3.1 - 3.9 AP ES Unit 3 Populations
1/39
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
40 Terms
K-selected species
Species that produce a few, often fairly large offspring but invest a great deal of time and energy to ensure that most of those offspring reach reproductive age.
r-selected species
Species that reproduce early in their life span and produce large numbers of usually small and short-lived offspring in a short period, low paternal care
Competition
the struggle between organisms to survive in a habitat with limited resources
Biotic potential
Maximum rate at which the population of a given species can increase when there are no limits on its rate of growth.
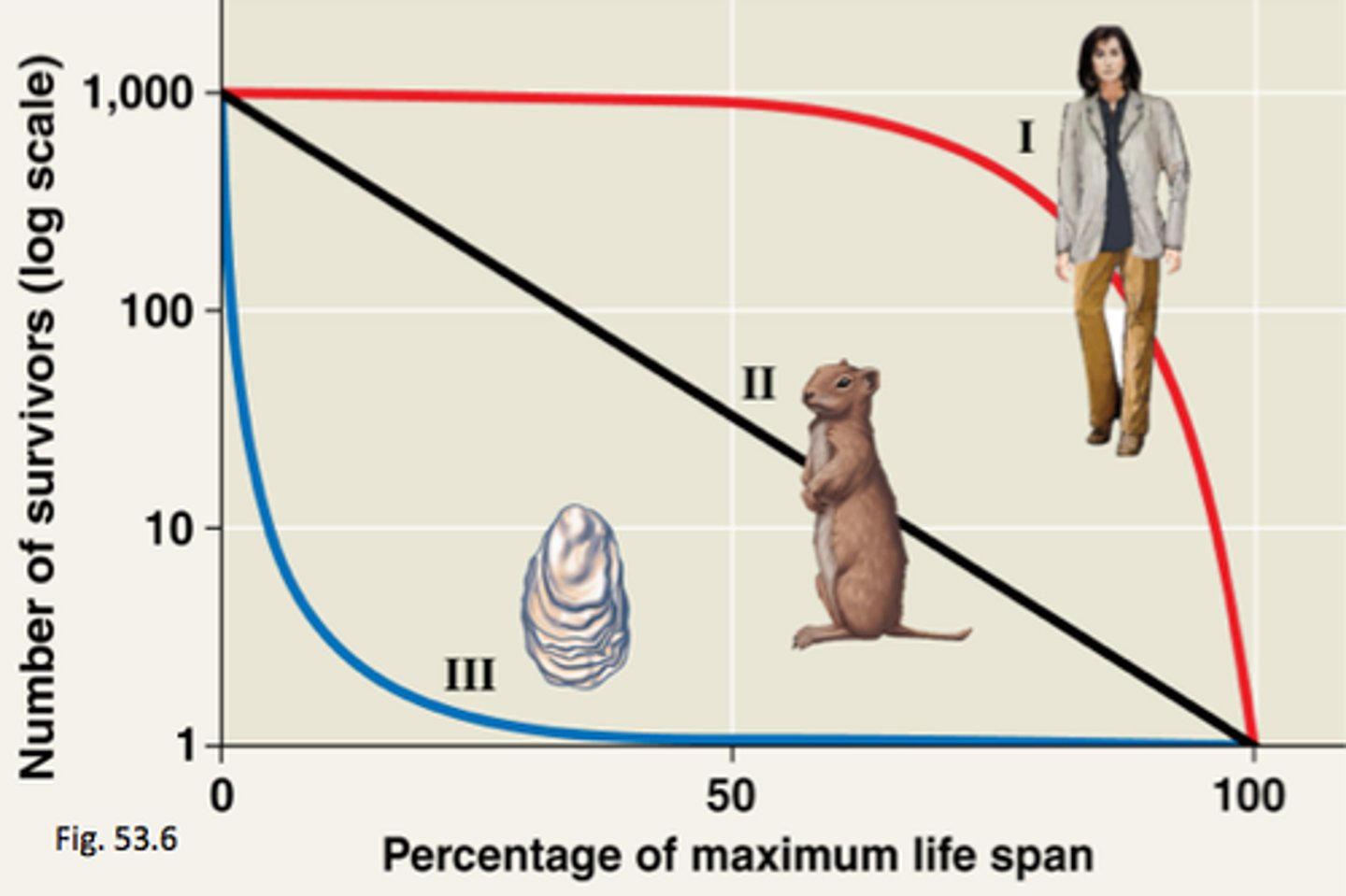
Survivorship curves
a graph that represents the distinct patterns of species survival as a function of age
Type I survivorship curve
A survivorship curve in which newborns, juveniles, and young adults all have high survival rates and death rates do not begin to increase greatly until old age.
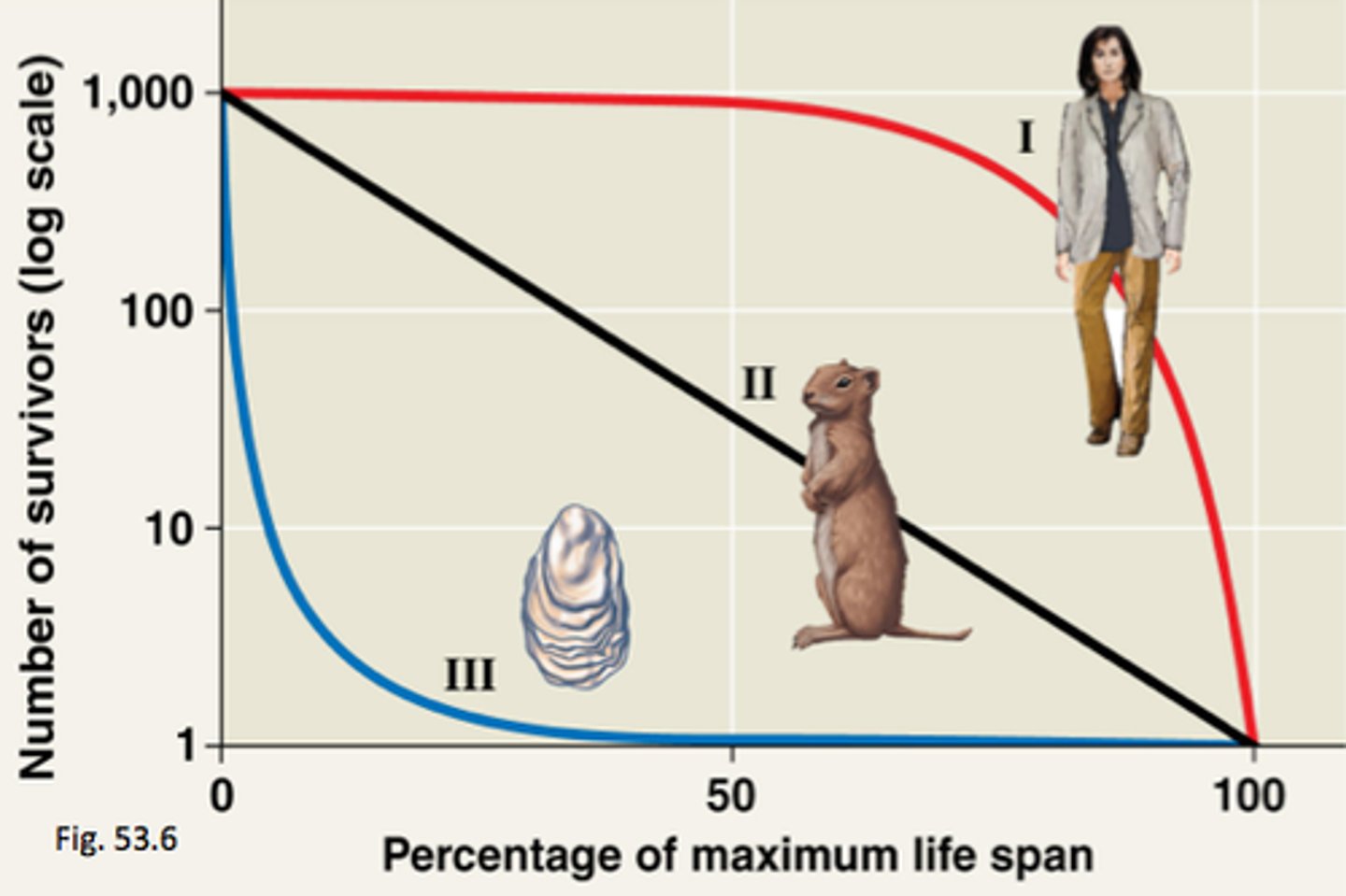
Type II survivorship curve
Experience roughly a constant mortality rate regardless of age. Prey animals such as birds can follow this pattern of survival.
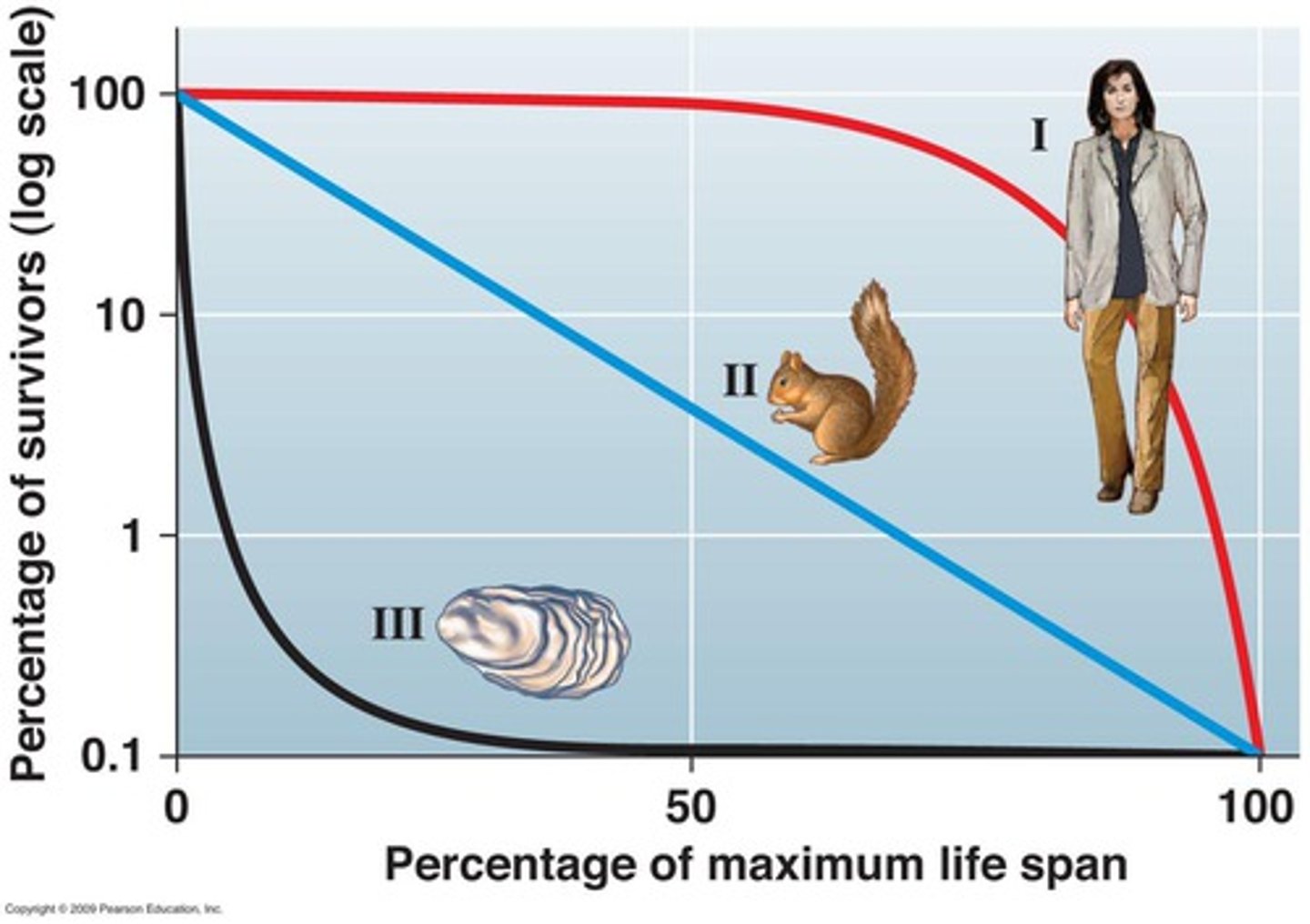
Type III survivorship
Experience the greatest mortality early on in life, with relatively low rates of death for those surviving. Usually r-selected.
J-shaped curve (exponential growth)
Growth where there is unlimited resources and no competition
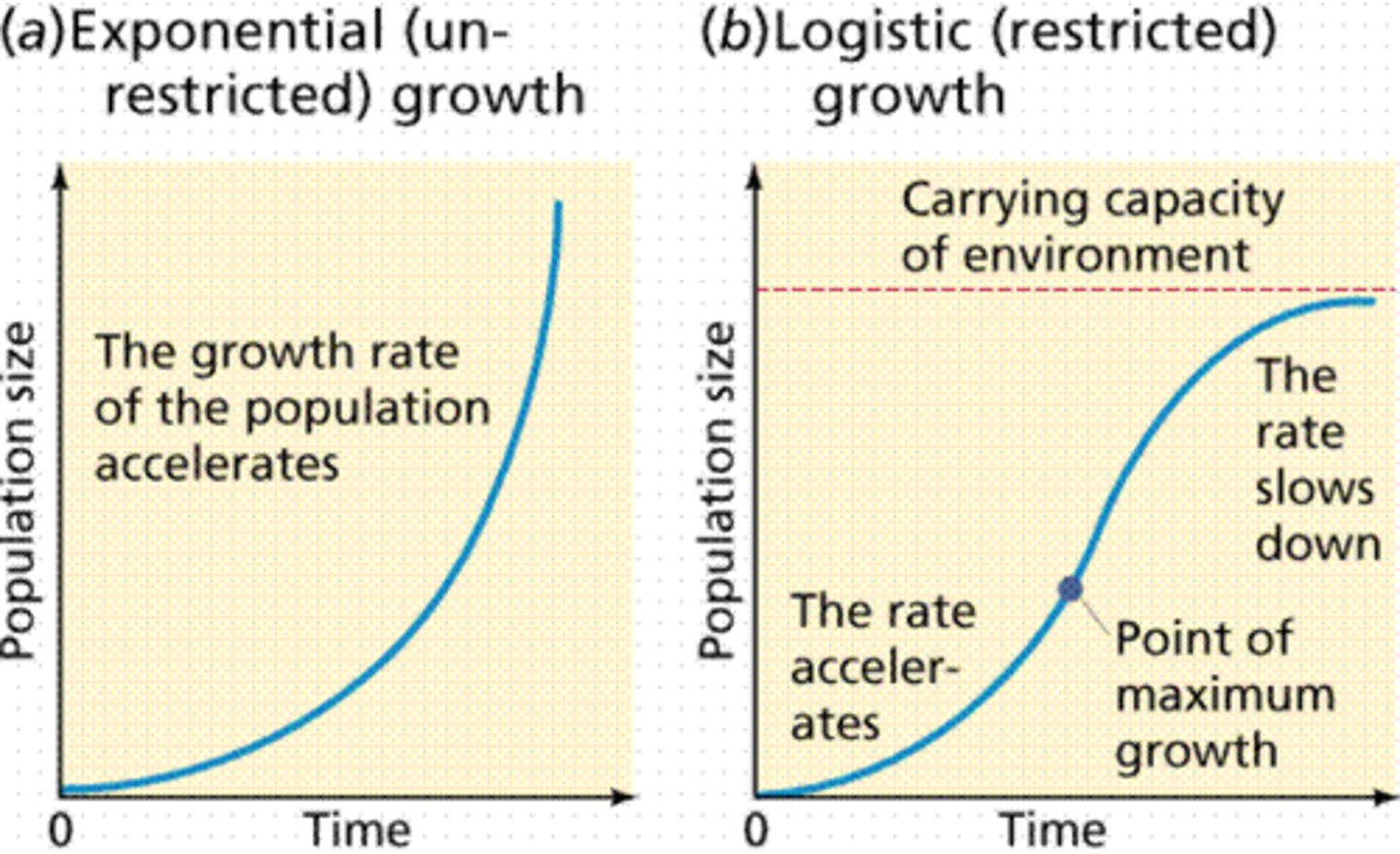
S-shaped curve (logistic growth)
Where the community has reached its carrying capacity
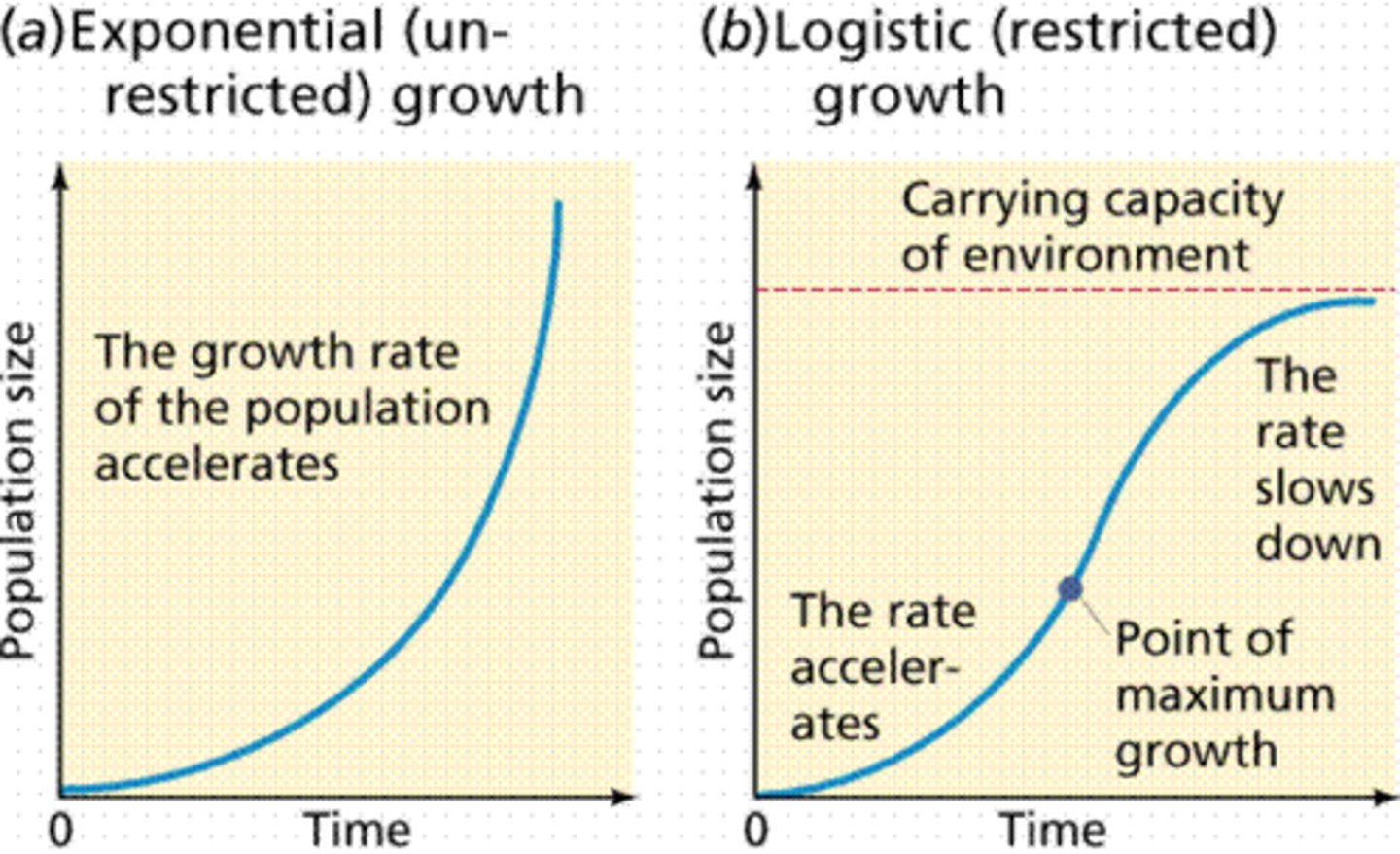
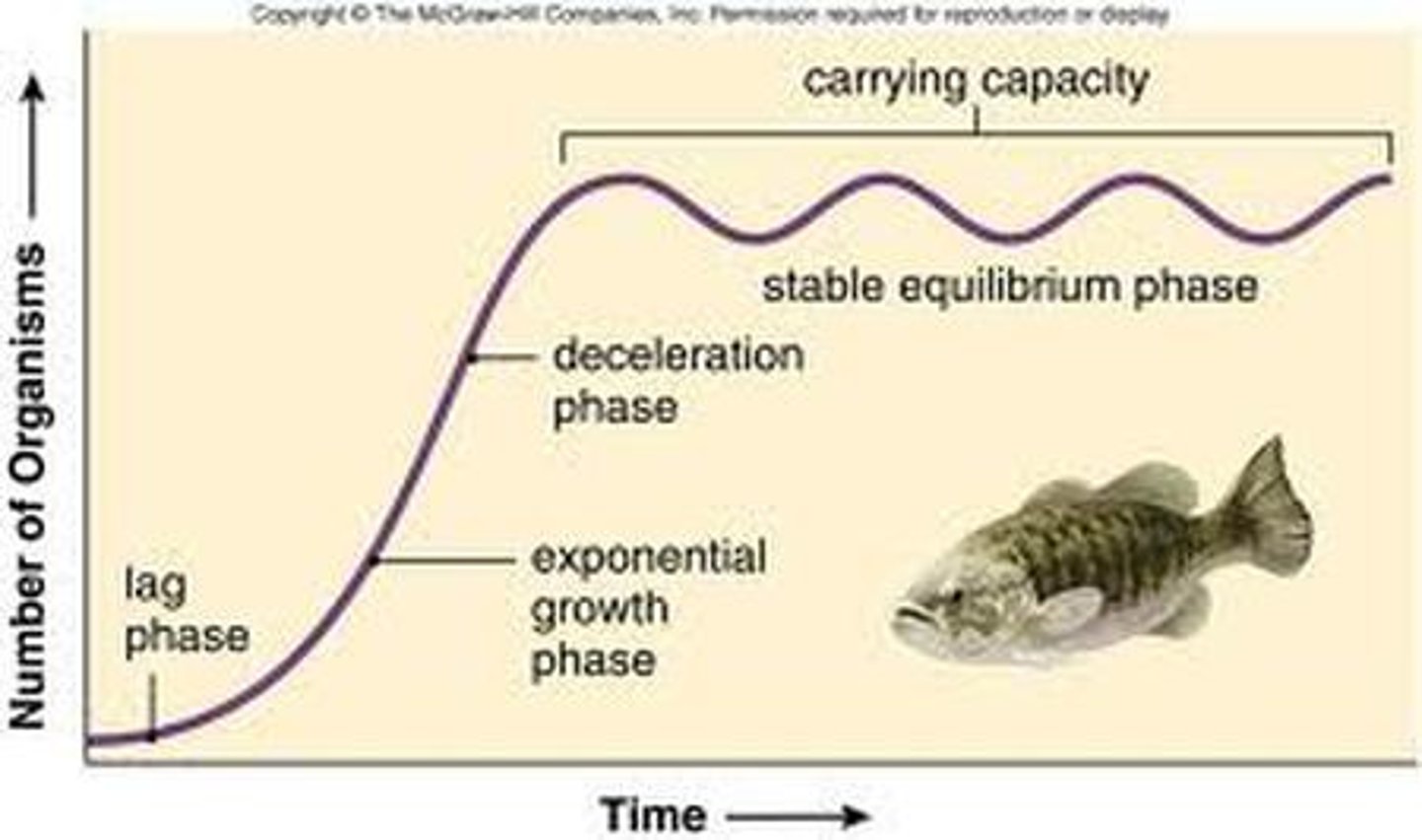
Carrying capacity (K)
Maximum population size that a particular environment can sustain
Ecosystem
A biological community of interacting organisms and their physical environment.
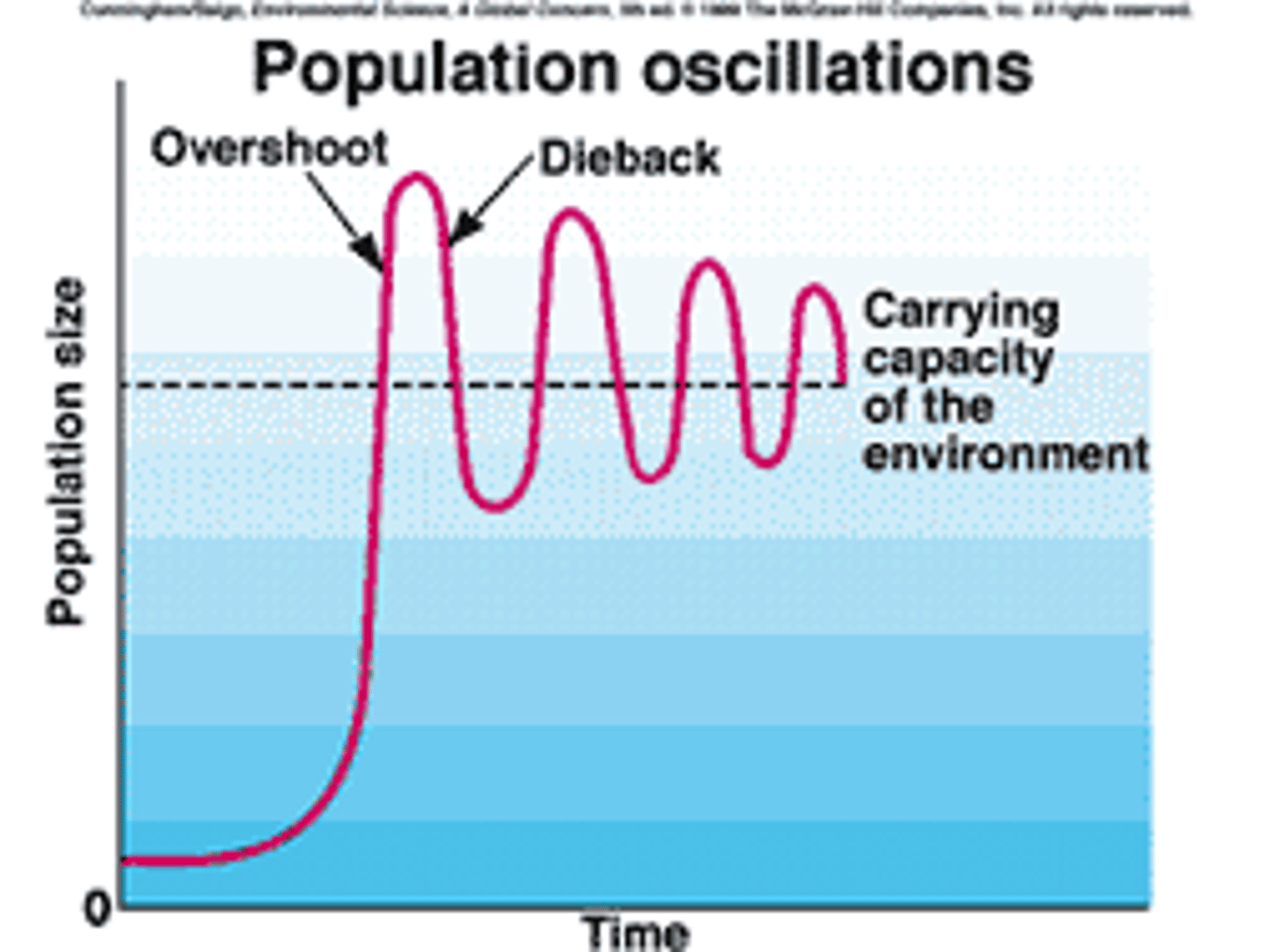
Overshoot
when a population becomes larger than the environment's carrying capacity
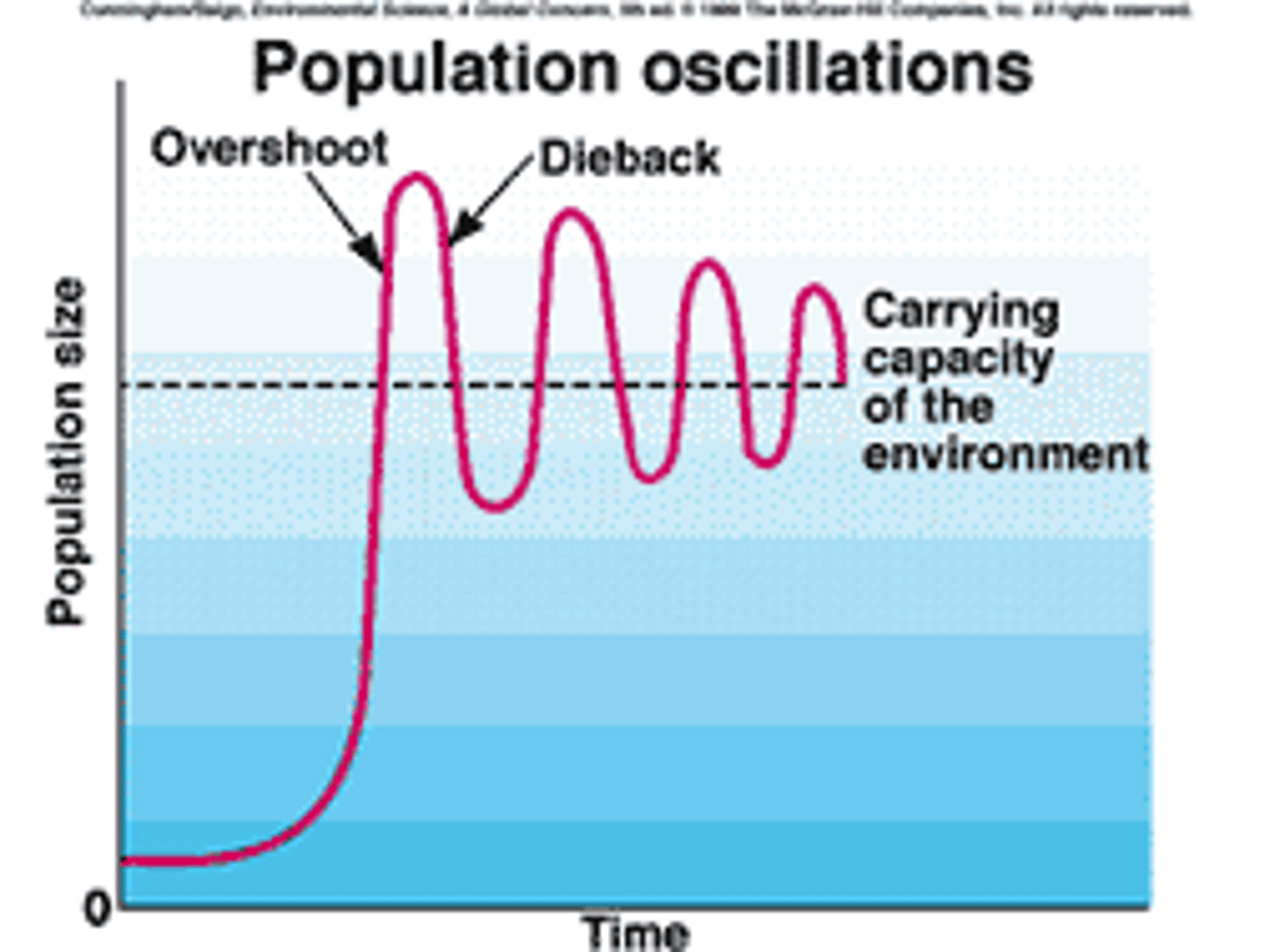
Dieback
Sharp reduction in the population of a species when its numbers exceed the carrying capacity of its habitat.
Age structure diagrams
broad base = rapid growth; narrow base = negative growth; uniform shape = zero growth
Population growth rates
-A country's is determined by its natural increase expressed as a percentage
-For example, a country's natural increase with a CBR of 22 and a CDR of 12 is 10 per 1,000, which translates to a rate of 1 percent
Total fertility rate (TFR)
The average number of children born to a woman during her childbearing years.
replacement fertility rate
the total fertility rate needed for a population to replace itself = 2.1
Mortality
death rate
Life expectancy
A figure indicating how long, on average, a person may be expected to live
Per capita
per person
Infant mortality rates
The percentage of children who die before their first birthday within a particular area or country.
population density
Number of individuals per unit area
Density-independent factors
limiting factor that affects all populations in similar ways, regardless of population size eg. flood, fire, other natural disasters
Density-dependent factors
factor that limits a population more as population density increases eg. food, shelters, water, spread of disease
Rule of 70
The equation used to calculate the doubling time for a population. Doubling time (in years) = 70/(percentage growth rate).
Doubling time
The number of years needed to double a population
Crude birth rate
The total number of live births in a year for every 1,000 people
Crude death rate
The number of deaths per year per 1,000 people.
Population momentum
continued population growth that does not slow in response to growth reduction measures
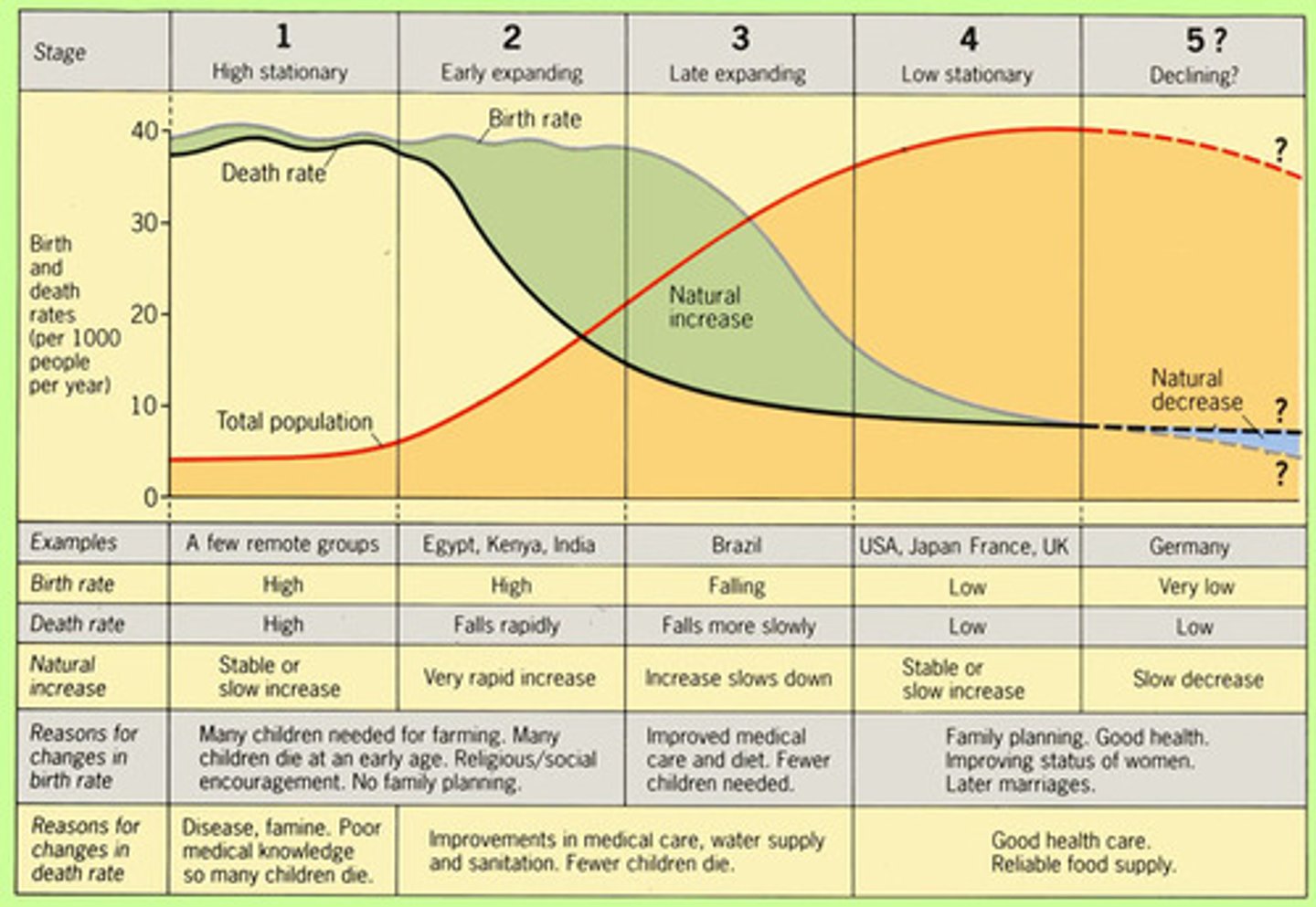
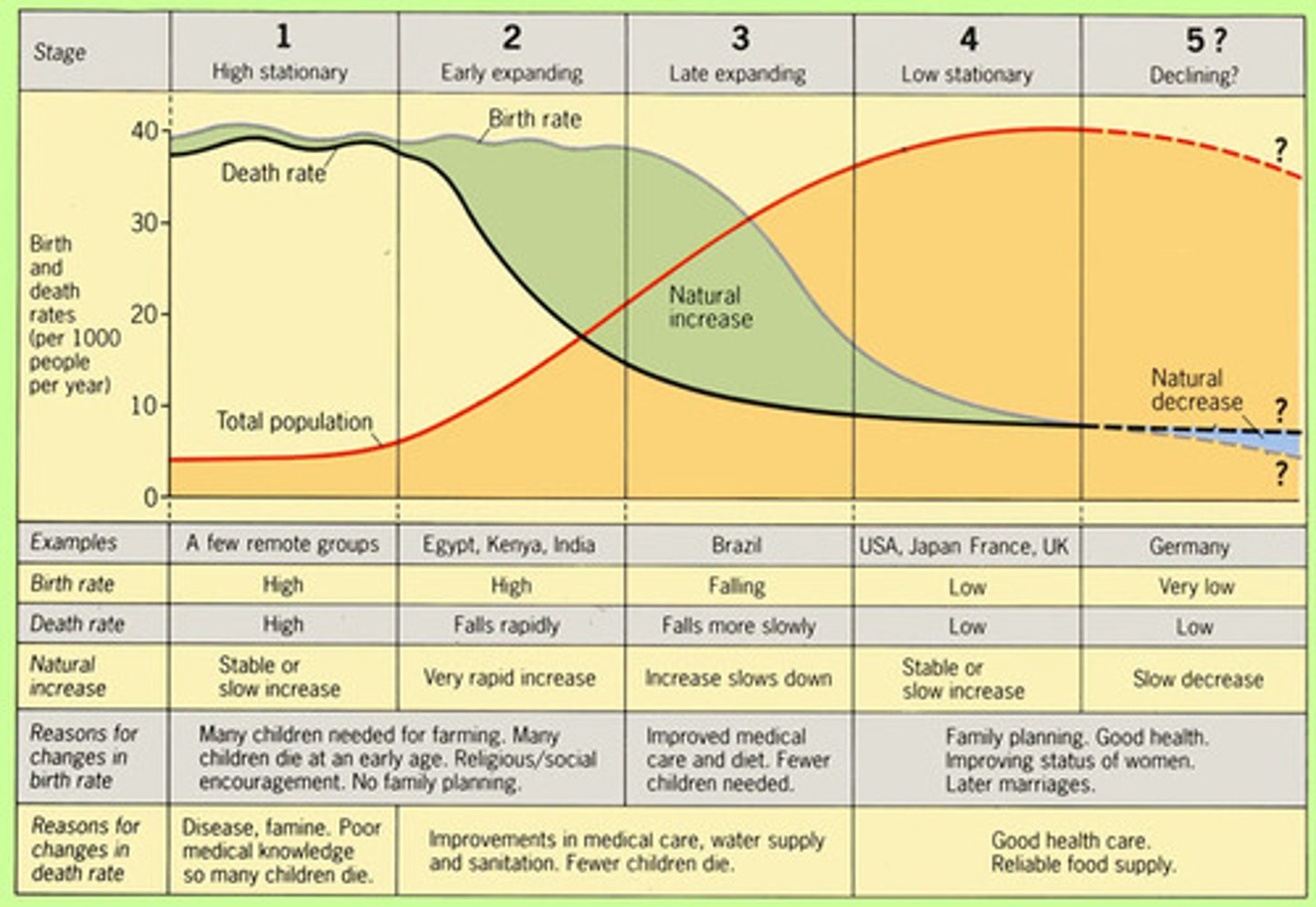
Demographic Transition Model
Refers to the transition from high to lower birth and death rates in a country or region as development occurs and that country moves from a preindustrial to an industrialized economic system
Developed countries
countries with strong economies and a higher quality of life
Developing countries
countries with less productive economies and a lower quality of life
post-industrial stage (Stage 4/5 Low Stationary)
(demographic transition) low birth & death rates
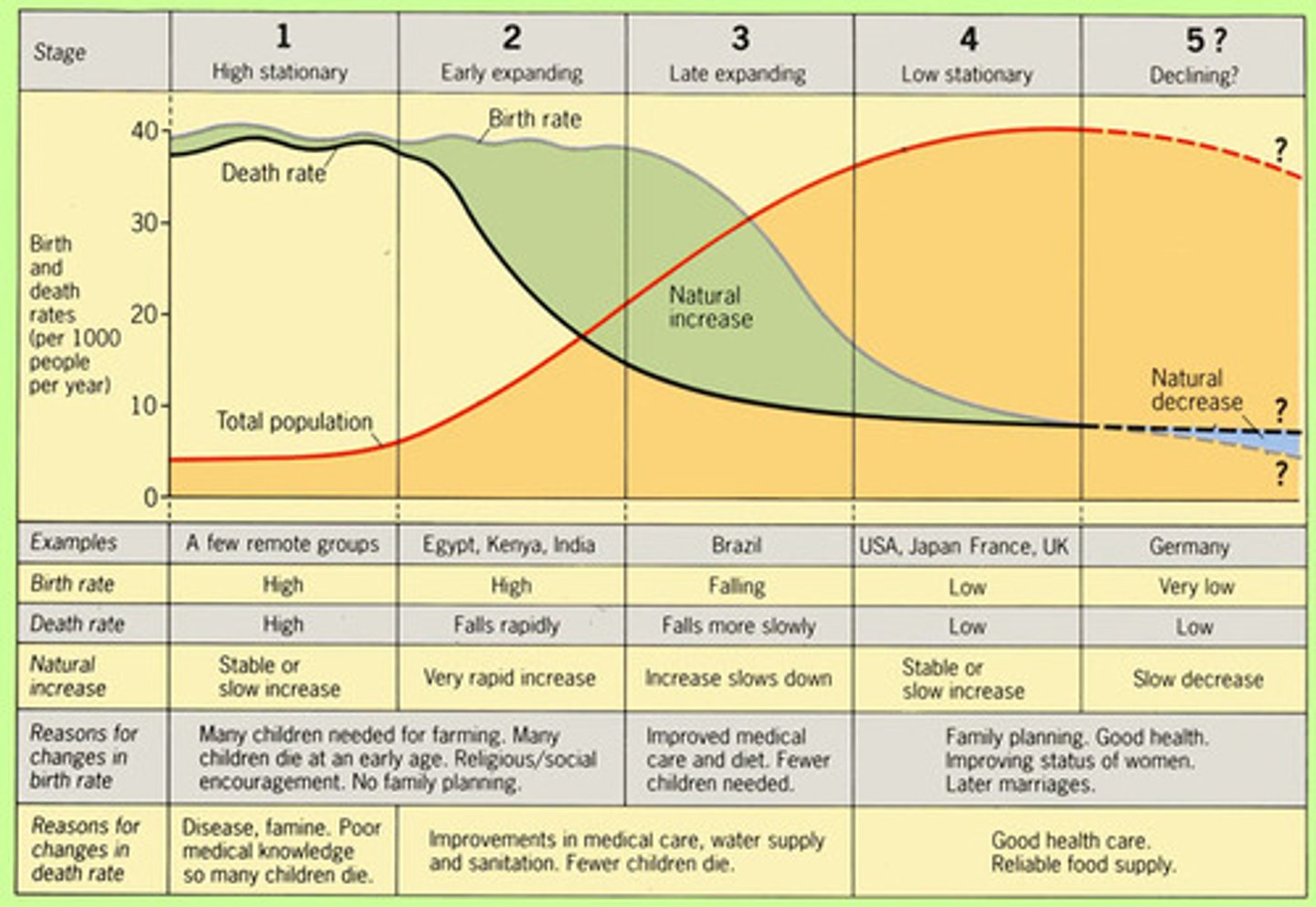
pre-industrial stage (Stage 1 High Stationary)
birth and death rates high, population grows slowly, infant mortality high
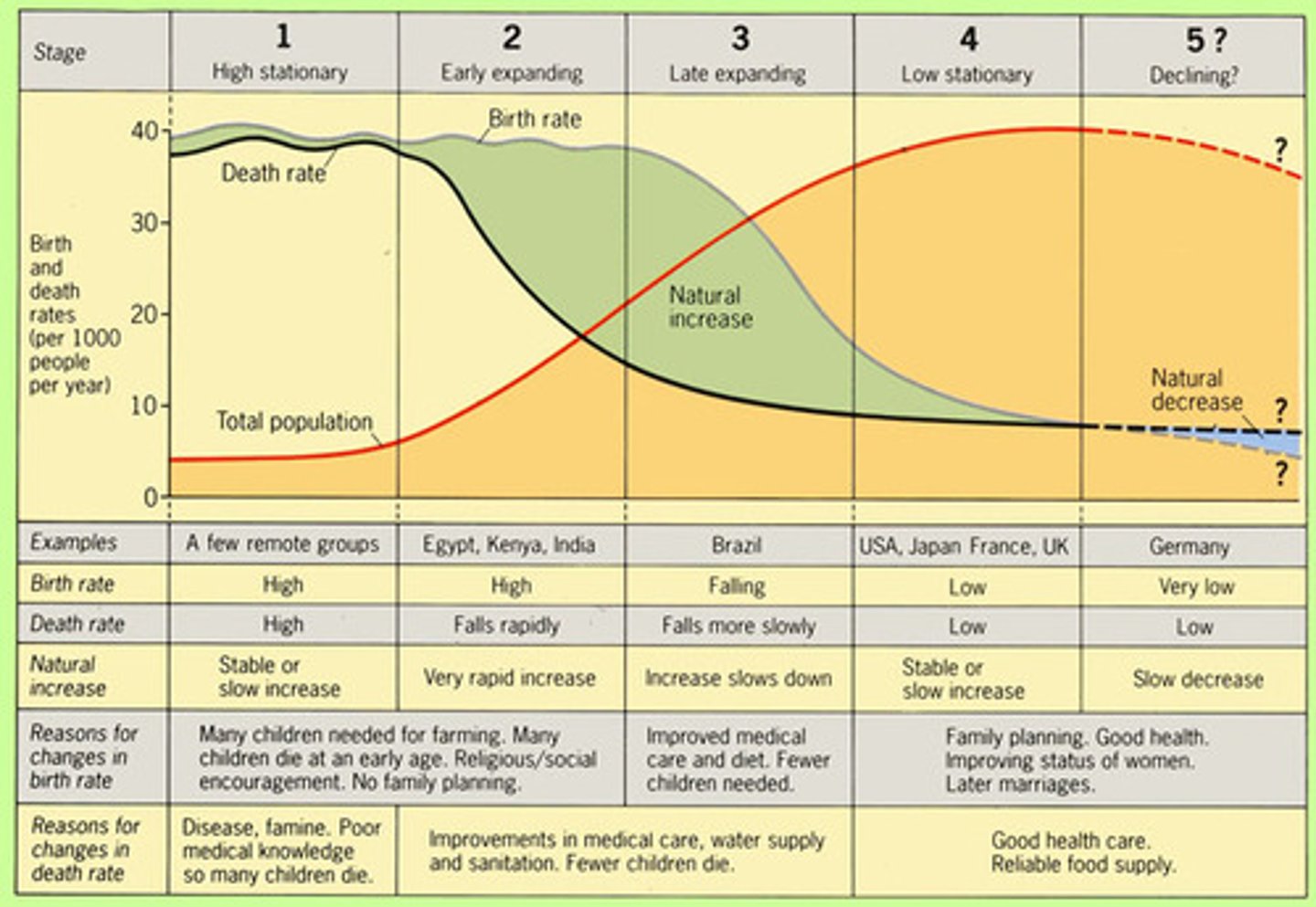
Industrial stage (Stage 3 Late Expanding)
(demographic transition) decline in birth rate, population growth slows
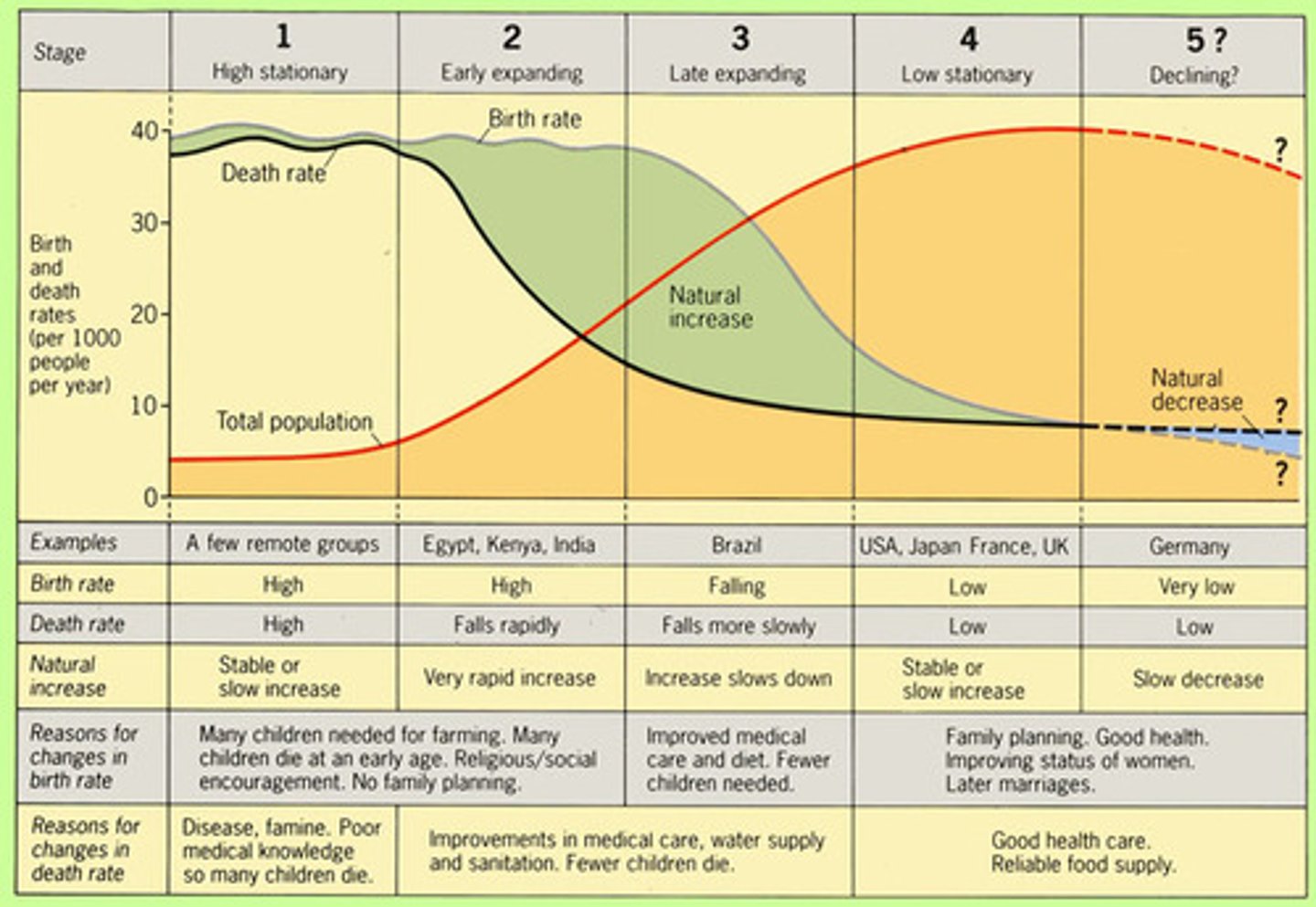
Transitional stage (Stage 2 Early Expanding)
(demographic transition) death rate lower, better health care, population grows fast
Birth control
Any method used to reduce births, including celibacy, delayed marriage, contraception; devices or medication that prevent implantation of fertilized zygotes, and induced abortions
Immigration
Movement of individuals into a population
Emigration
movement of individuals out of a population