lecture 1 and 2
1/38
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
39 Terms
central dogma: genetic info flows in onyl one direction from ___ to ___ to _____ / or ___ directly to _____
DNA RNA protein RNA protein
a DNA strand is a polymer of ______, DNA is double-______
nucleotides stranded
A protein coding gene always starts with a start codon, in eukaryotes its always ATG —> ____, while common stop codons are ___,___, and ____
MET TAA TGA TAG
a ______ is composed of a linear sequence of amino acids, each ____ is composed of one or more polypeptides, all of the proteins that a cell makes at a given time is called its ______
polypeptide protein proteome
Traits (phenotypes), ______ traits are related to form, shape, or structure of organism/ _____ traits are related to internal functions like ability to metabolize sugar/ _____ traits are related to responses, habits, actions of organism like migration patterns
morphological physiological behavioral
_____ are a variant of a gene, different ___ (Same) produce different proteins
alleles
sexually reproducing species are commonly _____, they have two copies of each chromsome termed _____, one from each parent, ____ (last) contain the same genes but not necessarily the same _____
diploids homologs alleles
_____ (sperm or egg) are usually ____, they have one copy of each chromosome,
gametes haploid
model organism; _____ ____ natural non-mutated form, ___ is modified by mutation, ____ ___ ____ mutations disrupt the function of protein product, _____ is the complete loss of function, ____ ___ ______ mutations enhance the functions of protein product
wild type mutated loss of function knockout gain of function
prokaryotes have no ____ and a _____ chromosome / eurkaryotes have ____-_____ nucleus and other ____-___ (same) _____
nucleus chromosome membrane bound organelles
prokaryote chromosomes contain a single molecule of ____ and only have ____ circular chromosome, the chromosome is condensed by ____-like proteins and is located in _____ region (not seperated from the rest of the cell by a membrane like nucleus)
DNA one histone nucleoid
prokayote reproduction: prior to division the cell replicates its _____, _____ replication starts from origin of replication, then the cell divides into two daughter cells by process called _____ ______
chromosome bidirectional binary fission
eukaryotes have multiple ___ chromsomes ( humans have 23 pairs, dogs have 39 pairs,), a ____ is an organized representation of chromosomes within a cell. chromosomes are only visible during _____ ____ ____
linear karyotype active cell division
DNA is packaged around histone proteins to form______ which are then packaged into dna protein complees called ______, when the cells not dividing _____ ____ regulates gene expression, chromatin is further ____ during cell division
nucleosomes chromatin chromatin remodeling condensed
_____ are the two ends of the chromosome, have a repetitive dna sequence/ ____ links a pair of sister chromatids during division, also have repetitive dna sequence, the _____ assembles at the centromere and serves as attachment point for mitotic spindle fibers
telomeres centromere
members of a pair of chromosomes are called _____, they are nearly identical in size, have same banding pattern and centromere locaiton, have the same genes but not necessarily same ______, the only exception are ____ chromosomes
homologs alleles sex
mitosis: ___ is non dividing state that cells enter where they exit the active cell cycle and stop dividing, ___ cells often do this and never divide again , liver cells cal enter this but reenter cycle after injury, this state prevents unnecessary cell division and allows cells to specialize
G0 neuron
mitosis: ____ ___ and ___ are collectively known as interphase,
G1 S G2
mitosis: in ___ — enters cell cycle, prepare to divide, ____ and ____ components begin to synthesize , proteins RNA organelles are formed, total chromosome number here is ____
G1 centromere centrosome 46
mitosis: ___ phase is where chromosomes are duplicated, centrosomes are duplicated, _____ are synthesized, at this point there are ____ single chromosomes and ___ chromatids
S histones 46 92
mitosis: ___ - accumulate materials for mitosis, repair DNA damage from replication, synthesis of proteins and organelles like ______,
G2 microtubulues
mitosis: ____ - nucleus envelope dissociates into small vesicles, ____ condense into more compact structures, ____ begin to separate
prophase chromatids centrosomes
mitosis: ______ — centrosomes move to opposite ends of the cell forming ____ ____, kinetochore microtubules grow from these poles and these attach to ____ at the centrosomes
prometaphase spindle poles kinetochores
mitosis: _____ are specialized microtuble organizing centers (MTOCs) and are where kinetochores attach, microtubules are formed by rapid polymerization of _____ proteins, there are three different tpyes of spindle microtubules: ____ which are important for positioning of spindle apparatus, ____ which push the poles away from each other and ______ which attach to the kinetochore
centrosomes tubulin aster polar kinetochore
mitosis: ______ — pairs of sister chromatids align themselves in the equator, each pair of chromatids is attached to both poles by kinetochore microtubules
metaphase
mitosis: _____ - each chromatid now an individual chromosome, ____ microtubules shorten while ___ microtubules lengthen
anaphase kinetochore polar
mitosis : _____ — chromosomes decondense into _____, ____ ____ reforms around each set, the ____ ____ breaks down
telophase chromatin nucleur envelope mitotic spindle
eukaryotic cell cycle: mitosis is followed by ______, in animals the formation of a _____ ____ , in plants formation of a ____ ____, each daughter cell has ___ chromosomes and is _____ (same chromosome number as parent), each cell also has ____ chromatids
cytokinesis cleavage furrow cell plate 46 diploid 46
in ____, parents (diploid) make gametes with half the amount of genetic material (____), gametes then fuse to create a new diploid, animal cells are either somatic (_N, humans =46 chromosomes) like body cells or germ (_N, humans = 23 chromosomes) like sperm and egg
meiosis haploid 2 1
_____ involves two successive divisions to reduce chromosome content
meiosis
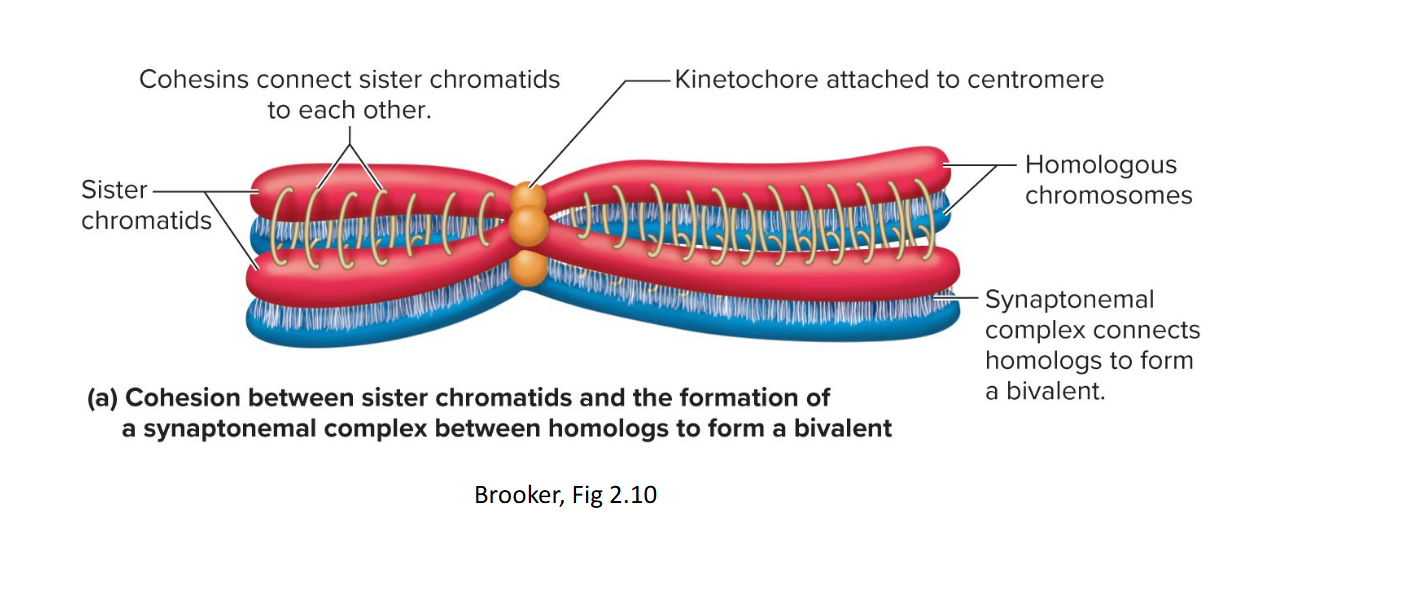
____ of meiosis I, chromosomes condense again, homologous chromosomes pair together in a process called ____ to form a ____ or two pairs of sister chromatids (also called a ____), DNA is exchanged between the homologous pair at various loci or ____ in a process called ____ _____, the # of chiasmata varies based on species and size of chromsome
prophase synapsis bivalent tetrad chiasmata crossing over
____ of meiosis I, nuclear envelope breaks apart, spindle apparatus formation is complete, each pair of sister chromatids is linked to ____ pole (unlike mitosis)
prometaphase one
____ of meiosis I, bivalents align along the metaphase plate, ____ _____ is caused by the random arrangement of homologs along the plate and provids genetic diversity
metaphase independent assortment
____ of meiosis I, homologous chromosomes seperate and sister chromatids stick together
anaphase
____ of meiosis I, sister chromatids have reached respective poles, DNA decondenses back into ______, nuclear envelope reforms , cleave furrow forms to divide the cell in half, ____ non-identical daughter haploid cells are formed , ___ chromosomes and ____ chromatids per cell
telophase chromatin 2 23 46
some simple eukaryotic species are _____ where they produce gametes that are morphologically similar while most are ______ where they are differnet, ____ cells are small and movile while ____ cells (ovum) are large and nonmotile they store a large amount of nutrients
isogamous heterogamous sperm egg
Oogenesis: diploid germ cells call oogonio undergo mitosis to produce diploid _____ _____, these intiaite _____ __ but enter a dormant phase, they are arrested in __ __ until the female starts puberty
primary oocytes meiosis I prophase I
Oogensis: at puberty the primary oocytes are periodically activated to progress through meiosis I, the division in meiosis I is asymmetric producing two ____ cells of unequal size: a large _____ oocyte and a small ____ ____ , the secondary oocyte enters meiosis 2 and produces a _____ ___ and a second ____ ____,
haploid secondary polar body haploid egg polar body
Spermatogenesis: a ____ spermatogonial cell (in testes) divides using ____ to produce two cells, one remains a spermatogonial cell and the other becomes a _____ _______, this cell advances through meiosis I and II to produce 4 ____ sperm cells
diploid mitosis primary spermatocyte haploid