Bacterial and Archaeal Cell Structure Overview
1/101
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
102 Terms
Bacteria
Single-celled microorganisms with diverse characteristics.
Archaea
Microorganisms similar to bacteria but genetically distinct.
Morphology
Study of the form and structure of organisms.
Coccus
Spherical-shaped bacteria.
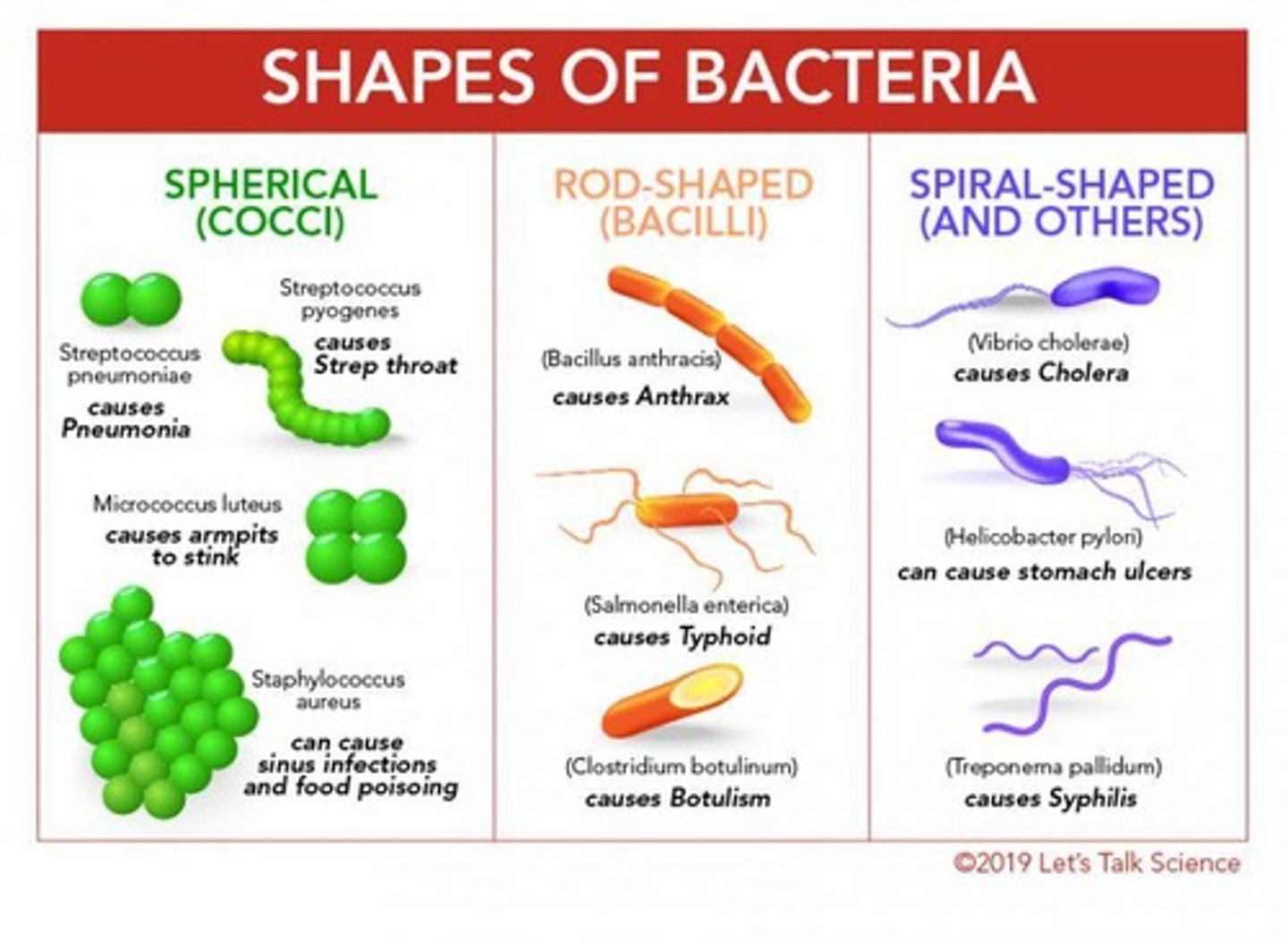
Bacillus
Rod-shaped bacteria.
Convex
Curved outward surface texture.
Streptococci
Chain arrangement of cocci bacteria.

Staphylococci
Grape-like cluster arrangement of cocci.
Diplococci
Pair arrangement of cocci bacteria.
Tetrads
Group of four cocci bacteria.
Sarcinae
Cube-like arrangement of cocci bacteria.
Bacilli (bacillus)
Rod-shaped bacteria
Coccobacilli
Short, oval-shaped bacteria, intermediate between cocci and bacilli.
Vibrios
Comma-shaped bacteria.
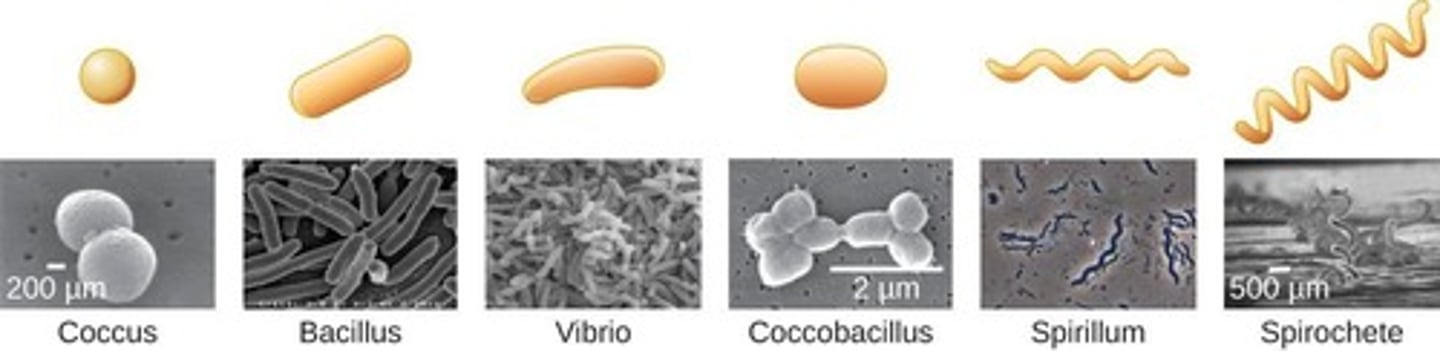
Spirilla
Rigid spiral-shaped bacteria.
Spirochetes
Flexible spiral-shaped bacteria.
Pleomorphic
Bacteria with variable shapes.
Mycelium
Network of fungal filaments, not bacteria.
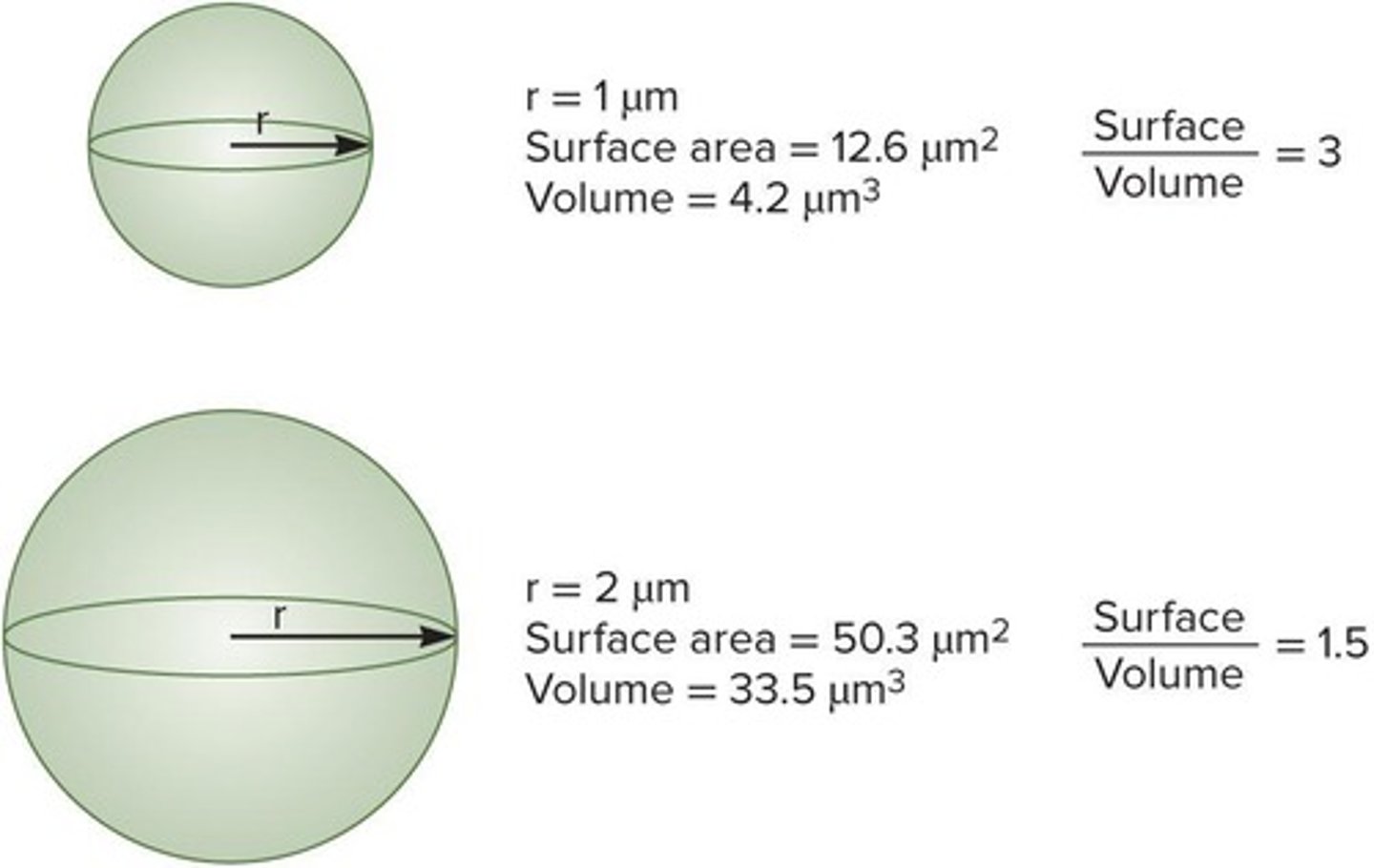
Surface to Volume Ratio
Measurement affecting nutrient uptake efficiency.
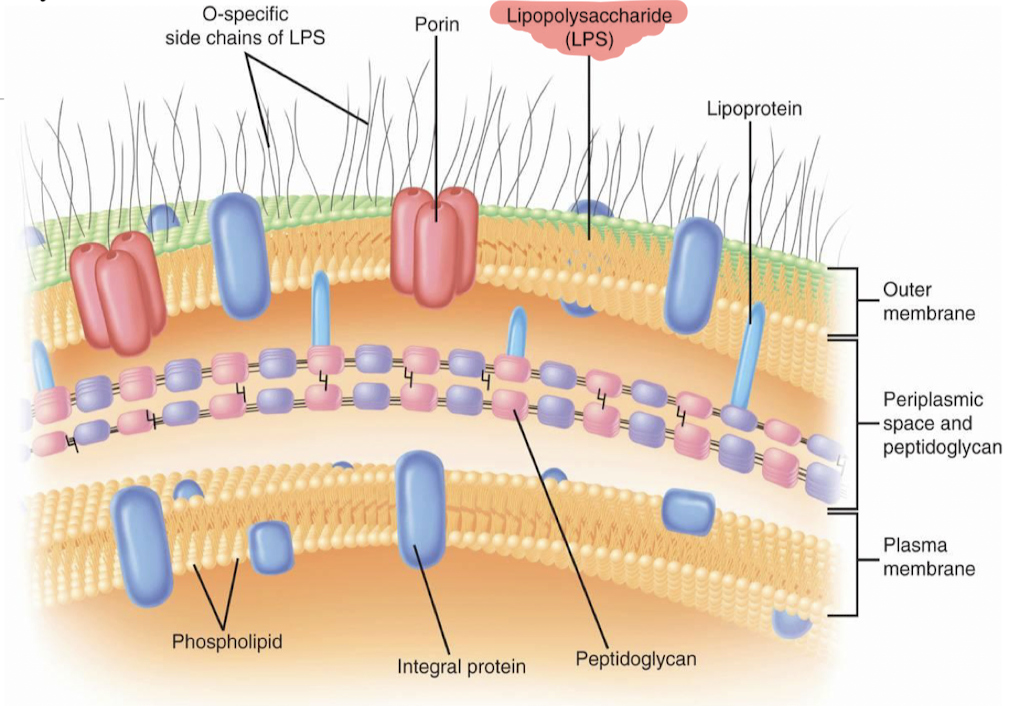
Cell Envelope
Outer structure including plasma membrane and cell wall.
• Plasma membrane
• Cell wall
• Layers outside the cell wall
• Capsule
• Slime layer
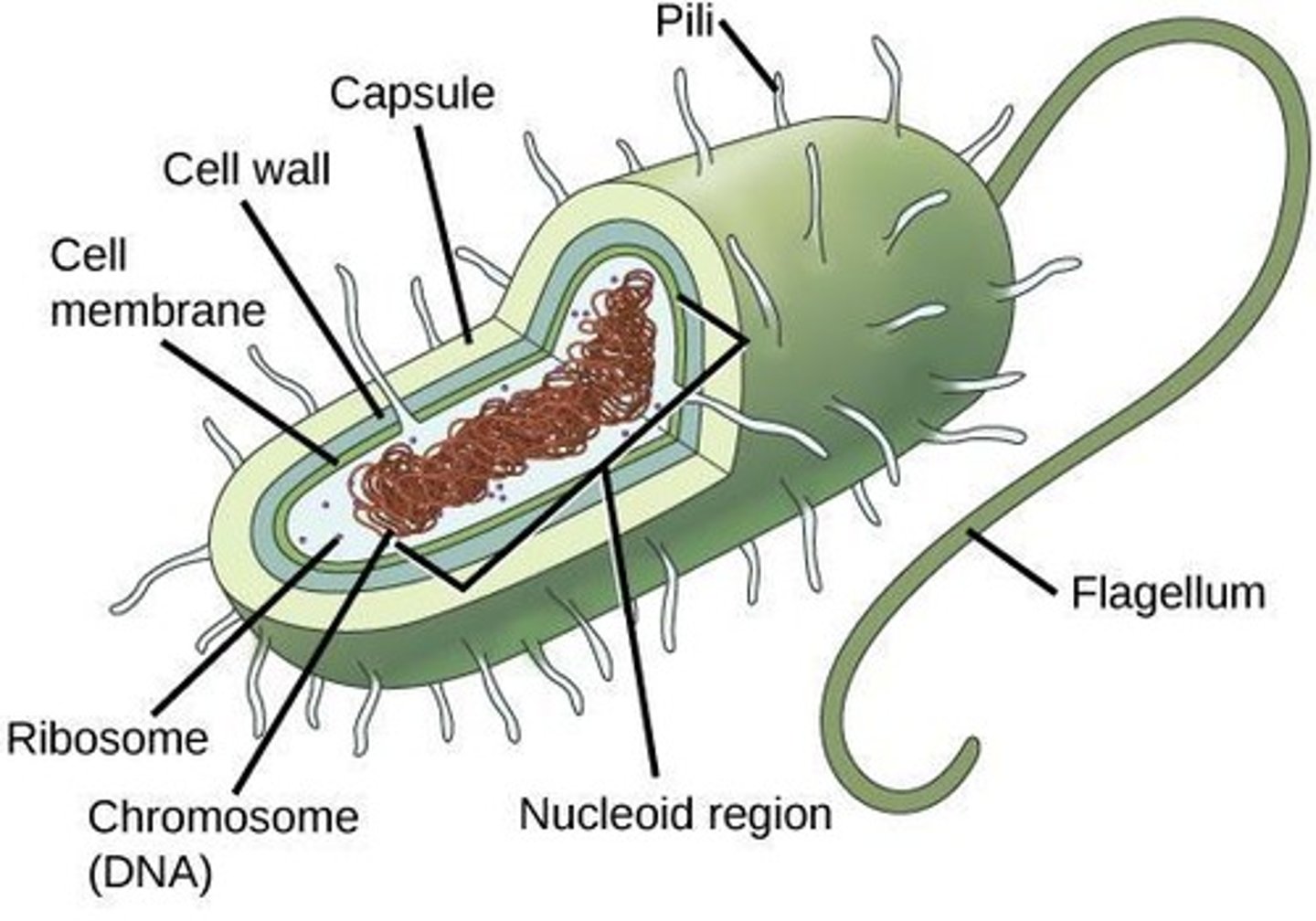
Plasma Membrane
Barrier enclosing cytoplasm, selectively permeable.
Cell Wall
Rigid structure providing shape and protection.
Capsule
Thick outer layer for protection and adherence.
Slime Layer
Loose, unorganized layer outside cell wall.
Membrane Proteins
Proteins that perform various functions in the membrane.
Amphipathic Lipids
Molecules with hydrophilic and hydrophobic regions.
Archaeal Membranes
Composed of unique lipids with isoprene units.
Isoprene Units
Five-carbon branched structures in archaeal lipids.
Ether Linkages
Connect glycerol in archaeal membranes, unlike esters.
Monolayer Structure
Some archaea have a single lipid layer.
Bacterial Membranes
Contain hopanoids instead of sterols for stability.
Hopanoids
Stabilize bacterial membranes, marking microdomain boundaries.
Saturation Levels
Reflect environmental conditions affecting membrane fluidity.
Macroelements
Essential elements like C, O, H, N, S, P.
Micronutrients
Trace elements required in small amounts, e.g., Zn.
Growth Factors
Organic compounds supplied by the environment for growth.
Amino acids
Building blocks essential for protein synthesis.
Purines
Nitrogenous bases in nucleic acid synthesis.
Pyrimidines
Nitrogenous bases in nucleic acid synthesis.
Vitamins
Organic compounds acting as enzyme cofactors.
Passive diffusion
Movement of particles without energy input.
Facilitated diffusion
Transport via protein channels without energy.
Active transport
Energy-requiring movement against concentration gradient.
Primary active transport
Direct use of ATP for transport.
Secondary active transport
Uses electrochemical gradients for transport.
Group translocation
Chemical modification during nutrient transport.
Siderophores
Molecules that bind ferric iron for uptake.
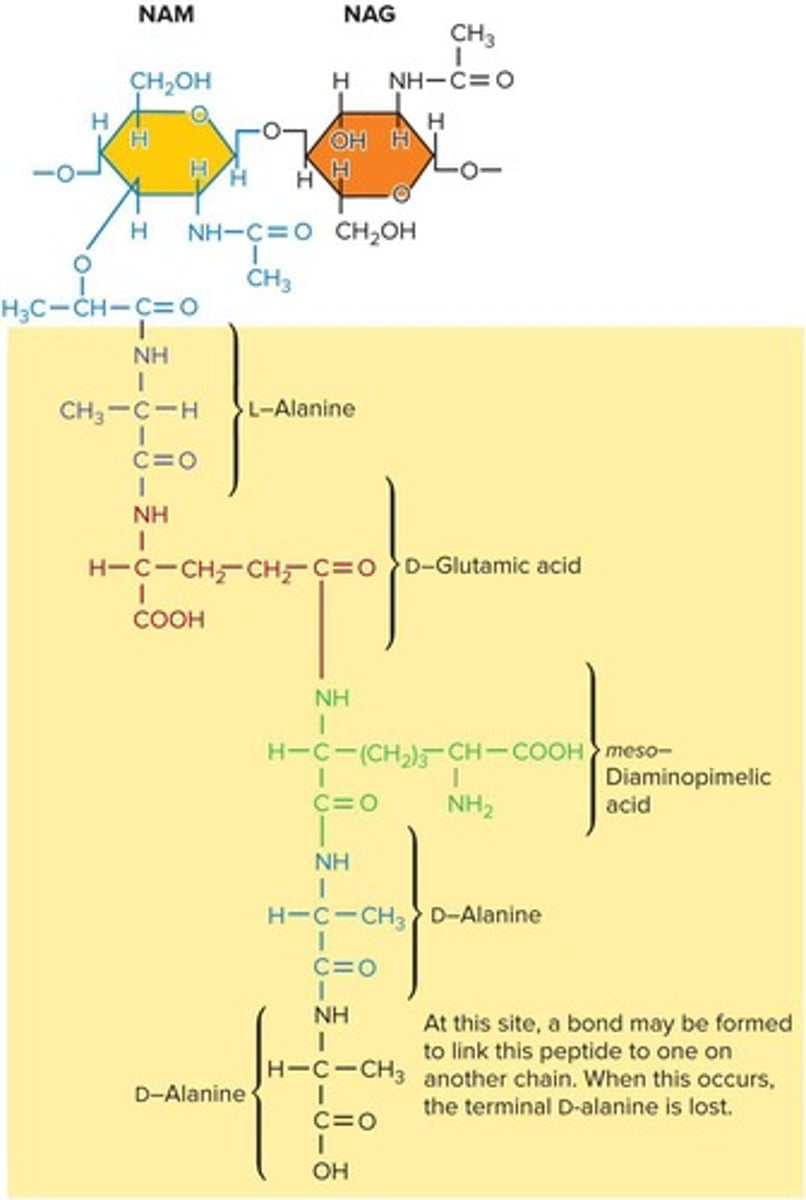
Peptidoglycan
Rigid polymer forming bacterial cell walls.
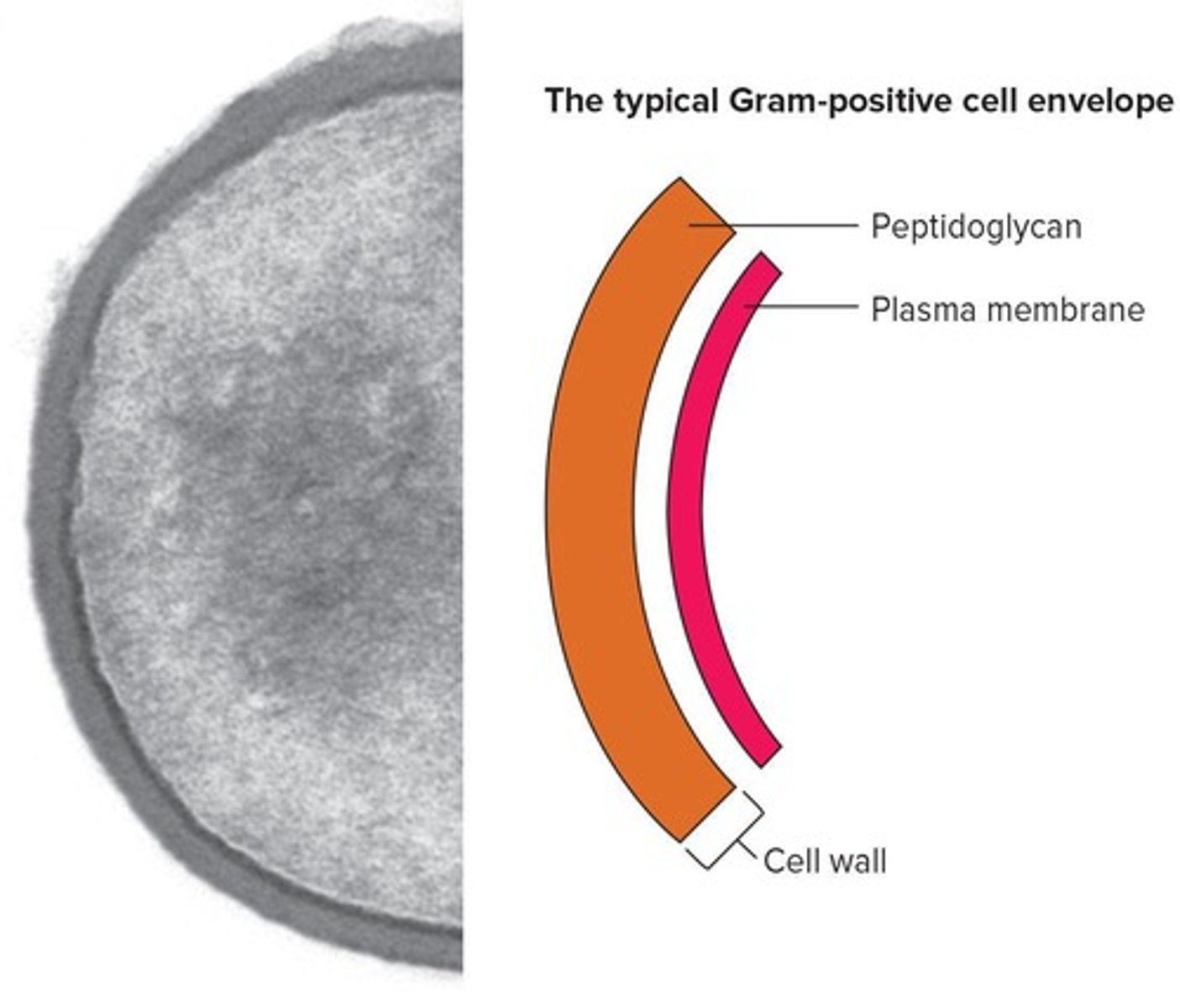
Gram-positive bacteria
Stain purple; thick peptidoglycan layer.
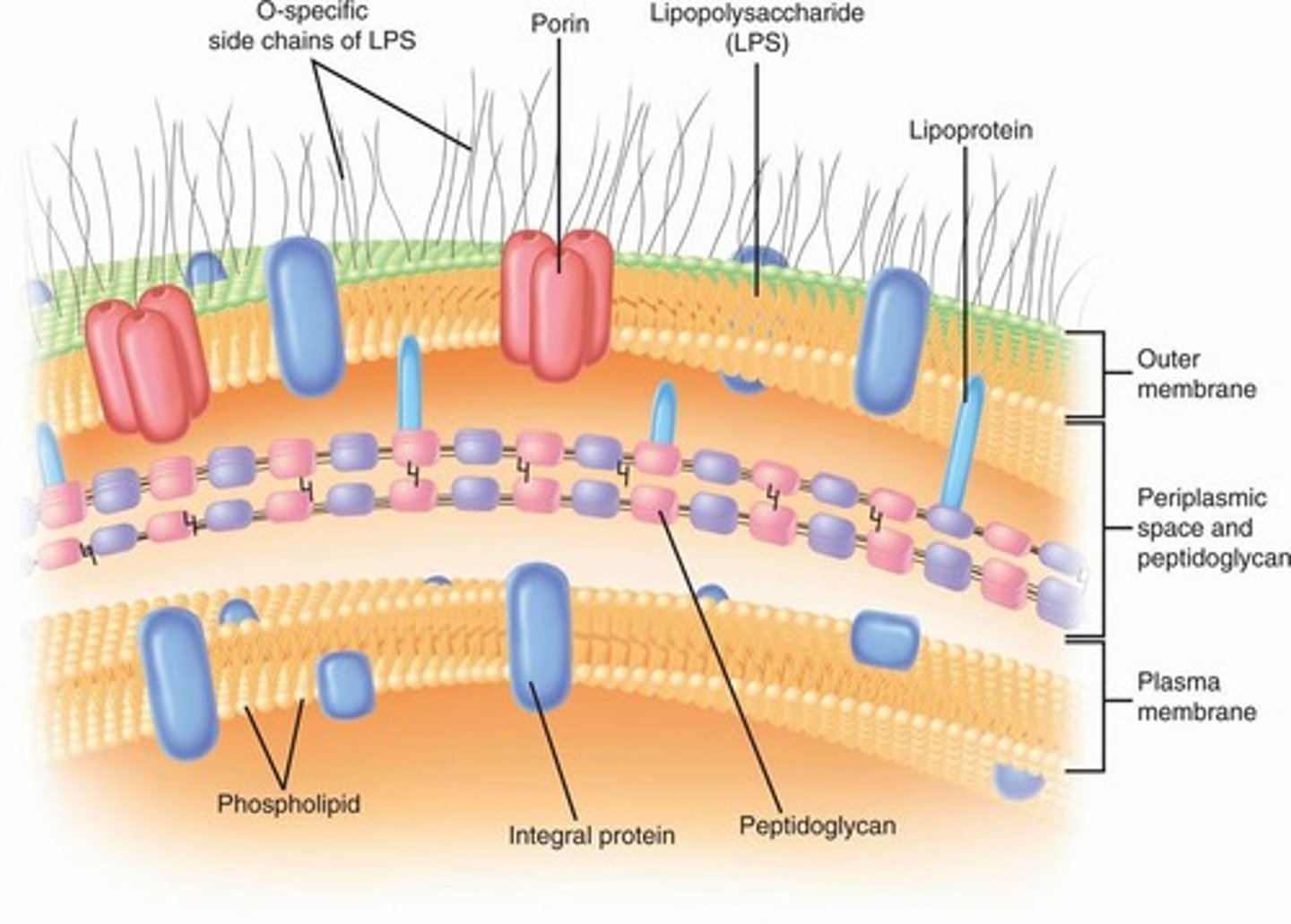
Gram-negative bacteria
Stain pink; thin peptidoglycan and outer membrane.
N-acetylglucosamine (NAG)
Sugar component in peptidoglycan structure.
N-acetylmuramic acid (NAM)
Sugar component in peptidoglycan structure.
Teichoic acids
Polymers aiding Gram-positive cell wall stability.
Lipopolysaccharide (LPS)
Complex of lipid A, core, and O antigen.
Lipid A
Endotoxin component of lipopolysaccharide.
Porin proteins
Form channels in Gram-negative outer membrane.
Periplasmic space
Area between cell wall and outer membrane.
Braun's lipoproteins
Connect outer membrane to peptidoglycan.
Gram-negative
Thinner peptidoglycan layer with larger pores.
Crystal violet
Stain lost in Gram-negative bacteria.
Alcohol treatment
Removes lipids, affecting cell wall integrity.
Archaeal cell envelopes
Lack peptidoglycan; may have S-layer.
• Lack peptidoglycan
• S-layer may be only component outside plasma membrane
• Separated from the plasma membrane by a peptidoglycan-like molecule called pseudomurein
• Some lack cell wall
Pseudomurein
Molecule separating S-layer from plasma membrane.
Cell wall protection
Lysozyme breaks NAG and NAM bonds.
Penicillin
Inhibits peptidoglycan synthesis in bacteria.
Hypotonic solution
Causes lysis if cell wall is compromised.
Isotonic solution
Allows cells to survive and grow normally.
Protoplasts
Gram-positive cells without a cell wall.
Spheroplasts
Gram-negative cells with partial cell wall.
Mycoplasma
Bacteria that never produce a cell wall.
Glycocalyx
Surface layer aiding in biofilm formation.
Capsules
Outermost layer providing protection and stability.
Slime layers
Loose polysaccharide layers aiding in adhesion.
S-layers
Protective layers maintaining shape and rigidity.
Osmotic stress
Pressure affecting cell integrity in different solutions.
Ribosomes
Sites of protein synthesis; 70S in bacteria.
Complex protein/RNA structures
• Sites of protein synthesis
• Bacterial and archaea ribosome = 70S
Ribosomal RNA
• 16S small subunit
• 23S and 5S in large subunit
Eukaryotic ribosome
• 80S
• Small subunit 40S
• Large subunit 80S
Nucleoid
Region containing bacterial DNA.
Plasmids
Small DNA molecules independent of chromosomal DNA.
Cytoskeleton
Structures aiding in cell shape and division.
Nucleoid
Region containing bacterial chromosome and proteins.
Plasmids
Extrachromosomal DNA in bacteria, replicates independently.
Cytoskeleton
Protein filaments aiding in cell shape and division.
FtsZ
Protein forming ring during bacterial cell division.
MreB
Protein maintaining shape in rod-shaped bacteria.
Motility
Movement mechanisms in bacteria, including swimming.
Chemotaxis
Movement toward attractants or away from repellents.
Bacterial Flagella
Threadlike structures enabling bacterial motility.
Monotrichous
Single flagellum at one end of the cell.
Amphitrichous
Flagella at both ends of the bacterial cell.
Lophotrichous
Cluster of flagella at one or both ends.
Peritrichous
Flagella distributed over the entire cell surface.
Flagellar Structure
Composed of filament, basal body, and hook.
Flagellar Movement
Rotational movement causing run-tumble behavior.
Archaella
Similar to flagella, involved in adhesion and motility.
Endospore
Dormant structure resistant to harsh conditions.
Activation
Prepares endospores for germination through heating.
Germination
Process where endospores detect nutrients and swell.
Outgrowth
Emergence of vegetative cell from endospore.
SASPs
Small proteins protecting DNA in endospores.
Supercoiling
DNA folding aided by nucleoid proteins.