AP Computer Science Principles: Unit 4
1/69
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
70 Terms
What is a bit?
a single unit of data that can only have one of two values (such as a 1 or 0)
What is a byte?
Eight bits (e.g.10110101)
What is bandwidth?
the transmission capacity of a system (measured by the amount of data (measured in bits) that can be sent in a specific amount of time)
What is latency?
time between the transmission and the receipt of a message
How can number storage limitation cause overflow errors?
Certain programs limit how many numbers they can store (e.g. if limit is 4 bits, then storage goes up to 1010). After a number that is long enough goes over the limit, it causes overflow, which returns an overflow error (e.g. infinity or NaN)
What are floating point numbers?
a binary version of scientific notation. It's called floating point because the decimal point "floats" to just after the first digit. (e.g. 2.1273647e+32)
How can floating points lead to round-off errors?
Floating points round off the last digits of a infinite/large number, which can cause a rounding that might be incorrect when manipulated (e.g. 1/3=0.3333, but when multiplied by 3, it states 0.99999 and not 1)
What does an ethernet cable use? What are its features?
It uses electricity to send bits. Best for close distances, but cheap and has potential signal loss

What does an fiber optic cable use? What are its features?
It uses light to send bits. Best for far distances, fast, and lower potential signal loss, but expensive and hard to work with
What is a web browser?
An app used to access web pages

What is an URL?
Uniform Resource Locator: an address for accessing specific web data located on a server

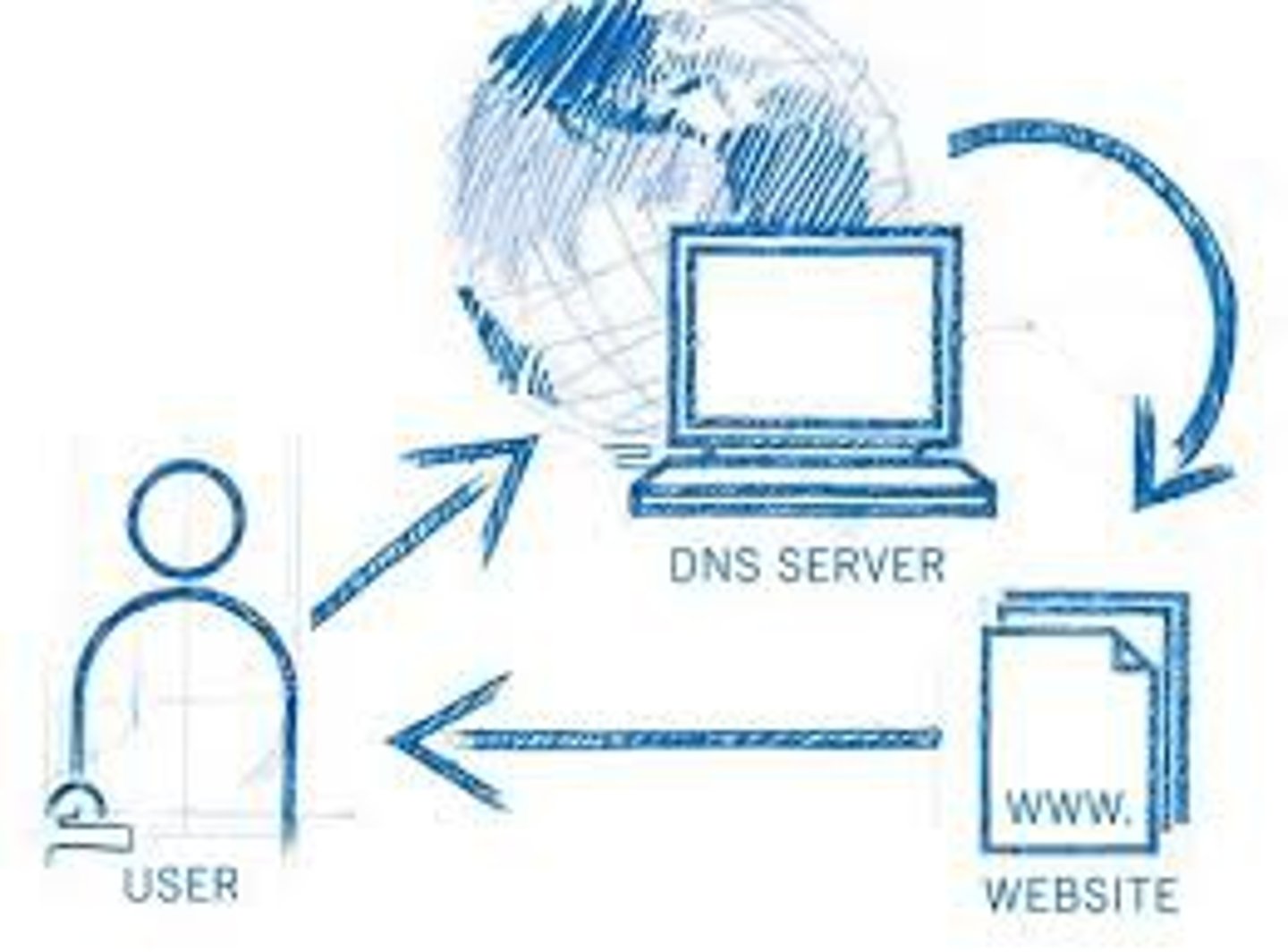
What is a DNS server?
Domain Name System server: a computer or computers hosting data for other to access
What is HTTP?
HyperText Transfer Protocol: language used to communicate between web browsers and servers

What is HTML?
HyperText Markup Language: language used to tell a web browser how to make a page look

What two components does HTML decide seperately?
(1) the text on the web page
(2) each seperate picture and video
(a seperate HTML code for every one of those)
What are the steps of accessing a web page?
(1) Open web browser
(2) type in URL or other
(3) HTTP code [get () request] is sent to DNS
(4) DNS returns HTTP containing HTML files to make up page
What is a cookie (computer science-wise)?
What websites use to remember who you are (like an ID card)
How does sending information on web browsers work?
(1) Input information (like google search or login)
(2) Information sent in HTTP "post" request
(3) Goes to domain name server
(4) Pertaining data sent back
(5) In returning data cookie is attached for website to remember user
(6) Next time server logs on when he sends information the cookie will be attached so domain server will know who it is
What is SSL and TLS?
Secure Sockets Layers: A layer of security wrapped around a user's communications to prevent snooping or tampering
Transport Layer Security: Successor to SSL
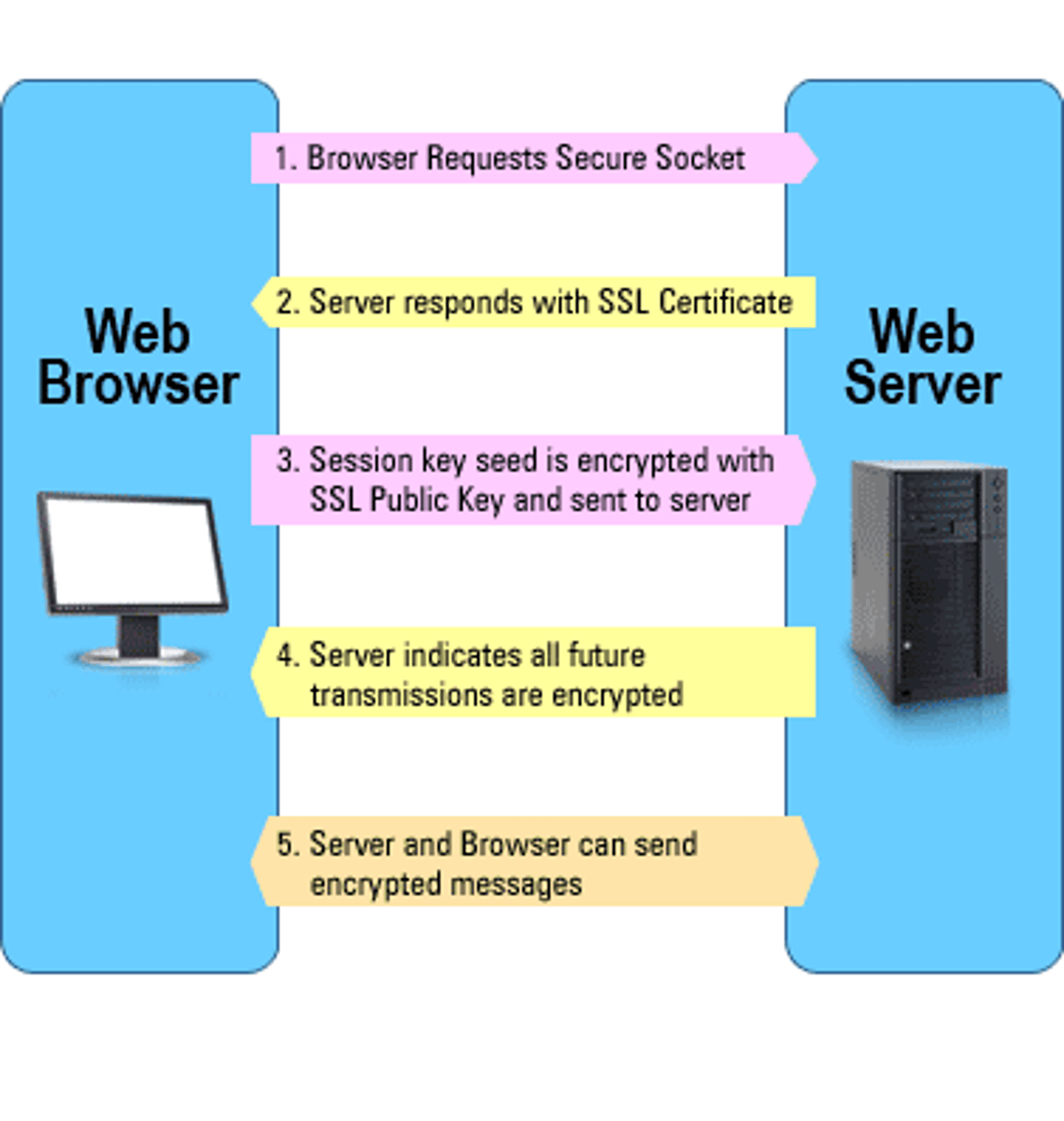
How does one know is SSL/TLS is active on their browser?
There would be a lock sign next to the URL

What is HTTPS?
HyperText Transfer Protocol Secure: Ensure HTTP requests are secure and protected
Why are digital certificates important in internet safety?
Digital certificates (issued by certificate authorities) ensure that the information being sent by a certain website is legit and also allows a secure SSL/TLS connection
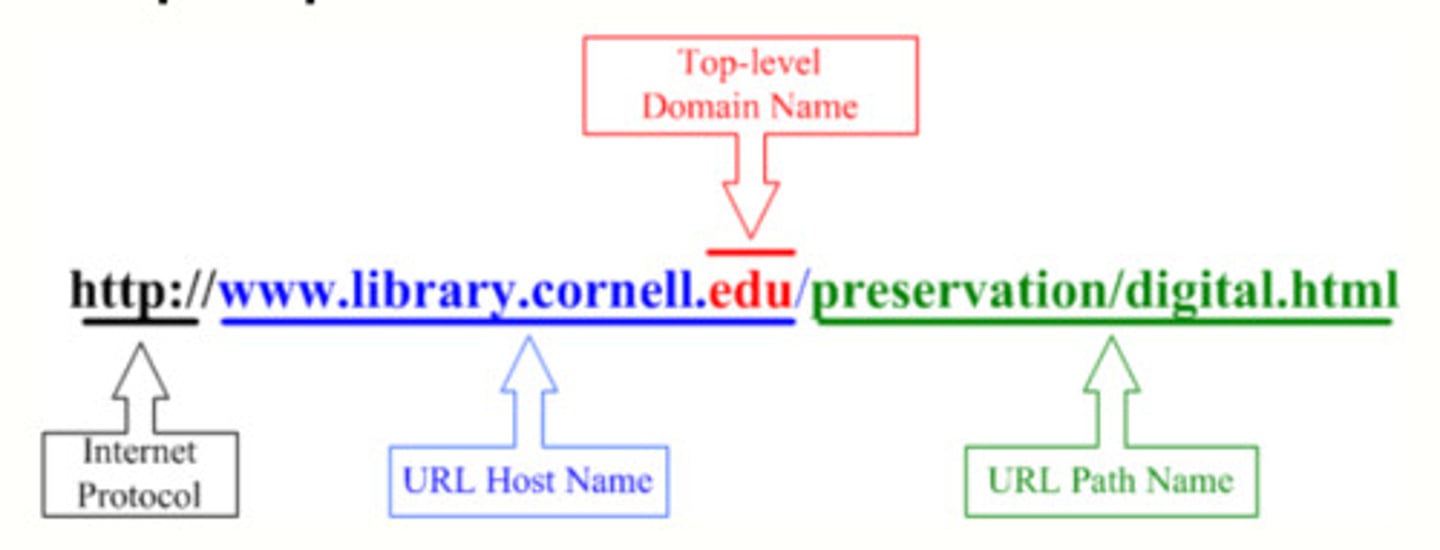
What are the three things that make up a URL?
Protocol: standard for communication between browsers and servers (usually http or https)
domain name: the name of the server that hosts the data
path: the location of the data in a hierarchy of folders on the server
How is the Internet designed to be redundant? Why?
There are multiple pathways among the physical connections of the Internet; If one or more pathways break down, there would still be another way to transmit a message from sender to receiver
How does Internet redundancy impact fault tolerance and scalability?
(1) It impacts fault tolerance (the ability to work around problems) by increasing the number of possible pathways.
(2) It increases scalability (ability to function even as size changes) by making the internet more expansive to more devices and people
How is the Internet hierarchal?
Two hierarchal internet addressing systems are domain named and IP addresses. They work like a postal system, getting more specific in each addressed step.
What are nodes?
Connections points that link pathways
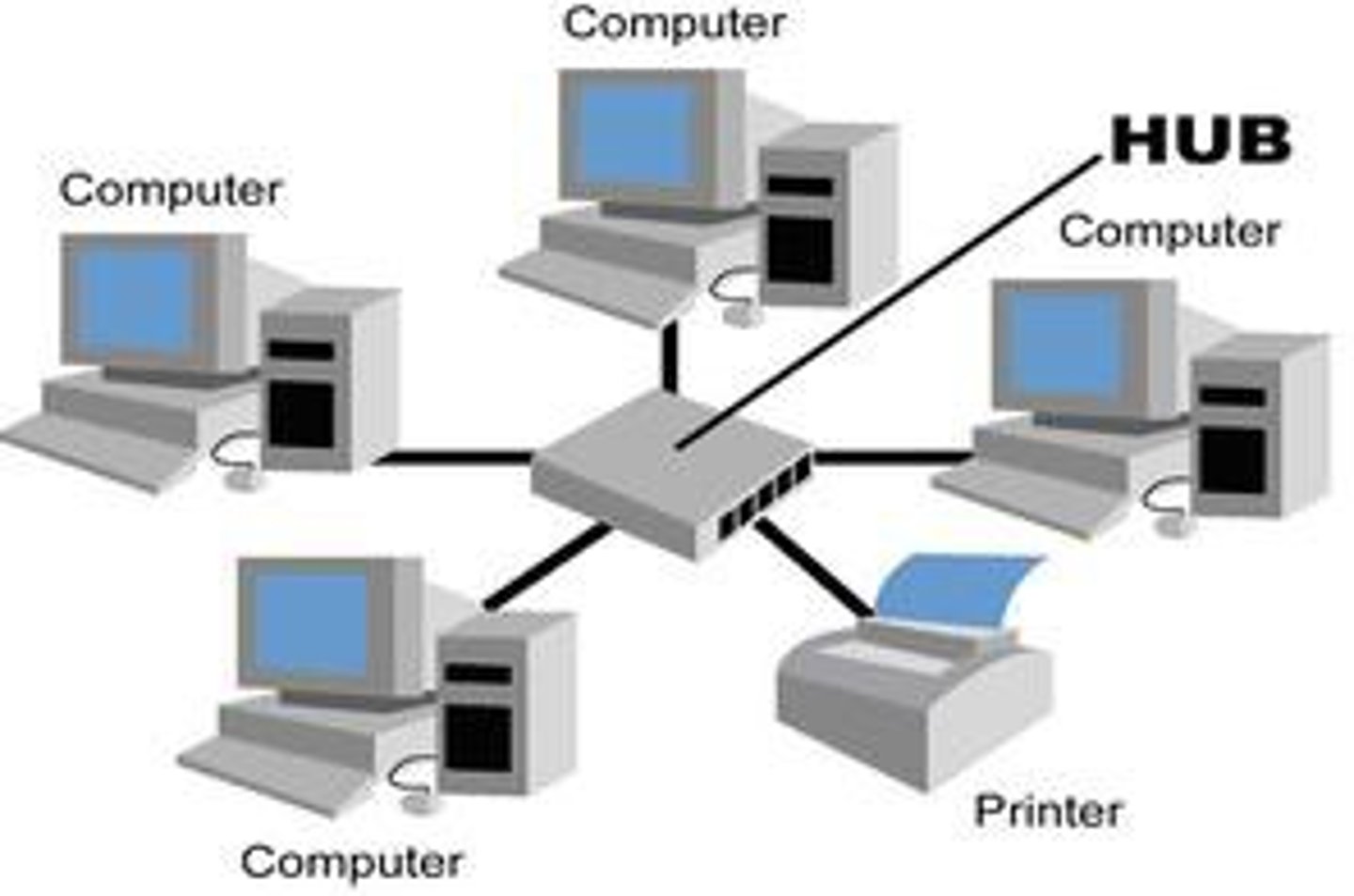
How are domain names and IP addresses related?
People use domain name to visit websites, and computers translate those domain names into IP addresses to locate and send data
What is a root domain, primary domain, and subdomain?
Root domains: top level (e.g. .gov, .edu, .org)
Primary domain: Segment after root (In the URL code it comes before (e.g. about.berkeley.com, about berkeley is the primary domain)
Subdomains: Subsections of the primary domain (e.g. the "about" section in the above address)
What is an IP address?
Internet Protocol (IP) address: unique numerical addresses assigned to every device on the Internet.
What is IP?
Internet Protocol: An addressing system that finds paths to distant computers
What is IPv4?
An IP address made up of four bytes
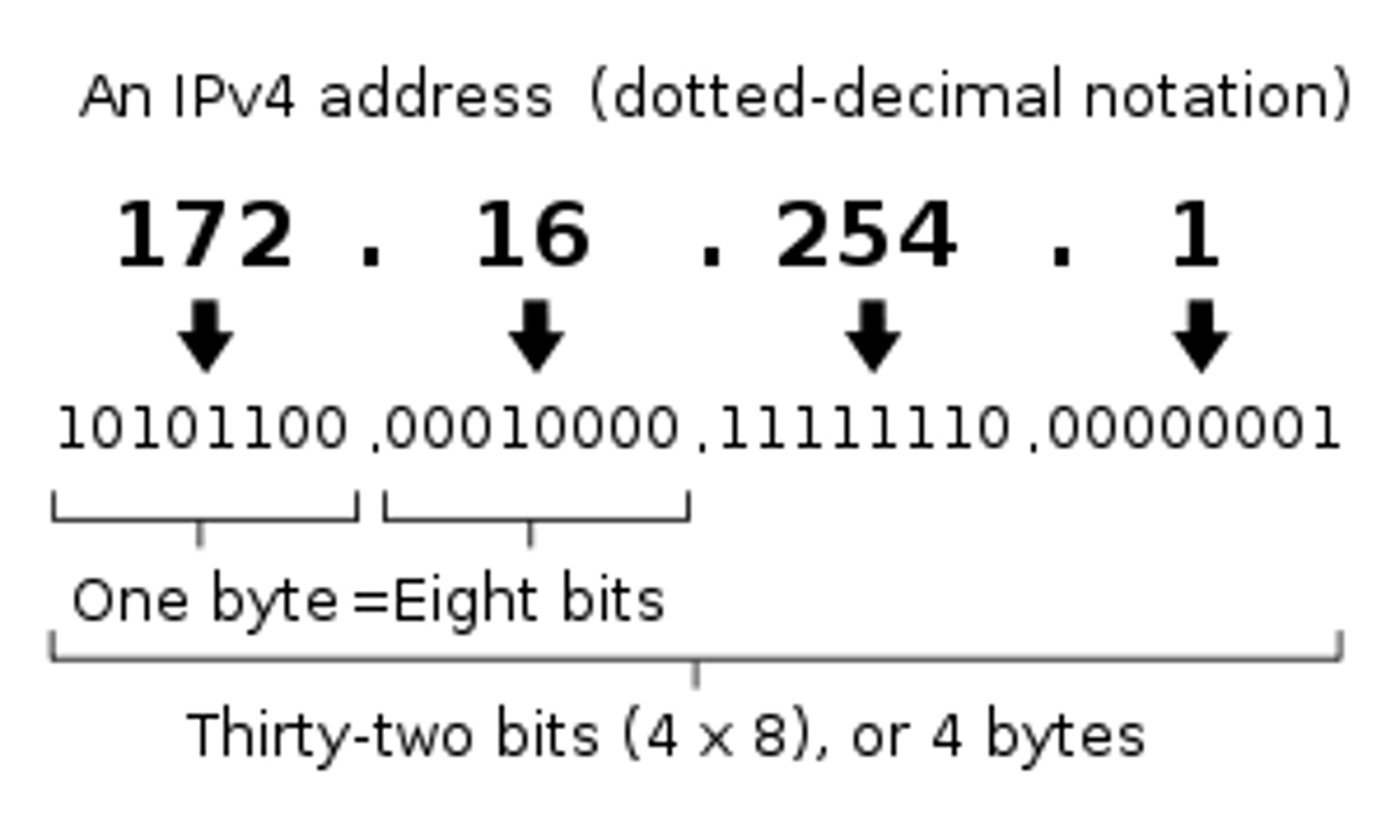
What is IPv6?
An IP address solution to the limit of the iPv4. It is made up of 128 bits summarized by hexadecimal
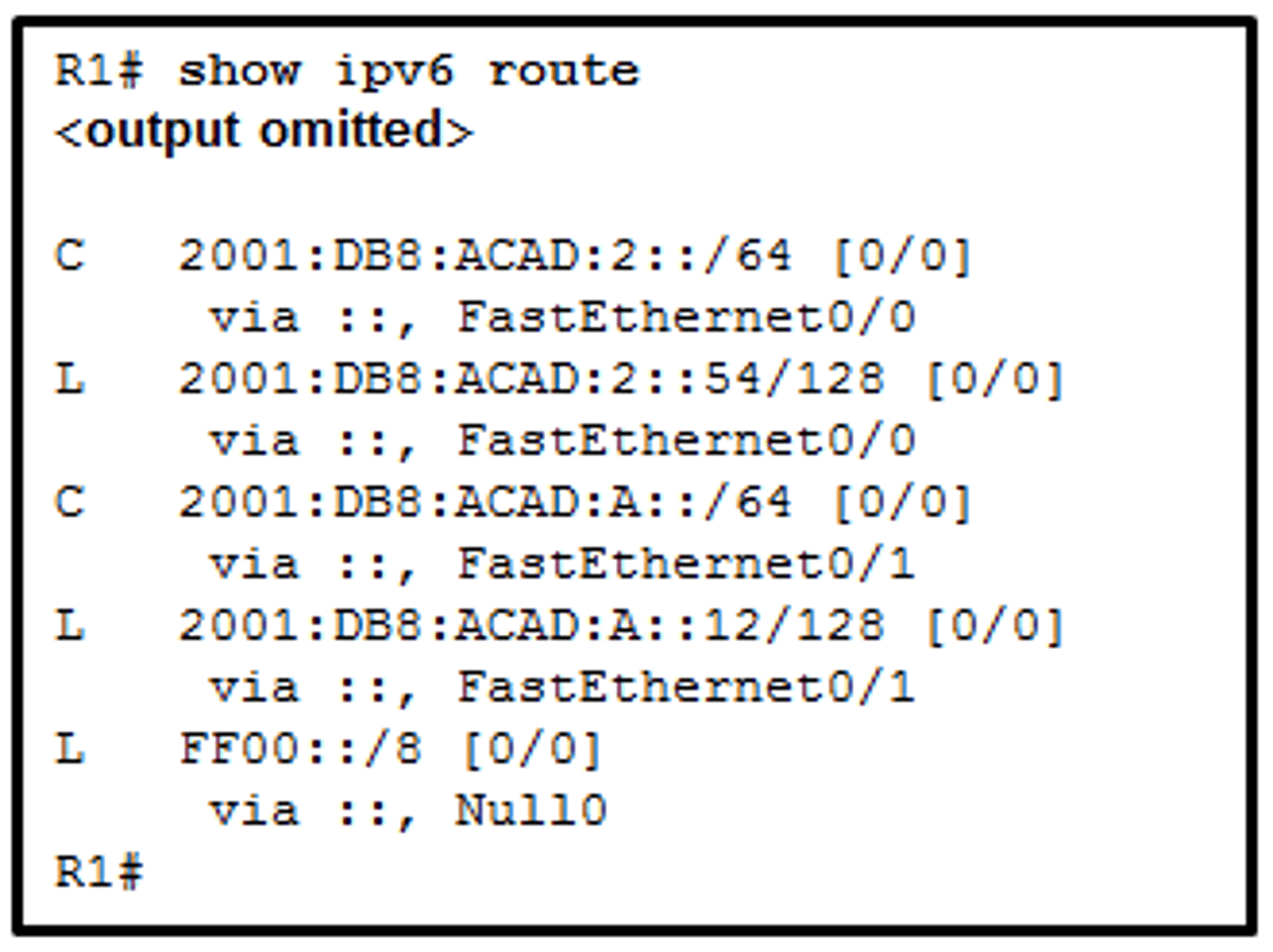
What is TCP?
Transmission Control Protocol: a reliable transmission system that sends and tracks binary sequences of data that are split into small packets sent seperately
What are packets?
Small chunks of one whole data sent individually throughout the web on their own path
What are routers?
Connection points that route traffic between subnetworks of the Internet. They choose the cheapest, most direct path for packets to travel.
What are some important dates to remember?
1969: Arpanet network (predecessor to Internet) launched
1974: TCP/IP protocols developed
1984: DNS established
1991: World Wide Web goes public
1995: Internet become commercialized
1998: Google launched and ICANN takes responsibility for controlling the internet
What are application layer protocols?
highest level of abstraction because they manage how data is interpreted and displayed (e.g. HTTP and DNS). Give meaning to bits sent by lower levels.
What are transport layer protocols?
manage breakdown and reconstruction of message into packets (e.g. TCP)
What are Internet layer protocols?
Manage the pathways that the data travel across networks. (e.g. IP)
What is the Network Interface Hardware (Link Layer)?
All Internet devices connect through a physical interface that uses ad protocol to manage the connection to the local network
What is the meaning of open protocols?
All the protocols are open standards so they can be looked up and coded to make new hardware or software without permission. This means that the internet relies on cooperation.
What is an ISP?
Internet Service Provider: Provides Internet connection
What is a packet-switched system?
System through with digital data is sent by breaking the data into packets that contain both the data being transmitted and the address routing the data.
What is SMTP?
Simple Mail Transfer Protocol: Standards used for directing mail around the internet
What organizations "control" the internet?
(1) IETF: Handles protocols approval and development
(2) ICANN: Controls DNS and IP address
(3) ISOC: In charge of IETF and other
How is the US related to control of the Internet?
The internet was under US control officially until 2009. Critics state that it still is (Edward Snowden Problem)
What is the ARPA and its history?
The Advanced Research Projects Agency (ARPA) developed network in 1968 called ARPANET (Predecessor to Internet).
What is malware?
Programs that try to affect your computer badly
What is a software virus?
A executable program usually installed unintentionally on a computer. Can spread to other computers
What is DOS?
Denial of Service: Hackers overwhelm a website with too many requests that makes it crash
How does a DDOS attack work?
Distributed Denial of Service attack: Hacker uses virus to take control of MANY computers. The infected network is called a botnet. The attacker then launches DOS attack from the infected computers (called zombie computers) to crash a website
What is phishing?
A spam e-mail purposed to hack
What is antivirus software?
Software used to prevent viruses from attacking
What are firewalls?
Limits the kinds of connections outsiders can make to your computer.
What is encryption?
Scrambling a message to make it unreadable to the unintended audience
How does the Caesar Cipher work?
An algorithm that shifts the message by a certain number
How does a substitution cipher work?
Each letter has a unique symbol (not just other letters)
How does a one-time pad work?
Each message is encoded with a new key only used one time
What is brute force decryption?
Trying every single possible combinastion
What is public key encryption (a.k.a. RSA)?
A cryptographic system that uses two keys -- a public key known to everyone and a private or secret key known only to the recipient of the message.
What is PGP?
Pretty Good Privacy: An encryption program that provides cryptographic privacy and authentication for data communication
What is the difference between symmetric and asymmetric encryption?
Symmetric: Same key used to encrypt and dencrypt
Asymmetric: Uses public and private key
What are the seven steps of Internet searches?
(1) Gather Info: Most important sites indexed first by spiders
(2) Keep Copies: Cache sites to have copies (once on web, not taking down)
(3) Build an Index: Stored in an order: makes searches faster.
(4) Understand Query: Portray results pertinent to search
(5) Determine relevance: Counts frequent words
(6) Determine Ranking: Quality matters
(7) Present results: Self-explanatory
What are the problems and solutions of digital divide?
Problems: Lack of infrastructure; lack of literacy/knowledge
Solutions: Online volunteering service; libraries
What are some examples of people being harmed on the internet?
(1) John Doe and his parents
(2) Ken and the bombings Issue
(3) Sidney Blumenthal
(4) Jane and John Doe issue
(5) The guy in Australia
What is DOPA?
Deleting Online Predators Act: The bill, if enacted, would amend the Communications Act of 1934, requiring schools and libraries that receive E-rate funding to protect minors from online predators in the absence of parental supervision when using "Commercial Social Networking Websites" and "Chat Rooms". The bill would prohibit schools and libraries from providing access to these types of websites to minors or create restrictions to use of these type of sites. The bill also would require the institutions to be capable of disabling the restrictions for "use by an adult or by minors with adult supervision to enable access for educational purposes.
What is defamation or digital libel?
Defamation is the general term for a legal claim involving injury to one's reputation caused by a false statement of fact and includes both libel (defamation in written or fixed form) and slander (spoken defamation).
What is the CDA?
The Communications Decency Act of 1996 (CDA) was the first notable attempt by the United States Congress to regulate pornographic material on the Internet.
What is the good Samaritan Law?
Protects ISPs from liability