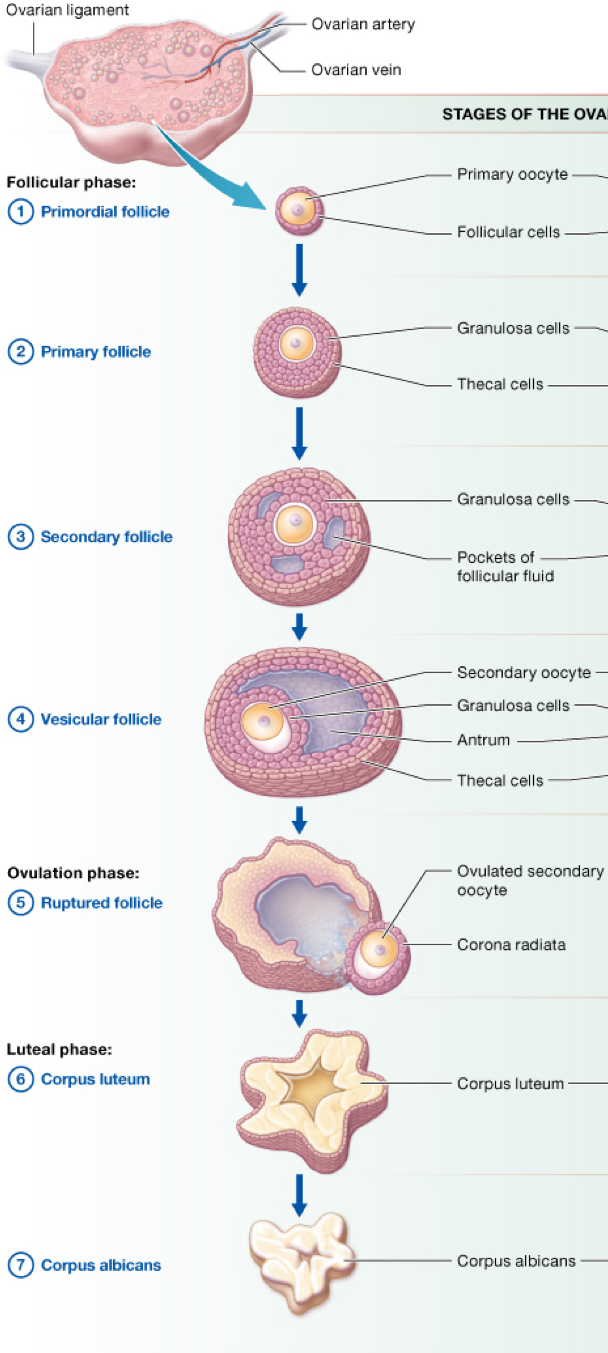
folliculogenesis
1/7
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
8 Terms
what is folliculogenesis
the development of the ovarian follicle in anticipation of ovulation
describe the steps that occur prior to birth
primary oocytes develop within primary follicles with consist of only a single layer of follicular cells. this remains unchanged in the ovarian cortex until puberty commences.
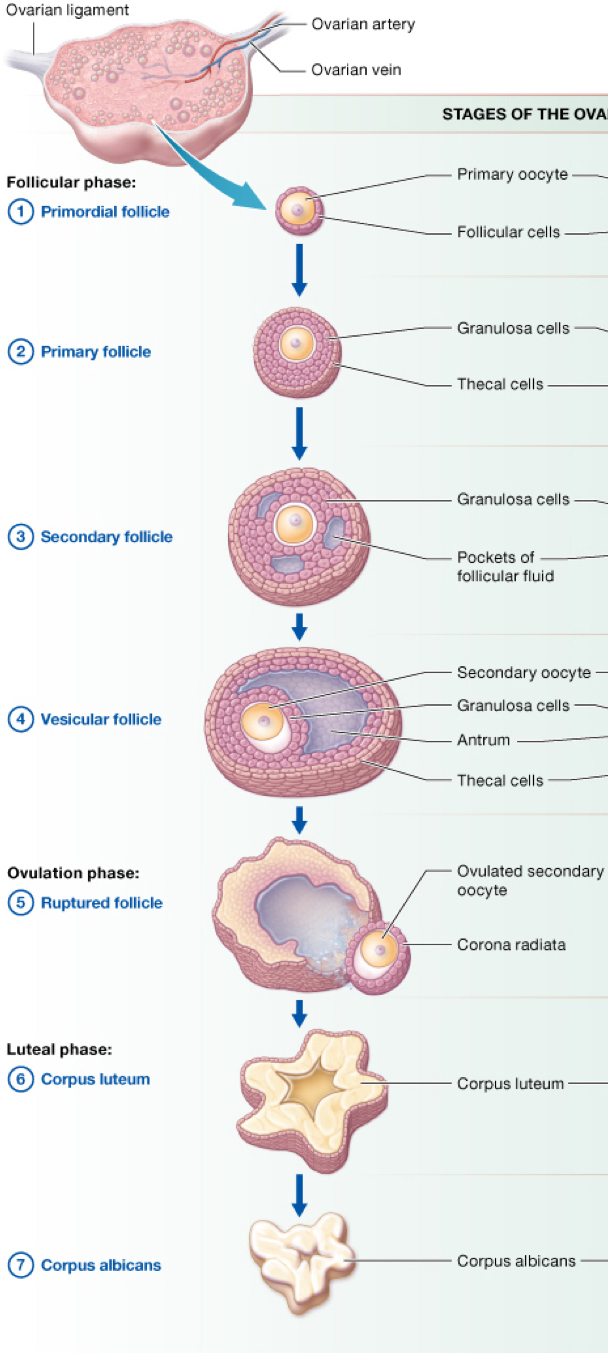
describe the steps that occur once puberty begins and meiosis I commences
the follicle changes into primary follicle the difference is that the follicular cells have thickened into a more cuboidal type of cell called a granuloses cell
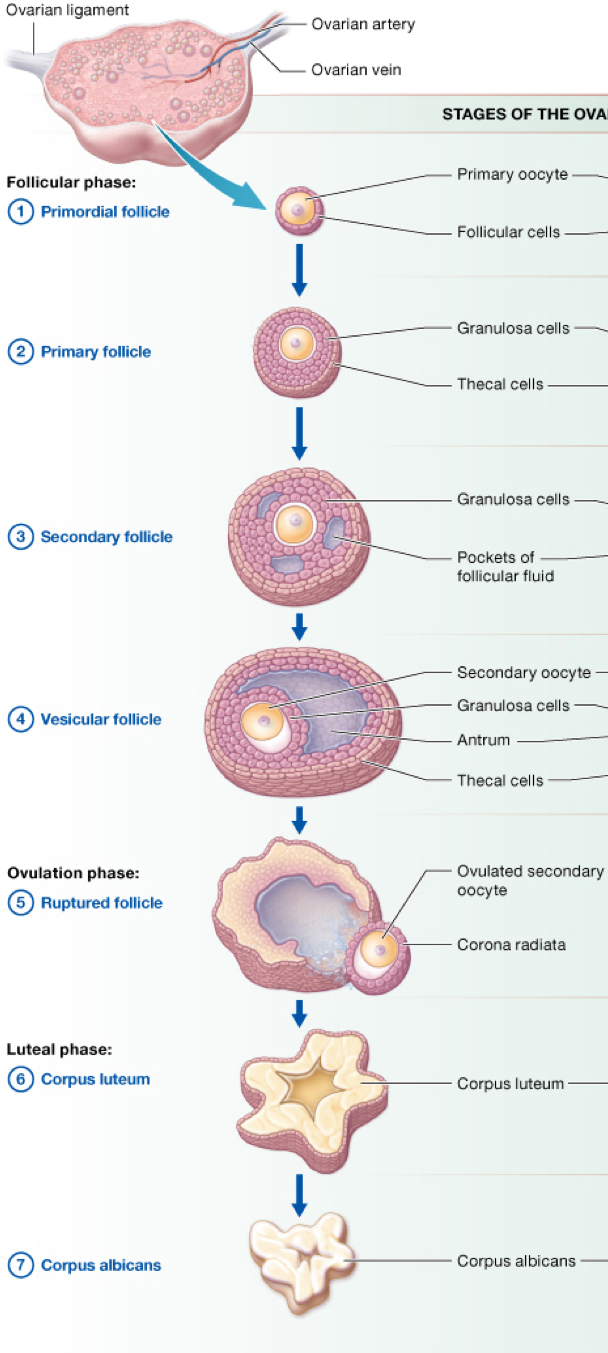
desribe the step that occure at the end of meiosis I
the new secondary oocyte is now housed in a secondary follicle and is surrounded by several layers including a clear zona pellucida, 2 layers of granulosa cells and an outer layer called theca folliculi cells
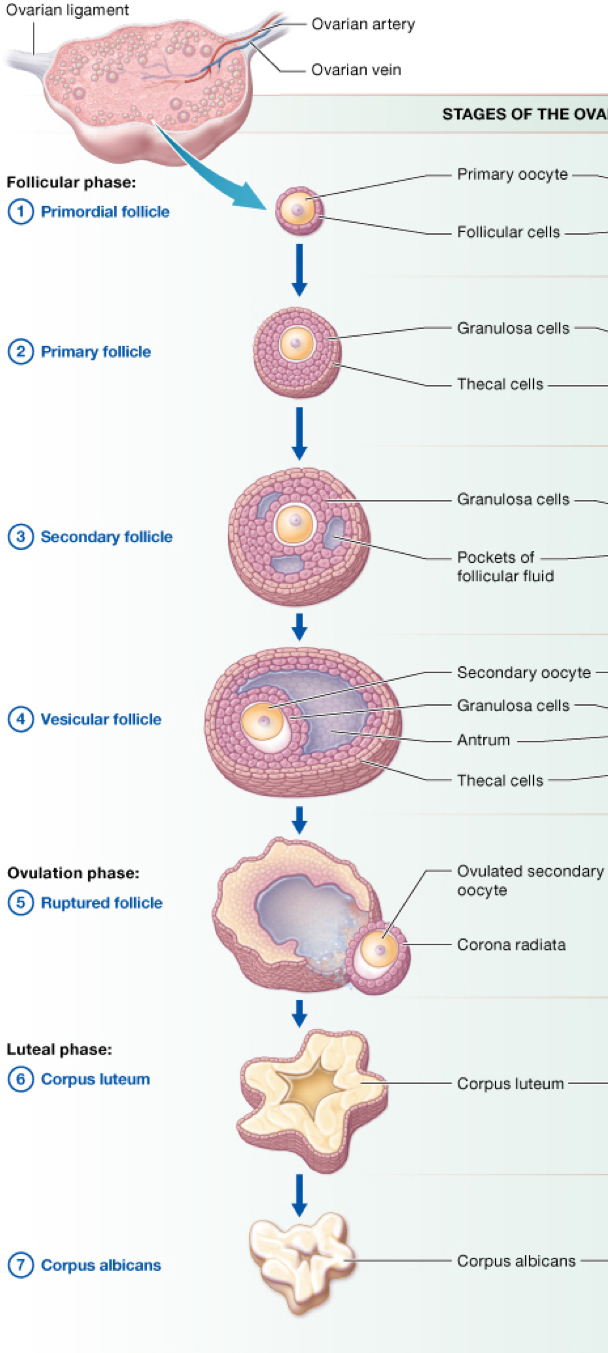
describe a tertiary follicle before ovulation
have several more layers including the zona pellucida and corona radiata cell (inner ring around ovum) a pool of estrogen and 2 layers of theca cells to protect the follicle
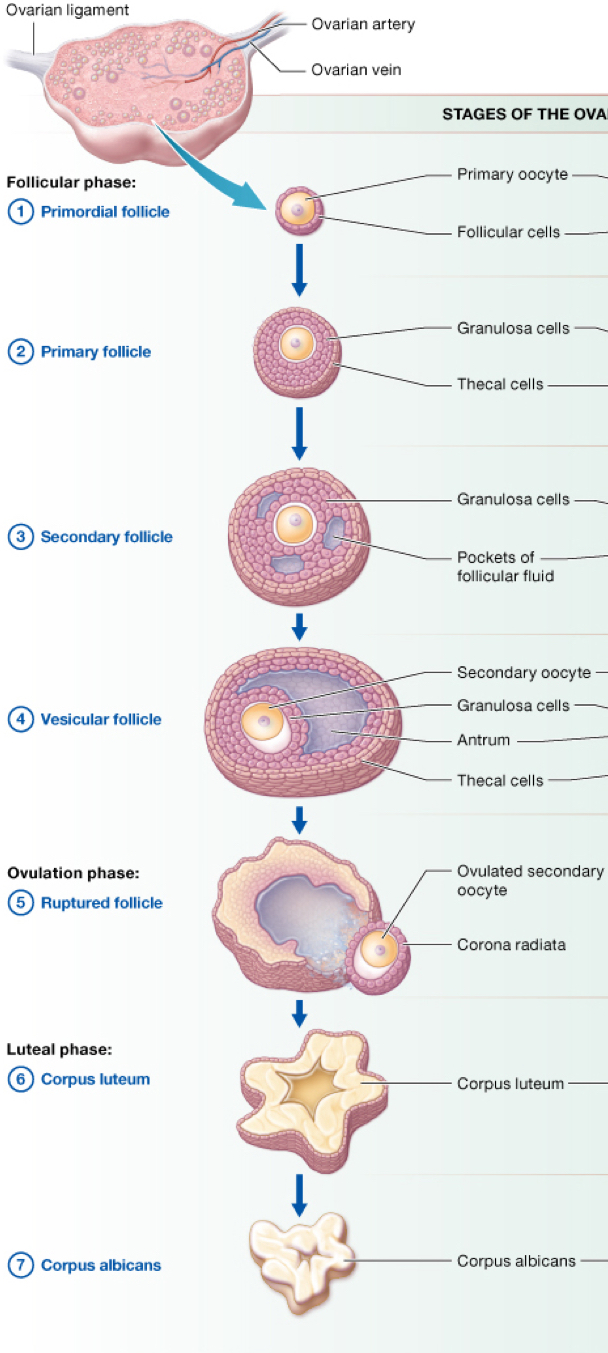
describe vesicular follicle during folliculogenesis
follicle is ready to be ovulated. as the egg is released the outer layer of granulosa cells bleed slightly into antral lake signifying successful release of egg (secondary oocyte still surrounded by zona Pellucidar and cumulus oophorous cells
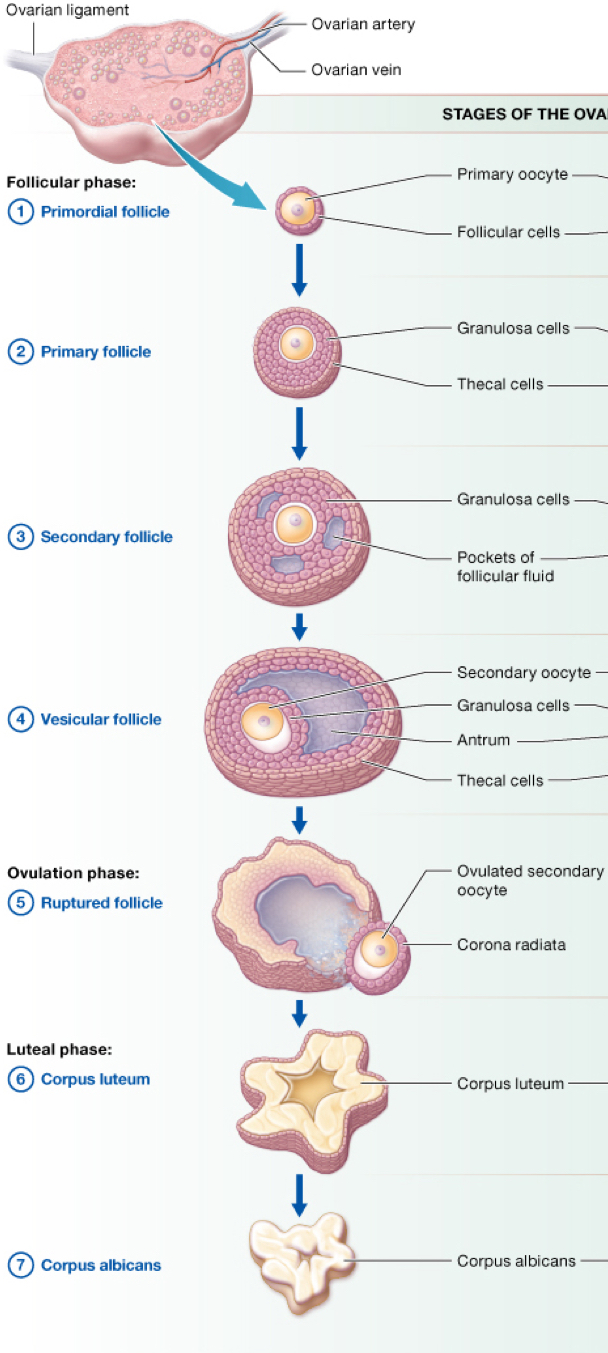
describe what happens during the luteal phase
the corpus luteum (remnant follicle) stays behind in the ovary releasing progesterone in order to sustain the oocyte and to signal the uterise to begin building up endometrium.
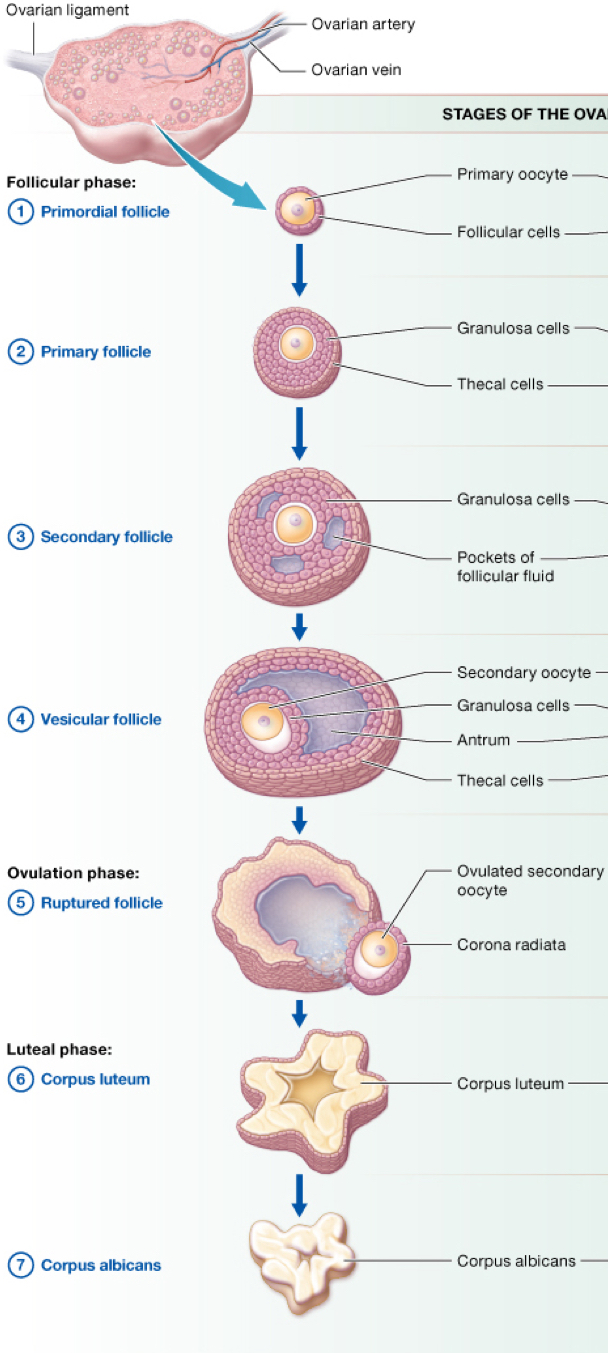
what happens if the egg is not fertilized
the corpus luteum becomes a corpus albicans which is a white fibrous scar