bio unit 5 test
1/42
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
43 Terms
what is biotic factors
living factors
what is an abiotic factor
non-living factor
Biotic examples
people, grass, trees
abiotic examples
weather, climate
population
consists of all the individuals of the same species living in a defined area
community
all living organisms living close enough together for potential interactions
ecosystem
includes both the living aspects (biotic factors) and the non-living aspects (abiotic factors)
autotrophs
(self-feeders) make their own organic nutrients using an external energy source (producers)
heterotrophs
(other-feeders) obtain organic nutrients from other organisms (consumers)
what do the arrows mean in a food chain or food web
point in the direction of flow or who is eating who
what type of organisms do all organisms in a food web eventually become food for
decomposers
what is the job of decomposers
feed on all trophic levels, convert dead organic matter into inorganic matter
ex of a decomposer
prokaryotes, bacteria, and fungi
what percentage of the energy available to primary consumers will be available to tertiary consumers
1%
how much energy will be available to secondary consumers
10%
what does "energy flows, but nutrients cycle" mean
energy enters an ecosystem from the sun and exists as heat (it is not reused). Nutrients like water and nitrogen cycle though the biosphere and are constantly reused
what is a habitat
where an organism lives
what is a niche
the role of an organism in its environment
what is a keystone species
plays an important role in its community, if it is removed it will have drastic effects
uniform
organisms are evenly spaced out (seen in species that compete for a scare environmental resource like water)
random
organisms have unpredictable distribution (seen in species that do not interact strongly)
clumped
organisms clustered together in groups (patchy distribution of resources in environment)
exponetial growth
idealized unlimited growth ("J" shaped curve)
logistic growth
idealized population growth that has been slowed down by limiting factors ("S" shaped curve)
density dependent factors
limited food, living space, disease
density-independent factors
fires, storms, floods, earthquakes
carrying capacity
the maximum population size that a particular environment can sustain
r-selected species
species that live in an unstable environment, population growth in rapid (house fly)
k-selected species
species that live in a stable environment, controlled by density dependent factors (elephant)
growing
is this population pyramid growing, stable, declining
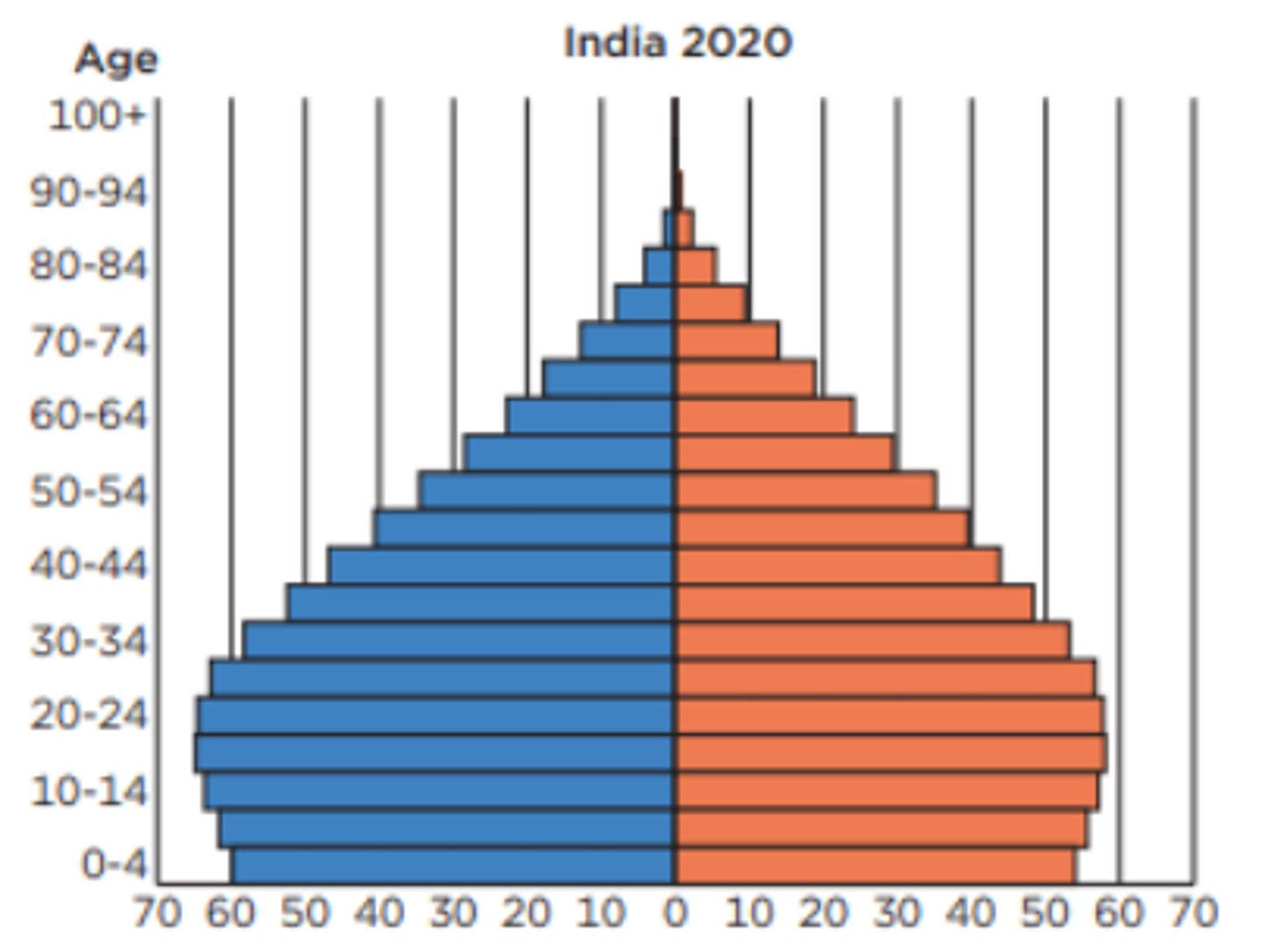
stable
is this population pyramid growing, stable, declining
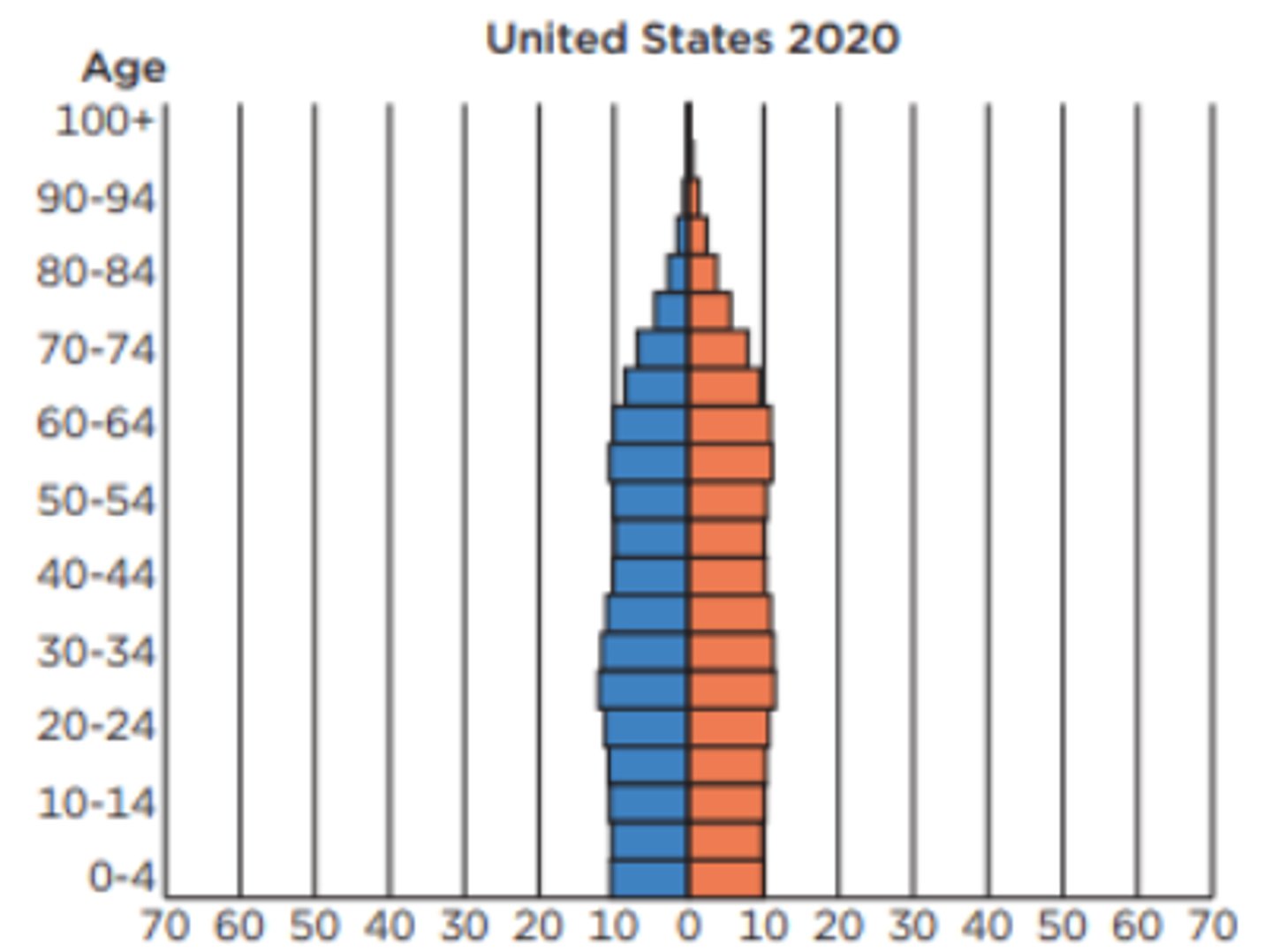
declining
is this population pyramid growing, stable, declining
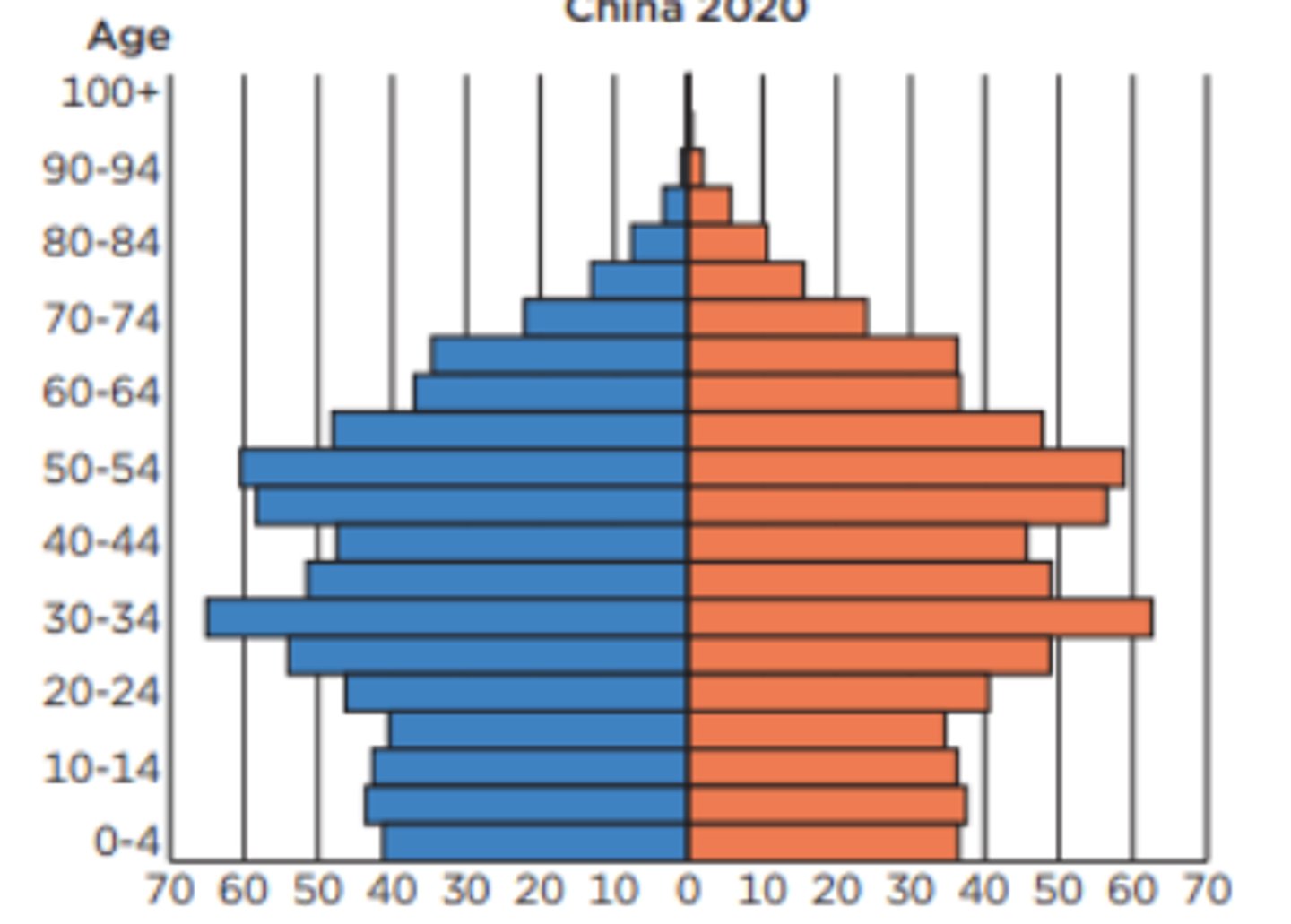
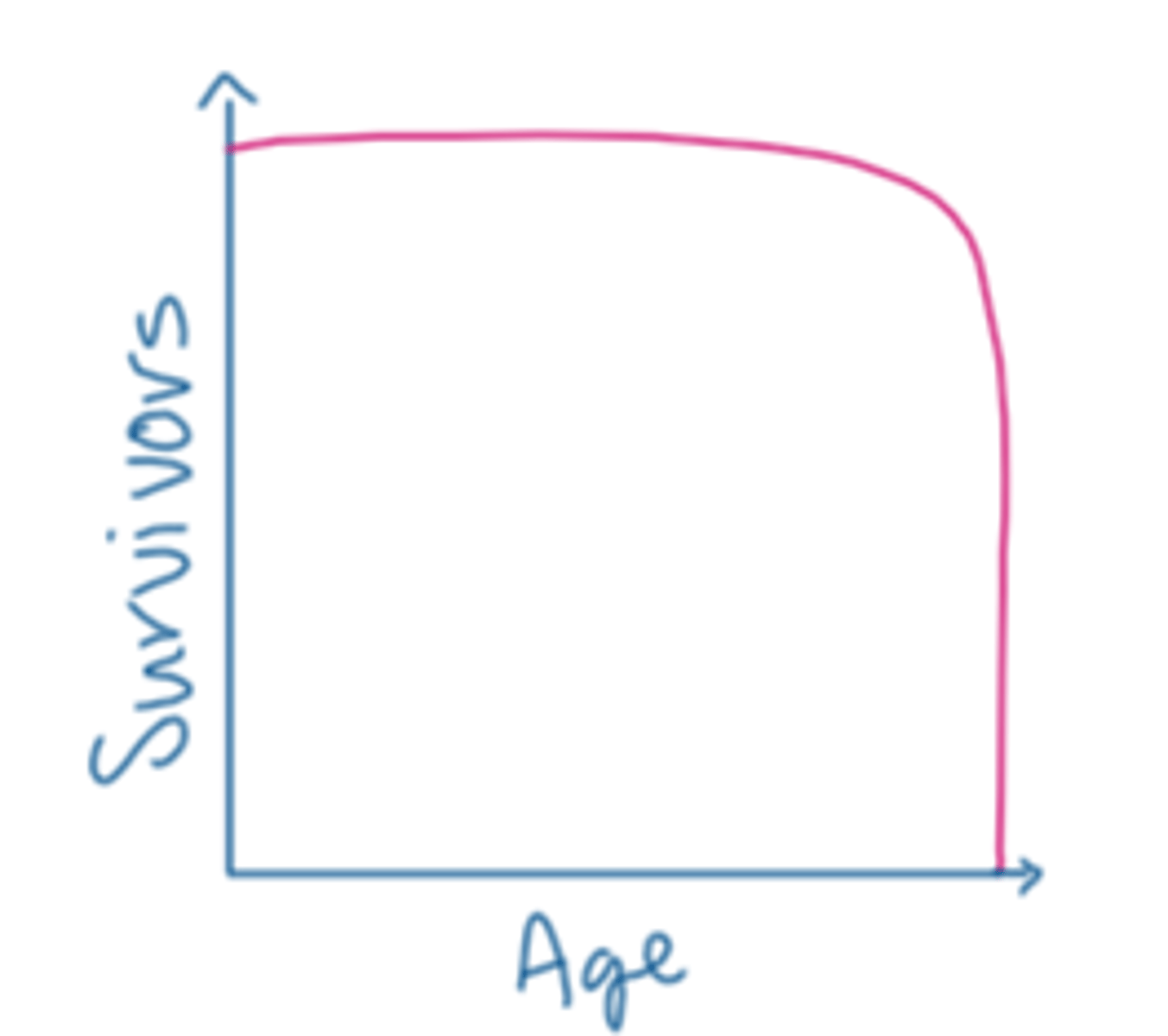
type 1 survivorship
low death rate, many individuals live to old age (humans)
type 2 survivorship
moderate death rate, individuals die at all ages (birds)
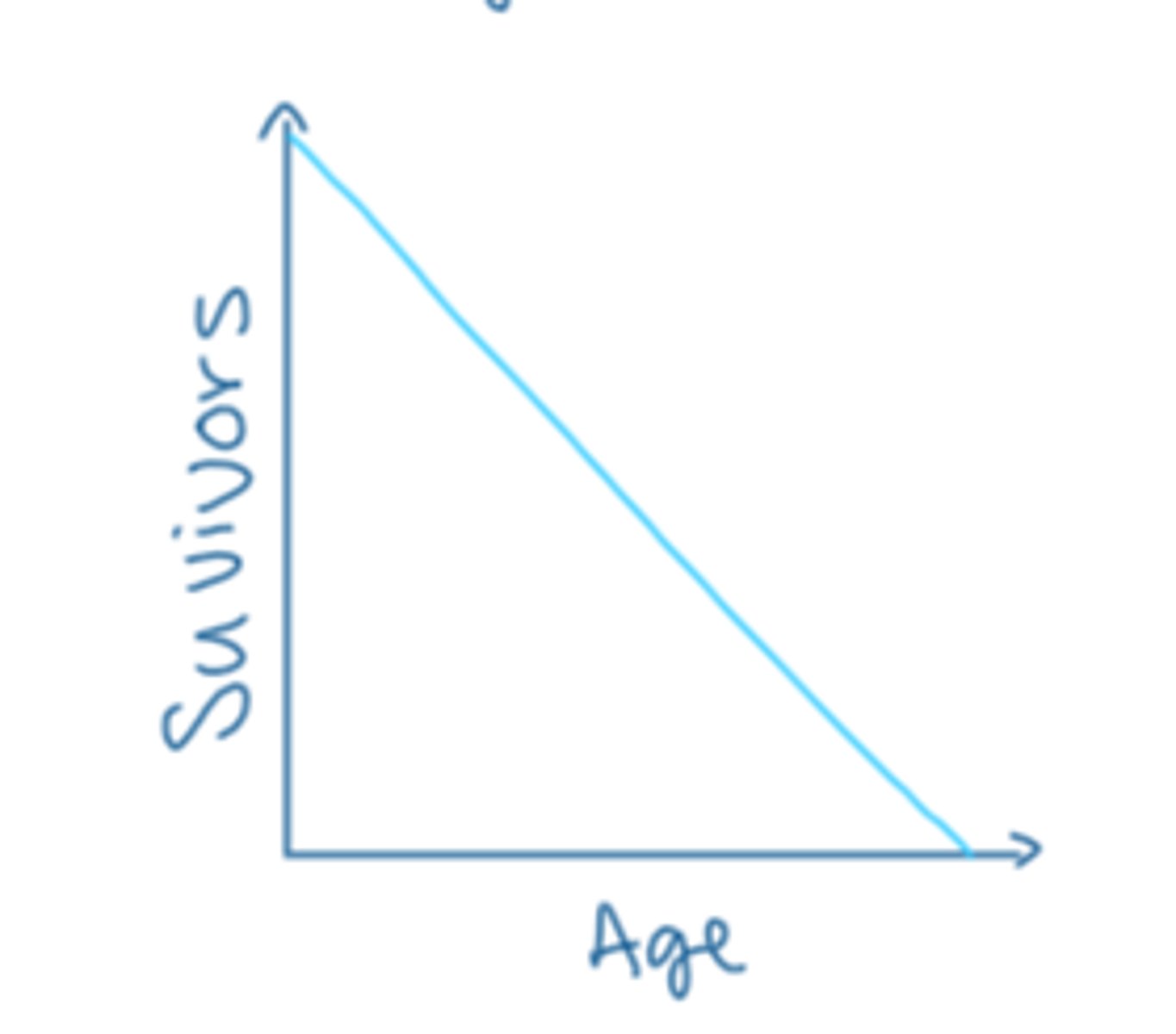
type 3 survivorship
high death rate, many individuals die young and few live to old age (insects)
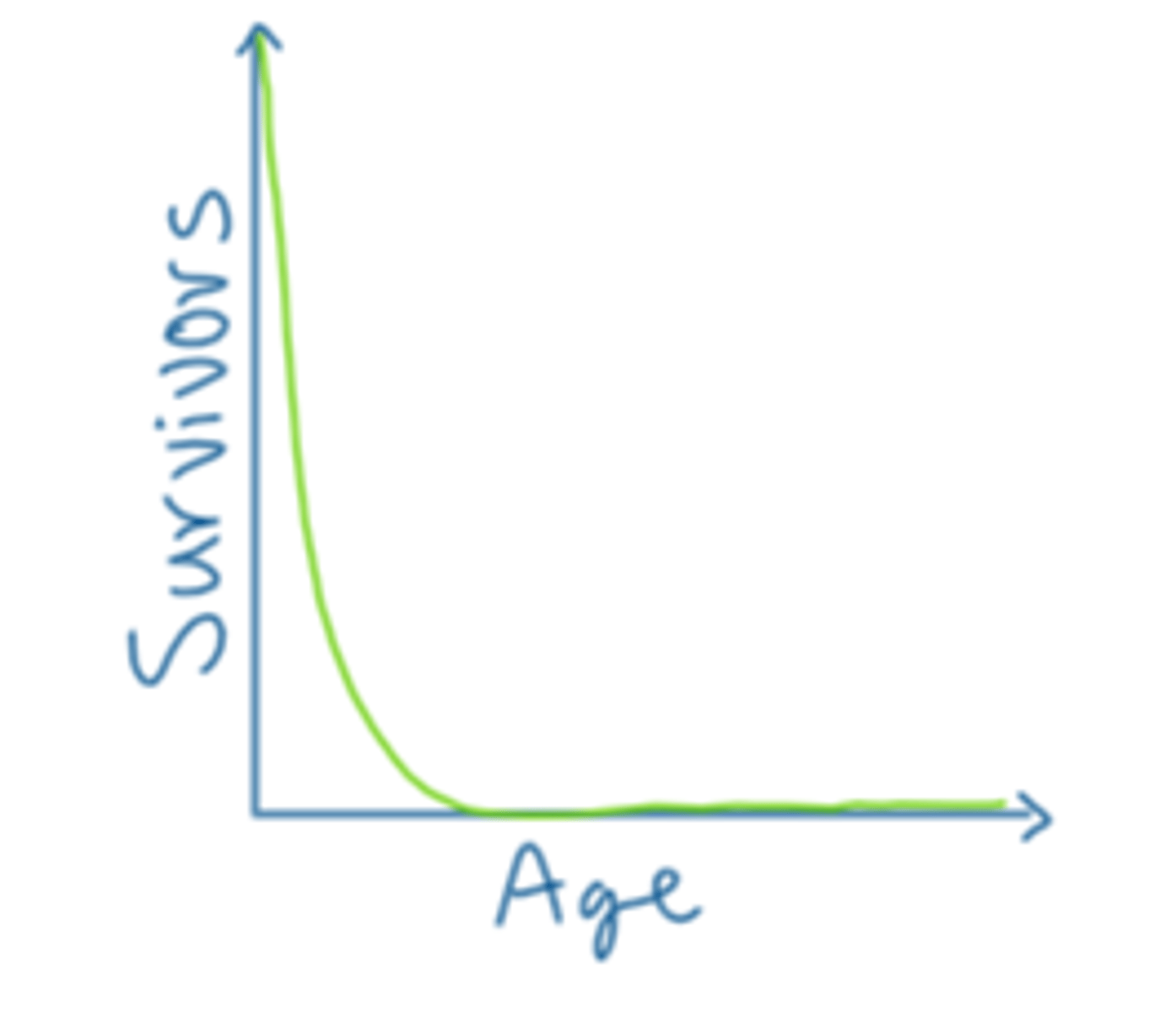
intraspecific competition
occurs between members of the same species (same species compete for mates in the same area)
interspecific competition
occurs between members of different species (different species compete for the same prey)
symbiosis
a relationship between 2 different organisms that live closely together
mutualism
both organisms benefit from the relationship (bees and flowers)
commensalism
one organism benefits and the other is neither helped nor harmed ( barnacles attaching to a whale)
parasitism
one organism benefits at the expanse of the other (fleas on a dog)
food web
a network of interconnected food chains
Food chain
Linear sequence of matter and energy flow through an ecosystem