SOC1370 Race Relations in the U.S. Exam 1
1/50
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
51 Terms
Race
The socially constructed idea that the human species is divided into distinct groups based on inherited physical and behavioral differences
Ethnicity
Shared cultural traits and or national origin
Majority;Minority
Majority group: any social group that is dominant in society
Minority group: any social groups that are oppressed or stigmatized in society
Social Construction
Perceptions and ideas shared by a group which is actively and creatively produced by human beings, they are neither natural nor given
Stratification
Hierarchical ranking of groups that results in the unequal distribution of resources in society which generates social inequality
Marx's theory of stratification and inequality
Material conditions are the sole factor in the production of inequality
Class struggle is the reason for social change
The system of inequality benefits the ruling class
Weber’s theory on stratification and inequality
3 dimensions of stratification:
Class (ownership of wealth
Prestige (honor, esteem)
Power (social and political influences)
Intersectionality
People belong to multiple groups which can intersect to create different experiences and affect life chances differently.
Ascribed Status
A social position assigned at birth, often based on characteristics such as race, gender, or family background.
Institutional discrimination
Unfair and unequal treatment of individuals or groups that is built into the policies, practices, and procedures of institutions like governments, schools, and businesses
Social Mobility
The up and down movement of persons and groups between or within a society’s various social class strata
Assimilation
Assimilation is the process by which individuals or minority groups adopt the cultural norms, values, and practices of a dominant culture, often resulting in the loss or dilution of their original cultural identity. This may involve changes in language, behaviors, and social practices, culminating in varying degrees of integration into the mainstream society. Assimilation can be voluntary or enforced and often influences socioeconomic opportunities and social interactions between cultural groups.
Acculturation
A kind of assimilation where minority groups adopt the majority group’s culture
Anglo-conformity
Inevitability of assimilation into the middle-class white anglo-saxon protestant culture
Melting pot theory
All the diverse peoples will blend their cultural differences into an altogether new breed - the American
race relations cycle
Four staged of race relations:
Contact
Conflict
Accommodation
Assimilation
Gordon’s classic theory of assimilation
There are separate distinct phases of adjustment to America:
Cultural assimilation
Minority groups adopt and learn the majority group’s culture and traditions
Marital assimilation
Minority groups intermarry with the majority groups
Identificatory assimilation
Minority groups begin to develop a sense of peoplehood based exclusively on their host society
Structural assimilation
Primary: Minority groups participate in intimate relationships like churches and schools of the dominant class
Secondary: Minority groups participate in large organizations like politics and corporations of the dominant class
Assumes assimilation is a linear evolutionary process
segmented assimilation
Quick upward mobility and integration into the societal mainstream: When groups are received favorably and possess high levels of human capital.
Downward assimilation: little upward mobility due to limited resources, lack of stable employment and income, little child education, and weak community ties.
Limited/selective assimilation: immigrant parents support children’s educational success, put reinforcement on traditional cultural values, and limit acculturation into American youth subculture.
pluralism (types of pluralism)
Cultural pluralism: Groups have not yet acculturated or integrated and they maintain a distinct separate identity
Structural pluralism: groups have acculturated but not integrated
Integration without acculturation
Enclave minority group
A group that maintains its distinct cultural identity while participating in the larger society, often through economic cooperation and social networks. e.g. little Italy and Chinatown
middleman minority group
A group that occupies an intermediate position in the social hierarchy, often acting as brokers or intermediaries between the dominant culture and other minority groups, typically engaging in commerce and trade.
Italian vs. Jewish immigrants
Italian:
Mainly from southern Italy of peasant status and rural origins who were ill-prepared for industrial jobs and were not considered white and subject to enclaves. Obtained economic success slower because they placed emphasis on family loyalty.
Jewish:
Mainly from Russia, Poland, and eastern Europe and were not considered white and subject to enclaves. Obtained economic success faster because they placed value in education and self-sacrifice.
structural mobility
A form of social mobility that occurs when changes in the structure of society, such as shifts in the economy or labor market, enable individuals or groups to improve their social status.
ethnic options
White people have an option when ethnicity applies to them and when it doesn’t and suggests that ethnicity is subjective and voluntary
Symbolic ethnicity
A concept where individuals express their ethnicity in a superficial or voluntary manner, often for social identity, without the burdens of day-to-day ethnic obligations. e.g. celebrating saint patricks day
Third generation interest
The phenomenon where the grandchildren of immigrants develop a greater interest in their ancestral heritage and cultural identity compared to their parents. This is due to the security that they are provided from being deeper rooted into America than their parents.
Prejudice (affective, cognitive)
Prejudice refers to preconceived opinions or attitudes about a person or group, often rooted in stereotypes and lacking direct experience with the individual or group in question. Affective prejudice is based on emotional responses, leading to feelings such as fear, hatred, or disdain towards a specific group. Cognitive prejudice involves the beliefs and stereotypes that people hold, which shape their understanding and perception of others based on race, ethnicity, gender, or other characteristics.
Discrimination
The practice of differential and unequal treatment of others, usually along racial, religious, ethnic, or gender lines
Scapegoat hypothesis
The scapegoat hypothesis posits that individuals or groups may be unfairly blamed for problems or negative outcomes experienced by others. This phenomenon often arises in situations of social tension, where people seek to project their frustrations or anxieties onto a vulnerable minority or subordinate group, leading to prejudice and discrimination against them as a means of displacing responsibility for societal issues.
Authoritarian Personality
One who desires an authoritarian social system and seeks obedience, subordination, and servile acceptance of authority. This perpetuates a fear of people who are different from one’s group and leads to prejudice against those with less power.
Stereotype
Oversimplified generalizations applied to an entire group without regard to individual differences
Sociological explanations of prejudice
Prejudice is the product of multiple causes that mainly stems from the relationships between racial groups
socialization
An individual learns to adjust to a group or society and behave in a manner approved by the group or society
split labor market
A concept suggesting that labor markets are divided along racial, ethnic, or gender lines, leading to competition between groups for jobs and wages. Ethnic antagonism results from exploitation by employers and economic competition between multiple groups of laborers with wage differentials
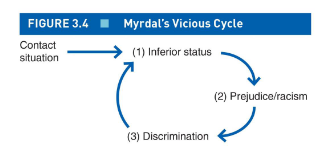
The vicious cycle
Contact situation leads to inferior status, which allows prejudice or racism, which leads to discrimination and perpetuates the inferior status.
social distance
The degree of intimacy that a person will accept in their relations with members of other groups
patterns of relationships between prejudice and discrimination
All-weather liberal: Not prejudiced and will not discriminate, but because they do not talk to minorities and are close minded
Fair-weather liberal: not prejudiced but will discriminate because they benefit from it e.g. not speaking against a racist joke
Timid Bigot: Have strong prejudice but will not discriminate
Active Bigot: Have strong prejudice and will discriminate
contact hypothesis
The theory that increased interaction between different racial or ethnic groups can reduce prejudice and improve relationships as long as the groups have equal status, common goals, interaction in noncompetitive tasks, and active endorsement of authority.
modern racism
A subtle and indirect form of racism the explains racial disparity as attributable to culture rather than biology
hate crimes
Criminal acts motivated by prejudice and bias against a particular group, often based on race, ethnicity, religion, disability, or sexual orientation.
Major arguments of “Statement on Race”
The "Statement on Race" outlines that race is a social construct with no biological basis, emphasizes the importance of understanding the historical context of race, and advocates for equality and justice in addressing racial issues.
Major arguments of “Defining Race: Comparative Perspectives”
The paper examines the social construction of race, its historical context, and the implications of racial categories on identity and social dynamics.
Major Arguments of “Getting under my skin”
The essay discusses the complexities of identity, race, and the personal experiences of individuals affected by racism, emphasizing the need for deeper understanding and empathy.
Major arguments of “Drawing the color line”
Analyzes the historical context of racial categorization in the U.S. and its implications for social inequality.
Major arguments of “Fix the census” and “U.S. Census Race Categories”
These arguments highlight the need for more accurate and inclusive racial classifications in the U.S. Census, emphasizing how current categories fail to reflect the complexity of racial identities and the social implications of misclassification.
Major arguments of “Race: The power of an illusion. The difference between us.”
This work argues that race is a social construct with no biological basis, emphasizing that the perceived differences among races are largely superficial and culturally constructed.
one drop rule
A social and legal principle asserting that any person with even a single ancestor of African descent is considered black, reflecting the historical context of racial classification in the U.S.
miscegenation
The marriage or cohabitation between persons of a different race
mulatto
A person of mixed white and black ancestry, often used in historical contexts to describe individuals with one black and one white parent.
racialization
The process by which race is assigned to the group based on certain bodily features or biological characteristics to mark certain persons for differential status and treatment
Thomas theorem/the definition of the situation
The outcome of a situation depends on an individual’s perception of it and not by the situation itself