Chem 2 lab FINAL
1/68
Earn XP
Description and Tags
scaryyy
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
69 Terms
When sodium hydroxide reacts with a weak acid, what will the spectator ion be?
Na+
The weaker an acid is, the _______ its Ka and the _____ its pKa
smaller, larger
What ion is used in the Qualitative analysis lab part 1 to form insoluble chloride compounds?
Ag+ and Hg22+
Which ions are separated out as Group II metal hydroxides in the Qualitative analysis lab part 1 ?
Fe3+ and Mn2+
What are the hazards that needed to be kept under the hood for the part 1 qualitative analysis lab?
HCl, DMG, NH3
What ion or ions can be detected by using potassium thiocyanate?
Fe3+
The substance added to unknown tube to separate silver and mercury in the qualitative analysis lab part 2 was
HCl
The possibile ions that you can have Group B are
Mn2+ and Fe3+
A dark precipitate seen after adding 1M NaOH to solution B indicates which ions? (Qualitative analysis lab part 2)
Mn2+ and Fe3+
money fees are dark and scary
Which of the following lead you to identify Hg22+ in your unknown
HCl and NH3
Which ions will be in solution when identified?
Fe3+ and Cu2+
Felines see you
When electroplating Cu onto a coin, the mass of copper depends on what?
amount of current, number of electrons in the redox reaction, amount of time
In a concentration cell what is true?
Eo cell does not equal E cell
What is true of Q under standard conditions?
Q=1
in a _____ cell, current is produced from a spontaneous chemical reaction
voltaic
Although the Colorimeter measures % transmittance, it is converted into ______ for the graph.
absorbance
After graphing your line, you will be given a correlation value. This tells you how well the data fit the_____ . A good value is greater than ____.
line
0.9
Beer's Law states the ______ relationship between concentration and absorbance.
direct
When placing the cuvette into the slot, be sure to have the ______ sides lined up with the arrow.
smooth
What is the meaning of ‘Ka’ in terms of physical significance? What is the equation that defines it?
Ka is the measurement of the strength of an acid in solution.
the formula is
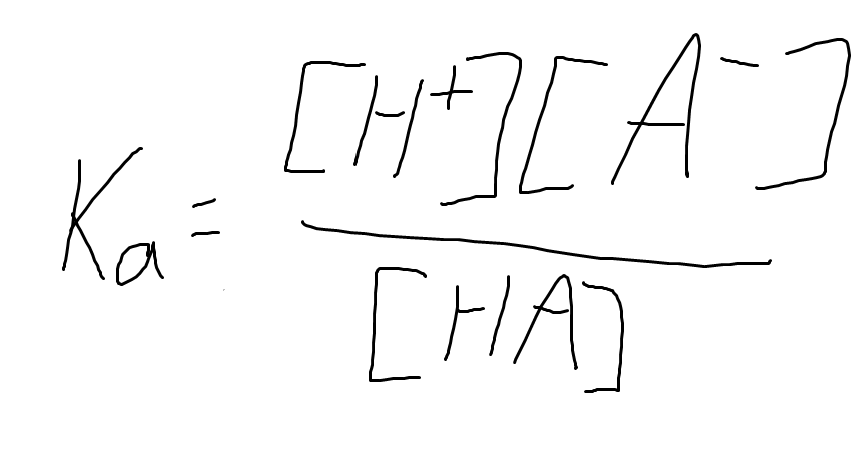
What is the relationship between the concentration of the acid, hydronium ion, and anion in that equation?
For a storing acid, the hydronium ion concentration is equal to the inital acid concentration
for a weak acid the hydronium ion concentration is less than the initial acid concentration
What is the pKA? how is it determined from the Ka?
The pka is a measure of a substance’s inherent tendancy to donate a proton. it is difference from the ka because it is the negative log of the acid disassociation constant (Ka)
How is the pH related to the pKa at the halfway point of a titration?
at the halfway point, the pKa of the acid is equal to the pH of the solution.
What indicator was used in the titration lab?
phenolphthalein
What was the color of the solution before the endpoint in the titration lab?
clear (CHECK)
What was the color after the endpoint in the titration lab?
light pink
fucking flow chart shit
What did a grey precipitate indicate?
Hg22+ (HgNH2Cl)
What did a White precipitate indicate the presence of?
Ag+ (AgCl)
What did a blue solution indicate the presence of?
Cu2+ (Cu(NH3)42+
What did a pink precipitate indicate the presence of? What did you have to add to get to it?
Ni2+ (Ni(DMG)2)
DMG
What did a Red solution indicate the presence of? What was added to get there?
Fe3+ (Fe(CNS)63-)
KSCN
What did a purple solution indicate the presence of? What was added to get here?
Mn2+ (MnO4+)
6M HNO2 and NaBiO3 were added to get to this
Which were the only identified that were precipitates?
Gray (Hg22+) and White Ag+ (chekc)
what is the proper procedure for using a centrifuge?
balance the centrifuge with a tube of water on the exact opposite side of where you put the tube containing the solution, run it for about 30sec- 1 min
What type of litmus paper would you use to test for acidity of a solution?
blue litmus paper
What type of litmus paper would you use to test to see if a solution was basic?
red litmus paper
if a metal is being ______ it is attached to the anode
oxidized
if a metal is being ______ it is attached to the cathode
reduced
What is the equation for beer’s law?
Beer's Law: A = (εl)c
What type of graph could be constructed using beer’s law? What would it look like? What would be plotted at each axis? Would data be linear?
you could construct a linear regression graph with beer’s law. It would look like a line going up
A = εlc to y = mx + b.
For beer’s law, which variables from the equation would be the slope of the line? What would be the intercept and what should it be theoretically
A=y
Eb=m
c=x
y intercept= 0
What are the reasons of making a standard curve for the beers law lab? What are the limitations?
to ensure precision and accuracy of your measurements
limitations: only valid for low concentrations and ideal conditions (?)
What are the formulas for how absorbance relates to % transmittance and how it relates to concentration?
A= 2-log(%T)
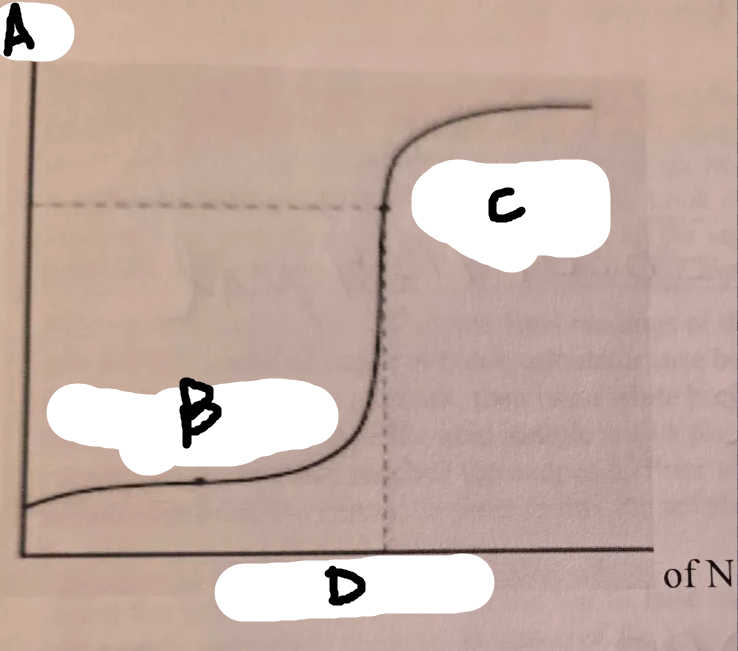
locate the pH on the graph
A
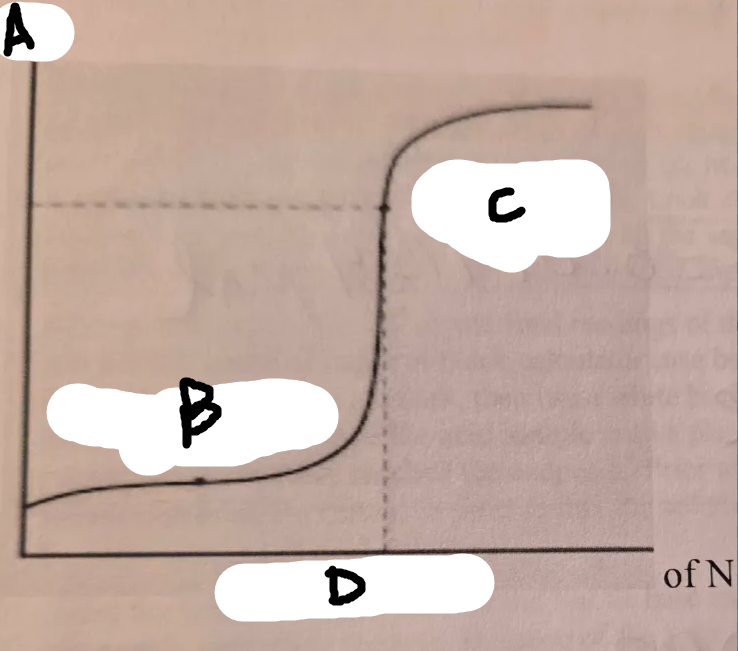
locate the volume added on this graph
D

locate the half equiv point on this graph
B

locate the equiv point on this graph
C
What is NH3
Ammonia
What is HgNH3Cl
Ammoniated Mercury
What is KNO3
Potassium nitrate
What is AgCl?
silver chloride
What is Cu(NH3)42+
tetraamminecopper(II) ion
What is Ni(DMG)2
dimethylglyocimate
What is NaOH
sodium hydroxide
What is KSCN
potassium thiocyanate
What is Fe(CSN)63+
hexacyanoferrate (III)
What is MnO4+
Permanganate
Which reagent leads to the precipitation of group I cations as chlorides?
3M HCl
Which reagent dissolves some precipitates, forms compexes such as Cu²+
6M NH3
Which reagent precipitates Ag+ as AgCl?
6M HNO3
Which reagent precipitates group II sulfides?
H2S (?)
Which reagent distinguishes Fe3+ and Mn2+
NaOH
Which reagent Identifies Fe3+
KSCN (red)
What reagent oxidzes Mn2+ to MnO4-
HNO3 and NaBiO3
(purple)
What reagent identifies Ni2+
DMG (pink)
What is NaBiO3
Sodium bismuthate
What reagenet led to the precipitation of Ag+
6M HNO3