homeostasis and cellular transport in Eukaryotic Cells
1/86
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
87 Terms
Plasma Membrane
A selectively permeable phospholipid bilayer forming de boundary of the cells
Substances that enter and exit
Including Ions, Proteins, Molecules, Solutes and liquids.
Two Layers
Of lipid molecules sheets
Hydrophilic
Each lipid has a sheet, with water-attracting side.
Hydrophobic
Water-repeling Side
Double-layer System
Allows the membrane to be selectively permeable
Hydrophilic & Hydrophobic disposition
Hydrophobic tall facing the interior Hydrophilic heads face the exterior and the cytoplasm
Selective Permeability
Allow several types of transport
Fluid Mosaic Model
Most common existing hypothesis of a cell membrane organization
The fluid aspect of the membrane is
The phospholipids are held together by hydrophobic interactions
The hydrophobic interactions of a membrane are
Much weaker than covalent bonds.
The membrane is made of
Different proteins clustered in groups and embedded in the fluid matrix of the lipid layer
Integral proteins and peripheral proteins are
Two mayor populations of proteins in the cell membrane
Integral proteins are called too…
“Transmembrane” Proteins because often span the entire membrane
The hydrophilic region of this proteins are…
In contact with the water in both sides of the membrane
The hydrophobic regions is
Between the lipids layers
What is the most important role of the proteins of membrane?
Transport
Description of the transport of proteins of membrane
Shuttle molecules and ions in and out of the cell
Function of proteins peripheral (aren’t a part of the cell membrane)…
These proteins add structure to the cells by binding with fibers
Another function of peripheral proteins are
They also serve like attachments site for enzymes or as cell-recognition site
Other componentes of the membrane mosaic
Carbohydrates or sugar molecules
Whit who bond the carbohydrates of membrane
Bond with either lipids or proteins of the cells membrane
Specialized sites on the cell surface
The carbohydrates bond with the lipids or the proteins form this sites that allow cells to recognize each other
What may do the carbohydrates of membrane?
Carbohydrates can tell the difference between body cells and foreign invaders
At the membrane level which of these proteins , carbohydrates or lipids simulates the immune system?
Carbohydrates
Passive transport
The movement of substances across a cell membrane whiteout the use of energy by the cell
How happen the Passive Transport
Spontaneously & Automatically
What the passive transport rate depends on on?
Permeability of the cellular membrane
Passive transport consists of
-Diffusion
-Facilitated Diffusion
-Osmosis
Diffusion
Movements of molecules from an area of higher concentration to an area of lower concentration
How long diffusion is?
Process continues until the concentration becomes equal throughout a space
Concentration Gradient
When the concentration of a substance on either side of the membrane are drastically different becomes a ….
What influence the concentration gradients
The direction in which a given substance will flow
What direction will a liquid take according to its quantity in two compartments ?
From the compartment with the most liquid to the one with the least
Regardless
Independientemente
Facilitated Diffusion
Involve transport proteins that can function as either channels or carriers .
Why the molecules are unable to pass through the pores of a selectively permeable membrane.
Because are to larges o due to their charge o polarity.
What are Transport Proteins
The Facilitated diffusion involves Transport Proteins, this protein function as either channels or carriers.
Channel Proteins
Molecules through the membrane (pores & channels) big for large molecules o with the polarity to accepts polar or charged molecules.
Carrier Proteins
Embedded in plasma membrane, this proteins bind to a substance and help it across the membrane. Generally specific for one substance.
What happens at the proteins carrier when insoluble molecules reach their receptors carrier ?
The Proteins undergo structural changes to allow the insoluble molecules to cross the plasma membrane. This process is called Facilitated Diffusion
Osmosis
Is the diffusion of water from areas of high concentration to areas of low water concentration across a selectively permeable membrane.
Diffusion can refer
To any number of particles or molecules.
What do the Osmosis to maintain homeostasis:
Move the water in whatever direction to equalize the concentration of water and any solutes present.
Which are the different types of solutions?
Isotonic
Hypotonic
Hypertonic
Isotonic Solution
The concentration of solutes within and outside the cell is equal. Water is moving across the semipermeable membrane at an equal rate in both directions.
Hypotonic Solution
The concentration of solutes outside the cell is lower than the concentration of solutes inside the cell. Water present outside the cell will move down its concentration gradient into the cell.
What can case a hypotonic Solution over the cell?
The cell will Swell o even Burst if the process occurs in excess.
Hypertonic Solution
The concentration of solutes outside the cell is higher than the concentration of solutes inside the cell. Water will move down its concentration gradient into out of the cell, causing the cell to Shrink.
The Osmotic Pressure is caused by…
Difference in water concentration within and outside of the cell.
-Diffusion
-Facilitated Diffusion
And Osmosis are forms of passive transport
Meaning they requiere No Energy
Active transport occurs …..
When cells must use energy to move molecules, ions, proteins, liquids or solutes into regions that already have a high concentration of these substances.
Why is different Passive Transport and Active Transport
The first one the substances follow their concentration gradients. While the second one the cells use Energy to move substances against their concentration.
Why is importan the Active Transport?
To Mantain a Membrane Potential
Membrane Potential
Voltage Difference , between one side of the selectively permeable membrane and the other.
The Membrane Potential is the Difference on (Voltage) on the Cells
The Difference between the two sides typically falls between -40 and -80 millivolts.
How is the charges observed inside the cel.
Cells typically are more negative on the inside than the outside. Due to a higher concentration of a negative ions.
How Active Transport Contributes with the Membrane Potential ?
By Pushing Ions and other molecules against their gradients.
Mention some tiles of gradients
Chemical Gradient
Electrical Gradient
Electrochemical Gradient
What is the Electrochemical Gradient ?
Are the Combined Effects of electrical and chemical effects
Electrochemical Gradient Means..
Means that Electrical and the Chemical Gradient have and effect on the movement of substances.
Which direction can Encourage the Chemical & Chemical gradients?
Could be in the same direction or they may negate (one gradient opposed another)
How is the interaction between the Active Transport & the Electrochemical Gradient
By expending energy in the form of Adenosine Triphosphate
ATP
Electrical Gradient
Is the difference in the concentration of electrical charges on either side of a membrane.
Sodium-a Potassium Puno
This one facilitates active transport and regulates internal cellular physiology by monitoring the levels of of sodium and potassium ions.
Why are important sodium & potassium in the cell.
Both are integral to optimal functioning within the cell, to metabolic functions, and to signal transmission.
The Sodium-Potassium pump works to keep
The concentration of Potassium inside the cell high and the concentration of Sodium inside the cell relatively low.
How is the concentration of Sodium & Potassium outside the cell.
Potassium = Low
Sodium = High
The Cell remain more negative because of
The Sodium-Potassium pump
Why is important the cell remain Negative
Signal Transmission
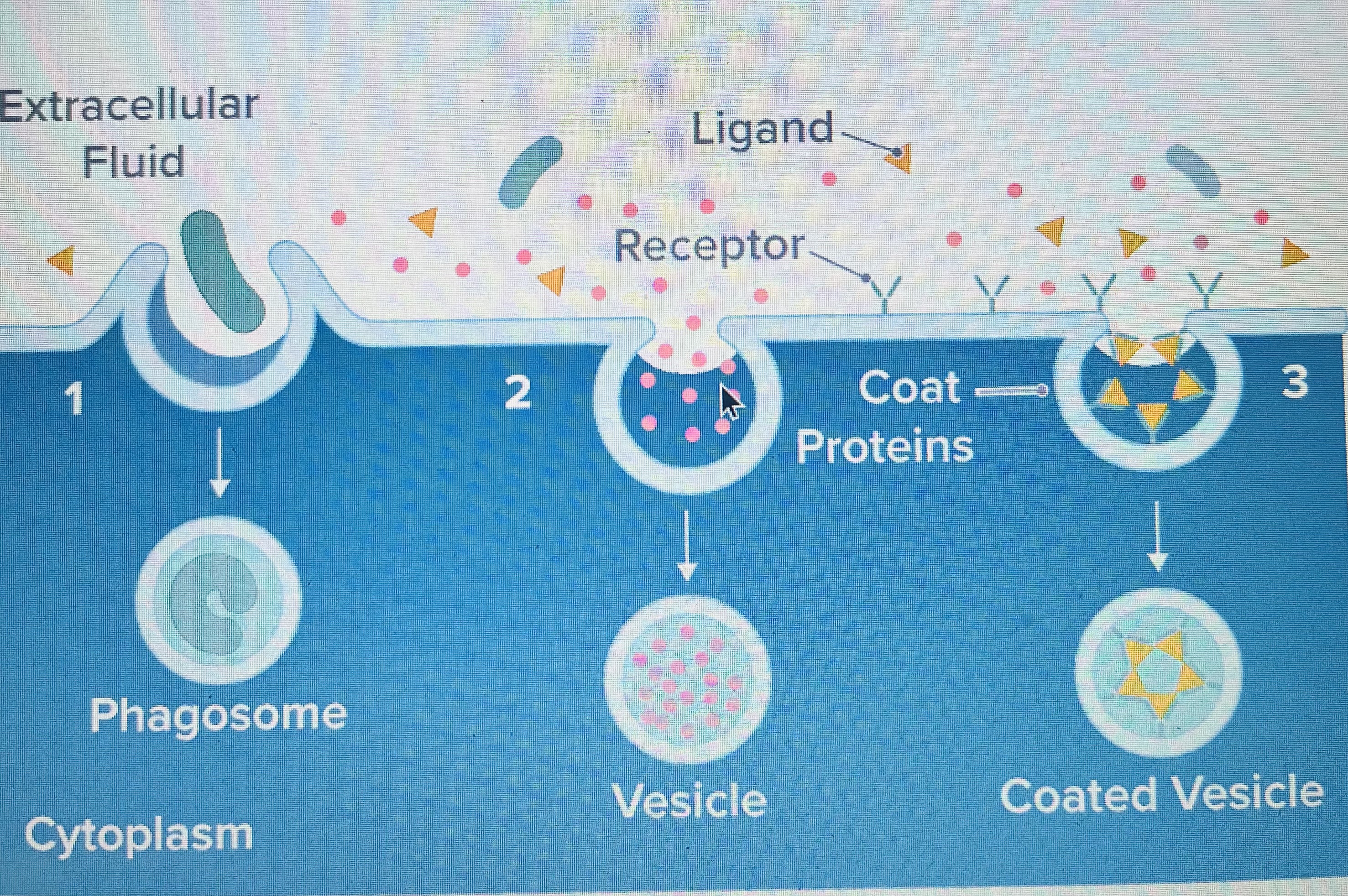
1 Phagocytosi
2Pinocytosis
3Receptor-Mediated
Cell Eating
Cell Drinking
Endocytosis
Phagocytosis
Is the movement of food or other particles through the cell membrane
What Phagocytosis consist of
The cell membrane encases the partí cles in a package called a food vacuole.
What happens with the food vacuole after the Phagocytosis?
The Vacuole fuses with a lysosome and the enzymes break the food into a usable materials for the cell.
Pinocytosis
When the plasma membrane wraps itself around liquid outside the cell.
Pinocytosis (Liquid)
In this case , the cell isn’t absorbing a solid particle but rather dissolved molecules and ions.
Pinocytosis is not…
Pinocytosis is nonspecific, and everything dissolved is brought into the cell.
Receptor-Mediated
Endocytosis
It is more specific than Pinocytosis and requires the recognition of the molecule by receptors on the cell membrane.
How work the receptors
In the Endocytosis
These receptors point to the outside of the cell and create pits in the cell plasma.
How work the drugs
“Trojan Horse”
Make the drugs HITS these receptors on cancer cells.
Drugs target cellular processes that led to death the cell.
Homeostasis
Tendency of living things to mantain a steady state.
Negative Feedback Loop
To stop or reverse the effects of the stimulus
Positive Feedback Loop
Enhance the Stimulus
Sodium-Potassium Pump
Uses ATP To move
3 Sodium to outside
2 Potassium to inside
Endocytosis
Bulk transport of
Food
Molecules
Liquids
Endocytosis
use three different ways
Phagocytosis
Pinocytosis
Receptor-Mediated Endocytosis