UE Orthotics for Spinal Cord Patients
1/26
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
27 Terms
prevent deformity, prevent overstretching of muscles, maintain integrity of joints and arches of hand, increase functional use of hand, increase independence in early SCI
Why do we splint for SCI UE?
promote tenodesis, maintain long length, preserve natural hand function, cosmesis, hygine, increase function, spasticity
outcomes for splinting
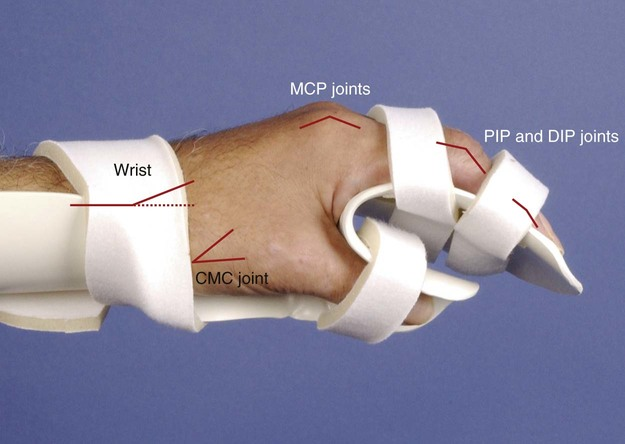
Wrist- neutral to 30 degrees extension, Normal transverse and longitudinal arches, moderate tendon shortening for tenodesis, Thumb- abducted and opposed, preservation of web space
functional position of hand
easier to prevent than remediate deformities, better acceptance, increase independence, decrease frustration
why early intervention?
MMT, Sensory, Existing Deformities, Patient Interview, ASIA level
Functional hand components
-maintain functional position
-observe and address tone increase
-educate on PROM
-educate on proper UE position
-provide wrist support for day
-provide wrist/finger support at night
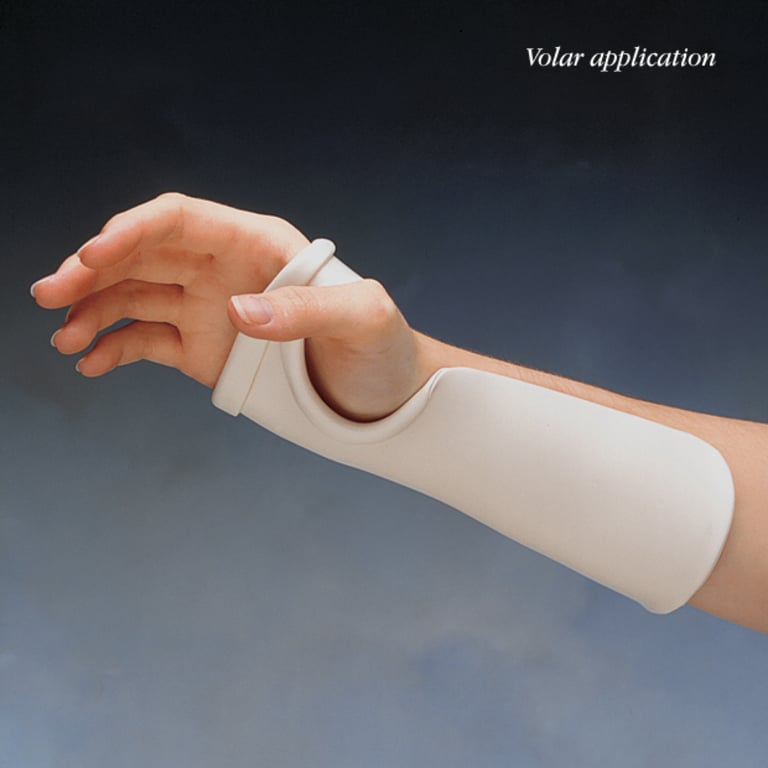
C1-C4 hand
Cock Up Splint
Day splint for C1-C4 that provides wrist extension with forearm support, wrist neutral to 30 degrees extension, supports arches, fingers are free, custom fit
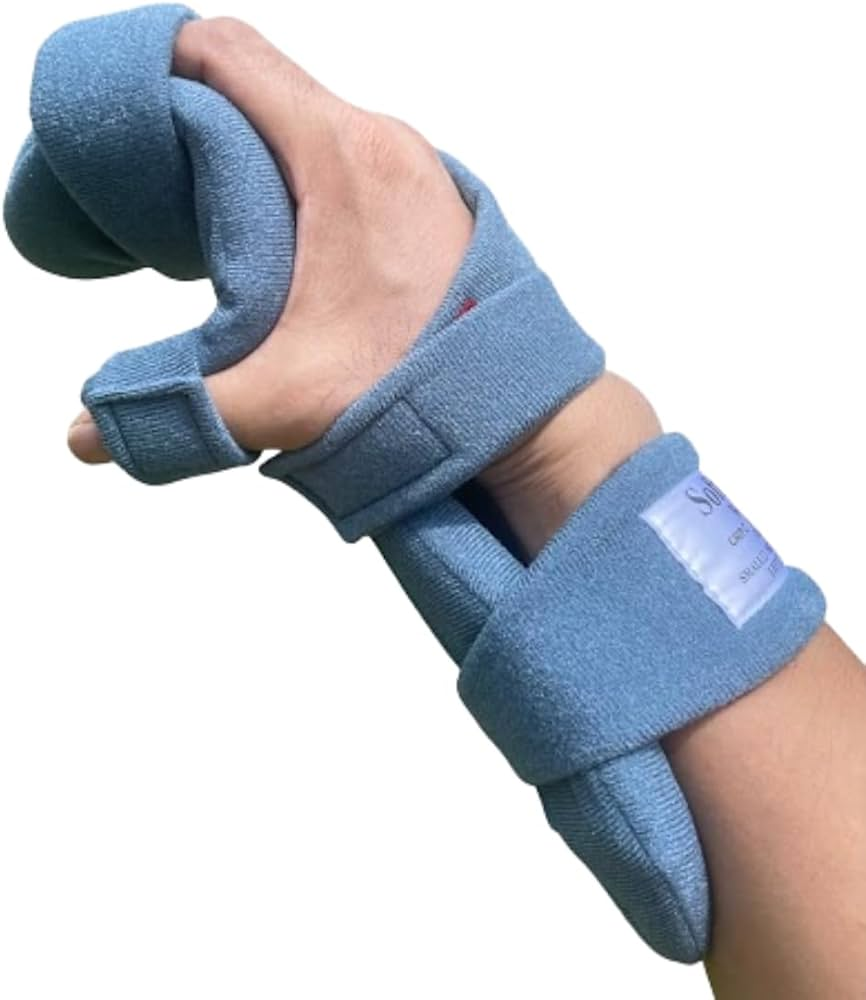
resting hand splint
Night splint for C1-C4 that provides functional position, wrist in 20-30 degrees extension, MPs 15-20 degree flexion, fingers abducted 10-20 degrees flexion, thumb abducted and opposed under first finger, web space and arches supported
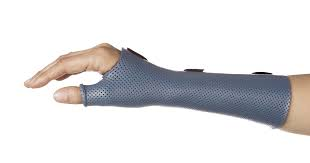
Long Opponens Splint
C5 hand splint with wrist in neutral, thumb placed in opposition in PINCH position, used to stabilize objects in functional tasks
elbow flexors, hand contractures
C5 has strong ______ which puts them at risk for _______

Intrinsic Minus Hand (Claw Hands)
imbalance between strong intrinsic and weak intrinsic muscles, MCP hyperextension and PIP/DIP flexion
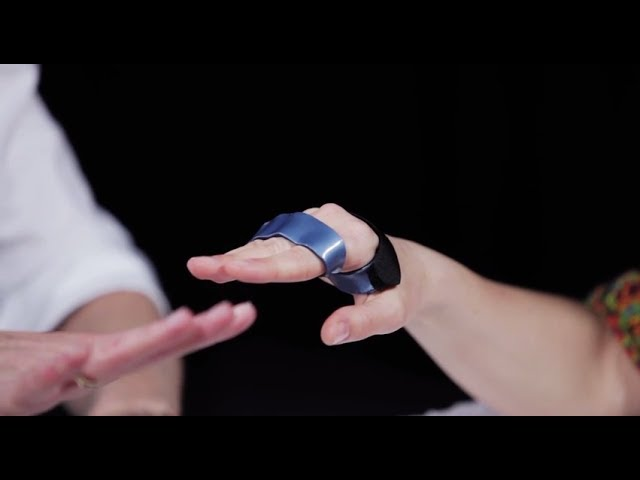

MCP Block Splint
splint for intrinsic minus hand/claw hand
wrist drop
C1-C5 is at risk of
tight web space
C1-C7 is at risk of
extended flat hand, functional webbing in hand dies
C7 is at risk of
wrist extensor contracture due to supination with gravity
C5 is at risk of
C1-C7
what levels are at risk of tight web space?
C1-C5
what levels are at risk of wrist drop?
C7
what levels are at risk of flat hand?
C5
what levels are at risk of wrist extension contracture?
weight lifting cuffs, bowel stimulator, catheter holder, universal cuff
examples of adaptive equipment
functional electrical stimulation (FES), tendon transfer, nerve transfers, joint fusion
long term alternatives to splinting
wrist extension, elbow extension, and finger flexion
most common tendon transfers are for
above 4
tendon transfer must have muscle grade _________
lose one muscle grade
a transfered muscle will _______
immediate on/off, no dependency period, increased cost, less likely to wear long term
risk and benefits of neuroprosthesis
dependency period, risk loss of function, infection, deformity, cost, permanent
risks of surgery