3RD QTR: ORAL COMMUNICATION
1/38
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
39 Terms
COMMUNICATION
Communication is a systemic process by which people interact through the exchange of verbal and nonverbal symbols to create and interpret meanings.
MISCOMMUNICATION
Failure to understand adequately
Can lead to confusion, animosity, misunderstanding
Human communication is incredibly complex
Every person interprets the message they receive based on their relationship with that person
Emotion might cloud understanding
Recognize that passive hearing and active hearing are not the same Listen with your eyes, ears, and gut
Take time to understand as you try to be understood Be aware of your personal perceptual filters
Don’t assume that you perception is the objective truth
TRANSIMISSION MODEL
Simple
TRANSACTIONAL MODEL
Complex, exchange of ideas between two parties Our perception filters continuously send message
PRINCIPLES OF SPEECH WRITING AND DELIVERY
Speech writing and delivery are essential skills that allow speakers to convey their message clearly, persuasively, and memorably.
Sourcing Information
MODELS OF COMMUNICATION
Representation of what something is and how it works. A communication model is designed based on the different theories or perspectives
BARNLUND’S MODEL
Dean Barnlund (1970) presents the complex and multi-layered system of communication, where messages are sent back and forth
LINEAR / TRANSMISSION
One way
INTERACTIVE
Two-way with feedback
TRANSACTIONAL
Two-way with immediate feedback
ARISTOTLE’S MODEL OF COMMUNICATION
Linear
Speaker → Speech → Occasion → Audience Effect
LASWELL’S MODEL OF COMMUNICATION
Linear
Who → What → Which channel → To whom → With what effect
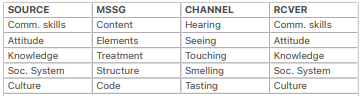
BERLO’S SMCR MODEL OF COMMUNICATION
SHANNON-WEAVER’S COMMUNICATION MODEL (1948)
Noise
Information Source: Sender
Transmitter: Encoder
Channel
Noise
Reception: Decoder
Destination: Receiver
Feedback (parallel to the noise, because the kind of feedback the receiver will have depends/varies on the noise)
OSGOOD-SCHRAMM MODEL OF COMMUNICATION (1954)
Non-linear, but a cycle
Message → Decoder/Interpreter/Encoder → Message → Encoder/Interpreter/Decoder → Message
FIELD OF EXPERIENCE
Overlap (if there’s no overlap, nothing will happen)
WHITE’S MODEL OF COMMUNICATION
Symbolizing, expressing, transmitting, receiving, decoding, feed backing, monitoring, thinking, etc.
Communication as a circular and continuous process. Communication may be observed from any point in the cycle
TRANSACTIONAL MODELS
Most dynamic of communication of models
WOOD’S MODEL OF COMMUNICATION
Both communicators send a nd receive messages simultaneously
Involves encoding and decoding, with an emphasis on the role of noise and the shared meaning btwn individuals
Elements: Communicator A, Communicator B, Message, Decoding Reaction, Response, Noise, Shared Messages, Interpretation of Meaning
HAMILTON’S MODEL OF COMMUNICATION
Both senders and receivers interact
Emphasizes the importance of motivation, frame of reference, a consistency in verbal and nonverbal codes
Elements: Person A, Person B, Stimulation, Motivation, Encoding, Decoding, Frame of Reference, Code (Verbal, Vocal, Nonverbal), Channel, Feedback, Environmental, Noise
DUNN & GOODNIGHT’S MODEL OF COMMUNICATION
Sender and receiver are active participants, continuously sending and receiving messages
Physical and Psychological factors, greatly influence how messages are interpreted
SENDERS
Convey messages by converting their thoughts into symbols or observable signals such as words (Codification)
RECEIVERS
Hear the signals and convert the symbols into their thoughts (Decoding, deciphering, interpretation)
MESSAGES
Ideas or thoughts that are transmitted from sender to receiver
Meaning depends on the interpretation of hte receiver
SCHEMA
Similarity btwn the culture and experience of both parties
Field of experience
VERBAL AND NONVERBAL SYMBOLS
Observable signals transmitted from sender to receiver
Dont have meaning in themselves
VERBAL
Coming from the mouth of the speaker
NONVERBAL
Coming from the body movements
CHANNELS
Medium through which the msg is sent
Connects sender n receiver
NOISE
Anything that reduces the quality of the signal sent (weakens the communication)
FEEDBACK
Message transmitted by receiver in response to message of speaker
Feednacl enables sender to make adjustments (improving pronunciation)
INTRAPERSONAL
Talking to yourself, involves deliberation and meditation
INTERPERSONAL
Exchange of ideas, information, and msgs, btwn 2 or more ppl
FUNCTIONS OF COMMUNICATION
Based on speaker’s purpose for communication (verbal n nonverbal cues)
REGULATION AND CONTROL
Control others by managing their behavior
SOCIAL INTERACTION
Primary reason why we communicate (connected w one another)
MOTIVATION
Purpose is to persuade or try to persuade another person to change their opinion
INFORMATION
Speaker wants to make others aware of certain data
EMOTIONAL EXPRESSION
Move another person to action, appeals to listener’s feelings