IGCSE Business 0450 C1
1/65
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
66 Terms
Define the concept need and give examples
Goods or services essential for survival. e.g. food, water, shelter, clothing
Define the concept want and give examples
Goods or services not essential, but desired to improve quality of life. e.g. Mobile phones, holidays, branded clothes.
Unlimited, but resources to fulfil them are limited.
Define the concept scarcity
A shortage of resources to meet all wants and needs.
Define the concept opportunity cost
The next best alternative foregone when making a choice.
Helps in resource allocation
- Forces decision-makers to weigh alternatives carefully
e.g. A student has £10. They buy a book instead of going to the cinema. the opportunity cost is the cinema experience

Explain why the economic problem exists
- Unlimited wants (phones, cars, luxury items…)
- Limited resources (factors of production)
- Result: Scarcity → people must make choices
- Every choice involves an opportunity cost
Define the factors of production and examples
Land: All natural resources, e.g. minerals, ores, gas, fields
Labour: Number of people available to work , e.g. employees , teachers
Capital: Machinery, equipment and finance (money) needed , e.g. machines
Enterprise: The person who has an idea for a new business and takes the financial risks of starting up and managing it in the hope of making profit, entrepreneurs
Entrepreneurs do what when creating a business?
- Combines the other 3 factors of production
- Takes financial risks
- Aims to make a profit
Describe the main objectives of business activity
- Businesses produce different types of goods and services:
- Satisfy consumer needs and wants
- Combine factors of production to produce goods/services
- Add value to resources
- Create employment
- Generate profit
- Improve living standards
Define adding value and state the formula for it
more than it cost to produce it, in order to gain more profits
Added Value = Selling Price – Cost of Materials
Describe how businesses add value
Branding → Nike, Apple
Design/features → Smartwatch with fitness tracking
Quality → Durable shoes, reliable tech
Customer service → Easy returns, personalised support
Packaging → Eco-friendly or eye-catching designs
Convenience → Delivery services, mobile apps
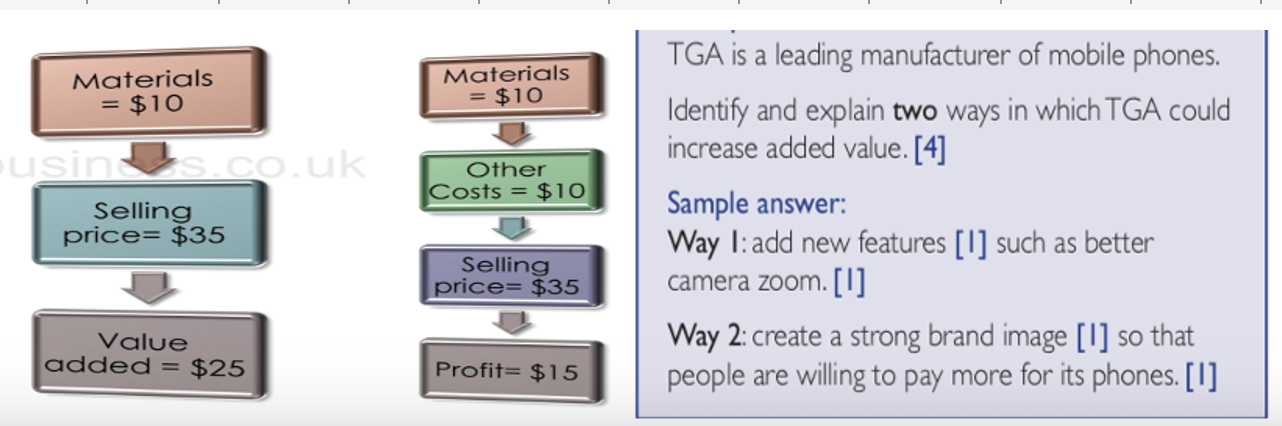
Describe the importance of added value
- Supports higher pricing
- Builds customer loyalty
- Increases profitability (earns profit)
- Essential in competitive markets
Define specialization
When individuals, firms, or regions focus on specific tasks they are talented in to improve efficiency.
Specialisation makes the best use of limited resources.
Define division of labour
A form of specialisation where production is split into separate tasks, each done by a different worker.
Outline the advantages/disadvantages of division of labour
Advantages: - Increased efficiency, work faster so produce more products
- Workers become more skilled at their task
- Lower costs for businesses
- Higher product quality
- Shorter training time
Disadvantages: - Boredom from repetition - Lack of flexibility – workers can’t easily switch tasks
- Dependency – if one worker is absent, production may stop
- Lower motivation → higher turnover, absenteeism
State the 3 sectors , what they involve and examples of each one
Primary: Using natural resources. e.g. Farming, fishing, forestry, mining.
Secondary: Using natural resources. e.g. Car manufacturing, construction, food canning, furniture making.
Tertiary: Providing services. e.g. Shops, banks, transport, restaurants, hotels, insurance
State the name given to the sectors which are connected
Chain of production:
1) Primary sector provides raw materials.
2) Secondary sector processes them.
3) Tertiary sector sells or supports the products.
Explain the changing importance of sectors
- Developing Countries (e.g., Rwanda, Vietnam)
- Primary sector is largest.
- People work in agriculture.
- Low demand for services.
- Developed Countries (e.g., UK, USA)
- Tertiary sector is largest.
- High income = more demand for services.
- Goods are often imported.
- Emerging Economies (e.g., China, India)
- Growing secondary and tertiary sectors.
- Rapid industrialisation.
State the reasons for sector changes
- Industrialisation: Shift from primary → secondary.
- De-industrialisation: Shift from secondary → tertiary.
- Raw materials running out (e.g. deforestation).
- People want more services (e.g. holidays, insurance).
- Cheaper goods imported from abroad.
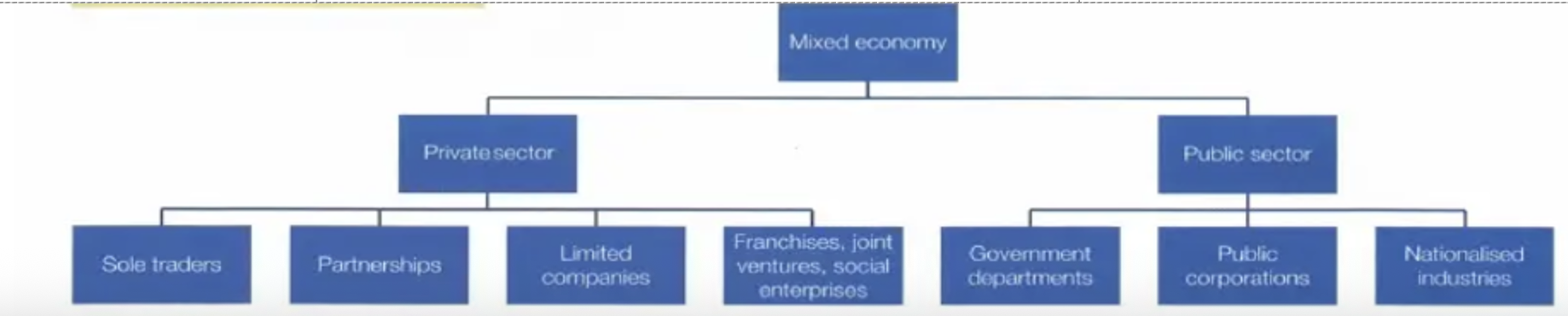
Describe what a mixed economy contains
- Private sector (owned by individuals).
- Public sector (owned by the government).
Explain the private sector including advantages and disadvantages
Owned: By individuals or companies.
Goal: Make profit.
Makes decisions based on:
What people want to buy.
How to produce at low cost.
Advantages:
More efficient (profit-driven).
Better quality due to competition.
More investment from owners.
Disadvantages:
Less focus on social benefits.
May cut jobs to save money.
Explain the public sector
- Owned: By government.
- Goal: Provide essential services e.g. education, healthcare, roads, public transport, defence
- Paid for: By taxes.
- Often free or low-cost for users.
Define entrepreneur and state the advantages and disadvantages of becoming one
An entrepreneur is a person who:
Has an idea for a business
Takes the financial risk of starting and running it
Aims to make profit
Organises the factors of production (land, labour, capital)
Advantages:
Keep all profits
Make own decisions (independence)
Flexible work and follow personal interests
Might earn more than being an employee
Disadvantages:
Risk of failure and losing money
May lose income from other jobs (opportunity cost)
Hard to get loans/finance from banks
Need a wide range of skills/experience
Explain the key characteristics of a successful entrepreneur and why it matters
Innovative → Think of new ideas and products
Risk-taker → Willing to take calculated risks
Decision-maker → Makes important business choices
Leader → Motivates others, communicates clearly
Determined → Keeps going when things get tough
Self-confident → Believes in themselves and the idea
Multi-skilled → Understands all areas (finance, HR, etc.)
Hard-working → Puts in long hours to make the business work
Define business plan
It is a document that explains how a business will work and succeed and used to attract investors and plan operations
describe the main parts of a business plan
- Business details – idea, owner, employees needed
- Location – where and why it’s a good place
- Objectives – clear goals
- Market research – customer needs, size of market, competitors
- Marketing plan – how the product will be promoted and sold
- Financial info – expected sales, costs, revenue, profits
- Sources of finance – savings, loans, etc.
- Cash flow forecast
State how business plans help entrepreneurs:
- Attract finance (banks, investors)
- Identify risks and weaknesses
- Help with decision making
- Give direction and set SMART objectives
- Improve chance of success
State why governments support start-ups:
- Create jobs → reduce unemployment
- Encourage competition → better quality and lower prices
- Help grow the economy
- Start-ups may grow → pay more taxes
- Offer cheaper products due to low costs
State governments support start-ups:
- Advice and training
- Grants for capital or training workers
- Low-interest loans
- Tax reductions in early years
- Free/cheap premises
Explain why it is important to compare business size
- Investors – to decide where to invest.
- Banks – bigger = safer to lend to.
- Competitors – to compare performance.
- Suppliers – prefer large businesses (buy more).
- Government – for taxes.
- Workers – job security.
Explain the ways to measure business size and its limitation
Number of employees → Bigger firms usually employ more workers.
But → Not accurate if businesses use machines instead of people.
Capital employed → More money spent on buildings, machines, etc.
But → Different industries need different capital amounts.
Value of output → How much they produce (in money).
But → Some small businesses sell expensive items (e.g., luxury goods).
Market share → % of sales in the total market.
But → May not reflect actual size (e.g., niche market with big market share).
Explain why businesses should grow
- Higher profits = more reinvestment, more dividends.
- Easier to borrow – big firms are seen as safer.
- Avoid takeovers – big firms are harder to buy.
- Increase market share – stronger brand, more power.
- Benefit from economies of scale – lower costs per unit.
- Personal reasons – power, success.
- Diversification – reduce risk by entering new markets.
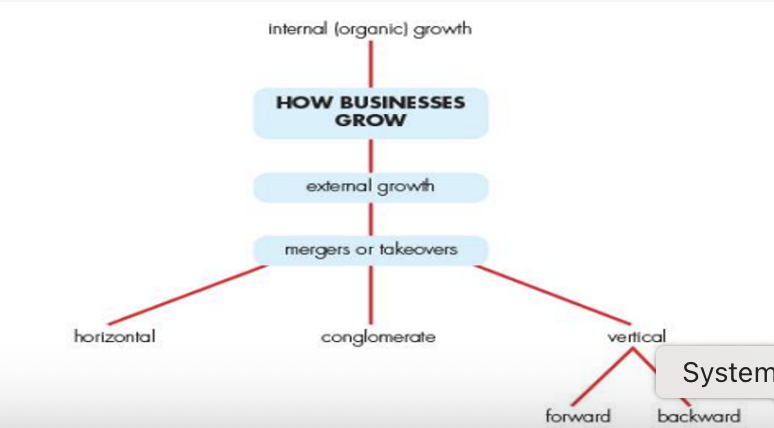
Explain different ways in which businesses can grow, e.g. internal/external
Internal (Organic) Growth
- Open new shops or expand to new areas/countries.
- Launch new products.
- Invest in technology/machinery.
- Advertise more.
External Growth (Mergers & Takeovers) - Merger = Two businesses join.
- Takeover = One business buys another.
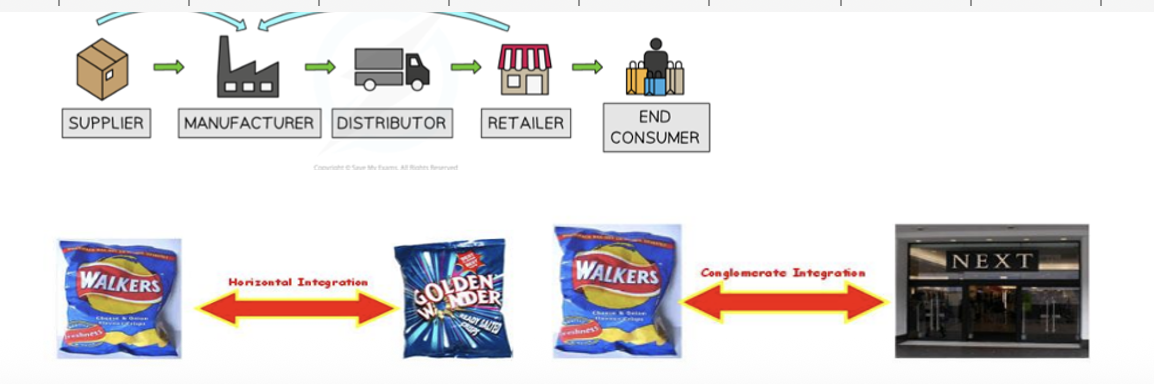
Explain the types of external growth (integration)
Horizontal → Same industry & same stage. e.g. 2 banks merge
Vertical – Forward → Later stage (closer to customer). e.g. manufacturer buys retailer
Vertical – Backward → Earlier stage (closer to raw materials). e.g. retailer buys supplier
Conglomerate (Diversification) → Different industries. e.g. Cosmetic firm buys drink company
Explain the problems linked to business growth and how these might be overcome
Internal:
Slower growth
Cash flow problems
Lack of capital or tech
Hard to manage more staff
External:
Conflict between staff from different businesses
Lack of expertise to manage larger business
Poor communication in large firms
Lose control (e.g., in a partnership)
State the solutions for the problems linked to business growth
- Grow slowly using profits
- Hire skilled managers
- Communicate well
- Plan growth carefully
Explain the reasons of why businesses stay small and give examples
Owner’s choice → Wants full control, personal service, low risk.
Small market → Only serves a local area or niche market.
Type of business → Personal services (hairdresser, plumber).
Lack of capital → Banks won’t lend easily to small/new firms.
State 4 advantages and disadvantages of keeping a business small
Advantages:
Closer customer relationships
Quick to adapt to changes
Unique/premium products
Low costs (e.g., work from home)
Disadvantages:No economies of scale
Harder to compete
Tough to hire top talent
Limited resources
Explain the main causes of business failure
Poor planning/objectives → No clear goals or business plan.
Liquidity problems → Not enough cash to pay expenses.
Wrong location → Far from customers.
Poor management → Lack of experience = bad decisions.
No investment in tech → Can’t compete in price/quality.
No change/adaptation → Doesn’t respond to trends/fashion.
Poor marketing → No research = no customers.
Lack of finance → Can’t borrow enough money to grow.
Strong competition → Bigger firms offer better/cheaper products.
Economic conditions → Recession, taxes, inflation reduce customer spending.
Over-expansion —> Growing too fast without enough resources.
State why new businesses fail more often
- Lack of experience/skills
- No customer base yet
- Hard to raise finance
- Tough competition
- Weak marketing
- Cash flow issues
- No clear objectives
Define sole trader
- One owner, runs and controls the business
- Keeps all profits
Explain the advantages and disadvantages of being a sole trader
Advantages:
Easy and cheap to set up
Full control and quick decision-making
All profits go to the owner
Disadvantages:Unlimited liability (personally responsible for debts)
Difficult to raise finance
Heavy workload and no continuity (ends if owner dies)
Define the term partnership
- 2 to 20 people share ownership
- Share profits and responsibilities
- Have a partnership agreement
Explain the advantages and disadvantages of a partnership
Advantages:
More capital available
Shared workload and decisions
Different skills and expertise
Disadvantages:Unlimited liability
Profits shared
Possible disagreements
No continuity if a partner leaves
Define the term Private Limited Company
- Shares sold privately (e.g., to family or friends)
- Limited liability (owners are not personally responsible for debts)
- Has a separate legal identity
Explain the advantages and disadvantages of a Private Limited Company
Advantages:
Limited liability
Can raise capital by selling shares
Continuity (business survives if a shareholder dies)
Disadvantages:
Can’t sell shares to the public
More legal requirements and costs
Must publish annual accounts
Define the term Public Limited Company
- Can sell shares to the public (stock exchange)
- Large businesses
Explain the advantages and disadvantages of a Public Limited Company
Advantages: Can raise large capital
Limited liability
Continuity
Disadvantages: Expensive and complicated to set up
Risk of takeover
Less control for original owners
Must publish accounts
Explain the term franchise
- A franchise is a business where the franchisee buys the right to use the franchisor’s brand, products, and business system.
- The franchisee runs the business but must follow the franchisor’s rules.
- The franchisor provides support like training, marketing, and a proven business model.
- The franchisee usually pays fees or royalties to the franchisor.
- Example: Opening a McDonald's outlet as a franchisee.
List the advantages and disadvantages of a franchisee
Advantages: - Uses a well-known brand (easier to get customers)
- Training and support from franchisor
- Lower risk of failure (business model is already proven)
Disadvantages: - Expensive to start (franchise fee + setup costs) - Little freedom to make your own decisions
- You must share your profits with the franchisor
List the advantages and disadvantages of a franchisor
Advantages: - Can expand the business quickly without spending much
- Earns money through fees and a % of franchisee’s profits
Disadvantages: - Loses some control over how each franchise is run - If a franchisee gives bad service, it can hurt your brand
Define joint venture
Two or more businesses work together on a project, sharing costs, profits, and risks
List the advantages and disadvantages of joint ventures
Advantages: - Shared risks and costs
- Local knowledge
- Access to new markets
Disadvantages: - Profits shared - Conflict in decision-making
- Mistakes affect all partners
Explain the differences between unincorporated and incoporated
Unicorporated:
Legal identity is same as owner
Liability is unlimited
E.g. sole trader, partnership
No continuity
Setup is quick and easy
Incorporated:
Legal identity separate from owner
Liability is limited
E.g. private Ltd, public Ltd
Continuity
Setup is complex (legal documents…)
Define ownership and who it applies to
Person or people who legally own and control the business
Determines control and responsibility
Applies to Sole traders, Partnerships, (private) Ltd, (public) Plc
Define unlimited liability and who it applies to
Owner is personally responsible for all business debts and risks personal assets to pay depts
Applies to: Sole traders, Partnerships
Define limited liability and who it applies to
Owner only loses money invested in the business
Personal assets protected if business fails
Applies to: Private and Public Limited Companies
Define risk and who it applies to
Chance of losing money or assets due to business failure
Lower in limited liability businesses
Applies to: All business ownerse
Explain what choosing the right business form depends on
- Number of owners
- How fast it needs to start
- How much capital is needed
- Willingness to risk personal wealth
- Size and future growth plans
Illustrate a business growth stage
New small business → Sole Trader
More owners → Partnership
Growing business → Private Limited Company (Ltd)
Very large → Public Limited Company (PLC)

Define business objective
A specific target a business wants to achieve.
Explain why business objectives are so important
- Gives direction and motivation.
- Helps managers make decisions.
- Aligns everyone towards the same goal.
- Measures success and progress.
- Helps with planning and using resources efficiently.
Explain 5 common business objectives
- Survival: Short-term goal, especially for new or struggling businesses.
- Profit: Key for established businesses to reward owners and grow.
- Growth: Helps reduce costs, build brand, and expand.
- Market Share: Increases influence, revenue, and competitive advantage.
- Corporate Social Responsibility (CSR): Focus on social, ethical, and environmental responsibility.
Explain why objectives change and include examples of objectives
Business change because of:
- Business size and stage.
- Market or economic changes (e.g. COVID).
- Competition.
- Social Enterprises:
- Private businesses with social aims.
- Profits are reinvested to support social causes.
Objectives include: - Social (e.g. helping disadvantaged people)
- Environmental (e.g. protecting the planet)
- Financial (e.g. reinvesting profits)
State what a stakeholder is including what types there are and their objectives
Stakeholders are people or groups interested in a business.
2 types of stakeholders:
Internal: Owners, managers, employees.
External: Lenders, suppliers, customers, government, local community.
Their objectives are:
- Owners/Shareholders: High profit and share value.
- Managers: High salary, job security, company success.
- Employees: Fair pay, job security, safe conditions.
- Lenders: Loan repayment with interest.
- Suppliers: On-time payment and long-term contracts.
- Customers: Good quality, fair prices, good service.
- Government: Jobs, tax revenue, economic growth.
- Local Community: Jobs, environmental care, local support.
Explain 3 main conflicts between skateholders
- Owners want high profit; employees want higher wages.
- Customers want low prices; producers want high prices.
- Local communities want clean environment; factories may cause pollution.
Explain the differences between public and private sector objectives
Private Sector Objectives:
- Profit
- Survival
- Growth
- Market share
- Reward to shareholders
- Customer service
- Public Sector Objectives:
- Provide essential services to the public:
- Accessible
- Affordable
- Inclusive
- Do not focus on survival or profit