Exam 2 Chem
1/80
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
81 Terms
1 cal
4.184 J = 4.184 J/g*C
1000 calories
1 kcal = 1 Cal (food)
Exothermic
heat is released from the "system" (the reacting substances) into the "surroundings"
Endothermic
where a system absorbs heat energy from its surroundings
State function
Does not matter how you got there
Change in enthalpy
Extensive property
Heat of fusion
Melting
Heat of vaporization
Boiling
Qsys= -Qsurr
Qmetal= -Qwater
Enthalphy aka delta h
= qrxn/quantity (mols)
Bomb calorimeter
qrxn = -(qbomb + qwater)
qbomb
Cbomb * delta T
If no mass or water of a solution are given, solve for qbomb
qrxn = -qbomb
Coffee cup calorimeter
qrxn = -(qbomb + qsol)
Hz
1/s or s-1
Nm
1×10^-9 m
Pm
1×10^-12 m
Å
1 × 10^10 m
Amplitude relates to
Brightness
Visible light wavelengths
400nm (violet) to 750 nm (red), green light is shorter than red
Electromagnetic spectrum increasing frequency
Radio, microwaves, infrared, visible light, uv, X-ray, gamma rays
As an object is heated up, the light it emits changes from red to
Light blue
Photoelectric effect
Light of sufficient frequency shines on a metal surface and a current flows
Delta E of an atom is the same for E of photon
= hv or hc/y
Energy of radiation (photons) units
J/photon
Energy levels (n) also called
Stationary states
The smaller the n value,
The smaller the radius of the orbit, and the smaller the energy level
The electron in the atom does not radiate energy while
In orbit around the nucleus
Energy level n=1 can absorb a proton and go to n=2 if
The photon has the same amount of energy as (n2-n1)
Ionize
When an electron is ejected from an atom, final = infinity
Emission
Higher to lower
Absorption
Lower to higher
Rydberg equation
1/y=R(1/(n1)²+ 1/(n2)²), where n2 > n1 (wavelength in meters)
Lyman series produces UV
Terminates at n=1, 90-100nm
Balmer series produces visible light
Terminates at n=2 400-750nm
Infrared
Terminates at n=3 1000’snm
When electrons in the hydrogen atom drop from outer orbits to three specific energy levels,
Spectral lines are emitted
DeBroglie Wavelength
y = h/m*u where m = mass in KG not grams and u = speed in m/s and wavelength in m
Wave-particle duality
the concept that matter at the quantum level can exhibit both wave-like and particle-like properties, meaning that depending on the experimental conditions, a single entity can behave like a wave or a particle simultaneously
Heinsenberg’s Uncertainty Principle
it is impossible to know both the exact position and momentum of a particle simultaneously
Uncertainty of electron
Delta x = mdeltau greater than or equal h/4pi, m= MASS IN KG, u=uncertainty in speed/velocity, delta x= uncertainty in position
Quantum mechanics
Wave nature of objects on the atomic scale
Principal quantum number (n)
Level/shell of orbital (higher number is further away and higher energy level)
Angular momentum quantum number (l)
Sublevel/subshell of orbital, indicates shape, 0-n-1
L=0
S
L=1
P
L=2
D
L=3
F
Magnetic quantum number ml
Orientation of orbital, -L to 0 to +L
S orbital shape
Spherical
P orbital shape
Dumbbell
D orbital shape
Double dumbbell, clover
Total number of orbitals in a shell
n²
Maximum number of orbitals in a subshell
2 * L + 1
Spin quantum number ms
Magnetic field generated by electron, +1/2 or -1/2
For a given n value,
The higher the L value the higher the sublevel energy
Electron repulsions/ electron shielding
the phenomenon where inner shell electrons in an atom partially block the positive charge of the nucleus from the outer shell electrons, reducing the effective nuclear charge experienced by the outer electrons
An electron is attracted to the positive charge if the nucleus
Also known as Z nuclear charge
Higher nuclear charge lowers
Orbital energy, which stabilizes the atom by increasing electron attractions
Effective nuclear charge
Several electrons in same orbital repel a little and shield
Since p can hold 6 electrons while s can hold 2
More shielding will happen in p, so it is easier to remove an electron
Order of electron energy
S<P<D<F
Aufbau principle
Filling up orbitals with lowest energy
Hunds rule
One arrow in each first
As you go down a group
Atomic radius/size increases
As you go across a period
Atomic size/radius decreases and effective nuclear charge increases
Transition elements do not follow the pattern
Small increase down a group from period 4 to 5 but none from 5 to 6
Across a period, remain the same size since shielding counteracts increasing effective nuclear charge
As you go up a group
Ionization energy increases
As you go across a period (L to R)
Ionization energy increases
IE value greatly increases when
Removing a core (inner) electron
Electron affinity
Energy released when an electron is added to a neutral gaseous atom (negative number)
Second ea value is
An endothermic process
Metallic character
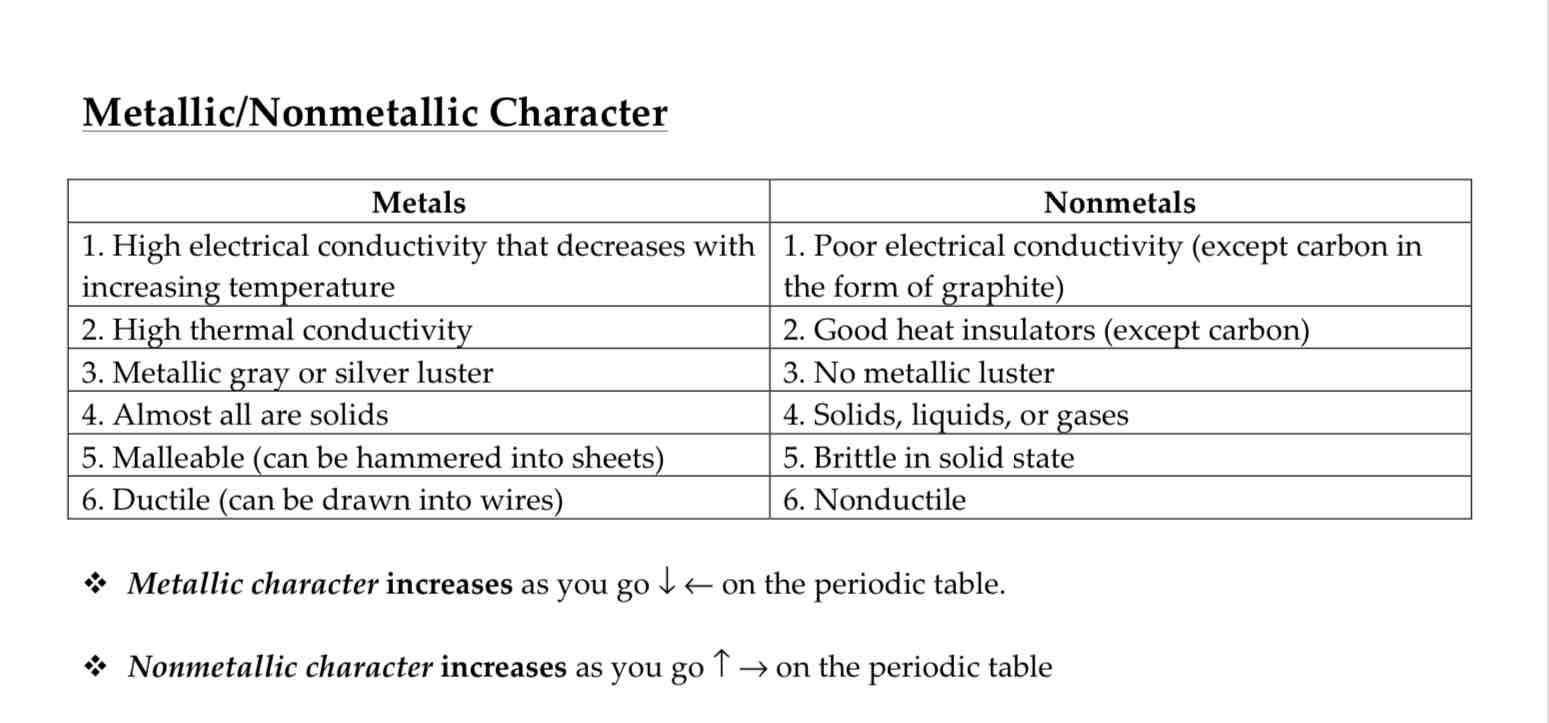
Acidity and Basicity

Removing an electron
Highest n value first then f,d,p,s
Adding an electron
Lowest n value with room then s,p,d,f
Isoelectric
Same number of electrons
Paramagnetic
Unpaired electrons & attracted by magnetic field
Diamagnetic
All of its electrons are paired & not affected by magnetic field
Ionic size/ radius
Cations (+) are smaller, anions (-) are bigger
For isoelectric ions,
The one with the most protons will be smallest