5. Intro to Software Security
1/5
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
6 Terms
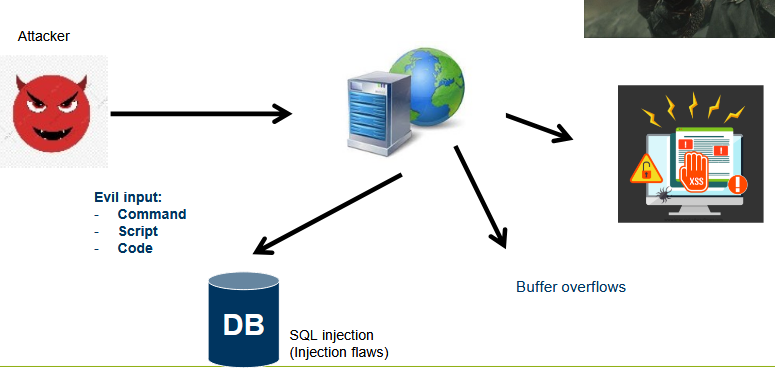
What is the most common Software Security Flaw?
No input validation
What are the 2 input validation strategies?
Syntactic → Enforce correct syntax of structured fields (e.g. data, number, string).
Semantic → Enforce correctness of given values in specific context (e.g. start date is before end date).
What are the 2 techniques for input validation?
Blacklisting:
Specify (parts of) inputs that are forbidden.
Hard to cover everyt
Client vs. Server-side validation
Server-side:
Requiered for security.
Client-side:
Can be controlled by attacker.
Validation can improve user response & lower server load.
=> But all validation from client must be redone at server!
What is the Morris Worm and how did it work?
First self-replicating malware.
Used “Finger” (Unix) to see who is logged into a remote system. Read username from network and copied it into a 512 byte buffer.
Morris Worm sent 537 bytes, overflowing the buffer and overwriting the return address → Pointed to executable.
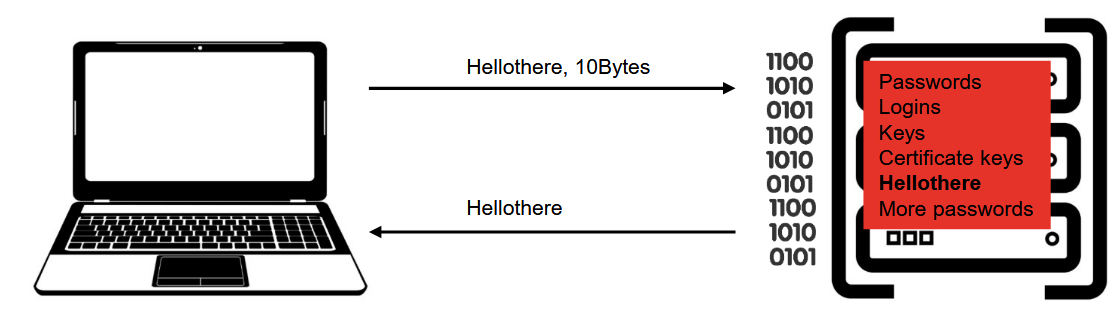
What is the Heartbleed bug and how did it work?
Bug in the OpenSSL Hearbeat implementation.
Intendet use: Server replies with sent input of sent size.
Problem: Users could specifiy sizes larger than the actual input → Data leakage.