Ch 16: Chemical Equilibrium
1/50
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
51 Terms
What does it mean for a process to be reversible?
The products of the reaction can react to form reactants
In regard to the rate, what does it mean for a system to be in equilibrium?
The rates of the forward reaction and reverse reaction are the same
What does it mean when we say equilibrium is a "dynamic state"?
Both forward and reverse reactions continue to occur, but there's no net change in reactant or product concentrations over time.
True or False: At equilibrium, chemical reactions stop occurring.
False. Reactions continue in both directions, but concentrations remain constant.
What remains unchanged at equilibrium?
The concentrations of reactants and products.
In what ways can equilibrium be established?
Starting with only reactants, only products, or any mixture of both.
True or False: Equilibrium can only be reached if both reactants and products are present initially.
False. It can be reached from reactants only, products only, or a mix.
What is the reaction quotient?
Qc = a fraction with product concentrations in the numerator and reactant concentrations in the denominator
each conc. is raised to a power = to its stoichiometric coefficient in the balanced chemical equation
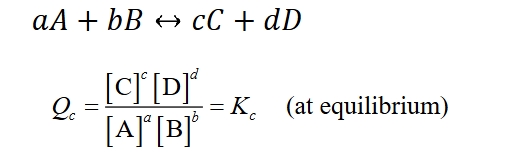
What is the law of mass action?
the rate of a chemical reaction is directly proportional to the product of the concentrations of the reactants, each raised to the power of their respective stoichiometric coefficients.
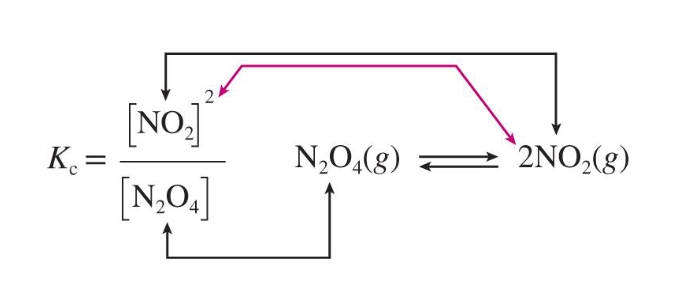
What is the equilibrium constant?
Kc = (Conc of product/s raised to stoichiometric coefficient)/(Conc of reactant/s raised to stoichiometric coefficient)
What is the reaction quotient of Ag+(aq) + 2NH3(aq)to Ag(NH3)2+(aq)?
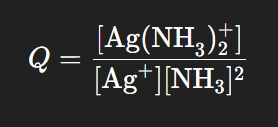
What is the reaction quotient for N2(𝑔) + 3H2(g) ⇄ 2NH3(𝑔)?
*if we were using partial pressure (atm): Qc = (PNH3)2/(PN2)(PH2)3 where P = pressure
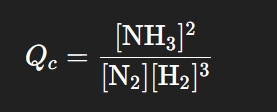
If Kc > 1 then _____ are favored
If Kc < 1 then _____ are favored
Products are favored; there are more products present
Reactants are favored; there are more reactants present
When is it better to use Qc vs Kc?
Only use Kc when the system is at equilibrium
Qc is used when the system is not known to be at equilibrium
What does it mean for a chemical reaction to be heterogeneous?
When the species in a reversible chemical reaction are not all in the same phase
ie some are gas, some are solid, etc.
If you are asked to find the Kc of a heterogeneous reaction, what are the rules you need to follow?
Only gas and aqueous appear in equilibrium
Pure solids and pure liquids do NOT appear in equilibrium
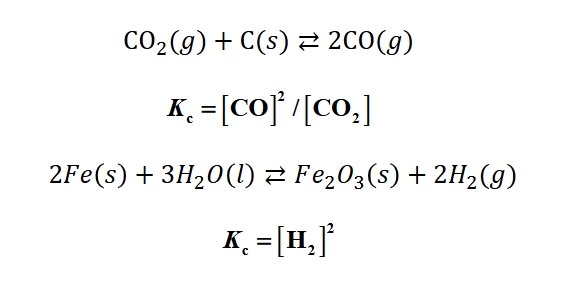
(True/False): Reversing a chemical equation inverts the equilibrium constant.
True, og Kc becomes 1/Kc
What is the new equilibrium constant for:
2C(g) to A(g) + B(g) if the original is A(g) + B(g) to 2C(g) and Kc = 4.39 × 10⁻³
4.39 × 10⁻³
1 / (4.39 × 10⁻³)
√(4.39 × 10⁻³)
1 / (4.39 × 10⁻³)
What happens to Kc when a reaction is multiplied by a factor n?
Kc is raised to the power of n, (Kcⁿ)
For the reaction:
2A(g) + 2B(g) ⇌ 4C(g)
What is the relationship to the original Kc if the original reaction is A(g) + B(g) to 2C(g).
Kc2
True or False: Dividing a reaction by 2 results in taking the square root of the original Kc.
True
What is the new Kc when two reactions are added together?
Multiply the individual Kc values: Kc₁ × Kc₂
Given:
A + B ⇌ C (Kc₁ = 4.39 × 10⁻³)
C ⇌ D + E (Kc₂ = 1.15 × 10⁴)
What is Kc for the overall reaction: A + B ⇌ D + E?
50.5
Which manipulation results in Kc = √(original Kc)?
Dividing the reaction by 2
What is the relationship between Kc and Kp?
Kp = Kc(RT)Δn
where R=0.08206 L(atm)/K(mol) and Δn is the moles of products - moles of reactants
What is Kp?
The equilibrium constant that expresses the ratio of the partial pressures of products to reactants in a gaseous chemical equaiton.
How are K and ΔG° related?
They relay the same information:
K>1 then -ΔG° (spontaneous reaction)
K<1 then +ΔG° (nonspontaneous reaction)
What does it mean if Qc < Kc?
The ratio of initial concentrations of products to reactants is too small.
To reach equilibrium, reactants must be converted to
products.The system proceeds in the forward direction
What does it mean if Qc = Kc?
The initial concentrations are equilibrium concentrations.
The system is at equilibrium
What does it mean if Qc > Kc?
The ratio of initial concentrations of products to reactants is too large.
To reach equilibrium, products must be converted to
reactants.The system proceeds in the reverse direction.
What is the relationship between ΔG and ΔG°?
ΔG = ΔG° + RT In Q
R is the gas constant(8.314 J/K mol).
T is the Kelvin temperature.
Q is the reaction quotient.
Which determines spontaneity, ΔG or ΔG°?
ΔG
What is the relationship between ΔG° and K?
ΔG° = −RT In K
*at equilibrium, ΔG=0 and Q=K
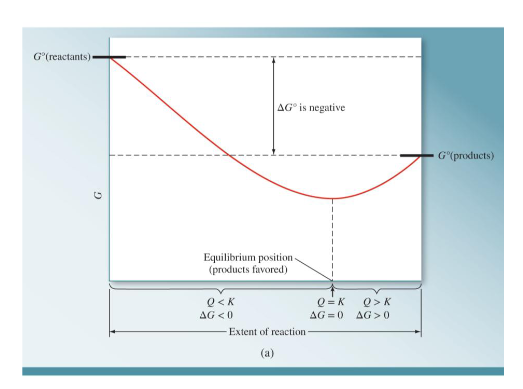
What does a graph look like when the G° of the reactants is less than the G° of the products? Draw a graph and include the sign of the ΔG°, when Q<K, when Q=K, when Q>K, when ΔG <0, when ΔG=0, and when ΔG>0.
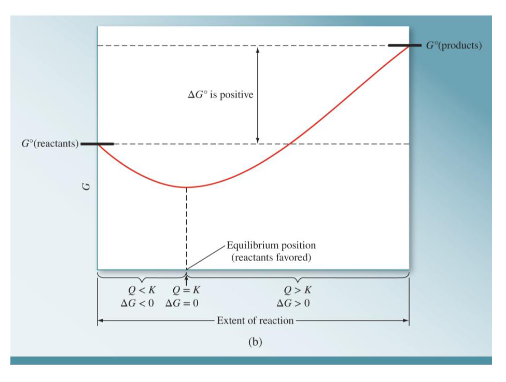
What does a graph look like when the G° of the reactants is more than the G° of the products? Draw a graph and include the sign of the ΔG°, when Q<K, when Q=K, when Q>K, when ΔG <0, when ΔG=0, and when ΔG>0.
If products are favored in a reaction at equilibrium, what does that mean for the K, lnK, and ΔG° values?
K is >1
lnK is postive
ΔG° is negative
If reactants are favored in a reaction at equilibrium, what does that mean for the K, lnK, and ΔG° values?
K < 1
lnK is negative
ΔG° is positive
If neither products nor reactants are favored in a reaction at equilibrium, what does that mean for the K, lnK, and ΔG° values?
K = 1
lnK is 0
ΔG° is 0
What is an ICE Table?
A table used to help determine initial conc. change in conc. and equilibrium conc. of all parts of a reaction.
*Practice how to use this, there will be an extra credit ? on this
What does the Le Châtelier’s principle state?
that when a stress is applied to a system at equilibrium, the system, will respond by shifting in the direction that minimizes the effect of the stress.
ie substances are added or removed from a system to reach equilibrium
What causes the equilibrium to shift to the left (towards the reactants)?
The removal of reactants or the addition of products.
What causes a reaction to shift to the right (towards the products)?
reactants are added or products are removed
What happens to the equilibrium position when the volume of a gaseous system is decreased? Increased?
when V is decreased, the equilibrium shifts toward the side with fewer moles of gas to reduce pressure
When V is increased, the equilibrium shifts toward the side with more moles of has to increase pressure
What factor can change the value of the equilibrium constant in a chemical reaction?
temperature changes can alter the equilibrium constant.
In an endothermic reaction, is heat a reactant or a product?
Heat is a reactant.
What happens to the equilibrium position and Kc when heat is added to an endothermic reaction?
The equilibrium shifts toward the products, and Kc increases.
What happens to the equilibrium position and Kc when heat is removed from an endothermic reaction?
The equilibrium shifts toward the reactants, and Kc decreases.
In an exothermic reaction, is heat a reactant or a product?
Heat is a product.
What happens to the equilibrium position and Kc when heat is added to an exothermic reaction?
The equilibrium shifts toward the reactants, and Kc decreases.
What happens to the equilibrium position and Kc when heat is removed from an exothermic reaction?
The equilibrium shifts toward the products, and Kc increases.