BIN300 - W1: what is statistical genomics?
1/36
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
37 Terms
Genome
Totality of genes on all chromosomes (1930s)
Genetic material of organism DNA
DNA discovered in the 1950s
chromosomes → double helix: two strands of DNA
DNA codes to make all cell types
DNA code
…ACGATAAGAAACT…
nucleotides
cytosine (C), guanine (G), adenine (A), thymine (T)
DNA contains the code for live
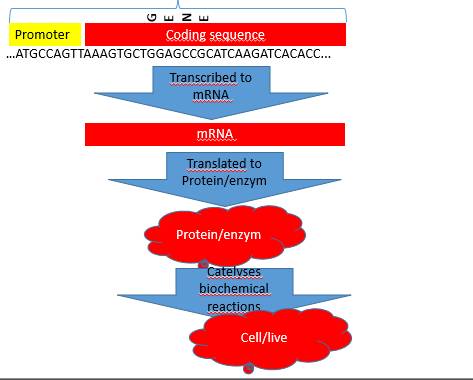
Genomics
investigations into the structure and function of large numbers of genes/nucleotides in a simultaneous fashion
large scale research of genomics
high throughput, new tehcnologies required, e.g. recording, analyisng etcsu
subdisciplines genomics
structural, comparative, functional, bioinfomatics
why so much interest in genomics - exepctations are high for
new approaches for drug discovery, new understanding on cancer formation, new approaches to genetic engineering
disease resistance, improved nutrient contents of food, new selection methods involving new traits, gene-editing
genetic mapping
order of genes (distance between them)
physical mapping
where are the genes in the sequence of the genome
sequencing of entire genomes
human genome, 3 million baspeairs, cattle, horse, chicken, dog, pig, sheep, salmon
structural genomics
genetic mapping, physical mapping, sequencing of entire genomes
comparative genomics
many species: too many genomes to sequence? not a problem since genomes are similar, e.g. sequence species A gives info over B
Study of relationships of genomes
across species, across breeds within species, between individuals, acorss genes (gene families)
functional genomics
from genotype to phenotype
mutagenesisf
genotype
mutant, changed DNA sequence
phenotype
all biologicla consequences, on physiological level, on animal/trait level
mutagenesis
study effects of mutations
invoking changes in DNA of model organism, studies the effect of DAN changes, expect similar effects in other species
proteomics
structure function and spatial localisation of protiens
proteome: all proteins in a cellp
physiomic
proteom => biochemistry and physilogy of organismp
phenomics
biochemistry → anatomy and function
bioinformatics
genomics studies not 1 gene but all 30.000
very large quentities of data, coming from high throughput machinery
bioinformatics
computational, algortihimic and statistical analysis of large amounts of genomics data, database techniques, prediction of genes from DNA sequence, prediction of protein structure, i.e. how it folds
statistical genomics
biostatics part of bioinformatics
detection of genes for complex traits, quenatitiative trait loci (QTL)
genomic selection, use of genomics data for selection
gene
inherited phyiscal DNA that affects traits
locus
position on chromosome
alleles
alternative forms of genes
allele frequency
number of allele A/ total number of alleles
segregation
sampling of alleles in meiosis, individual AB → gamete A or gamete B
genes are lying on chromosomes
true
polymorphic gene
more than 1 allele
genotype
allelic constituitation at 1, …., all loci
for 1 locus: A1A2H
homozygous
same 2 alleles at locus A
E.G. A1A
Heterozygouos2
2 different alleles at locus A
E.G. A1A2
quantitative traits
continuous variation, e.g. height or weightph
phenotype
recordable effect of genotype
qualitative traits
2 or few alternative forms, e.g. brown vs white coat, or blue vs borwn eyes
QTL
A quantitative trait locus (QTL) is a region of DNA associated with a specific phenotype or trait that varies within a population. Typically, QTLs are associated with traits with continuous variance, such as height or skin color, rather than traits with discrete variance, such as hair or eye color.