Cellular Respiration and Mitochondrial Function
1/44
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
45 Terms
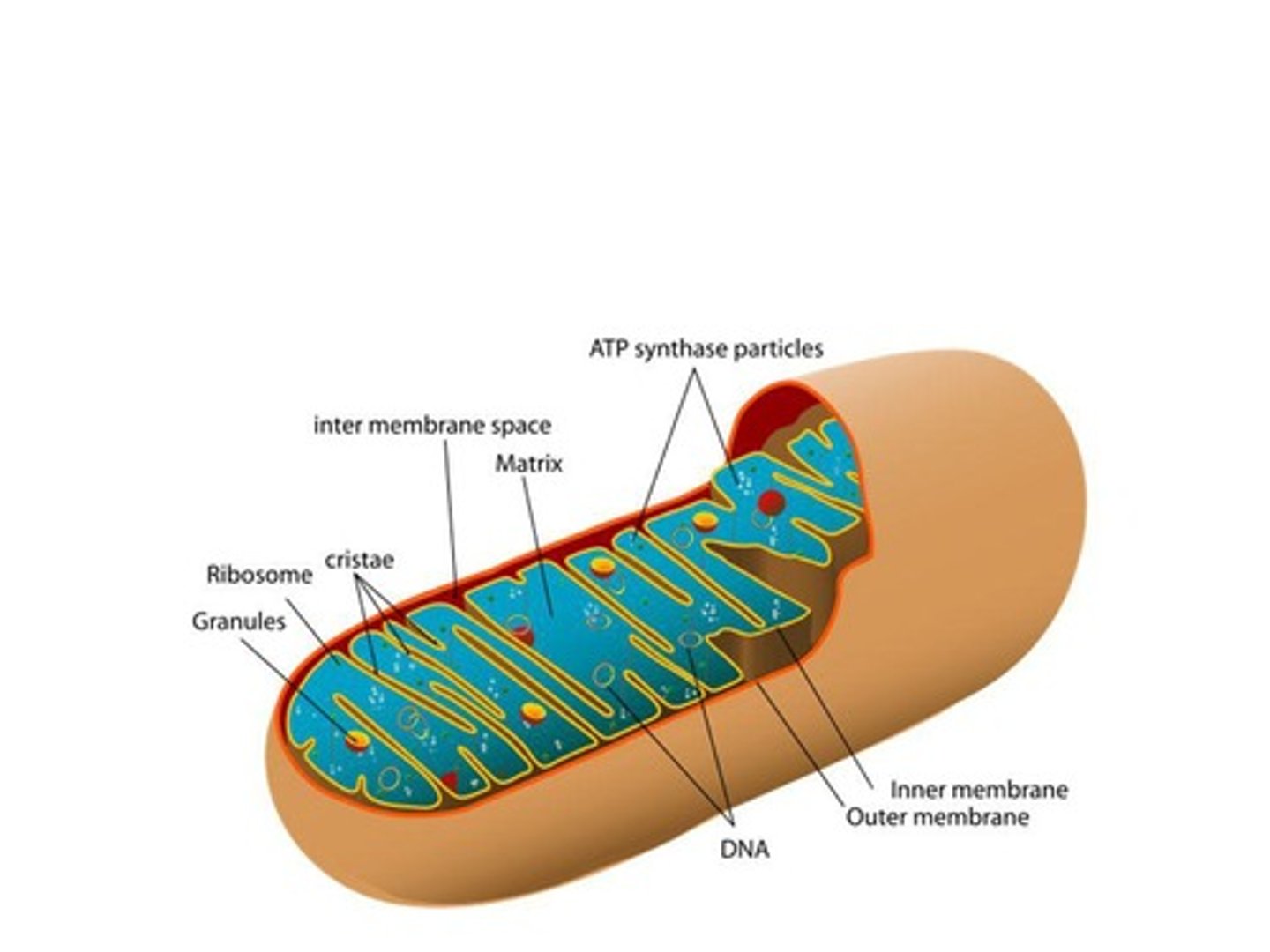
Mitochondria
Cellular organelles that generate ATP through cellular respiration.
Cellular Respiration
The process by which cells harvest chemical energy stored in organic molecules to generate ATP.
Organic molecules + oxygen
Reactants that yield CO2 + H2O + energy during cellular respiration.
Starch
The major source of fuel for animals, which breaks down into glucose.
Oxidized
The process of losing electrons, as seen in the catabolic breakdown of glucose.
Reduction
The process of gaining electrons, as seen when NAD+ is reduced to NADH.
OIL RIG
A mnemonic for oxidation is loss, reduction is gain.
C6H12O6 + 6O2
The chemical equation representing glucose oxidation during cellular respiration.
6CO2 + 6H2O + energy
The products of glucose oxidation in cellular respiration.
Path of Electrons in Energy Harvest
The sequence of glucose → NADH → ETC → oxygen during cellular respiration.
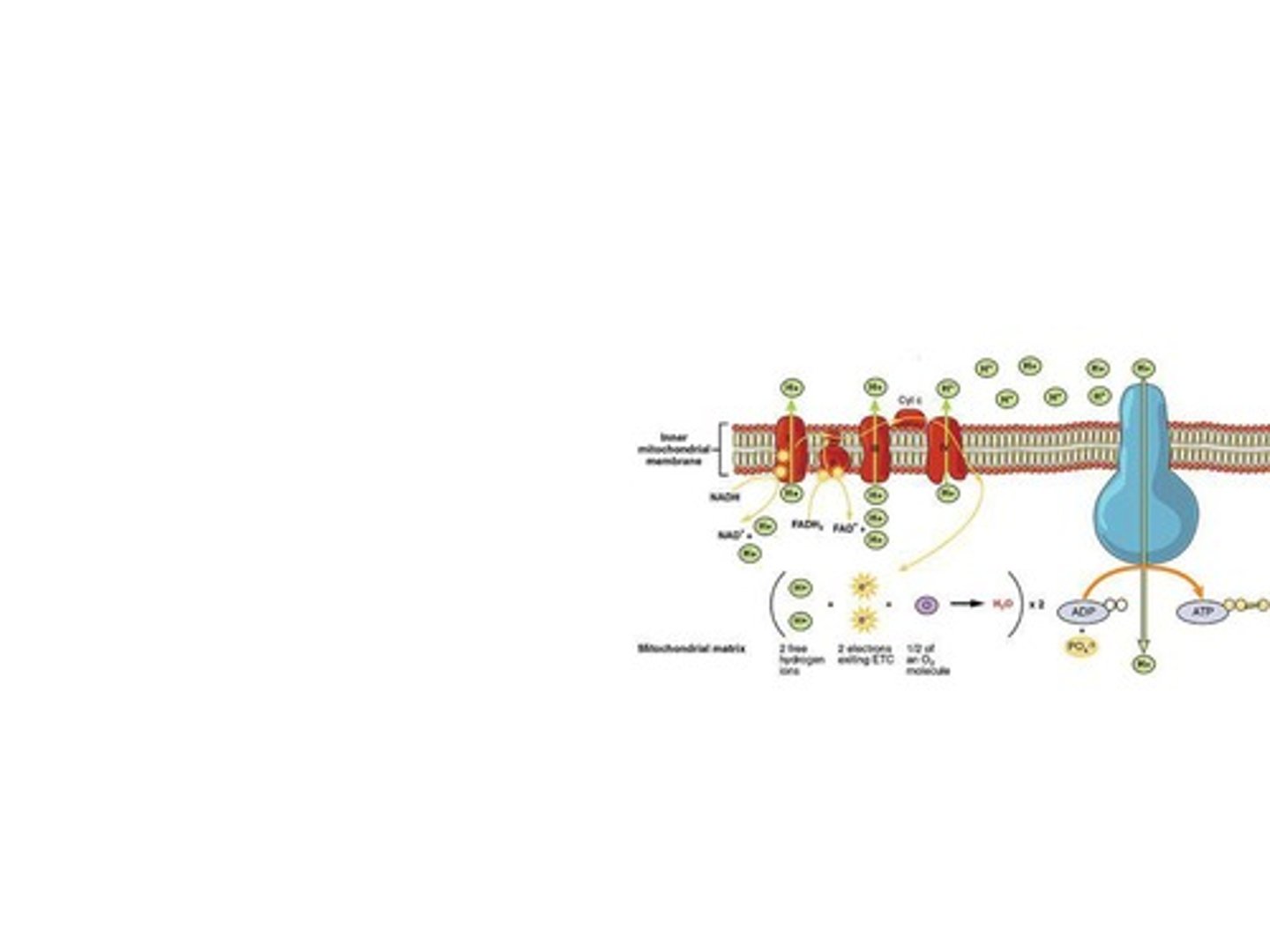
Electron Transport Chain (ETC)
A sequence of membrane proteins that shuttle electrons down a series of redox reactions.
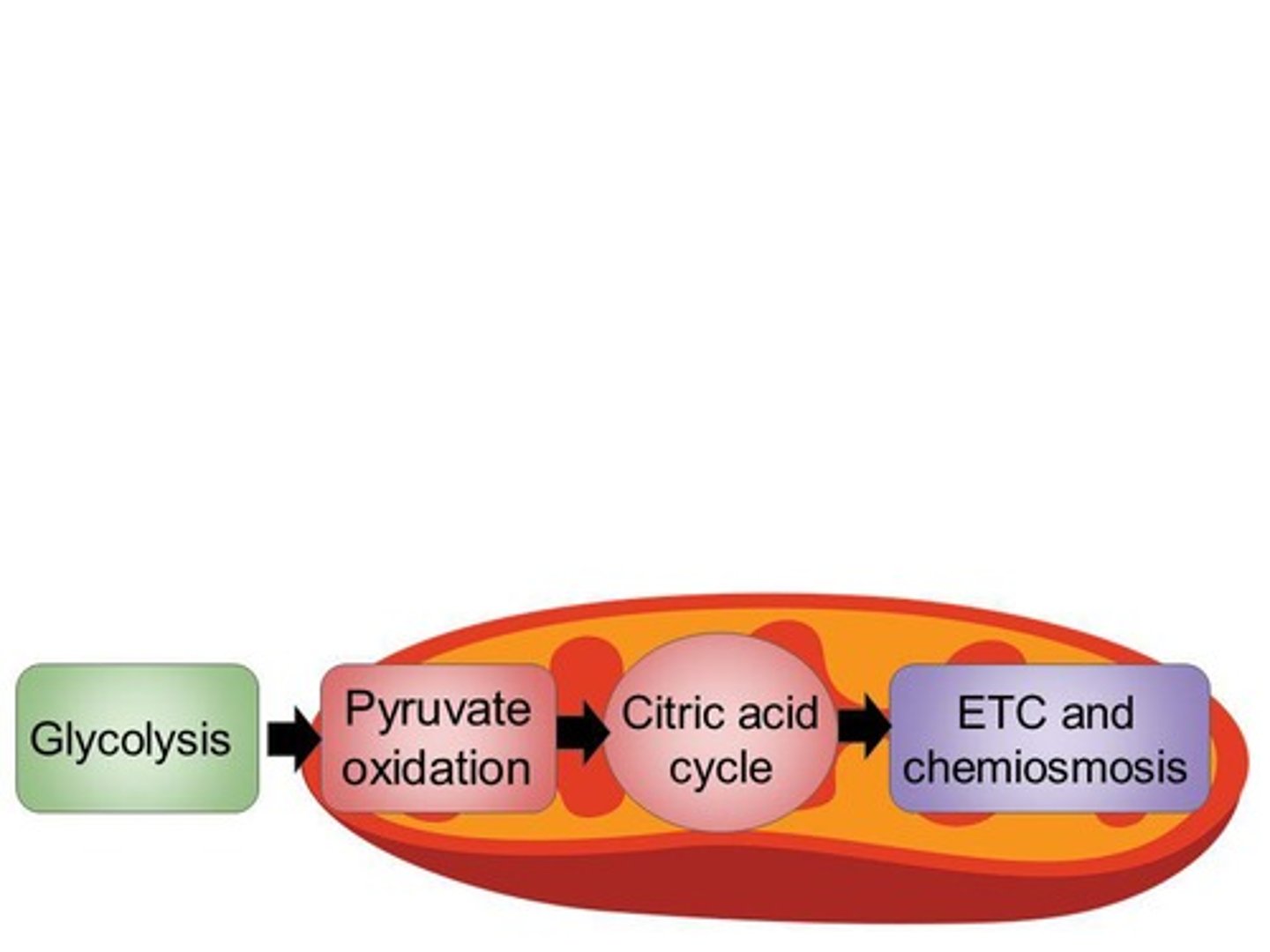
Stages of Cellular Respiration
Three stages: Glycolysis, Pyruvate oxidation and the citric acid cycle, Oxidative phosphorylation.
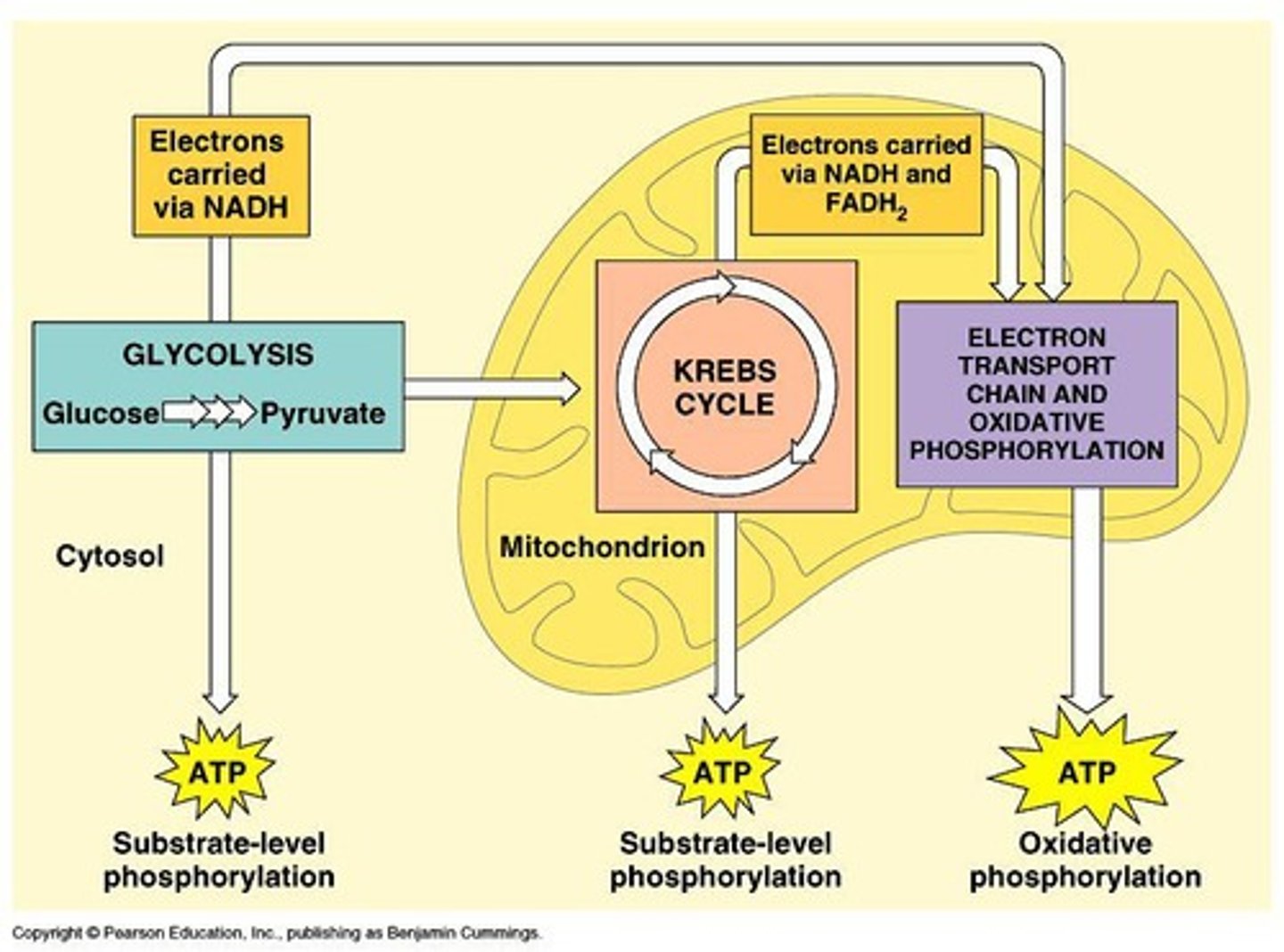
Glycolysis
The first stage of cellular respiration that occurs in the cytosol and splits glucose into 2 pyruvates.
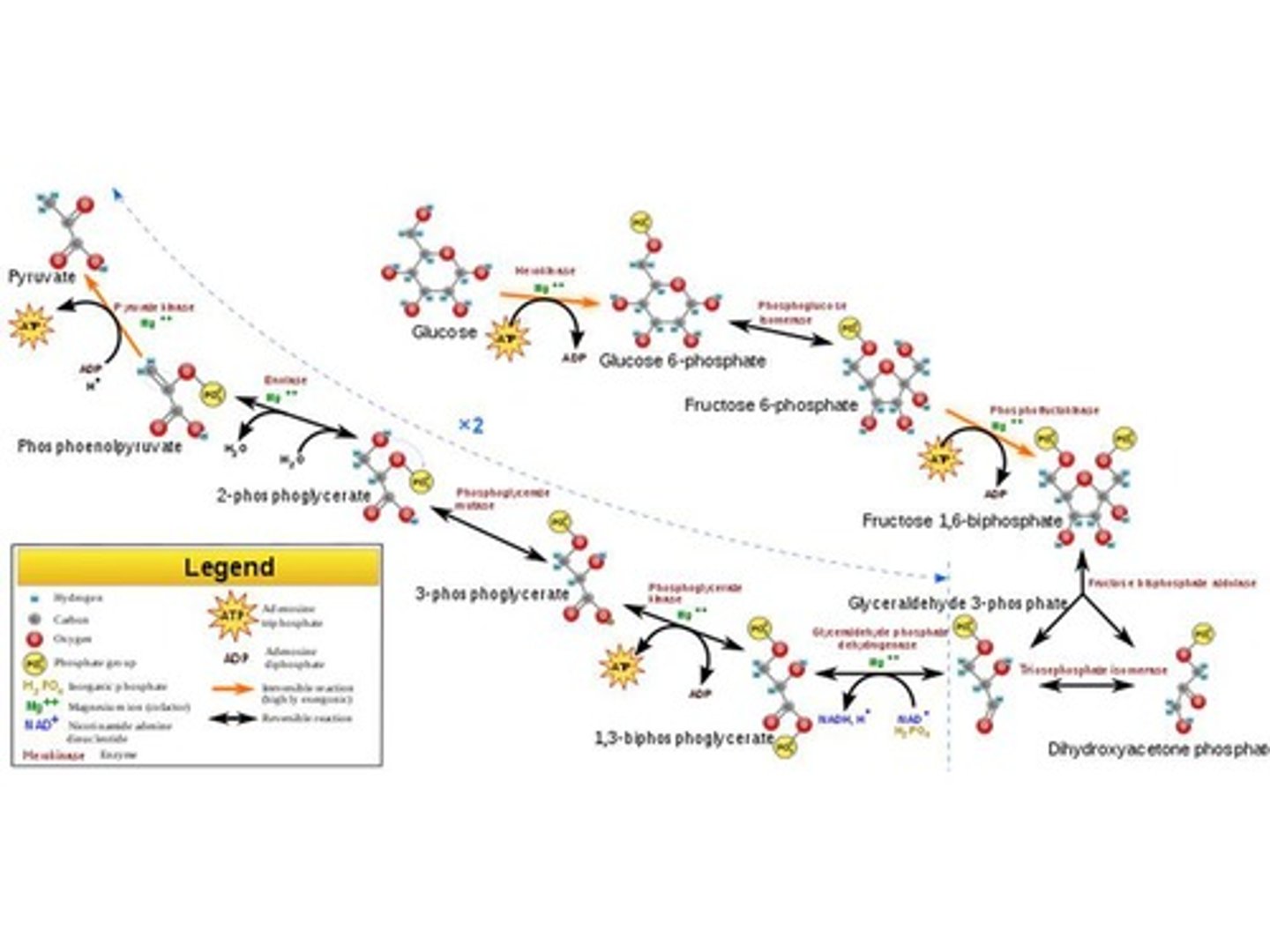
Energy Investment Stage
The phase of glycolysis where ATP is used to phosphorylate glucose compounds.
Energy Payoff Stage
The phase of glycolysis where energy is produced by substrate-level phosphorylation.
Net Energy Yield per 1 Glucose
2 ATP and 2 NADH produced from glycolysis.
Pyruvate Oxidation
The process where pyruvate is oxidized into acetyl coA if oxygen is present.
Citric Acid Cycle
Also known as the Krebs cycle, it occurs in the mitochondrial matrix and processes acetyl CoA.
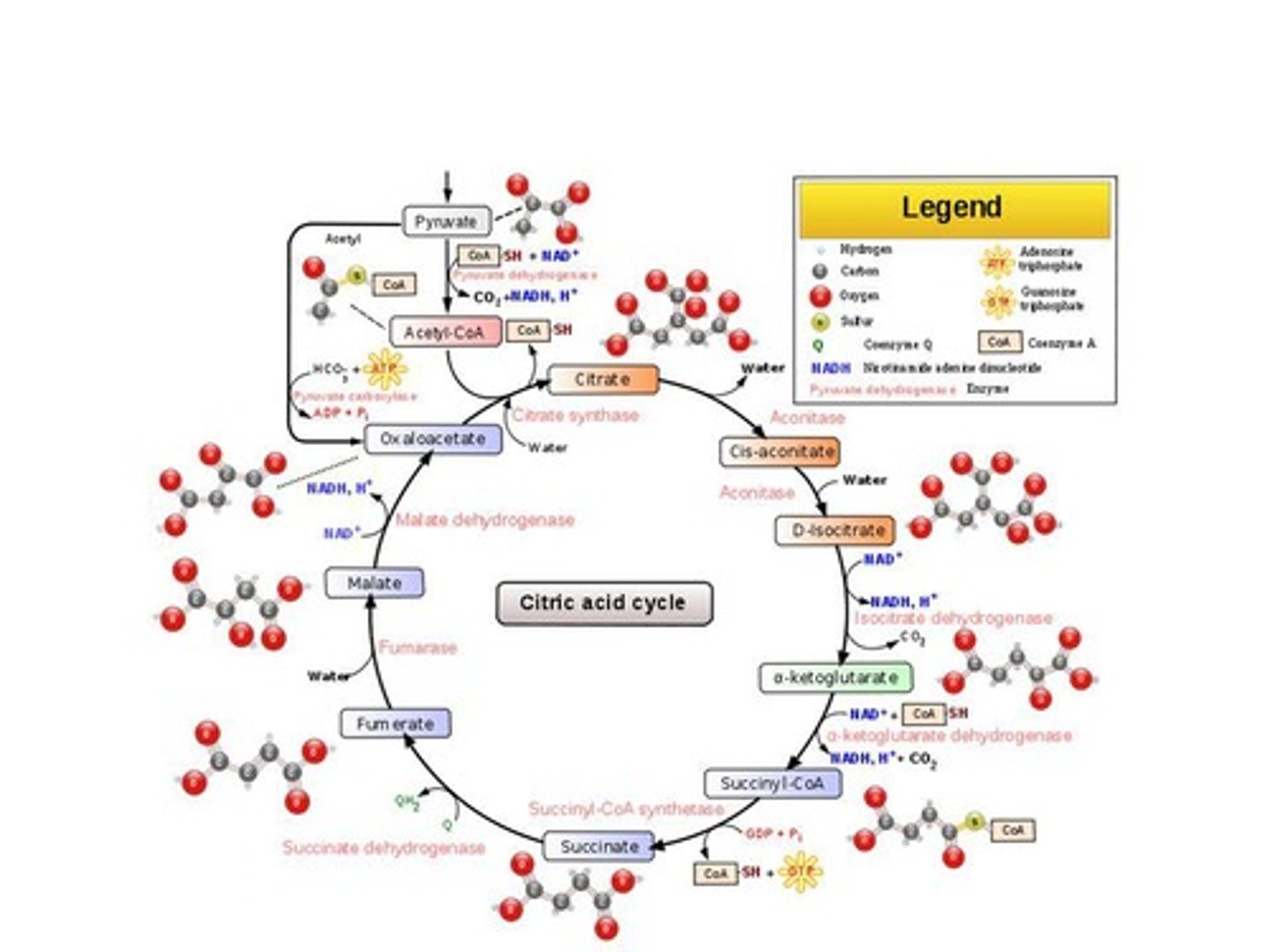
Citric Acid Cycle Outputs
2 ATP, 6 NADH, 4 CO2, and 2 FADH2 produced per glucose molecule.
Quick Check - Glycolysis Occurrence
Glycolysis occurs in the cytosol.
Quick Check - Glycolysis Production
Glycolysis produces pyruvate.
Quick Check - Net Production of ATP
The net production of ATP from glycolysis is 2 ATP.
Quick Check - Citric Acid Cycle Occurrence
The citric acid cycle occurs in the mitochondrial matrix.
Oxidative Phosphorylation
Process generating ATP via electron transport chain.
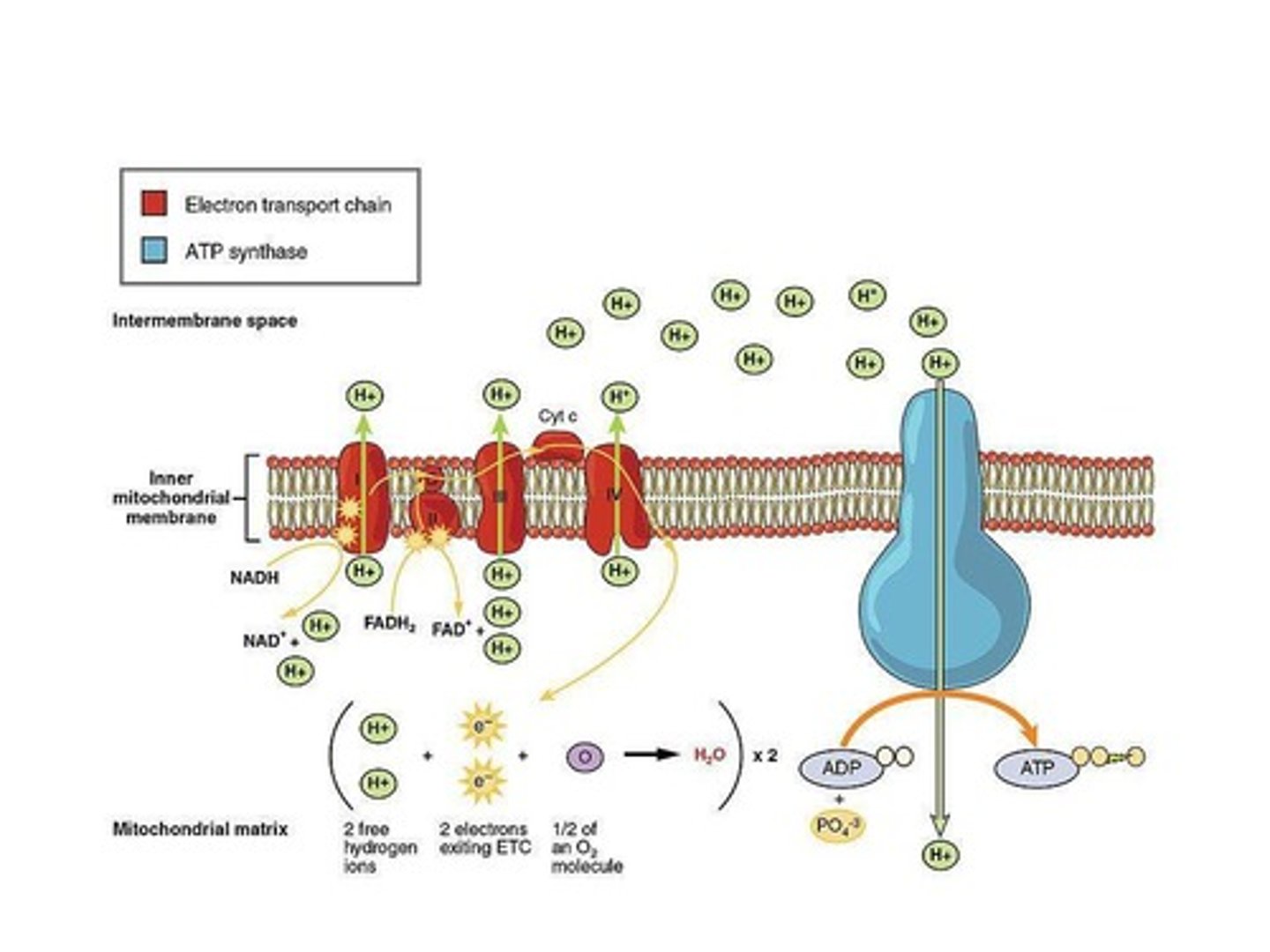
Cristae
Folds in mitochondria increasing surface area.
Proton Gradient
H+ concentration difference across mitochondrial membrane.
Final Electron Acceptor
Oxygen, forming water with electrons and protons.
Chemiosmosis
Process using H+ gradient to synthesize ATP.
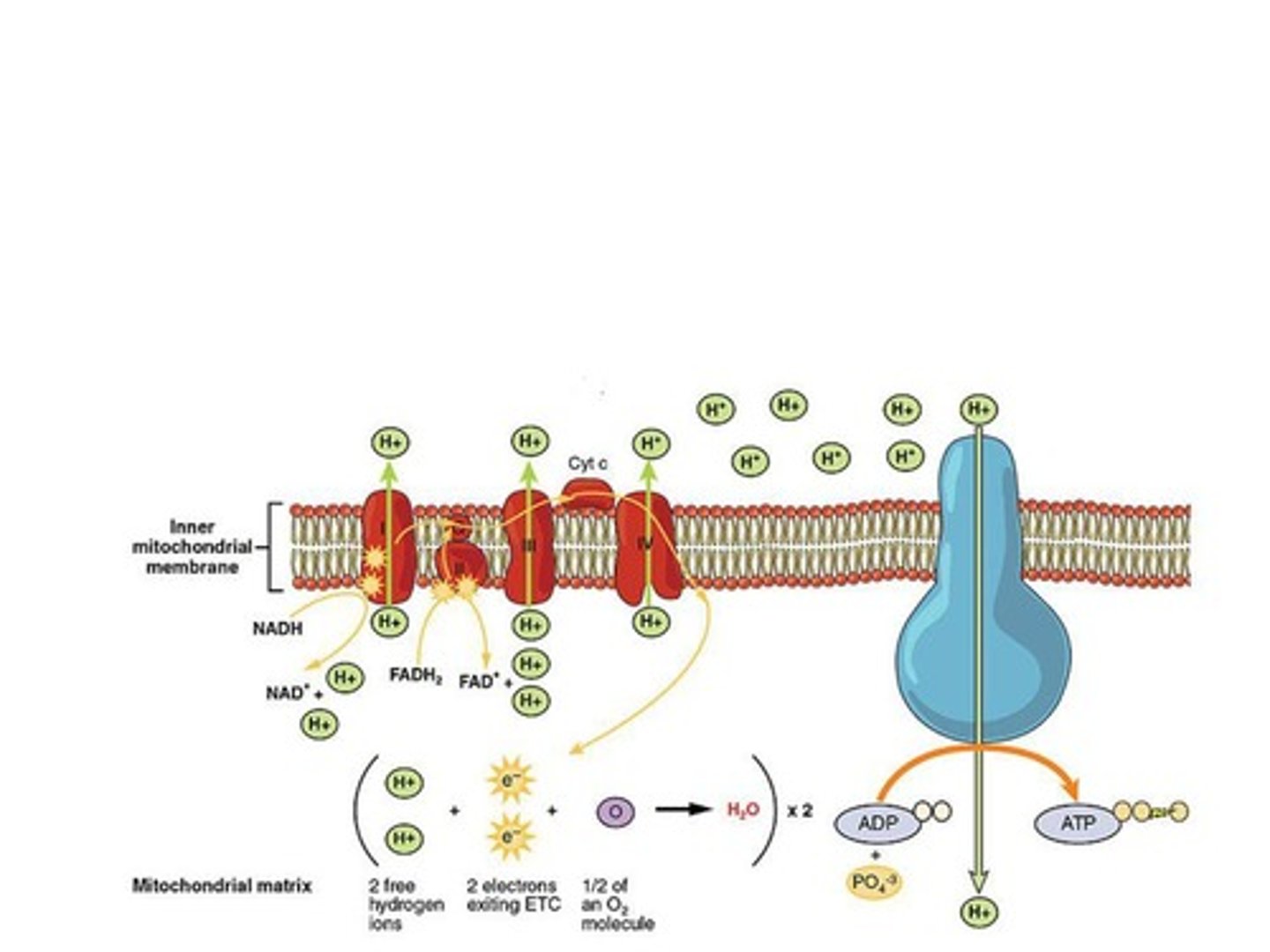
ATP Synthase
Enzyme converting ADP + P into ATP.
Anaerobic Respiration
ATP generation without oxygen using ETC.
Fermentation
ATP production without ETC, recycles NAD+.
Alcohol Fermentation
Conversion of pyruvate to ethanol by yeast.
Lactic Acid Fermentation
Conversion of pyruvate to lactate in muscles.
Lactic Acidosis
Condition from lactate buildup lowering blood pH.
NADH
Electron carrier generated in glycolysis and Krebs.
FADH2
Another electron carrier produced in Krebs cycle.
Total ATP Yield
30-32 ATP produced per glucose molecule.
Exergonic Flow
Energy-releasing movement of electrons in ETC.
Hydrogen Ions (H+)
Protons pumped into intermembrane space during ETC.
Oxygen's Role
Drives electron flow in the electron transport chain.
Muscle Cells
Use lactic acid fermentation when oxygen is low.
Shimmying
Muscle reaction in fish due to oxygen deprivation.
pH Effect
Influences ion concentration and mitochondrial activity.
Mitochondrial Permeability
Outer membrane's ability to allow H+ passage.
ATP Production
Energy currency generated during cellular respiration.