-23)