biological basis of mental disorders
1/32
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
33 Terms
mental illness
a disorder that affects a person's thoughts, emotions, and behaviors
biological basis of mental illnesses
-disorders of brain, influenced by abnormalities in neurochemical processes impact on neurotransmitters
-abnormalities in brain structure/function
-genetics, inheritability (influence)
-environmental factors → interact with genetic predisposition
-childhood trauma, stress
-outcomes → neuroplasticity
modern approaches to mental illnesses
-integrate bio/psych/social factors
-treatments → combine bio and psych therapy → helpful!
-bio-psycho-social model
addiction
-compulsive drug-seeking behaviour
-inability to control substance use
-chronic
mesolimbic dopamine pathway
one of two major dopamine pathways; may be involved in psychotic reactions and in drug reward
mesolimbic dopamine pathway route
from ventral segmental area (midbrain) to nucleus accumbens (reward system) to amygdala, hippocampus and other limbic structures
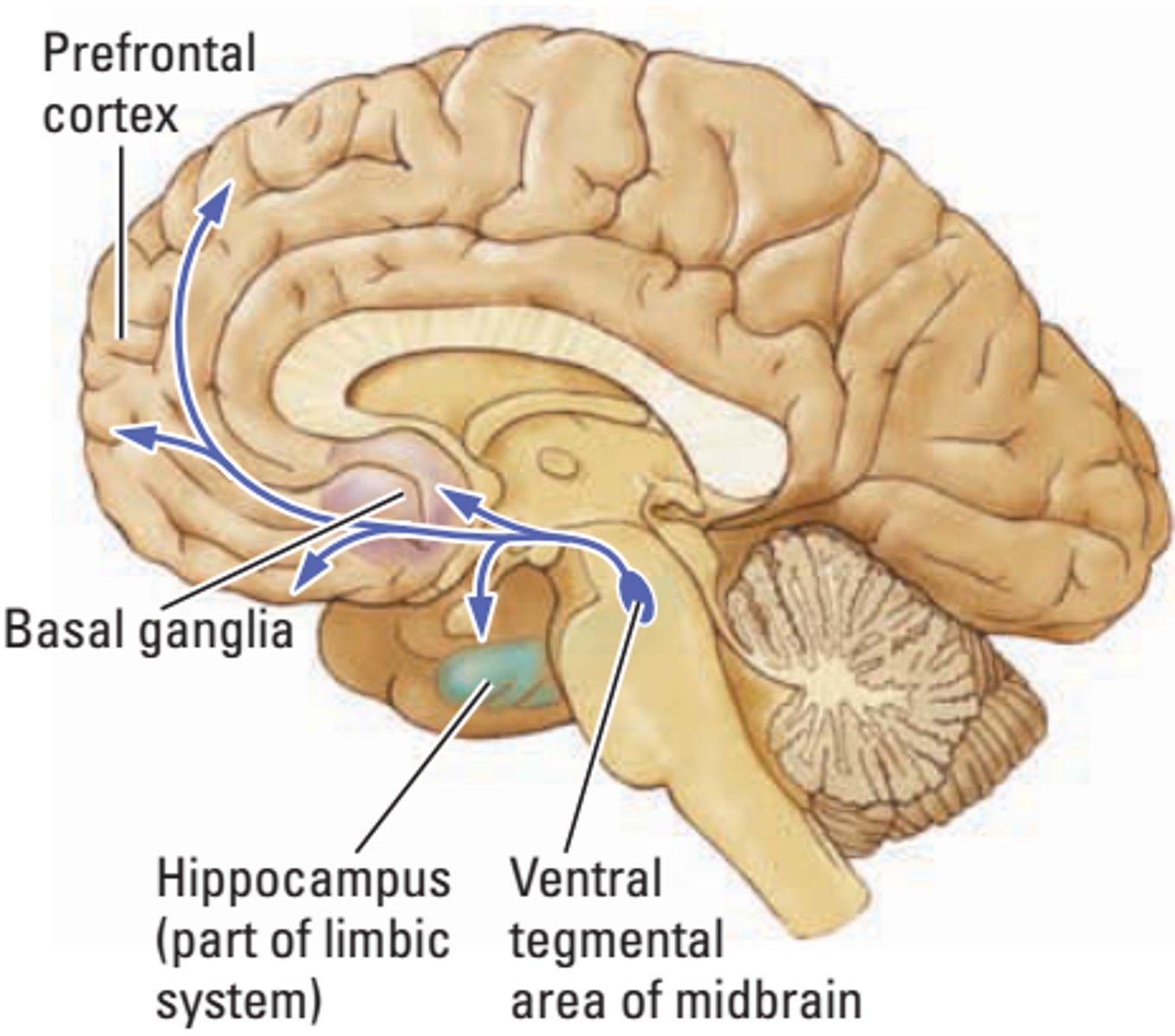
mesolimbic system
A reward-based area in the brain implicated in substance-related disorders.
Mesocortical reward pathway
Cognitive control, decision-making, loss of control, emotional regulation
Mesocortical reward pathway route
from ventral tegmental area to dorsolateral prefrontal cortex to anterior cingulate gyrus
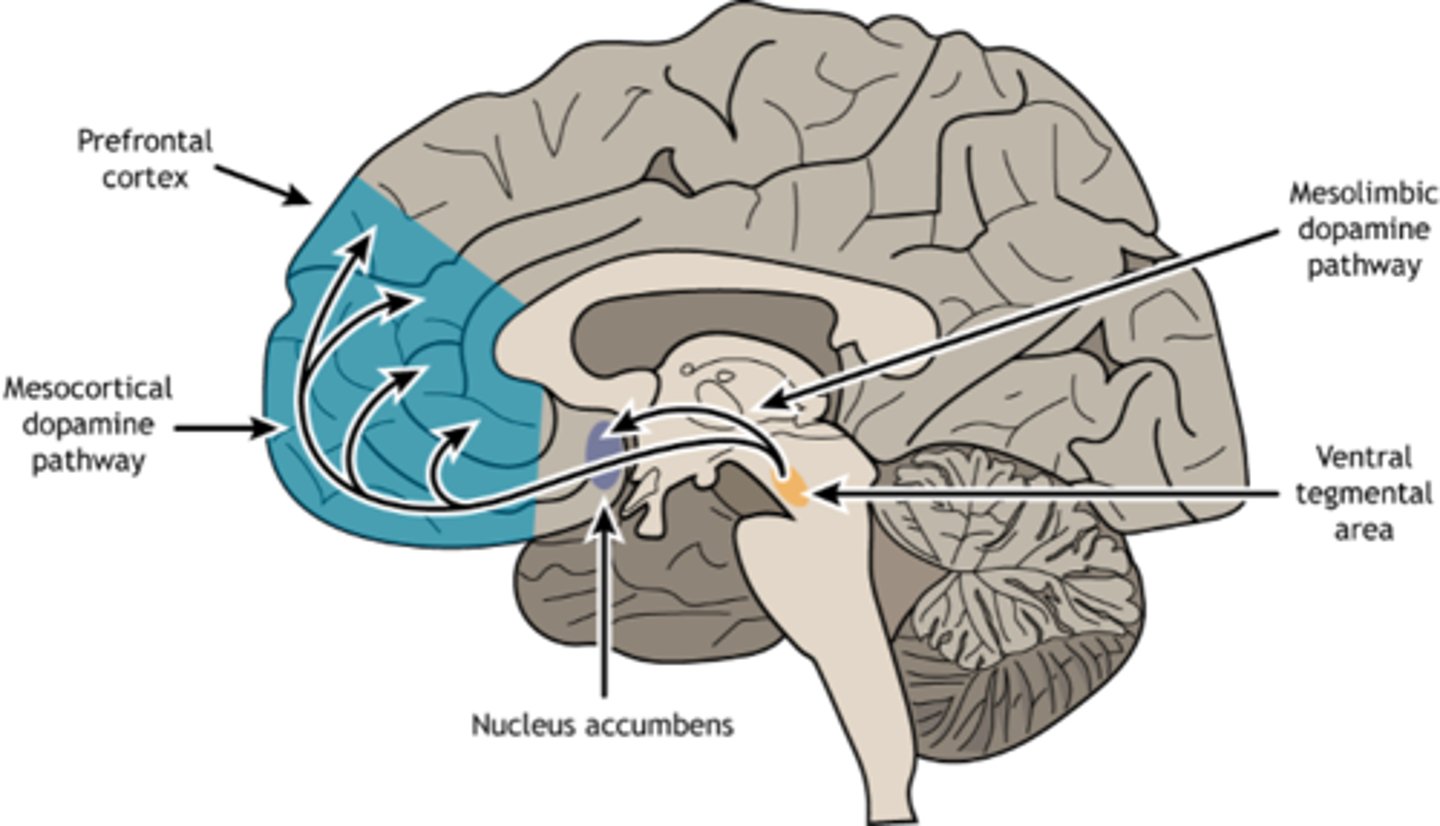
how do the mesolimbic and mesocortical pathways make addiction more prevalent
mesolimbic → drive craving
mesocortical → impaired control mechanism to reduce ability to resist urges
substances affecting brain functions
-Alcohol enhances the effects of GABA
-Opioids release large amounts of dopamine
-Stimulants block the reuptake of dopamine
genetic factors in addiction
-Addiction is partly heritable
-Genes involved in metabolism
environmental factors in addiction
-stress or trauma or peer influence
-interact with genetic predispositions
long term effects of addiction
-Neuroplasticity (adapts to drugs)
-Tolerance (more tolerant, less resposive)
-Withdrawal (brain relies on it)
pharmacologial interventions of addiction
manage withdrawal symtoms, reduce cravings and block pleasurable effects
mood disorders
psychological disorders characterized by emotional extremes
mdd
-persistent feeling of sadness, hopelessness and lack of interest in activities
-fatigue, changes in sleep and appetite, difficulty concentrating, thoughts of death
bipolar
-extreme mood swings
-manic episodes → feel euphoric, energized and extremely confident
-depressive episodes → mirror symptoms of depression
neurochemical imbalance theory
disruptions in levels of functions of 3 key neurotransmitters: serotonin (feel good), norepinephrine (flight or fight), dopamine (reward)
schizophrenia
a group of severe disorders characterized by disorganized and delusional thinking, disturbed perceptions, and inappropriate emotions and actions
positive symptoms of schizophrenia
-excess or distortion of normal functions
-delusions and hallucinations
negative symptoms of schizophrenia
the absence of appropriate behaviors (expressionless faces, rigid bodies)
cognitive symptoms of schizophrenia
problems with working memory, attention, verbal and visual learning and memory, reasoning and problem solving, processing, and speech
dopamine hypothesis of schizophrenia
argues that delusions, halucinations, and agitation associated with schizophrenia arise from either too much dopamine or from oversensitivity to dopamine in the brain
glutamate hypothesis of schizophrenia
a hypothesis suggesting that schizophrenia is caused by the reduced activation of NMDA receptors in the brain
-reduced in prefrontal cortex may lead to negative and cognitive symptoms
GABA dysfunction (schizophrenia)
Dysregulation of GABA may contribute to cognitive symptoms
Future directions in biological research on mental illness
-advancing understanding of bio basis, develop more precise, individualised treatment
-neuroimaging → functional and structural mri
-connectomics (study of brain networds)
-genetic research
-personalised medicine → tailor treatment based on indiviual's genetic makeup, brain structure and unique neurochemiclal profile
localisation of brain function issues
-how specific are certain brain regions to particular functions (some are certain, some are not)
-how flexible is the brain in redistributing functions after injury
-how much functional plasticity occurs after childhood
nature versus nurture issues
-are our traits and abilities the result of our DNA or life experiences
-how do genes and environment interact over time
-when do nature and nurture exert the mose influence on developing brain
-how well can we predict behaviours, cognitive abilities, or mental health outcomes based on genetic and environmental info
gut microbiome and brain function
-how does the gut biome influence brain function and behaviour
-what are the mechanisms connecting the gut and brain
-how do alterations in the gut microbiome contribute to mental health disorders
mind-body problem/ consciousness and free-will
-is the mind a seperate entity or is it the result of brain activity
-how does subjective experience arise from the physical brain processes
-is consciousness and emergent property of brain complexity
-do humans have free will, or are out decisions governed by neural activity
interdisciplinary integration
-how can we create a coherent understanding across multiple levels of analysis
-how do we bridge the gap between molecular mechanisms and mental states
-what are the best approaches for integrating psychological and neuroscientific findings
artificial intelligence and neural modelling
-can AI truly replicate or simulate human-like cognition
-what are the limitations of ai in replicating the human brain
-can ai help us understand consciousness