ECON TEST 1
1/32
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
33 Terms
Economizing Problem
Individuals, firms, and governments face unlimited wants but limited resources, leading to the need to make optimal choices under scarcity.
Opportunity Cost
The potential gain lost from choosing one alternative over others.
Models/Theories/Laws & Assumptions
Economists use models to simplify complex situations, with assumptions like purposeful behavior and ceteris paribus.
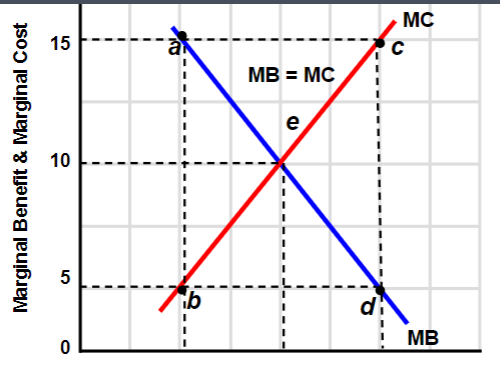
Marginal Analysis
Examining the additional benefit (MB) and cost (MC) of a product or service to determine optimal allocation.
Asymmetric Information + Moral Hazard/Adverse Selection
Adverse selection occurs when individuals lack information, while moral hazard leads to risky behavior without consequences.
Logical Fallacies
Errors in reasoning like Post Hoc, Composition, and Correlation vs. Causation.
Post Hoc
Fallacy in which an event is presumed to have been caused by a closely preceding event merely on the grounds of temporal succession.
Fallacy of Composition
Arises when an individual assumes something is true of the whole just because it is true of some part of the whole.
Broken Window Fallacy
Physical destruction of property destroys wealth
Requires stimulation of the economy to bring it back
PPF Curve
Represents possible combinations of two products, bows from the origin due to resource constraints when switching products.
Centrally Planned Economies vs
Contrasting systems like Command and Control vs. Invisible Hand by Adam Smith.
Central Planning
Designs of how things are meant to work
The “Invisible Hand” vs. The “Iron Fist”
The people, processes, and drive that leads people to create things through cooperation
Self-Interest, Dollar Votes, Consumer Sovereignty
Concepts where consumer choices determine production and markets operate based on self-interest.
Supply and Demand
Understanding determinants, changes in quantity, consumer vs. producer surplus, price ceilings/floors, and deadweight loss in markets.
Price Ceilings
People/companies cannot charge above a certain price
If below the point of equilibrium, then there is a shortage; if above then nothing happens
Price Floor
People/companies cannot charge below a certain price
If above the point of equilibrium, then there is a surplus; if below nothing happens
Market Failures
Occur when resources are misallocated due to externalities, leading to demand-side and supply-side failures.
Rivalry
Situation where 2 individuals/firms can't consume the same good.
Excludability
Ability to prevent non-paying entities like firms/companies from using a good.
Free Rider Problem
Occurs when individuals benefit from a good without paying for it.
Public Goods
Goods that are non-excludable and non-rivalrous.
Private Goods
Goods that are excludable and rivalrous.
Time Preference
Refers to the choice between instant gratification (high time preference) and delayed gratification (low time preference).
Laffer Curve
Graphical representation used to determine optimal rates, such as taxes, at the peak.
Demand Determinants
Change in consumer tastes and preferences
Change in number of buyers
Change of income
Change in consumers’ expectations
Normal Goods
When income goes up, demand goes up
Inferior Goods
If income goes up, you won’t buy more
Supply Detereminants
Change in resource prices
Change in technology
Change in the number of sellers
Change in taxes and subsidies
Change in producer expectations
Praxeology
Humans act rationally and logically; the study of human action, based on notion that humans engage in purposeful behavior (humans do things for a reason) with two main assumptions
Praxeology Assumptions
Individuals act rationally and self-interestedly in order to maximize their “utility”
Ceteris paribus - all else is held constant; all are equal
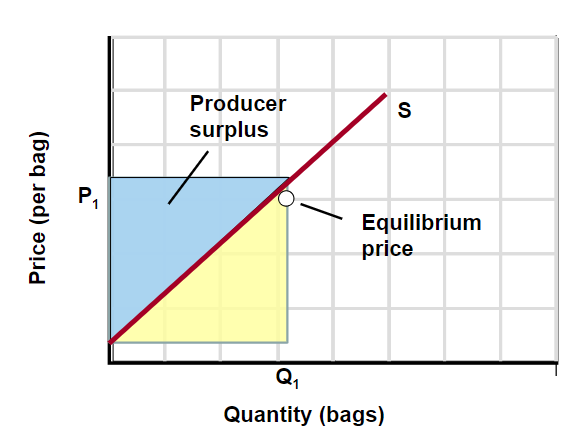
Producer Surplus
The difference between the actual price a producer receives and the minimum price they would accept
The extra benefit of receiving a higher price
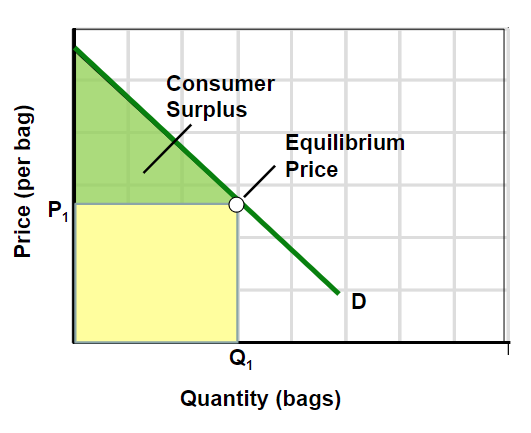
Consumer Surplus
The difference between what a consumer is willing to pay for a good and what the consumer actually pays
Extra benefit from paying less than the maximum price