bio 35 final - uci
1/94
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
95 Terms
cerebellum
motor coordination. (when removed, person has slanted walk, tremors, overshot movements)
frontal lobe
responsible for executive function (plan, organize, manage time, avoid saying or doing the wrong thing)
medulla oblongata
helps regulate breathing, heart and blood vessel function, digestion, sneezing, and swallowing
lobotomy
severs the connection between the entire frontal lobe to the thalamus. patient could still sense stimuli, but would lack the executive function necessary to react. makes patient mentally dull
Broca's area
language production. Behavioral test - ask questions that require the patient to respond verbally and with suffice answers
Wernicke's area
language comprehension. Behavioral test - ask questions that require the patient to respond by performing tasks
brain imaging
can predict responsiveness to antidepressants. An increase in rostral anterior cingulate cortex (rACC) activity can be linked to a positive outcome from using the antidepressant, sertraline.
SSRIs
block reuptake channels for seratonin
Monoamine Oxidase Inhibitors
block the enzymatic breakdown of dopamine, norepinephrine, and serotonin
Monoamine Hypothesis of Depression
the underlying pathophysiologic basis of depression is a depletion in the levels of serotonin, norepinephrine, and/or dopamine in the central nervous system. QUESTIONED!!
axons
can be up to a meter long! longest is the sciatic nerve
afferent nerves
Also called sensory nerves; nerves that carry information about the external environment to the brain and spinal cord via sensory receptors.
efferent nerves
Also called motor nerves; nerves that carry information out of the brain and spinal cord to other areas of the body.
endocytosis
process by which a cell takes material into the cell by infolding of the cell membrane. example in bio 35: vesicles are created from the presynaptic plasma membrane into the neuron to then transport neurotransmitters
exocytosis
release of substances out a cell by the fusion of a vesicle with the membrane. example in bio 35: a vesicle carrying neurotransmitters fuses to the plasma membrane to release its contents into the synapse
botox
a drug which keeps muscles from contracting and wrinkling the skin by blocking the exocytosis of muscle-contraction activating neurotransmitters
dynamin
function: helps pinch vesicles from the plasma membrane. the blocking of this protein blocks endocytosis.
action potential
Step 1: Na+ (sodium) channels open
Depolarize membrane potential away from the resting potential; toward equilibrium potential for Na+ (ENa)
Step 2: K+ channels open
Hyperpolarization of the membrane potential towards equilibrium potential for K+ (EK)
Step 3: after a delay, Na+ channels inactivate, helping K+ channels to hyperpolarization membrane potential
Hyperpolarization
the membrane potential becomes more negative. occurs when voltage-gated potassium channels open and also when voltage-gated sodium channels inactivate
depolarization
the membrane potential rapidly becomes morepositive. occurs when voltage-gated sodium channels open and sodium ions flood into the cell
tetrodotoxin
blocks voltage gated sodium channels, blocking depolarization
mesolimbic pathway
pathway of the reward system. mediates drug addiction
dopamine
regulates reward response. these neurons report an anticipation for a reward and an error in reward prediction, not the reward itself
impulsivity
the characteristic that is biologically exhibited by a lack of grey matter in the prefrontal cortex
amygdala
two almond-shaped neural clusters in the limbic system; linked to motivation, emotional control, fear and response and interpretations of nonverbal emotional expressions
hypothalamus
a neural structure lying below the thalamus; regulates fear, thirst, sexual drive, sleep, and aggression
channelrhodopsin
responds to blue light by allowing Na+ ions to enter the cell, depolarizing it. activates attack neurons in mice. activation of a particular brain area shows sufficiency
halorhodopsin
responds to yellow light by allowing Cl- ions into the cell, hyperpolarizing it. this deactivates attack neurons in mice, inhibiting aggressive behavior. this shows how a lack of a particular brain area can show necessity
sensory transduction
the process of converting various forms of energy located outside of the body (light rays, sound waves, mechanical forces, chemicals, etc.) into neural signals
cascade
When a photon strikes a rhodopsin molecule, it activates a G-protein (transducin). This triggers a phototransduction __________ which amplifies the effect of that single photon, thus causing there to be a sensitivity to it. this GPCR process is also used in taste and smell.
rhodopsin
a G protein coupled receptor. the pigment in rod cells that causes light sensitivity.
transducin
The G-protein that couples rhodopsin to the enzyme phosphodiesterase in rod photoreceptors
rods
retinal receptors that detect black, white, and gray. the more of this receptor at a certain angle, the better vision is at that angle in the dark. none at the 0 degree mark.
cones
retinal receptor cells that are concentrated near the center of the retina and that function in daylight or in well-lit conditions. detects fine detail and give rise to color sensations, especially at angles where these cells are more present
mood disorders
diagnosed by a self-report of behavior. there is currently no way to diagnose these based on brain scans
superior
what brain region is defined by being towards the top of the head?
anterior
which brain region is generally towards the front of the body?
posterior
which brain region is generally towards the back of the body?
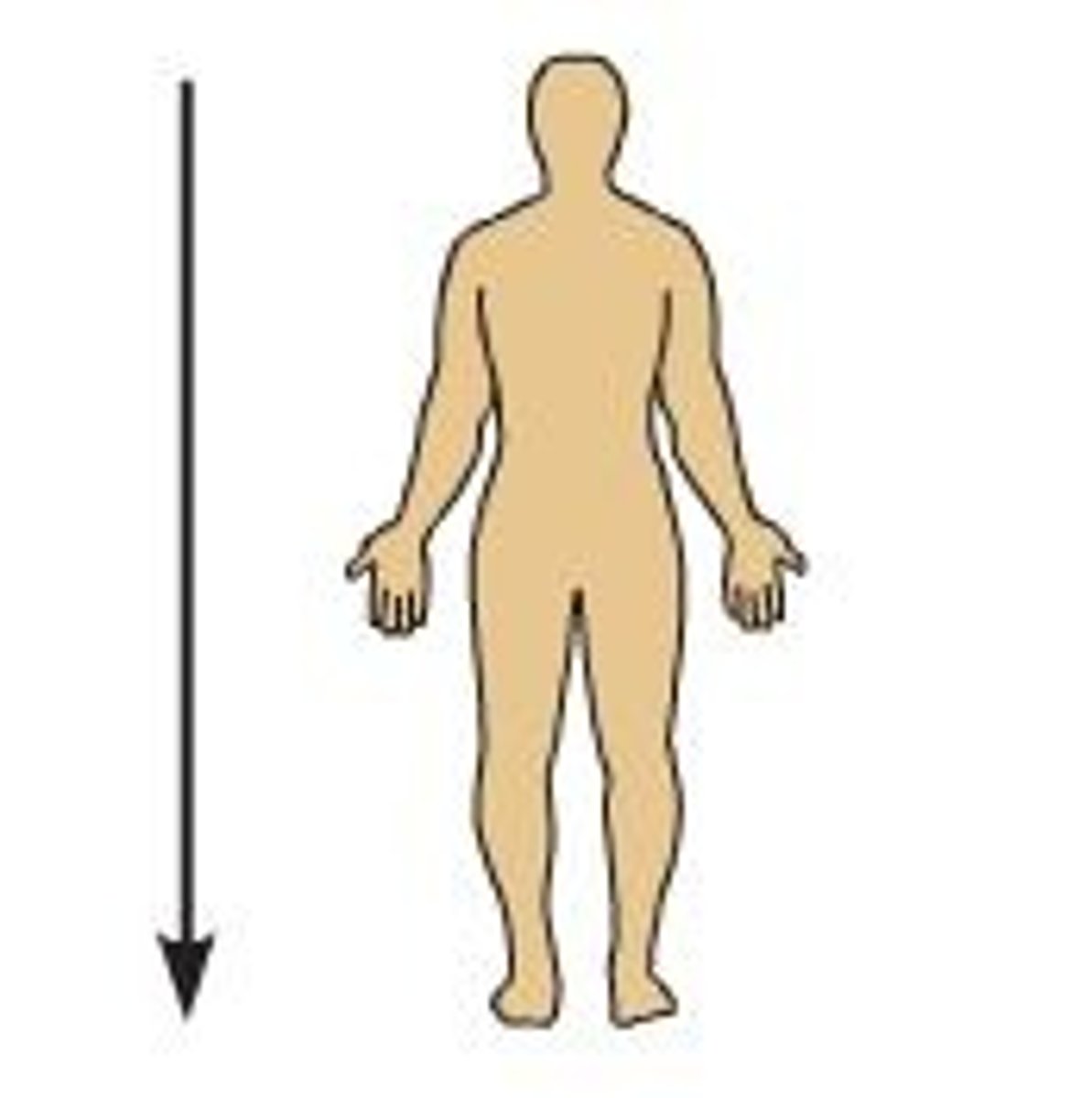
inferior
which brain region is generally lower, away from the head?
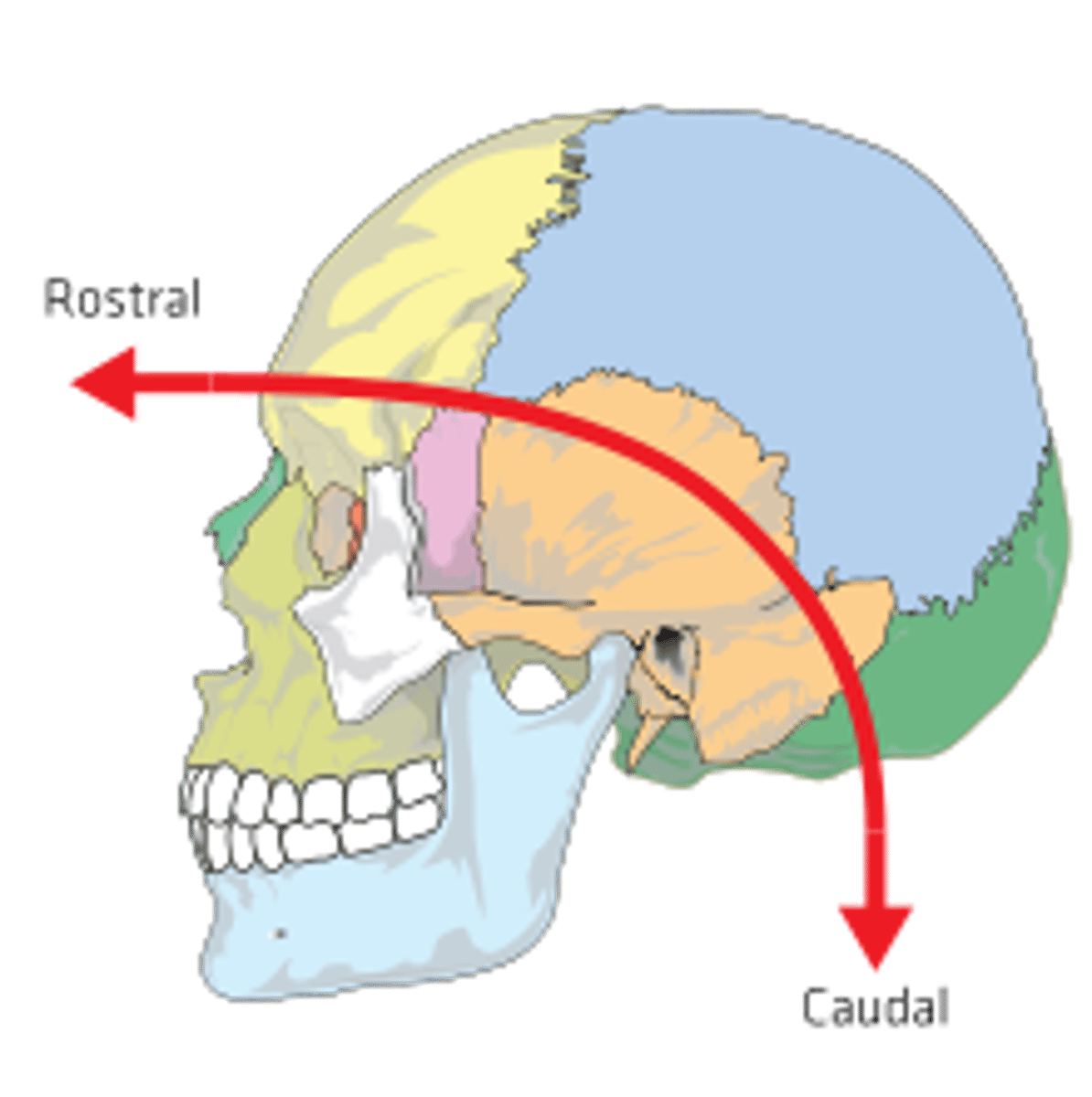
caudal
which brain region is generally the "tail end"?
rostral
which brain region is towards the forehead or nose?
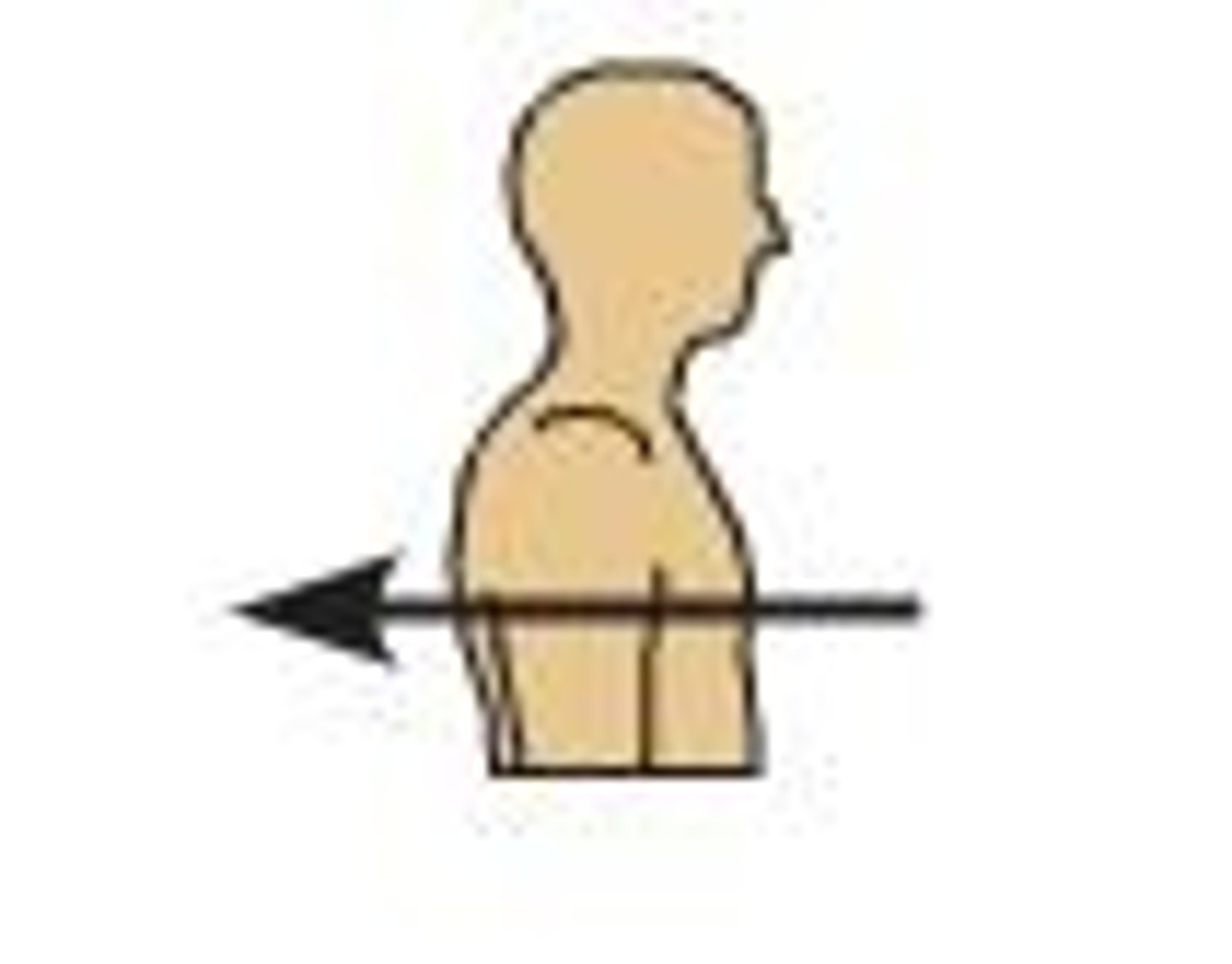
dorsal
which brain region is more back-oriented on the CNS axis?
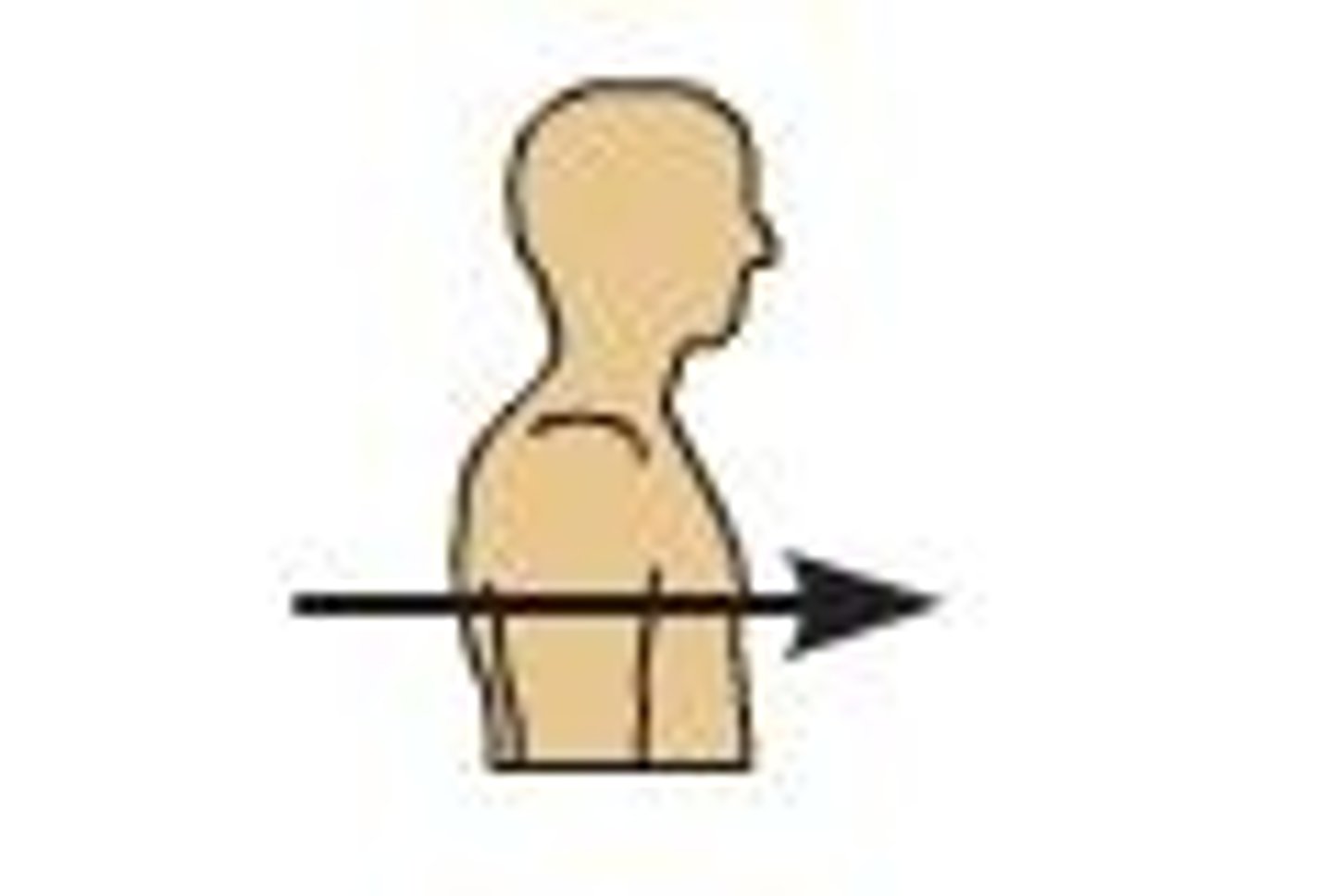
ventral
which brain region is more towards the front or belly on the CNS axis?
dorsal stream
responsible processing localization and action. People who have akinetopsia (the disorder that causes people to see motion in life as a slideshow) have a problem with this pathway
ventral stream
responsible for object identification. People who have prosopagnosia (the disorder that causes people to be unable to recognize faces) have a problem with this pathway
grandmother coding scheme
the idea that people have 1 cell dedicated to recognizing each person they remember. This coding scheme is very inefficient and requires a much larger number of active neurons
population coding scheme
the idea that people have a population of cells that are responsible for recognizing different people. This is the far more efficient coding scheme as it involves a much lower number of required active neurons
auditory transduction
converts air pressure waves outside the body into neural signals.
cochlea
has different levels of stiffness along it to make it differentially sensitive to different frequencies of sound.
tonotopic map
an arrangement of neurons within auditory brain regions such that the characteristic frequencies of the neurons gradually shift from lower at one end of the region to higher at the other end
peripheral vertigo
dislodged calcium carbonate crystals overactivate hair cells. The brain receives constant neural impulses that the body is upside down or falling when in actuality the body is stationary
T1R1, T1R2, T1R3, and T2R
examples of G-protein coupled receptors used in the gustatory system
TRP channels
these are non-selective cation channels activated through chemicals, temperature, light, sound, and touch. when opened, these produce a short depolarization. two examples are TRP-M4 and TRP-M5.
anosmia
loss of smell. commonly caused by whiplash; delicate olfactory nerves entering vertically through the cribriform plate are severed
chemotopic map
The pattern of activation in the olfactory system in which chemicals with different properties create a "map" of activation based on these properties
retinotopic map
the two dimensional representation of the retinal image in the neurons of the primary visual cortex
nociceptors
sensory receptors that enable the perception of pain in response to potentially harmful stimuli. since spicy is a feeling, not a taste, these receptors detect the physical spice in our food, such as capsaicin.
capsaicin
a nonpolar molecule responsible for the spiciness found in food. dissolves in other nonpolar substances like oil. this molecule's pain receptor is TRPV1.
antagonist
a molecule that, by binding to a receptor site, inhibits or blocks a response
agonist
a molecule that, by binding to a receptor site, stimulates a response
A delta fibers
large and myelinated neurons that are responsible for short-lived acute instances of pain, such as during cuts or burns.
C fibers
small nerve fibers, poorly myelinated or unmyelinated. slow conduction rate. post ganglionic fibers of sympathetic system. exteroceptors for pain, temp, and touch.
tactile acuity
the ability to detect details on the skin. highest when receptive fields are small
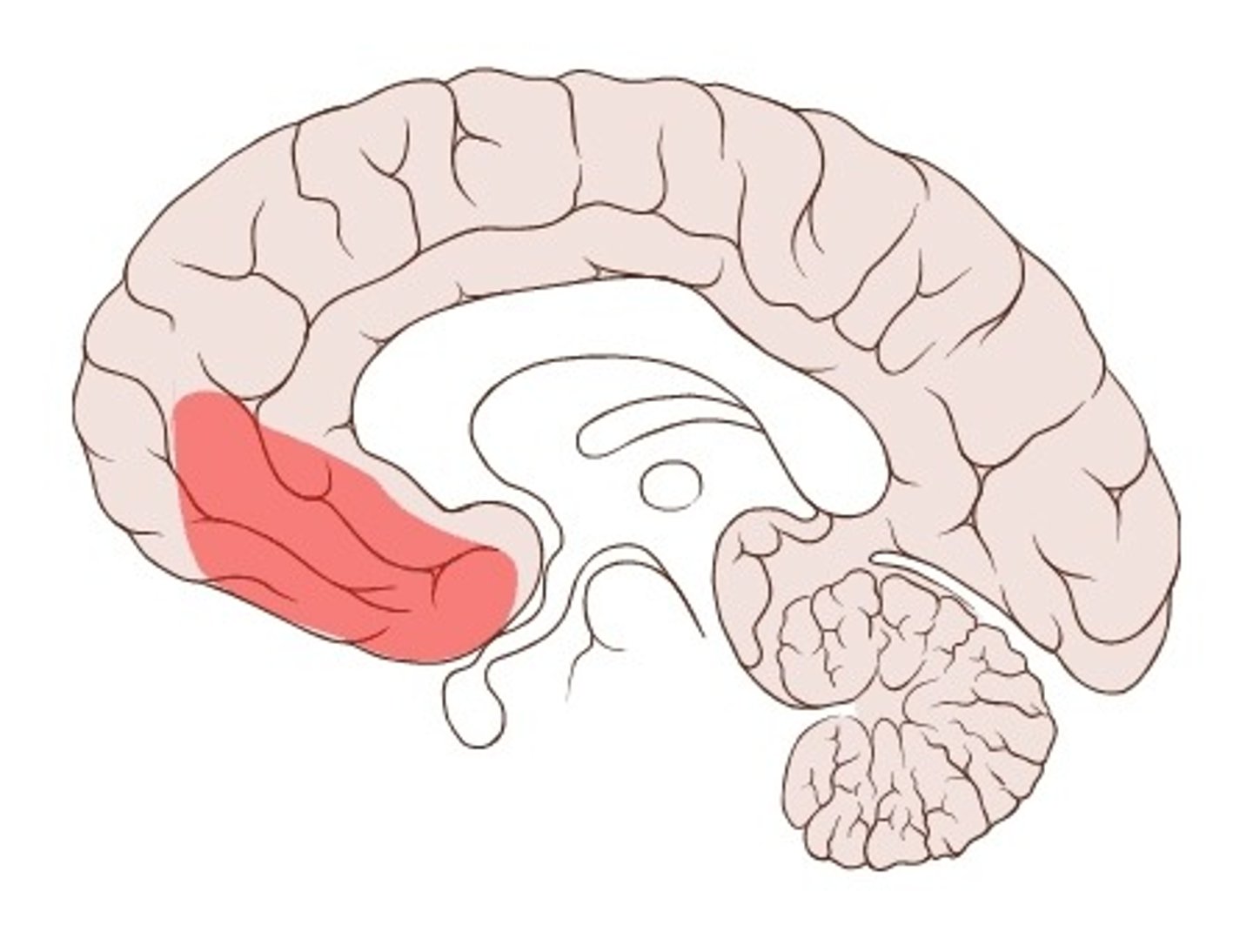
ventromedial prefrontal cortex
thought to play a substantial role in decision making and controlling emotional responses from the amygdala. a sever to this region would cause greater impulsivity
impulsive action
a failure to inhibit an inappropriate response. (ex. laughing at a funeral). this was shown in the rat gambling task when rats had premature responses
impulsive choice
decision making with small immediate rewards over more beneficial delayed rewards. (ex. playing video games instead of studying). this was shown in the rat gambling task when the rats chose specific high-risk gambling options
Risk averse rats
develop a pattern of preference for safe gambling option
risk seeking rats
do not stabilize a preference in gambling
repeated drug use
the cause of these brain changes:
1. enhanced reactivity to drug cues
2. reduced sensitivity to non-drug rewards
3. Interferences with the brain's capacity to exert self-control
4. higher sensitivity to stressful stimuli and dysphoria
electronencephalogram
amplified recording of the waves of electrical activity that sweep across the brain's surface (can't detect deeper down like hippocampus/amygdala)
circadian process
changes in alertness determined by biological clock and environmental cues as opposed to amount of time spent awake
homeostatic process
the pressure to sleep; depends on how long one has been awake, rather than the biological clock
place cells
types of cells found in Hippocampus whose activity becomes associated with particular parts of a familiar environment. We can checking if the same sequence of neurons used during a particular memory is also used during sleep
vegetative state
paradoxical combination of wakefulness without awareness
(cerebellum & cortex are sustained damaged)
Complex reflexes, e.g. yawning, swallowing
Opens eyes & shows spontaneously roving eyes (not purposely movement)
Sometimes smiles or frowns
Sometimes displays arousal and startle reflexes (e.g. loud sound can elicit eye-opening)
No purposeful responses to external stimuli
Cannot interact with people
Fecal and urinary incontinence (cannot control poop and pee)
coma
Neither wakeful nor aware
(all of the cortex & cerebellum & a lot of brain stem are affected)
Immobile with eyes closed
Unresponsive
In a transient/unstable state. Most patients recover awareness, die, or enter a vegetative state
minimally conscious state
wakefulness with minimal awareness and responsiveness
(parts of the cerebellum and the cortex are affected)
sustain gaze at moving target
reach for offered objects
speak a few words
express appropriate emotional reactions to stimuli
locked-in syndrome
full wakefulness and awareness but nearly completely paralyzed
(only pons damaged)
Don't have any voluntary movement of limbs, face, throat, and horizontal eye movement.
Can move eyes up and down and blink.
total brain failure
criteria for this mental state:
1. Exclude reversible causes
2. look for some motor function
3. look for brain stem reflexes
4. conduct apnea test
EEGs and radioactive tracers (PET scans) can confirm this mental state
alzheimer's disease
-characterized by extracellular amyloid beta plaques and intracellular tau tangles in neurons
-patients live with memory loss and behavioral disturbances
-gradual loss of structure and function, beginning around hippocampus
-having a form of the APOE gene increases risk
parkinson's disease
-characterized by the loss of dopaminergic neurons in substantia nigra
-patients exhibit resting tremor, postural instability, and gait disturbances
-lewy bodies and alpha synuclein aggregates
-some genetic factors, but most cases are gene-environment interaction (like pesticides)
ectoderm
outermost germ layer; produces sense organs, nerves, and outer layer of skin
mesoderm
middle germ layer; develops into muscles, bones, and much of the circulatory, reproductive, and excretory systems
endoderm
innermost germ layer; develops into the linings of the digestive tract and much of the respiratory system
neurulation
the process by which the neural tube forms
1) neural plate elongation (day 17-18)
2) neural plate folds (day 20-22)
3) neural tube closes (day 25-27)
morphogens
A substance that provides positional information in the form of a concentration gradient along an embryonic axis. ex: retanoic acid - released from caudal, concentration indicates spacial position of nervous system
cortex
outermost covering of the brain consisting of densely packed neurons, responsible for higher thought processes and interpretation of sensory input
in development, layers of this are formed inside out
embryonic stem cells
undifferentiated cells that are totipotent (can become any cell type)
somatic stem cells
adult stem cells that are pluripotent (can become most but not all cell types)
ex: neural stem cells - can become neurons and other neural cells
iPS cells (induced pluripotent stem cells)
derived from differentiated cells that have received treatment to revert back to pluripotent immature cells
hippocampus
neural center involving memory
a larger structure of this allows for greater capacity
ex: London cabbie drivers have large _______s because they have increased _____ activity when memorizing + driving the streets of London
placticity
the brain's ability to change by reorganizing after damage or by building new pathways based on experience
ex: rats trained for specific frequencies will have different tonotopic maps
ex: the homonculus changes to give appropriate representation to body parts based on frequency of use
synaptic plasticity
the ability of a synapse to strengthen or weaken over time, depending on its activity. a greater synaptic strength will increase post synaptic response
AMPA receptors
which receptor should be increased in order to increase post synaptic response?
postsynaptic glutamate receptors:
NMDA receptors - open when glutamate binds AND the postsynaptic neuron is already depolarized
AMPA receptors - open when glutamate binds. when open, cations flow in
LTP (long term potentiation)
A long-lasting increase in neural excitability in synapses along a specific neural pathway. protein synthesis is necessary for this
visual cortex
The visual processing area in the occipital and temporal lobes. Both sides of this (aka visual fields) processes information from both the left and right eyes.