Physics H - Universal Gravitation
1/35
Earn XP
Description and Tags
The Universe, Magnets, Black Holes
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
36 Terms
How long ago did the Big Bang occur?
almost 14 billion years ago
Is the Big Bang an explosion?
NO
What is the Big Bang?
rapid expansion of time and space
Is the universe expanding?
Yes, it is constantly expanding faster and faster
What is Hubble’s law?
The farther away a galaxy is, the faster it is moving away
cosmis background radiation
radiation leftover from the big bang
What do scientists think our solar system formed from?
a solar nebula
What is a solar nebula?
a giant, rotating cloud of gas and dust
How was the sun formed?
The nebula collapsed due to gravity and spun faster and faster until it was flattened into a disk. The material was pulled towards the center to form the sun.
When was the sun formed?
about 4.6 billion years ago
Planetismal
the asteriod-like bodies that formed the building blocks of planets
How did the planets form?
The planetesimals collided and grew larger by sticking together, eventually combining to make the planets
dark energy
a force that is causing the expansion of the universe to accelerate
dark matter
matter that does not give off electromagnetic radiation
How can scientists infer approximately how long the universe has been expanding?
they know the rate of expansion
What are two possibilities of what will happen to the universe in the future?
the universe will continue to expand
the force of gravity will pull everything back in, reverse big bang, crushed into a giant black hole
magnetism
refers to the properties and interactions of magnets
magnet
a device which carries a static magnetic field around it
magnetic field
a field present around a magnet which exerts a force on other magnetic materials
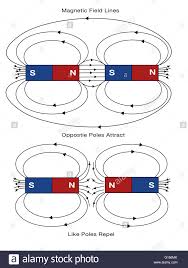
magnetic field lines
Imaginary lines that represent the strength and direction of a magnetic field, denser where the field is stronger (closer they are the stronger the force)
magnetic pole
the south and north end of a magnet
Where do magnetic field lines start and end?
start at north pole and end at the south pole
opposite poles attract and same poles repel
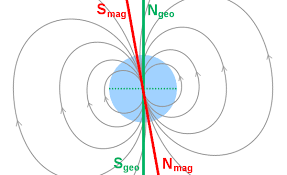
Geographical and magnetic poles of Earth.
temporary magnet
a metal that performs like a magnet in the presence of a magnetic field but loses magnetism when not in one
permanent magnets
placing materials into a very strong magnetic field
What are the few minerals that exhibit magnetic properties?
nickel, iron, cobalt, some of their alloys, and a few rare earth metals
What does an MRI (magnetic image resonance) do?
It uses magnetism and radio waves to map the inside of a person’s body
What is a black hole?
`an object so massive nothing can escape from it - not even light
How is a black hole formed?
when the center of a very massive star collapses in upon itself
Who was first person to suggest the existence of a black hole?
Karl Schwarschild
Who named them black holes?
John Wheeler
What is escape velocity of a black hole?
the object must be moving away from the black hole faster than a certain threshold - speed of light
What is the escape velocity of Earth?
2500 mph
What is the escape of a black hole?
speed of light - 671,080,888 mph
Why is the gravity of a black hole so strong?
a massive amount of matter is concentrated into a tiny space