infection control notes
1/154
Earn XP
Description and Tags
chapter 5
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
155 Terms
infection control
Methods used to eliminate or reduce the transmission of infectious organisms from one individual to another.
infectious
Caused by or capable of being transmitted by infection
Cleaning
Mechanical process using soap and water or detergent and water to remove all visible dirt, debris, and many disease-causing germs. also removes invisible debris that interferes with disinfection. The step before disinfecting.
Disinfecting
A chemical process for use with nonporous items that uses specific products to destroy harmful organisms including bacteria, viruses and fungi (except bacterial spores) on implements and environmental surfaces.
osha
Regulate and enforce safety and health standards to protect employees in the workplace. Address issues relating to the handling, mixing, storing, and disposing of products; general safety in the workplace; and your right to know about any potentially hazardous ingredients contained in the products and how to avoid these hazards. Requires Sds.
Environmental Protection Agency
Registers all types of disinfectants sold and used in the United States.
disinfectants
Chemical products that destroy most bacteria (excluding spores), fungi, and viruses on surfaces. Must have an epa registration number.
Laws
Determine the scope of practice and establish guidelines for regulatory agencies to make rules also called statutes.
Rules and regulations
State board writes the rules and determines how the law must be applied. establishes specific standards of conduct and can be changed or updated frequently.
disease
Any abnormal condition of all or part of the body, its systems, or its organs that makes the body incapable of carrying on normal functions.
infection
the invasion of body tissues by disease-causing pathogens
Transmission
The process by which pathogens move between individuals and objects. first step in getting sick.
Direct transmission
The transmission of pathogens through touching, kissing, coughing, sneezing, and talking. Examples:Parasitic infections and warts. Diseases spread by direct contact that cannot live for long periods of time away from a host.
Indirect transmission
Occurs through contact with an intermediate contaminated object, such as a razor, extractor, nipper, or an environmental surface upon which the pathogen resides. Examples: salmonella, ringworm, and MRSA
respiratory droplets
Large particles that do not stay suspended in the air for long, wearing a properly fitted mask should protect you from these pathogens. Example: influenza, SARS-CoV-2/ COVID-19
airborne transmission
Particles are much smaller and dryer, so they hang in the air longer, allowing for the pathogen to spread further
infectious disease
Disease caused by pathogenic microorganisms that enter the body. may or may not be spread from one person to another
cleaning
Mechanical process (scrubbing) using soap and water or detergent and water to remove all visible dirt, debris, and many disease-causing germs. Removes invisible debris that interfere with disinfection. required before disinfecting. can also be done using an ultrasonic unit or chemical cleaner.
disinfection
a chemical process that uses specific products to destroy harmful organisms (except bacterial spores) on environmental surfaces
spores
Bacteria capable of producing a protective coating that allows them to withstand very harsh environments and to shed the coating when conditions become more favorable to them
product labels
epa registration number, pathogens it kills, the words bactericidal, virucidal, and fungicidal, mixing and changing instructions
HIV (human immunodeficiency virus), HBV (hepatitis B virus), and MRSA (methicillin-resistant staphylococcus aureus);
What pathogens should disinfectants be effective against ?
contagious disease
also known as communicable disease; disease that is capable of being spread from one person to another. often spread through dirty hands/fingernails or contaminated items. Examples: cold, ringworm, conjunctivitis (pinkeye), and viral infections.
Contamination
The presence, or the reasonably anticipated presence, of blood or other potentially infectious materials on an item’s surface or visible debris or residues such as dust, hair, and skin.
Decontamination
The removal of blood or other potentially infectious materials on an item’s surface and the removal of visible debris or residues such as dust, hair, and skin.
Diagnosis
Determination of the nature of a disease from its symptoms and/or diagnostic tests
Germs
disease-producing organisms.
Occupational Disease
Illnesses resulting from conditions associated with employment, such as prolonged and repeated overexposure to certain products or ingredients.
Parasitic Disease
Disease caused by parasites such as lice and mites.
Pathogenic Disease
Disease produced by organisms such as bacteria, viruses, fungi, and parasites.
Toxins
Various poisonous substances produced by some microorganisms (bacteria and viruses).
Bacteria
single-celled microorganisms that have both plant and animal characteristics. Can be harmful and harmless. Can exist anywhere. Multiply best in warm, dark, damp, or dirty places. Can live and reproduce on their own.
microorganism
any organism of microscopic or submicroscopic size.
nonpathogenic
harmless microorganisms/ bacteria that may perform useful functions and are safe to come in contact with since they do not cause disease or harm. Help the body break down food, protect against infection, and stimulate the immune system. Found in yogurt, cheese, medicines.
Pathogenic
Harmful microorganisms that can cause disease or infection in humans when they invade the body
Inflammation
tissue of the body reacts to injury, irritation, or infection characterized by redness, heat, pain, and/or swelling.
Pus
A sign of a bacterial infection. fluid containing white blood cells, bacteria, and dead cells, and is the by-product of the infectious process.
local infection
Confined to a particular part of the body and appears as a lesion containing pus. Example: pimple/ abscess
systemic infection
pathogen has spread throughout the body rather than staying in one area or organ.
Staphylococci
pus-forming bacteria that grow in clusters like a bunch of grapes; cause abscesses, pustules, and boils. Can be spread by skin to skin contact or through items/ surfaces. Examples: food poisoning, toxic shock syndrome and some flesh-eating diseases. Can be resistant to antibiotics.
MRSA (methicillin-resistant staphylococcus aureus )
a type of infectious bacteria that is highly resistant to conventional treatments such as antibiotics. Appears as a skin infection, resulting in pimples, rashes, or boils that can be difficult to cure. Can become systemic/ fatal without proper treatment.
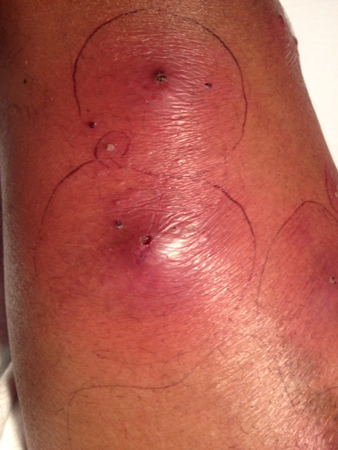
Mycobacterium
A large family of bacteria that is often found in soil and water. Associated particularly with pedicure bowls. Advise clients not to shave or wax their legs 24 hours prior to a pedicure.
virus
A submicroscopic particle that infects and resides in the cells of a biological organism. Capable of replication only through taking over the host cell’s reproductive function. Can live and reproduce only by taking over other cells and becoming part of them Examples: mumps, chickenpox, smallpox, rabies, yellow fever, hepatitis, polio, SARS-CoV-2 (which causes COVID-19), influenza, and HIV (which causes AIDS). Can not be treated with antibiotics.
10-14 days
How long does it take a virus to produce signs of illness ?
containment
staying home until not contagious.
Human papilloma virus/ Herpes simplex virus
can be transmitted both directly and indirectly.
bloodborne pathogens
disease-causing microorganisms carried in the body by blood or body fluids, such as hepatitis and HIV. spread is possible whenever the skin is broken.
Hepatitis
bloodborne virus that causes disease and can damage the liver. can be present in all body fluids and can live on a surface outside the body for long periods of time.
human immunodeficiency virus
causes acquired immune deficiency syndrome.
AIDS
a disease that breaks down the body’s immune system
Fungi
single-celled organisms that grow in irregular masses and include molds, mildews, and yeasts; can produce contagious diseases such as ringworm
Mildew
a type of fungus that affects plants or grows on inanimate objects but does not cause human infections in the barbershop
tinea barbae
also known as barber’s itch, a superficial fungal infection that commonly affects the skin; it is primarily limited to the bearded areas of the face and neck or around the scalp. may cause deeply inflamed patches of skin on the face or the nape of the neck.
tinea capitis
a fungal infection of the scalp characterized by red papules, or spots, at the opening of hair follicles.
Ringworm
a fungal infection of the skin that appears in circular lesions
Parasites
organisms that grow, feed, and shelter on or inside another organism (referred to as the host), while contributing nothing to the survival of that organism. must have a host to survive
External parasites
affect humans by way of the skin include ticks, head lice, fleas, and mites.
pediculosis capitis
infestation of the hair and scalp with head lice
Scabies
contagious skin disease caused by the itch mite, which burrows under the skin.
10 minutes
recommended time for bleach solution
Biofilms
secrete a sticky, hard-to-penetrate, protective coating that cements them together. microorganisms that adhere to environmental surfaces as well as the body. very hard to pierce with antiseptics, antimicrobials, and disinfection, ultimately keeping the body in a chronic inflammatory state that is painful and inhibits healing. resist the body’s defense mechanisms. Example dental plaque, algae. can harbor in foot spas.
cleaning then disinfecting
What are the two steps to proper infection control ?
Sterilization
the process that destroys all microbial life including spores, requires autoclave
autoclave
a piece of equipment that incorporates heat and pressure to sterilize. items must be cleaned prior to use. must have a spore test monthly.
anticeptics/ handwashing
drastically lower the number of pathogens on your hands.
pump containers
Should be used when washing hands, prevents bacterial growth in soap
friction
used when washing hands. pulls pathogens off the skin surface.
anticeptics
chemical germicides formulated for use on skin; registered and regulated by the Food and Drug Administration (FDA). Never use to disinfect instruments or other surfaces.
Hydrogen peroxide
Anticeptic, should never be used on an open cut, as it destroys the cells that begin the healing process in a wound.
Isopropyl alcohol
anticeptic effective in cleaning the skin, can not disinfect surfaces/ implements.
multiuse
reusable; items that can be cleaned, disinfected, and used on more than one person, even if the item is accidentally exposed to blood or body fluid
gloves/ safety glasses
should be worn while mixing disinfectants to avoid accidental contact with eyes and skin.
contact time
how long an item should be immersed in the disinfectant, or a surface left visibly wet, to be effective against pathogens
mixing ratio
dilution of chemical
concentrates
mostly have a 10-minute contact time disinfectants become more corrosive and damaging to implements if left too long.
wipes
mostly have a 2-minute contact time
pre mixed
does not have the word concentrate on it. must be used directly from the original container without being diluted.
efficacy
the effectiveness with which a disinfecting solution kills organisms when used according to the label instructions.
Complete immersion
must be enough liquid/ disinfectant in the container to cover all surfaces of the item being disinfected, including the handles, for 10 minutes or for the time recommended by the manufacturer
nonporous
made of a material that has no pores or openings and that cannot absorb liquids
porous
material that has holes or openings and is absorbent.
Quaternary ammonium compounds
quaternary ammonium cations designed for disinfection of nonporous surfaces; for use in noncritical (noninvasive) environments. usually disinfect implements in 10 minutes
tuberculosis
a disease caused by a bacterium that is transmitted through coughing or sneezing. passed through inhalation only
Tuberculocidal disinfectants
often referred to as phenolics, are proven to kill the bacterium that causes tuberculosis
Phenolic disinfectants
tuberculocidal disinfectants that are a form of formaldehyde, have a very high pH, and can damage the skin and eyes. Do not put in drain. known carcinogens. can damage plastic and rubber and cause certain metals to rust. should be used only in states that require their use.
chlorine bleach
the only bleach that disinfects, corrosive and can damage metals and plastics
bleach solution
should be mixed fresh every 24 hours or when the solution has been contaminated. , date the container to ensure that the solution is not saved from one day to the next.can be irritating to the lungs, so be careful about inhaling the fumes. use a soap detergent first to thoroughly clean and rinse the equipment.
10% bleach solution
nine parts water to one part bleach.
submerge
items in the disinfectant for 10 minutes
disinfectant containers
should be labeled with, at the least, product name, ingredients, date of mixing, and manufacturer’s information. must be large enough to contain all items to be disinfected
but not air tight
log book
record of all equipment usage, cleaning, disinfecting, testing, and maintenance
water
add disinfectant to water
UV light units
will not disinfect or sterilize implements.
work surfaces
clean and disinfect tables, stations, shampoo sinks, chairs, armrests, and any other surface that a customer’s skin may have touched. Clean doorknobs and handles daily.
soiled linens
store in covered or closed containers. Do not allow the neckband of capes to touch the client’s skin. use a barrier, such as disposable neck strips or towels, to prevent the client’s skin from touching the neckline of the cape.
dispense
Always use a pump or shaker when possible.
Chelating soaps
break down stubborn films and remove the residue of products such as scrubs, salts, and masks; also known as chelating detergents. works with hard water.
Standard Precautions
guidelines published by the CDC that require the employer and employee to assume that any human blood and body fluids are potentially infectious.
asymptomatic
showing no symptoms or signs of infection
Sharps containers
showing no symptoms or signs of infection