Liver A&P
1/55
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
56 Terms
Liver location
right hypochondrium and epigastric region (RUQ**)
Liver Functions
-filters blood
-detoxifies chemicals
-metabolizes drugs
-produces bile
how many lobes does the liver have?
2
Falciform Ligament
separates the right and left lobes of the liver and attaches the liver to the anterior abdominal wall
the right lobe of the liver is divided into _______ and _______ lobes
caudate and quadrate
The round ligament is a remnant of the ___ ___
umbilical vein
Glisson Capsule
fibroelastic capsule innervated by lower intercostal nerves
Distension of Glisson capsule can cause pain in liver dz
Porta Hepatis
-opening or fissure
-portal vein, hepatic artery proper, and hepatic ducts enter/leave the liver
Arterial supply to liver
Celiac trunk > common hepatic artery > hepatic artery proper > right and left hepatic arteries which then carry oxygenated blood to liver
Venous supply to liver
Hepatic portal vein > right and left branches that enter parenchyma
Blood rich in substances absorbed from GI tract (deoxygenated blood)
Hepatic portal vein is a convergence of _____ vein and __________________ vein and recieves _____________ blood that contains nutrients, drugs, etc
splenic vein; superior mesenteric vein; deoxygenated blood
Venous supply from liver
venous blood from liver flows through hepatic vein into inferior vena cava
Liver Lobules
-multiple in the liver
-made of hepatocytes
Hepatocytes
-functional cells of liver capable of regeneration
-secrete electrolytes, lipids, cholesterol, lecithin, bile acids into bile canaliculi
-synthesize plasma proteins which can be released into bloodstream
What are small capillaries btwn hepatocytes?
Sinusoids
-receive mixture of venous and arterial blood from branches of hepatic artery and hepatic portal vein
Central Vein
-where blood from the sinusoids drain
-located in the middle of each liver lobule (which then drain into the hepatic vein)
Subendothelial Space/space of Disse
-located between hepatocytes and sinusoid
-drains interstitial fluid into hepatic lymph system
subendothelial space (Space of Disse) contains _________ that regulate sinusoidal blood flow, participate in liver fibrosis, remove foreign substances from blood and trap bacteria
lipocytes (stellate cells) - contains Vit A
Sinusoids are lined with ___ and ____
permeable endothelium and Kupffer cells (macrophages)
sinusoids enhance transport of nutrients into ____
hepatocytes
Sinusoidal endothelial cells have Natural Killer cells that are important in our tumor defenses
Bile
alkaline, bitter-tasting, yellowish green fluid
Bile contains bile salts + …………..
cholesterol, bilirubin, electrolytes, and water
Bile salts are required for intestinal emulsification and ____________________
Absorption of fats
bile and bile salts are formed by hepatocytes and secreted into ___________
bile canaliculi - which empty into bile ducts and eventually drain into common bile duct
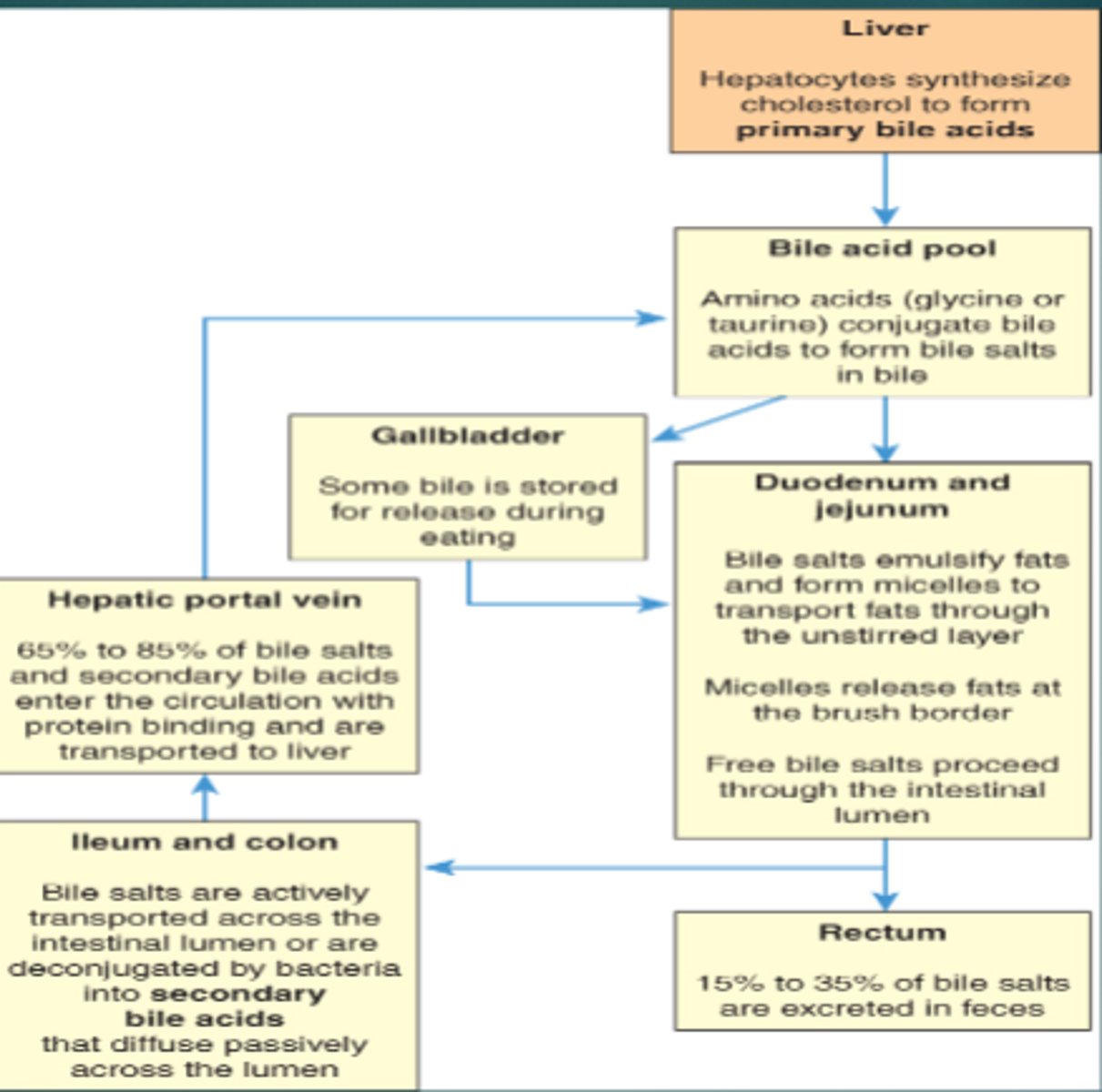
Primary Bile Acid Pool
-cholic acid, chenodeoxycholic acid
-made from cholesterol by hepatocytes
Bile salts are mostly absorbed in the _______________ and return to liver by the ______
Terminal ileum; portal hepatic system
Secondary Bile Acid Pool
-deoxycholic acid, lithocholic acid
-formed in intestines by bacteria
Enterohepatic Circualtion
recycling of bile salts
Billirubin is produced by the
destruction of aged RBCs and gives bile a greenish color and yellow tinge of jaundice
Unconjugated bilibrubin is…
lipid soluble (free) bilirubin > can cross membranes
Conjugated bilirubin
water soluble bilirubin > allows it to be excreted from body
conjugated bilirubin is deconjugated by bacteria in the distal ileum and colon to ________
urobilinogen (gives urine its yellow color and feces its brown color)
Stercobilin
gives feces brown color
Urobilin
gives urine its yellow color
Liver Heme Functions
-stores and releases blood
-synthesizes clotting factors (prothrombin, Factors 7,9,10)
Vitamin K
-essential for synthesis of clotting factors
-absorption depends on adequate bile production
2 functions of Liver Fat Metabolism
-hydrolyzes triglycerides
-synthesizes phospholipids and cholesterol
Hydrolysis of Triglycerides
-triglycerides broken into glycerol and free fatty acids
-produces ATP
-can be released into the bloodstream bound to proteins (lipoproteins)
where lipoproteins are stored
adipose cells
Phospholipids and Cholesterol are needed to produce ____
bile salts, steroid hormones, components of plasma membranes
what consumes aged RBCs in the spleen and liver
Macrophages (Kupffer cells in liver)
Heme
broken down into biliverdin and iron
Iron
attaches to transferrin and is stored in liver or used by bone marrow to make new RBCs
Bilverdin
converted to unconjugated bilirubin and released into plasma
unconjugated bilirubin binds to ______ for transport to the liver
albumin
bilirubin has to be _______ to be secreted in the bile
conguated
Protein Function
-muscle contraction
-energy source
-fluid balance
-immune protection
-regulation of chemical reactions and hormones
-structural support
-transport of molecules
-coagulation
Deamination
the removal of ammonia which converts amino acids into carbohydrates
ammonia is converted to ______ and excreted in the kidneys
urea
The liver synthesizes ___ and ____
plasma proteins (albumin, a/b globulins) and nonessential amino acids and serum enzymes (AST, ALT, LDH, GGT, AP)
liver releases _______ in states of hypoglycemia
glucose
liver takes up ______ in states of hyperglycemia
glucose
the liver stores glucose as __________ or converts it to fat
glycogen (glycogensis)
when all glycogen stores have been used, amino acids and glycerol are converted to glucose. What it this called?
Gluconeogenesis
vitamin stored in greatest quantity in the liver
Vitamin A
**D, B12, E, and K also stored
Ferritin
-how iron is stored in the liver
-stored when iron levels are high
-released when iron levels are low
Hepatic cells contain ____ that reversibly binds with iron to form ferritin
apoferritin
Metabolic Detoxification of the Liver
-alters chemicals (drugs), foreign molecules, and hormones
-makes things less toxic or less active (dec reabsorption which promotes intestinal/renal excretion)
-protective usually . End products can become toxins( ETOH > toxins (acetaldehyde and hydrogen)