37/38: Infectious diseases of pregnancy
1/89
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
90 Terms
ascending infection from vagina/cervix
maternal blood
penetrating trauma
mixing of blood basically
sources of vertical transmission
•Toxoplasmosis
•Other (varicella, parvovirus B19, listeria)
•Rubella
•Cytomegalovirus
•HIV
•Herpes, Hepatitis B & C
•Syphilis
list the TORCHHeS infections
screened for rubella and syphilis at first prenatal visit
-some countries also screen for toxoplasmosis
pregnant women should be screened during 1st trimester for these TORCH infections at their first prenatal visit
{hint: two of them}
HIV
syphilis
hep B and C
chlamydia
to recall:
The “Blood → Sex → Fluids → Cervix” pattern
Think of how each spreads:
Blood → HIV
Sex → Syphilis
Fluids → Hep B & C (blood/body fluids)
Cervix → Chlamydia
ALL women are screened for these during first trimester
HHSV and gonorrhea
diseases screened during first prenatal visit
only if high risk**
group B strep
screened in ALL women during 36-37 weeks gestation
(screened at term)
HIV, syphilis, chlamydia, gonorrhea
screened during third trimester if high risk
RUBELLA !!
&
-toxo and CMV
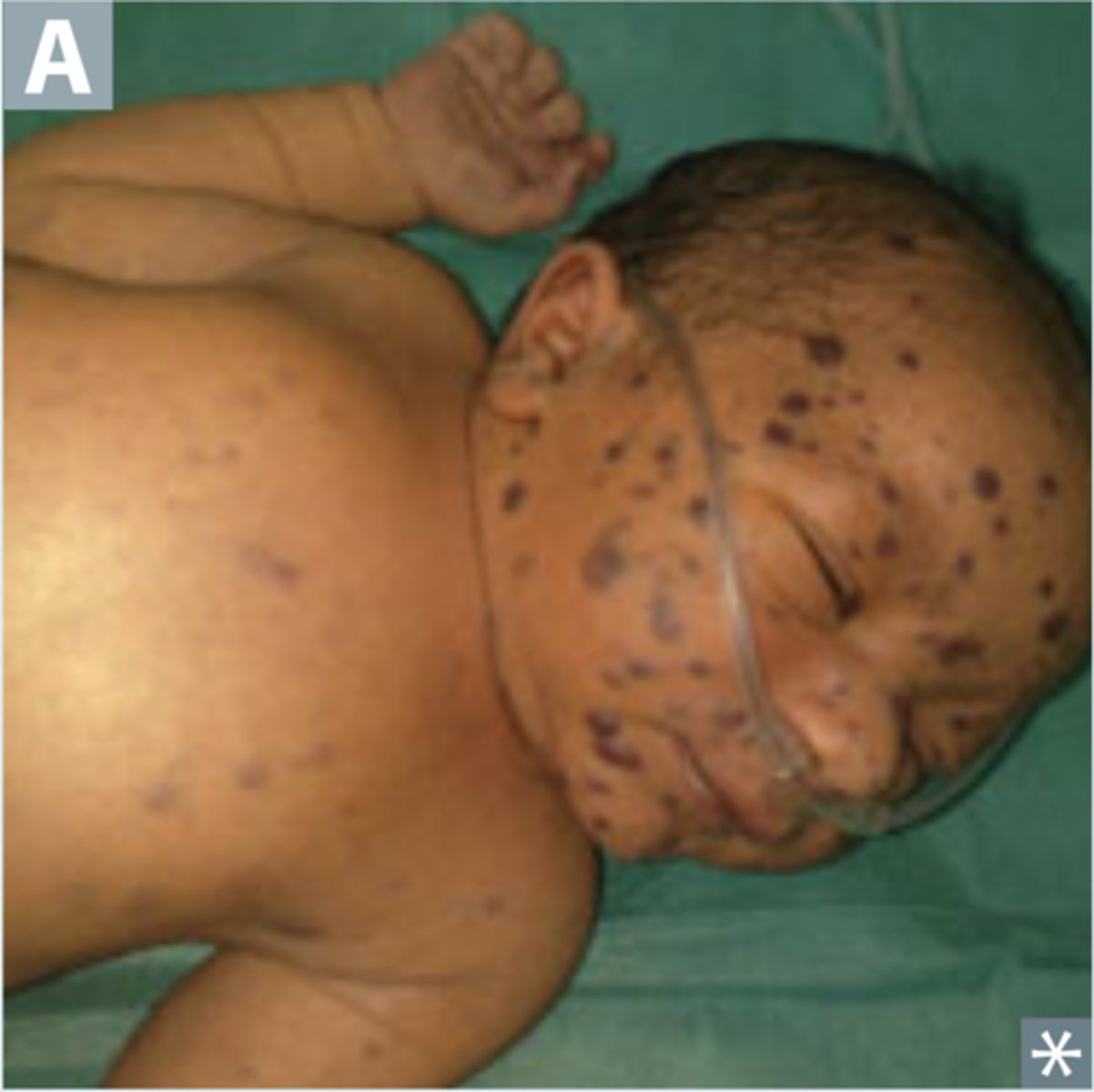
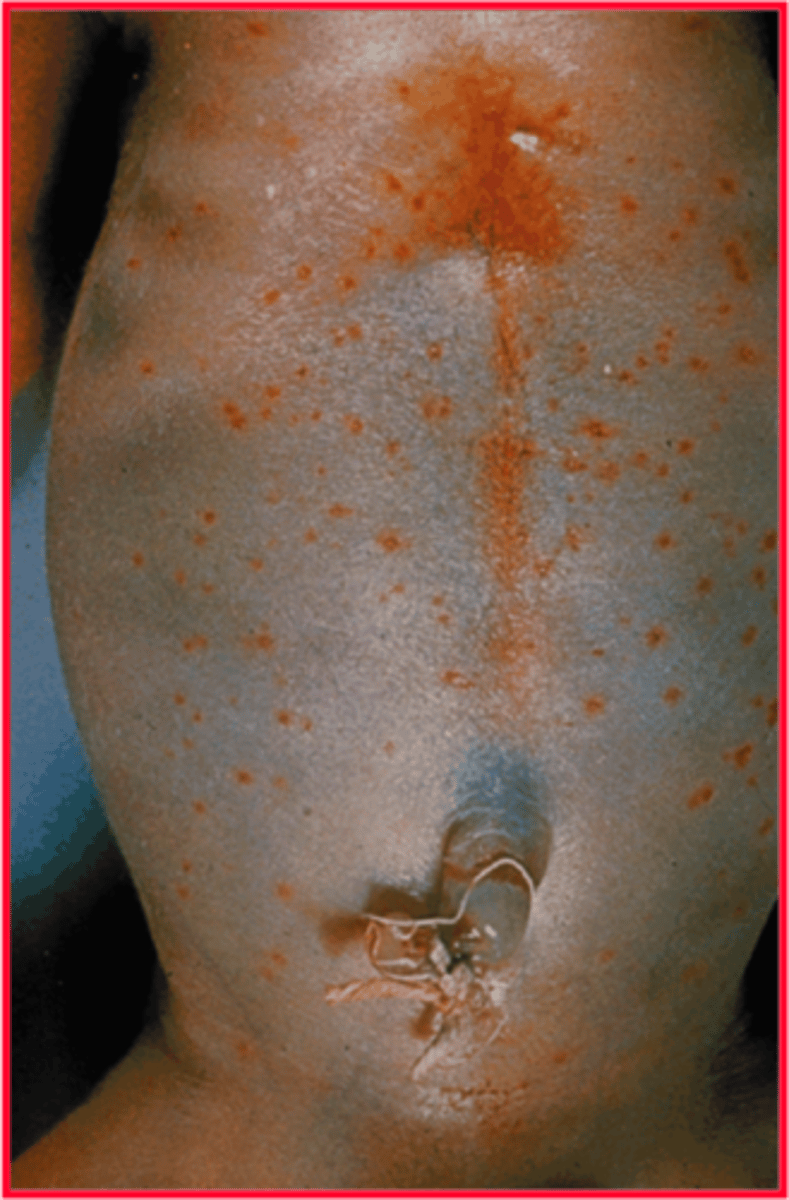
TORCH infections associated with blueberry muffin rash
blueberry muffin rash
extramedullary hematopoiesis in the dermis
T. gondii
(causes toxo … in TORCHS)
-intracellular parasite found in undercooked meat, unwashed fruit, and litter box
-cats the only definitive hosts
oocyts
--> tachyzoites in (acute form)
---> bradyzoites (chronic)
-oocytes infectious found in feces, contaminated foods
TO RECALL:
tachy as a baby, brady as an adult (like HR in humans)
acute and chronic forms of T. gondii
-typically asymptomatic and self limited; symptoms are typically mono like
-prior infection results in immunity
presentation of maternal toxoplasmosis
•Tachyzoite replication destroys infected cells
•Necrosis can become tissue calcification---> intracranial calcifications
pathogenesis of congenital toxoplasmosis
chorioretinitis, hydrocephalus, intracranial calcifications
-chorioretinitis is later sequelae
“Cats Hate Infants”
Because toxoplasma spreads from cats.
Cats → Chorioretinitis
Hate → Hydrocephalus
Infants → Intracranial calcifications
classic diagnostic triad of congenital toxoplasmosis
congenital toxoplasmosis
-more severe manifestations usually indicate infection earlier in gestation
-no symptoms at birth= still at risk
-PREVENTION
-treatment of acutely infected women reduce risk of fetal transmission, reduce severity
best option of toxoplasmosis treatment
-RNA virus, familly matonaviridae, genus rubivirus
-aka german measles
virus family of rubella
children: generalized maculopapular rash on face, spreads to trunk
adults: prodrome fever, generaliized rashes, polyarthralgias
presentation of rubella
{chilrden vs adult}
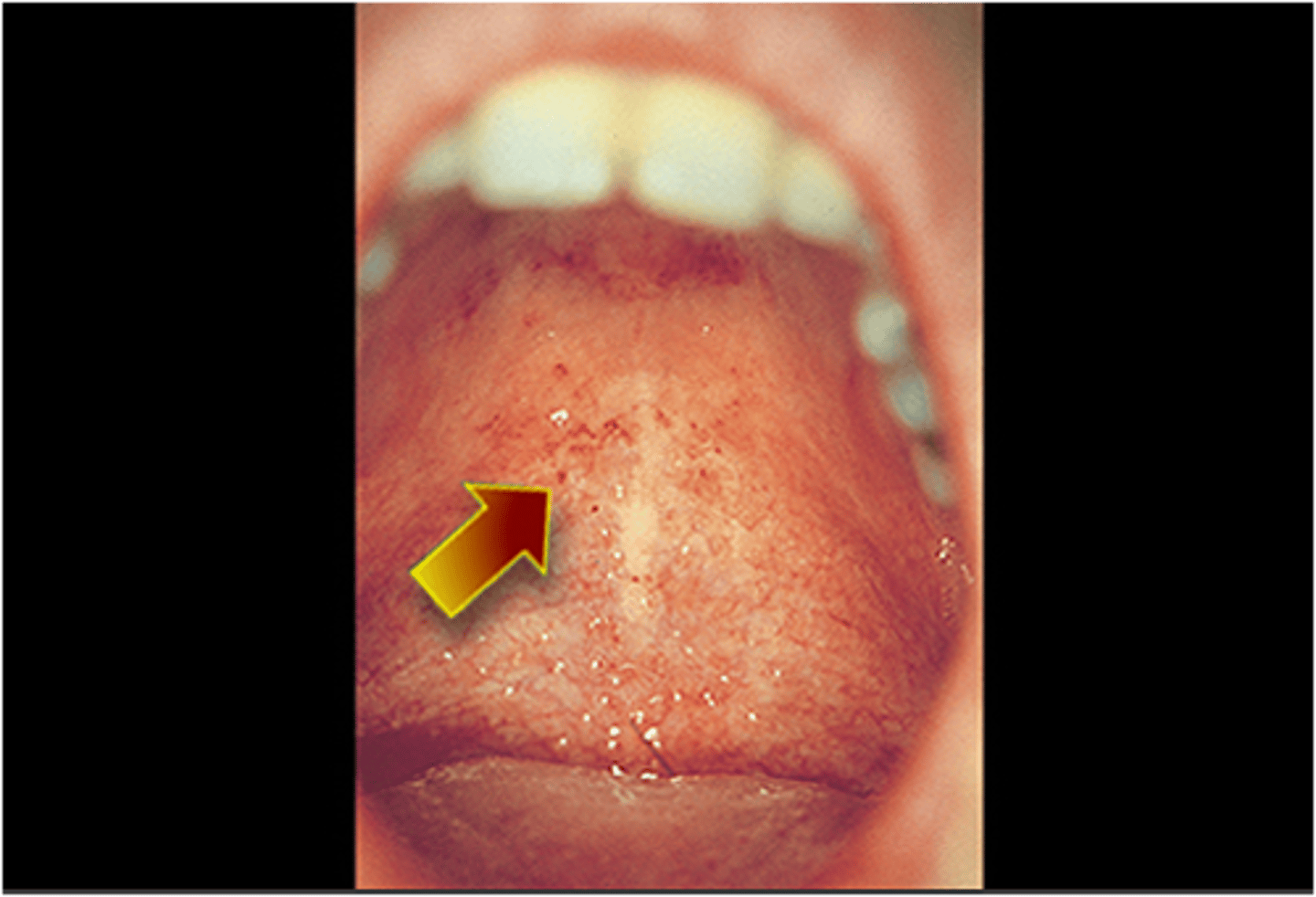
rubella
-associated with forchheimer spots (rose spots) on the soft palate
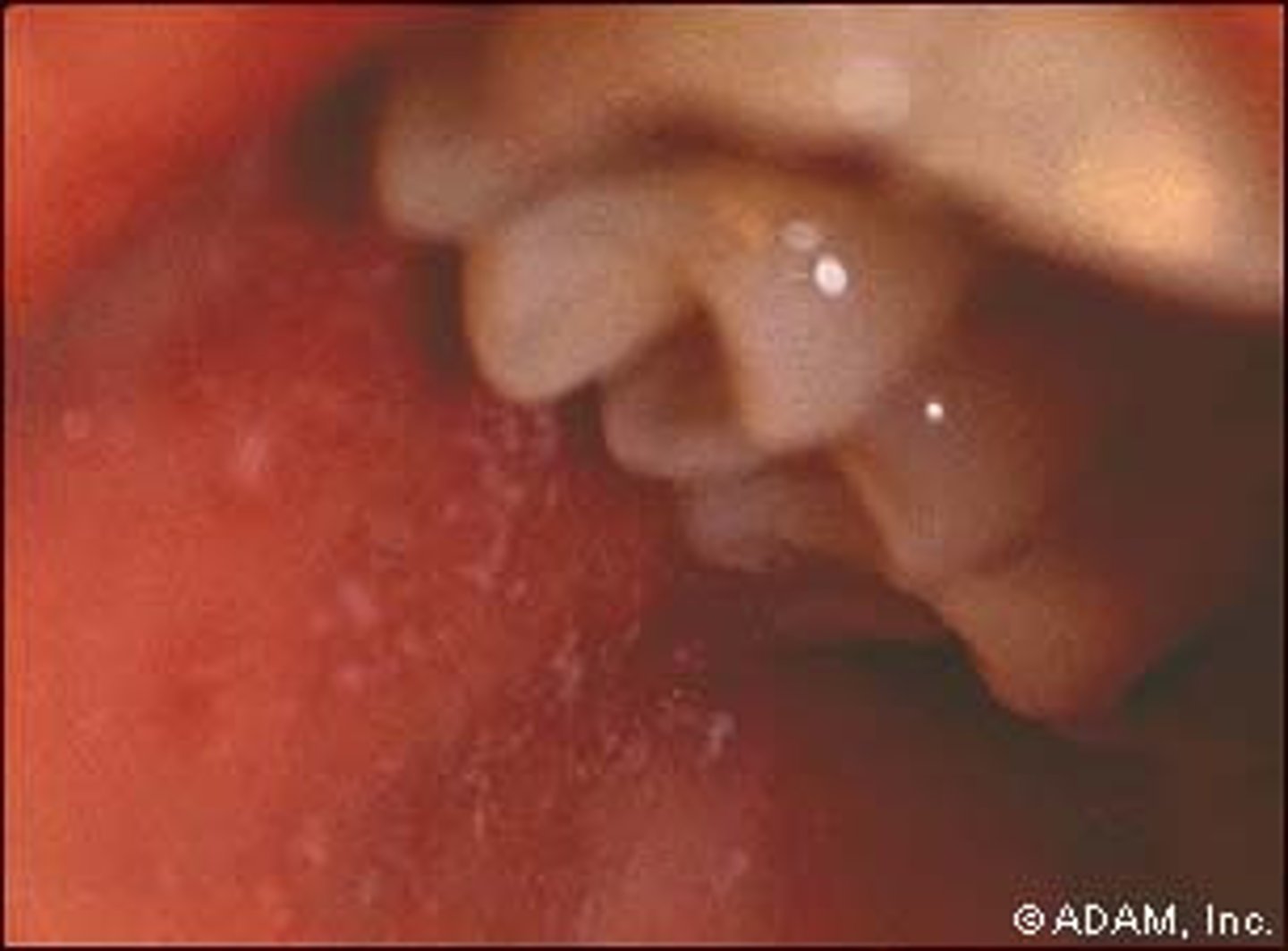
rubeola
associated with koplik spots, white spots on buccal mucosa
-pathognomonic for measles
highest risk in first 12 weeks
when is the highest risk of congenital rubella transmission?
sensorineural deafness, cataracts, congenital heat disease
(eye <3 ruby earrings)
clinical triad of congenital rubella syndrome
-prevent with vaccine prior to pregnancy and avoidance
-supportive care only,
close monitoring of infant over first year; no effective antiviral for baby
-isolate infected mom, shed virus in urine, stools secretions for one year
treatment of congenital rubella
rubella
virus that can be isolated from blood, urine, CSF, and throat swab specimens
human herpesvirus-5
-family herpesviridae; enveloped, dsDNA
virus family of CMV
cytomegalovirus (CMV)
leading cause of nonhereditary sensorineural hearing loss;
most common congenital viral infection
cytomegalovirus
•Lytic replication inside endothelial cells results in owl’s eye inclusion bodies
•Viral protein UL16 prevents expression of NK cell activating receptor ligands
cytomegalovirus
symptoms/presentation is inversely proportional to gestational age at time of transmission
-usually asymptomatic or subclinical
-symptomatic = mononucleosis (not EBV)
-primary infections have higher risk of transmission to baby
presentation of CMV in mom
congenital CMV
Chorioretinitis, Microcephaly, periVentricular calcifications
-petichiae, microcephaly
-intracranial calcifications, chorioretinitis
-hearing loss
-blueberry muffin rash
-hepatomegaly
-IV ganciclovir for infants with symptomatic congenital CMV
-maternal antiviral therapy not routinely recommended
treatment for congenital CMV
ssRNA, enveloped human retrovirus
virus type of HIV
-very LOW with combination of low viral load and ART therapy
-may occur antepartum, intrapartum, or posttpartum through breastfeeding
rate of vertical transmissio nof HIV
5 months
In untreated infants, the mean incubation period for developing an AIDS-defining condition after vertical transmission is
•Treat with ART within 12 hours of birth
•Bathe infant prior to administering vaccines****
tx of HIV in neonates
38 weeks
•Planned cesarean delivery at ____ weeks of gestation is recommended for women who have a HIV viral load greater than 1,000 copies/mL
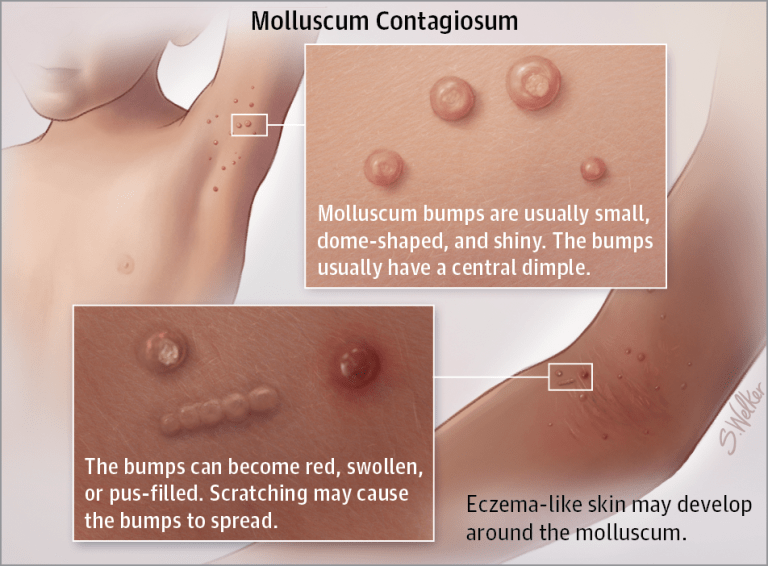
•Failure to thrive, neurodevelopmental delay, lymphadenopathy, Opportunistic infections (thrush, diaper rash), interstitial pneumonitis, frequent diarrhea, hepatosplenomegaly
-molluscum contagiosum
(benign viral skin infection)
presentation of congenital HIV
HIV
congenital infection defined by recurrent bacterial infections, lymphoid hyperplasia, chronic parotid swelling, progressive neurologic deterioration, pneumocystis jirovecii
dsDNA virus
•HSV-1 primarily cold sores; HSV-2 primarily genital herpes
•Either strain can cause genital herpes
viral family of herpes simplex
gingivostomatitis
inflammation of the mouth and gums associated with HSV 1
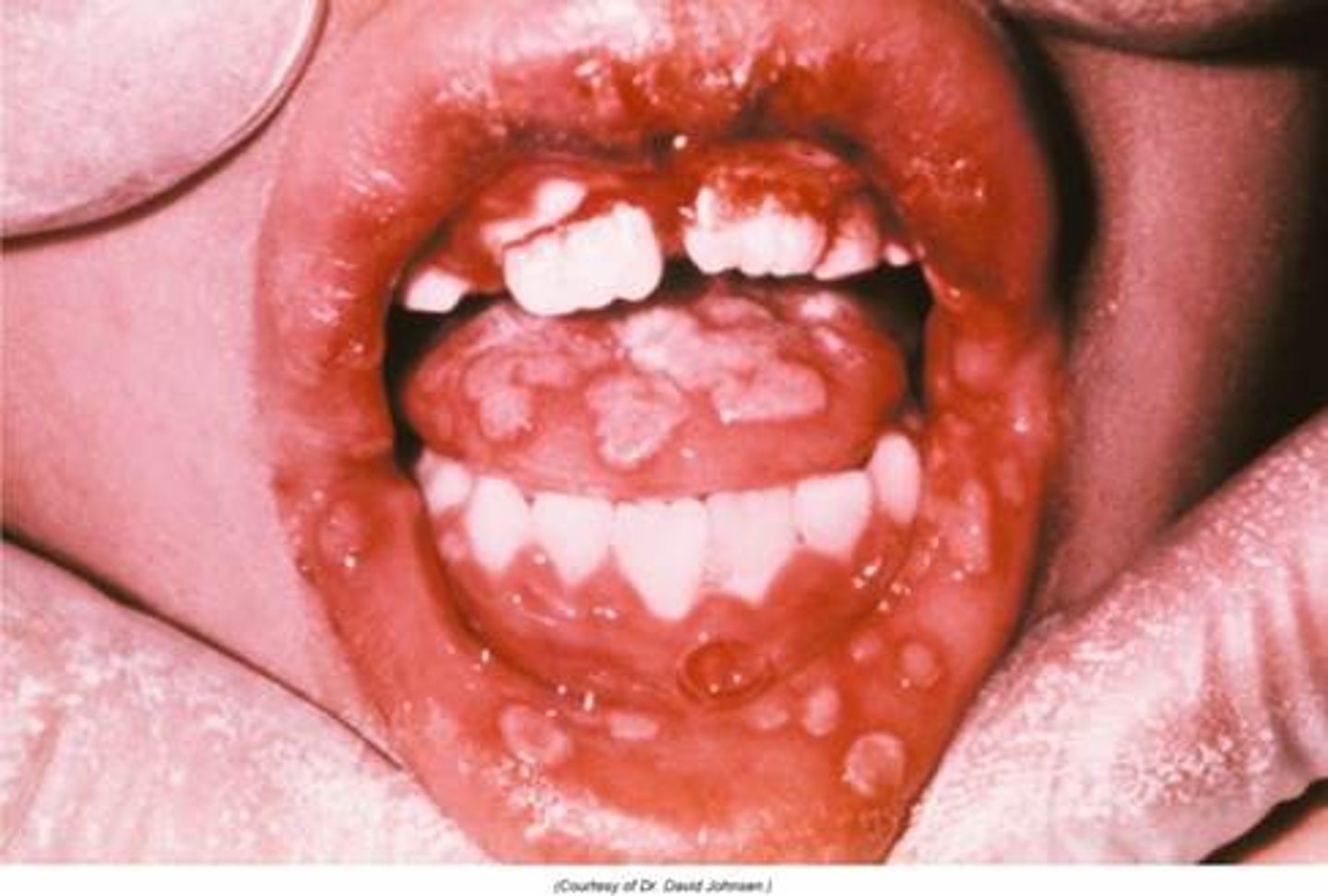
primary HSV
infection type of HSV that causes the greatest risk to fetus
•C-section recommended if herpes lesions (active)
are identified on the cervix, in the vagina, or on the vulva at the time of labor or spontaneous rupture of membranes
•Acyclovir is safe and can be used during pregnancy
if symptoms are severe and to reduce risk of viral shedding or C-section delivery
prevention of congenital HSV
-rash of skin, eyes, and mouth
-localized CNS disease
-disseminated disease involvign multiple organs
3 patterns of presentation of neonatal HSV
IV acyclovir until PCR of CSF is negative
---> then long term antiviral therapy
treatment of neonatal HSV
motile spirochete treponema pallidum
cause of syphilis
•Lesion at the site of inoculation (chancre)
•Painless; indurated then ulcerates
describe primary syphilis
•Systemic illness; typically resolves spontaneously
•Rash on palms and soles
describe secondary syphilis
require screeing at 1st visit, 3rd trimester, and delivery
recommendations for congenital syphilis screening in louisiana
•Spontaneous abortion/stillbirth
•Hydrops fetalis
•Prematurity
•Neonatal death
early infection gestation of syphyilis results in
Early congenital syphilis
-presents in first two years of life with snuffles, rash, skeletal abnormalities, IUGR
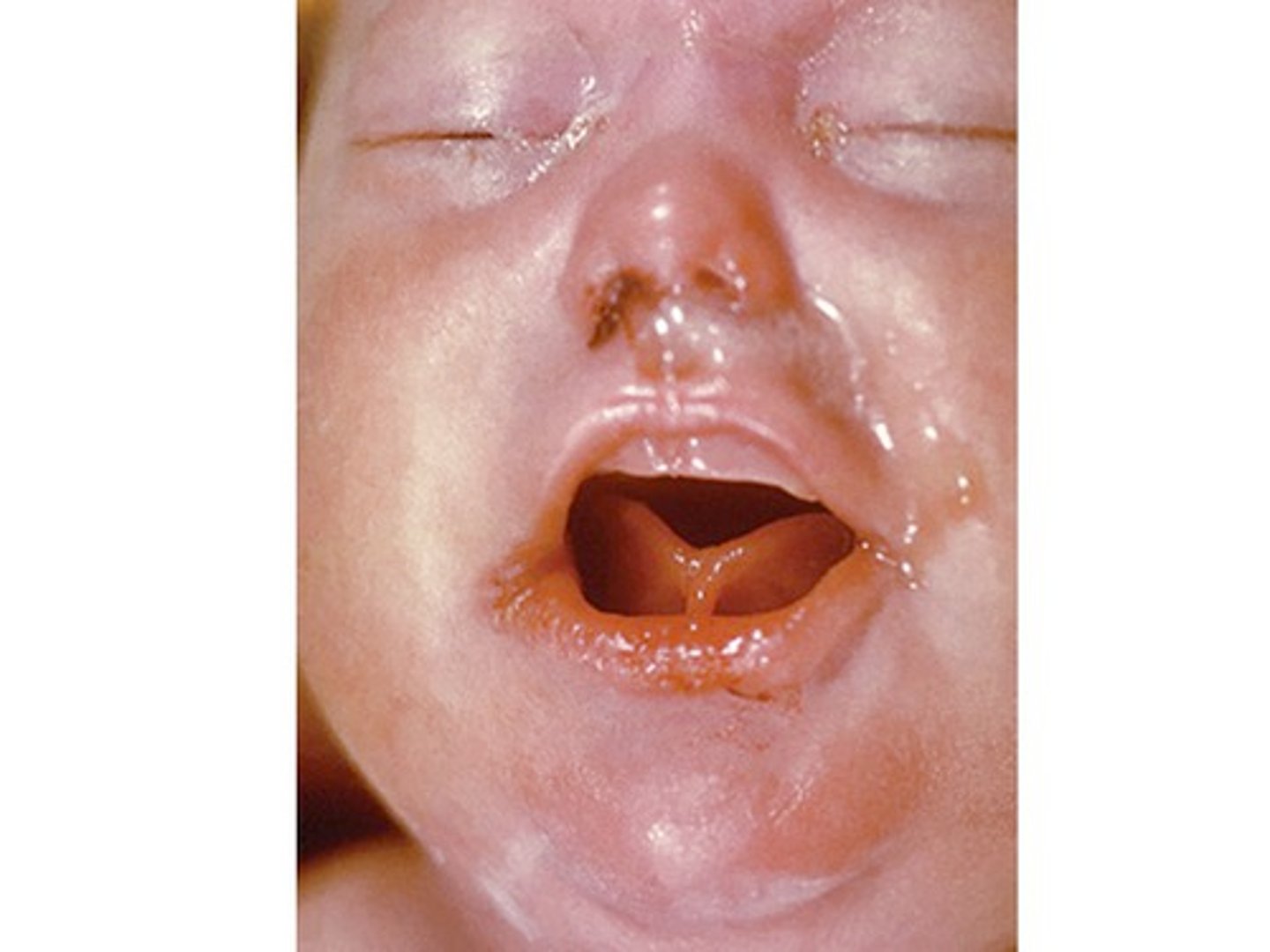
late congenital syphilis
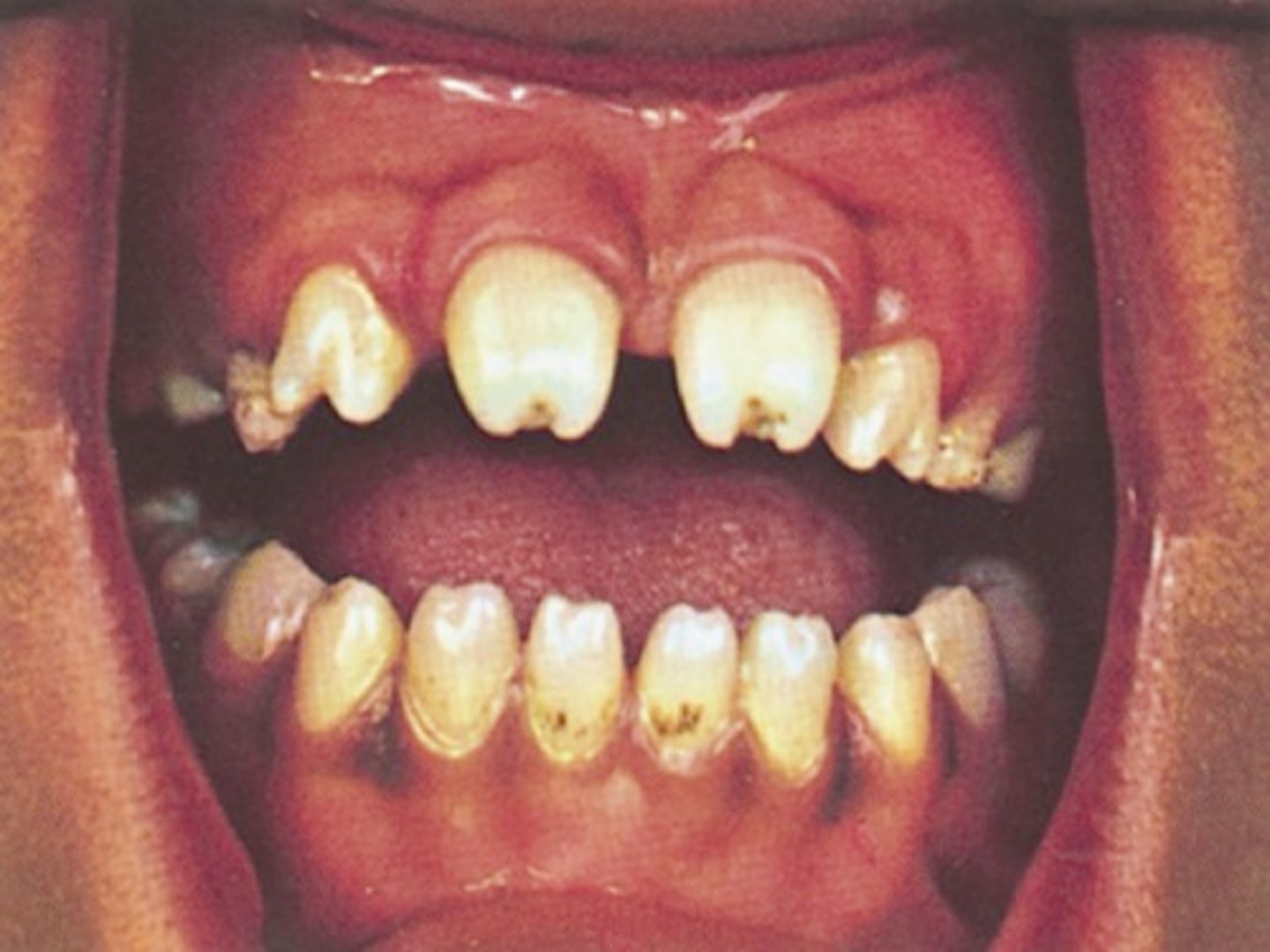
-after 2 years of age, presents with mulberry molars, saber shins, saddle nose , gummatous ulcers
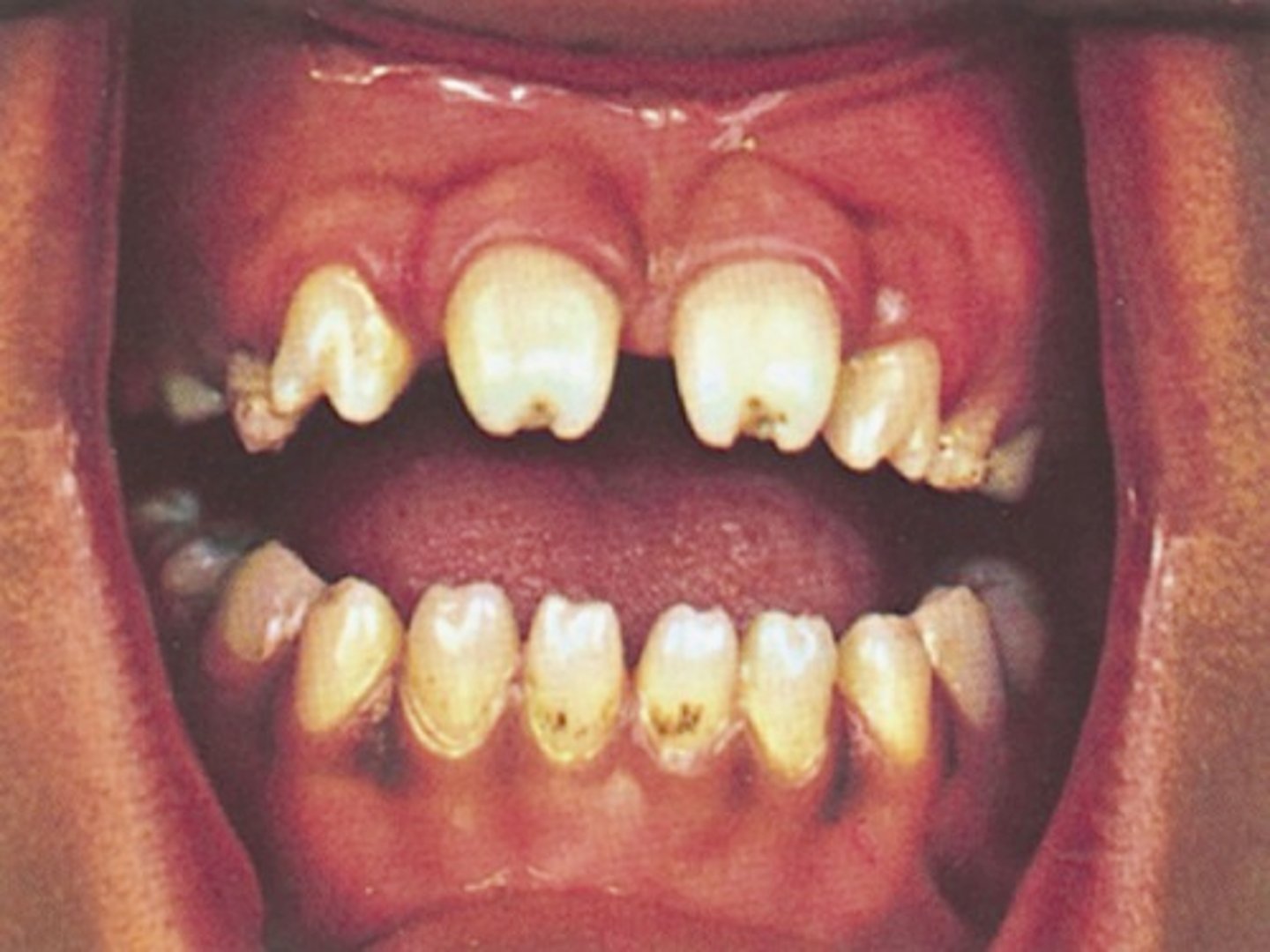
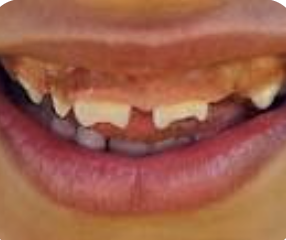
mulberry molars
Molars with multiple cusps that are caused by congenital syphilis.
interstitial keratitis, hutchinson incisors, 8th cranial nerve deafness
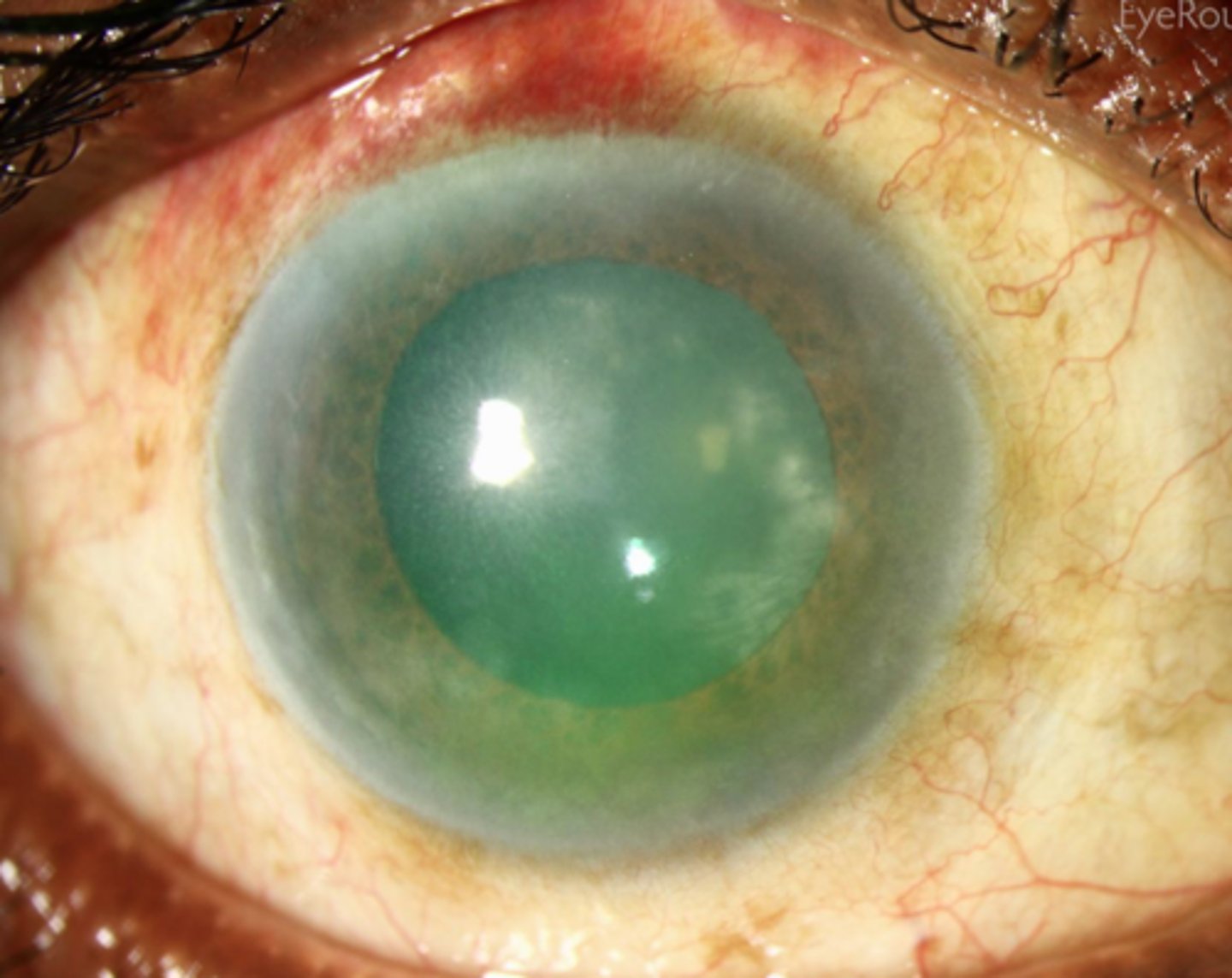
Interstitial keratitis:
is an inflammation of the cornea's middle layer (stroma) that causes eye pain, redness, blurred vision, and sensitivity to light
hutchinson incisors:
permanent teeth are typically smaller, spaced wider, and have a crescent-shaped notch on their biting surface.
8th cranial nerve damage
symptoms like hearing loss, tinnitus (ringing in the ears), and vertig
(vestibulocochlear nerve), which is responsible for hearing and balance.
what is the hutchinson triad of congenital syphilis
intersitial keratitis
development of a ground-glass appearance of the cornea and scleral vascularization, which have their onset around puberty; associated with hutchinson's triad
-screening with RPR or VDRL
-prmpt tx with pencillin based regimen
prevention of congenital syphilis
linear dsDNA virus; family herpesveridae
virus type of varicella zoster
congenital varicella
congenital virus with highest risk during second trimester
•Cutaneous scars (dermatomal distribution)
•Neurologic, ocular, GI, and limb abnormalities
•Low birth weight
presentation of congenital varicella synndrome
ranges from mild chicken pox to disseminated infection
presentation of neonatal varicella
•Administer varicella-zoster immune globulin to infants born
from women with active varicella infection at delivery
treatment of congenital varicella
•Test mom for immunity if no history of infection or immunization
•If nonimmune- the first dose of the varicella vaccine should be administered in the postpartum period.
The vaccine is a live attenuated virus and should be avoided in pregnancy and within 1 month of conception
prevention measurers of congenital varicella
parvovirus B19
causes 5th disease
(erythema infectiosum )
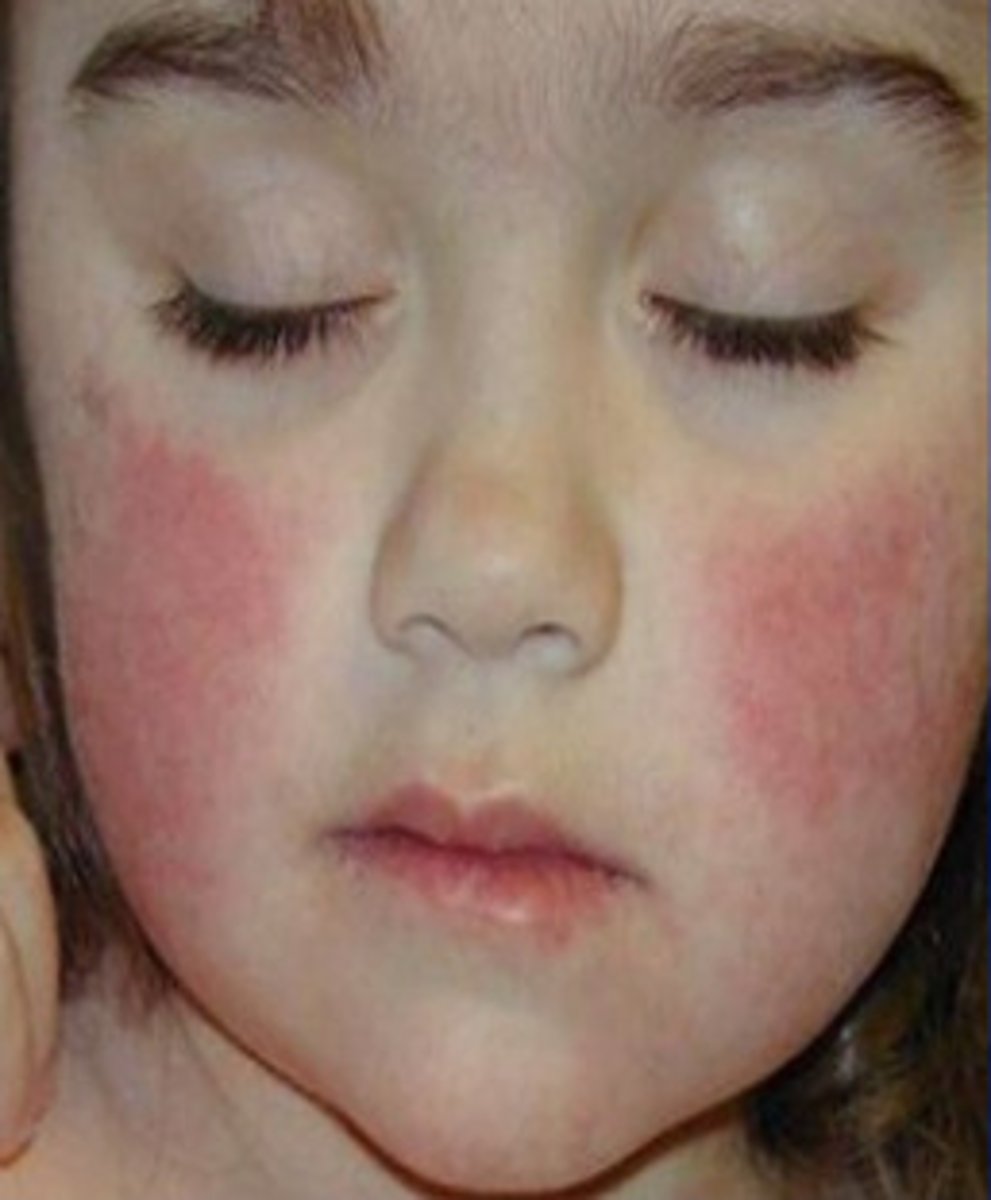
•May be asymptomatic
•Non-specific flu-like symptoms
•25% have rash +/- arthralgias
maternal presentation of parvo B19
parvovirus b19
-virus destroys RBC progenitors
-diagnosis via PCR of viral DNA in amniotic fluid
-most don't have adverse outcome;
risks highest with infection during 1st trimester
-fetal anemia and hydrops fetalis; rarely, fetal loss
fetal presentation of parvovirus B19
Hep C
•primary cause of chronic viral hepatitis in children in industrialized nations
-one of the most common and potentially serious infections in pregnant women
•Typically, asymptomatic
•Usually mild childhood liver disease
symptoms of congenital hepatitis
•Usually asymptomatic at birth
•Chronic antigenemia and elevated liver enzymes
•Most patients develop chronic infection
presentation of congenital hep B
the vaccination and HBIg within 12 hours of delivery
Breastfeeding is NOT contraindicated in women who are chronic carriers of Hep B:
IF their infants have received BOTH
HPV 6 and 11
•The most common sexually transmitted infection in US
•In adults, cause genital warts (condyloma acuminatum)
HPV 6 and 11
tho vertical transmission is rare, can lead to juvenile onset of recurrent respiratory papillomatosis
-c section does not prevent trannsmission
juvenile onset recurrent respiratory papillomatosis
-manifestation of HPV 6 and 11 in neonates that results in recurrent benign laryngeal tumors in children
•Progressive dysphonia, stridor, chronic cough, recurrent URTI, hemoptysis
•PE-> reveals multiple verrucous, polypoid growths overlying the true vocal folds, false vocal folds, subglottic region, and trachea.
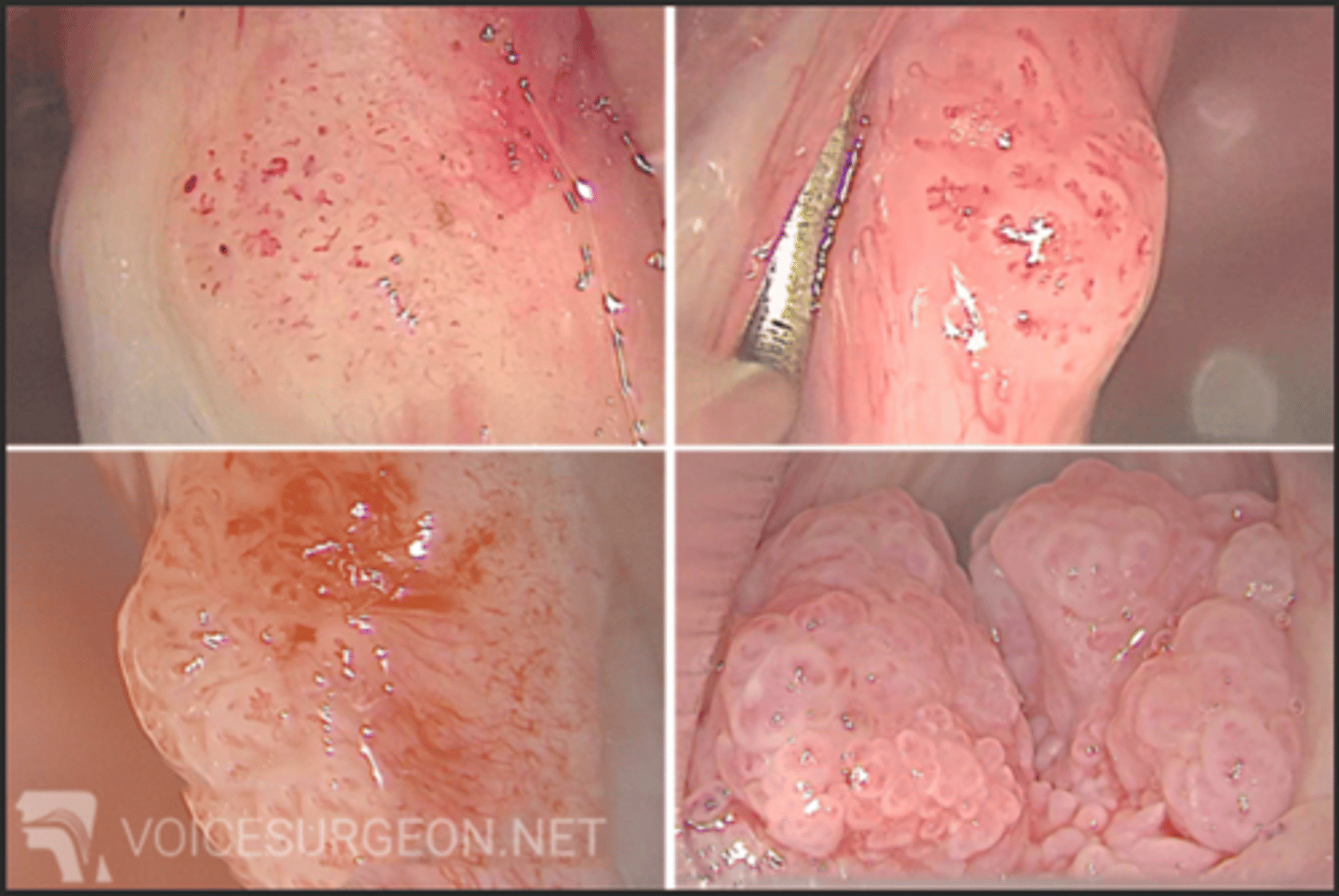
-require multiiple surgeries before puberty to remove papillomas
-antiviral therapy
-tracheostomy if airway obstruction
tx of congenital HPV 6 and 11
listeriosis
•Why pregnant women are advised to avoid: Unpasteurized dairy products, sprouts, uncooked meats, meat spreads, smoked seafood
-most commonly in 3rd trimester with non-specific flu like illness
maternal presentation of listeriosis
fetal death, preterm birth, infected neonate
-diffuse pustular rash**
-granulomatous infantiseptica**
fetal presentation of listeriosis
granulomatous infantiseptica
result of listeria in neonate
•Disseminated abscesses or granulomas in multiple organs
•Most are stillborn or die soon after birth
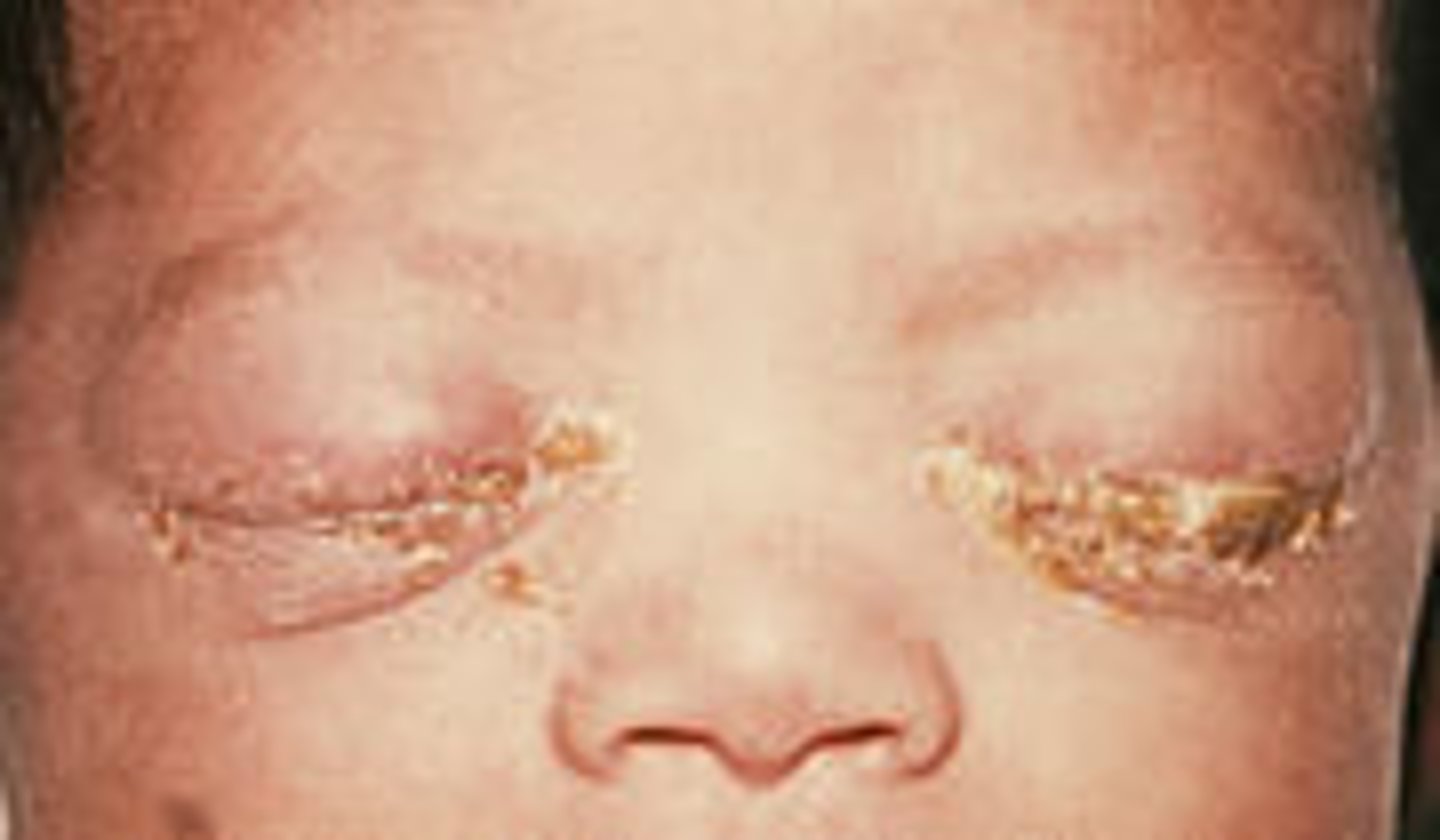
N. gonorrhoeae
-presents as opthalmia neonatorum 2-5 days after birth
Ophthalmia neonatorum, or neonatal conjunctivitis, is an eye infection in newborns that causes red, swollen eyelids and discharge
opthalmia neonatorum
purulent conjunctivitis with profuse exudate and eyelid swelling
-associated with N. gonorrheae
•Neonate treatment: ceftriaxone
•Prevention: maternal screening and treatment
•Neonatal prophylaxis with ophthalmic erythromycin
treatment/prevention of congenital gonorrheae
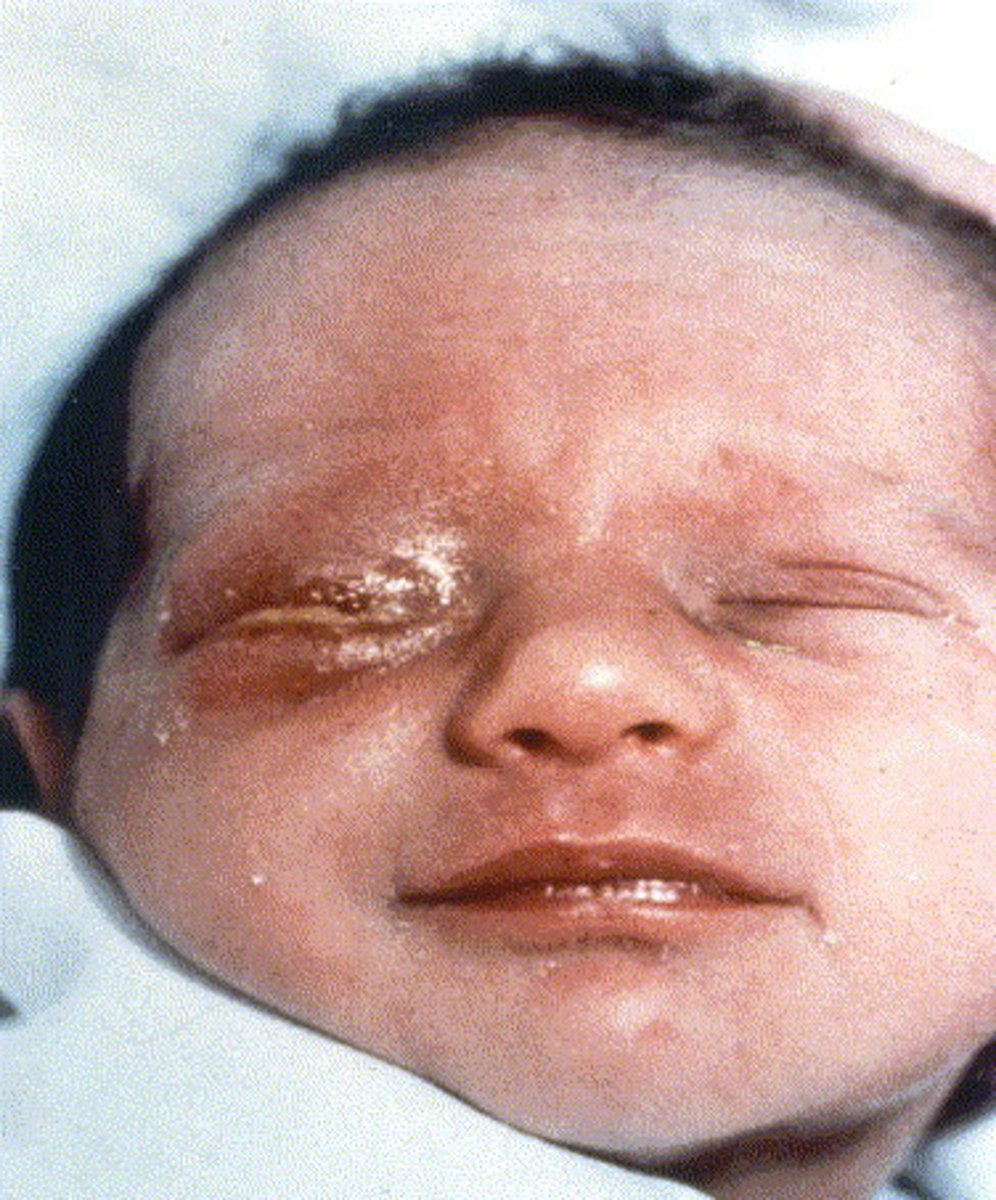
chlamydia trachomatis
-presents as inclusion conjunctivitis 5-14 days after delivery
-higher congenital transmission rate
inclusion conjunctivitis
Caused by Chlamydia trachomatis
•Neonate treatment: oral erythromycin
•Prevention: maternal screening and treatment
tx of congenital chlamydia
•Facultative, anaerobic, gram-positive cocci that form chains or diplococci
bacteria type of group B strep
•Causes asymptomatic bacteriuria, UTI, endometritis, chorioamnionitis in pregnant women
manifestation of group B strep in moms
-early onset before 7 days
-presents as sepsis, pneumonia, or meningitis
presentation of group B strep in neonate
•Neonate: ampicillin and an aminoglycoside
•Isolate organism from sterile body site to confirm diagnosis
tx of group B strep in neonate
group B strep (S. agalactiae)
•Gram + cocci in pairs or chains; encapsulated, beta hemolytic, catalase negative•Gram + cocci in pairs or chains; encapsulated, beta hemolytic, catalase negative
N. gonorrhoeae
•Gram - diplococci; facultative intracellular pathogen in neutrophils
•Fastidious; grown on chocolate or Thayer-Martin agar
chlamydia trachomatis
•Gram - rod; obligate intracellular pathogen in epithelial cells
•Distinct life stages: elementary bodies and reticulate bodies