Comptia A+ Core 1 .0: Mobile Devices
1/86
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
87 Terms
What are the two most common laptop batteries?
Do they have memory effect?
What is memory effect?
How should you charge batteries that have memory effect?
How should you charge batteries that don’t have memory effect?
Despite ______ and ______ not having memory effect, does their capacity still diminish over time?
Are the form factors for _________ and ________ the same for all laptops?
The two most common laptop batteries are
Lithium-ion (Li-ion)
Lithium-ion Polymer (Li-Po)
Li-ion and Li-Po have no memory effect
Memory effect occurs in Nickel-Cadmium and Nickel-Metal Hydride batteries and they gradually lose their maximum energy capacity if they are repeatedly recharged after being only partially discharged.
Batteries that have memory effect should be fully discharged before recharging them
Batteries that don’t have a memory effect should not be fully discharged as this will put stress on the battery. Discharge no lower than 20% and don’t leave charging at 100% for long periods of time, this will help preserve battery capacity over time.
charging a Li-ion or Li-Po still diminishes capacity slightly over time
different form factors for each laptop
note: some laptops have battery protection mode, which allows you to leave the charger plugged in but doesn’t keep charging after it hits the 100% mark, will only begin charging after certain threshold, like 40%
note 2: also avoid fast chargers as your daily charger
Laptop Keyboard
Is it easy to replace?
most used LT component
easy to replace (but not always simple)
single ribbon, few screws
Alternative: USB keyboard, but not as portable
Laptop Special Function Keys
What are functions keys? How many are there?
Fn Keys (F1 - F12) are special keys used to save keyboard space on a laptop by adding secondary features when used in combination with the Fn key or Num Lock key.
What type of memory (RAM) do laptops use?
Is it easy to replace?
Are different versions of RAM compatible with each other? Why?
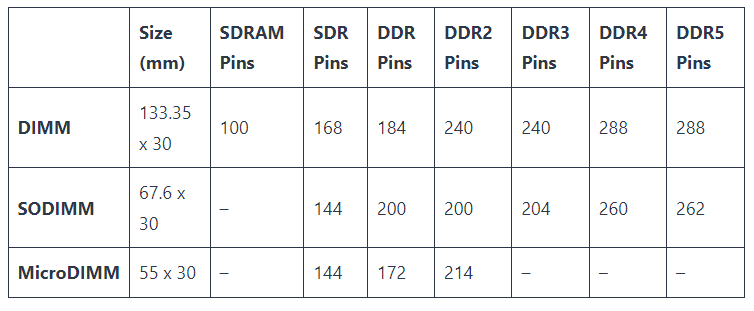
laptops use DDR - double data rate - memory, but in a miniaturized version called SO-DIMM
SO-DIMM : small outline dual in-line memory module
easy to install and replace
sometimes soldered to the system board
no upgrade available
will need full system board replacement
different versions of SODIMM are not compatible, the notch on the RAM module prevents the installation of incompatible memory types. Different RAM versions also have different pins
Laptop Storage
What are the four main laptop storage options?
Many of these drives use what type of computer bus interface? What was used before it?
How many pins does this computer bus interface use?
The four main laptop storage options for Laptops are
Magnetic Disk
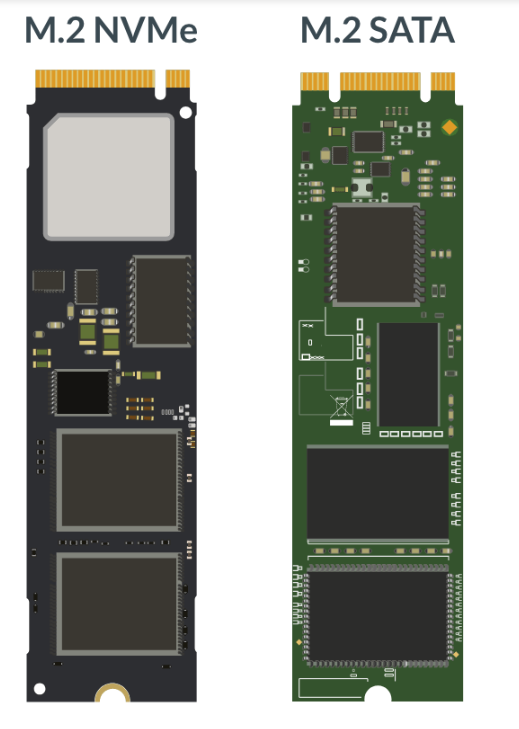
SSD (solid-state drive) (includes M.2 NVMe drives)
M.2
Hybrid
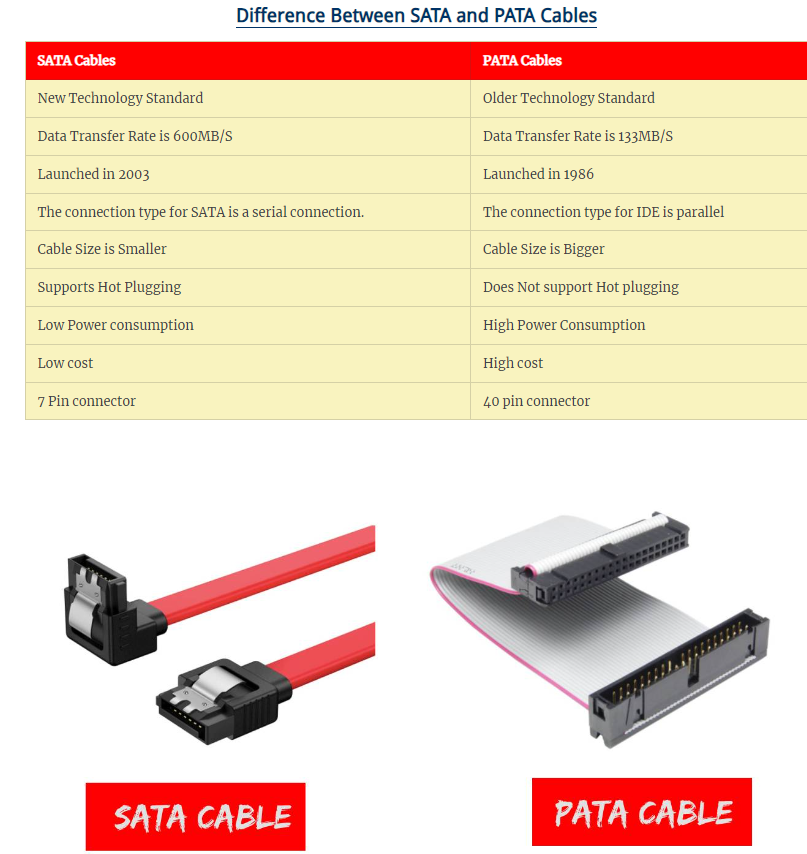
Many laptops now use Serial ATA (SATA) drives. Before SATA many drives and optical drives used Parallel ATA (PATA). NVMe doesn’t use SATA, instead it uses PCIe, which is faster.
SATA drives have two connectors: a 7 pin data connector and a 15 pin power connector
Replacing Laptop Storage
all internal; open a cover on the back or entire LT
can be very modular, two screws and the drive slides out
M.2 drives are even easier tore place; one screw only, similar to ram installations
Common SO-DIMMs found in laptops
SO-DIMM DDR2
module format: 200 pins
data rate:
bandwidth:
voltage: 1.8V
SO-DIMM DDR3
module format: 204 pins
data rate:
bandwidth:
voltage: 1.5V (1.35V for DDR3L)
size: 30mm high, 3.8mm thick, 67.6mm wide
not forward compatible with DDR3L slots
SO-DIMM DDR3L (low voltage version)
module format: 204 pins
data rate:
bandwidth:
voltage: 1.35V but also supports 1.5V
size: 30mm high, 3.8mm thick, 67.6mm wide
common for laptops to reduce power consumption
has PC3L
backwards compatible with DDR3 slots
SO-DIMM DDR4
module format: 260 pins
data rate:
bandwidth
voltage: 1.2V
size: 30mm high, 3.8mm thick, 69.6mm wide
SO-DIMM DDR5
module format: 262 pins
data rate:
voltage: 1.1V
size: 30mm high, 3.8mm thick, 69.6mm wide
Migrating from HDD to SSD
Install an OS on the SSD
move user documents between drives
install any required applications
can be time consuming
Image/clone the HDD using an image file
no OS installation needed
move everything from one to the other
imaging software required
sometimes included with the SSD
many commercial and open source options
when you create an image/clone file of the HDD you can use that image to create a single or multiple copies across multiple systems
Drive to Drive Image (direct drive cloning)
copy the HDD directly from one drive to the other, sector by sector, so both drives must be running simultaneously., No image file required.
What is 802.11?
802.11 enables the creating and operation of _______________
How are these wireless connections made?
Name all the different versions of 802.11
Do laptops have an Fn key to turn off and on WiFi?
What form factor does 802.11 use?
Refers to a set of wireless networking standards created by the Institue of Electrical and Electronics Engineers (IEEE) that define how wireless devices communicate over Wi-Fi networks
enables the creation and operation of WLANs (Wireless Local Area Networks)
wireless connections are made with an internal Mini PCIe card or Mini PCI
802.11 has multiple versions; 802.11a, b, g, n, ac, and ax networks
most laptops have an Fn key to turn off and on WiFi
can use the M.2 form factor (usually has one antenna for each technology or the mini PCIe
Bluetooth allows devices to connect _____________ and exchange data over____________ ______________.
What is the range of Bluetooth devices?
What type of network does Bluetooth allow you to create or join?
What frequency does BT operate on?
How does Bluetooth connect to a device?
What form factor does BT use?
allows devices to connect wirelessly and exchange data over short distances
class 1: highest power, transmits up to 100 meters (328 feet)
class 2: common in consumer electronics, transmits up to 10 meters (33 feet)
class 3: lowest power, transmits up to 1 meter (3 feet)
BT creates or allows you to join a personal area network (PAN)
uses 2.4 GHz frequency band, similar to Wi-Fi, but consumes lower power
requires device pairing
can use the M.2 form factor (usually has one antenna for each technology)
Cellular
What type of network does cellular allow you to join or create?
Through what module is cellular connection made?
wireless wide area network (WWAN)
connection can be made with either Mini PCIe or M.2 cellular modules, sometimes through USB based devices
NFC
Is NFC two way or one way communication?
Is NFC short range or long range communication? How far?
what is NFC used for?
What radio frequency does NFC use?
What is the data rate of NFC
What devices is NFC common on?
Can it be used as a payment method?
Can it be used as an alternative to using a password?
Is NFC risky to use?
Will airplane mode disable NFC?
Near Field Communication
two-way communication
short-range communication; 4 cm or less (touching)
data transfers, authentication, payments
NFC uses 13.56 MHz
can transmit 100 to 400 kb/s. Slower than Blue-tooth
common on mobile phones and smart-watches
can be used as a payment method
can be used as authentication to not require a password
can be risky, can be hacked, might need to be disabled in the OS
Airplane mode will disable it and all wireless transmissions
What is two factor authentication? How does it differ from biometrics?
What are the 2 most common types of displays a laptop might use?
LCD (liquid-crystal display)
TN (twisted nematic) - older, cheaper, worse color
IPS (in-plane switching) - much better color and viewing angles
VA (vertical alignment) - less common in laptops, more in TVs
OLED (organic light-emitting diode) - high end laptops
LCD
a flat-panel display that consists of two sheets of ____________ _____________surrounding a layer of _________ _____________ ___________
LCD with cold cathode fluorescent lamp backlight
How does it connect to the mother board?
How does it get it’s power? What type of voltage does it use?
How much power do they use compared to newer displays?
Are LCD with CCFLs still common in laptops?
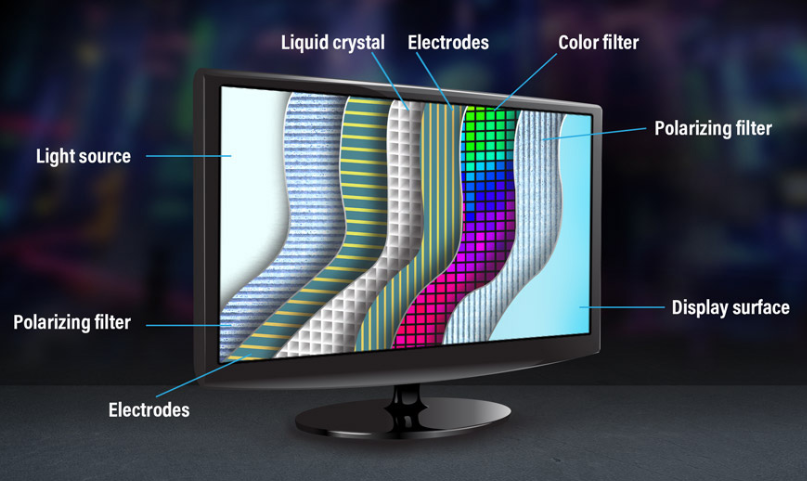
a flat-panel display that consists of two sheets of polarizing material surrounding a layer of liquid crystal solution
connects to mother board using a flex ribbon cable or all-in-one power/signal cable
gets power from inverter board, which turn DC to AC. Uses AC voltage.
generate a small amount of heat and very little interference but still use more electricity than newer types of displays. This is because it utilizes a high-powered bulb, cold cathode fluorescent lamp (CCFL)
Nowadays, most LCDs use LEDs. CCFL displays are outdated and bulky and are no longer common on newer laptops.
note: most LCD screens are thin-film transistor (TFT) active matrix displays (they have multiple transistor for each pixel) and these transistors are located behind the liquid crystal solution.
note: remember that the light source is behind the liquid crystal solution and behind panel
LCD
What are 3 advantages of LCD’s?
What are 3 disadvantages of LCD’s?
Advantages:
lightweight
relatively low power
relatively inexpensive
Disadvantages:
black levels are a challenge
requires a separate backlight, LED ( older models require florescent and therefore an inverter)
lights are difficult to replace
TN (Twisted Nematic) LCD
Use liquid display crystals that can ________ to allow _______ to pass through.
How is the color accuracy?
How is the contrast?
How are the viewing angles?
What is their response time?
What is their refresh rate?
What is their cost effectiveness?
Is it still used today?
Use liquid display crystals that can twist to allow light to pass through.
Worst color accuracy, covers only 95%-100% of the RGB color gamut but almost never reaches 100% (significantly smaller than IPS or VA gamut)
TN panels never hit wide gamuts like DCI-P3 or AdobeRGB
Worst contrast, 600:1-1200:1
Worst viewing angles, 170 horizontally, 160 vertically. Appears distorted from extreme angles and color inverses when viewing from below.
Fastest, response time, as low as 1ms. Highest refresh rate, 60Hz-240Hz
Most affordable, around $100 range
Was the first type of LCD, replaced bulky CRT monitors. No longer common. Best for gaming on a budget.
IPS (In-plane switching) and Super-IPS
LCD technology that ________ liquid crystals on a plane ___________ to a glass substrate.
How is the color accuracy?
How is the contrast?
How are the viewing angles?
What is their response time?
What is their refresh rate?
What is their cost effectiveness?
Is it still used today?
LCD technology that align liquid crystals on a plane parallel to a glass substrate.
Best color accuracy. Covers 95%-100% of the widest color gamut (DCI-P3) available
Good contrast, 700:1-1500:1
Best viewing angles, up to 178/horizontally and 178/vertically. Looks good from above or below
Good response time, 1-2ms. (in the middle)
Refresh rate is 60Hz-165Hz.
Most expensive, thousands of dollars for a high end model
Most common type of LCD monitor, best for editing photos, videos, paying video games and everything in between
VA (Vertical alignment)
Aligns liquid display crystals __________ to a glass substrate.
How is the color accuracy?
How is the contrast?
How are the viewing angles?
What is their response time?
What is their refresh rate?
What is their cost effectiveness?
Is it still used today?
Aligns liquid display crystals vertically to a glass substrate.
Good color accuracy (in between IPS and TN). Covers maximum of 90% of the widest color gamut available
Best contrast, 2500:1-6000:1
Good viewing angles (170/160), better than TN but can still degrade or distort at extreme angles
Slowest response time, 2-5ms. More latency, slower pixel transitions, more ghosting
Refresh rate is 60Hz-200Hz
Medium affordability, a few hundred dollars. A lot of value for the money
Not as common as IPS, but used in most flat screen TVs. Good for picture quality and watching movies
LCD LED Monitors
What type of backlight do these LCD monitors use?
Do they still require an inverter? Why?
what color are these diodes?
where are these LEDs placed?
Do LEDs use less power than CCFLs?
Are LED monitors more efficient than CCFLs?
Light-emitting-diode (LED) Monitors
These monitors use light emitting diodes as a backlight not CCFL
don’t need an inverter, no CCFL bulb
These diodes are red, green, and blue (RGB)
LEDs are around the edge of the screen or in a matrix behind the screen
LEDs use less power than traditional LCDs. DC voltage
Yes, LED monitors are more efficient than CCFL
OLED: Organic compound emits light when receiving an _________ __________.
Which is more expensive to manufacture, OLED or LED LCD displays?
Does OLED need an inverter?
Which is thinner, lighter, more flexible and mobile?
Does OLED need to use glass?
Which has the best blacks LCD or OLED
Does OLED have accurate color representation?
Does OLED require a backlight? If so, which?
Organic light-emitting diode, organic compound emits light when receiving an electric current.
OLED is more expensive to manufacture than LCD
doesn’t need an inverter, no CCFL bulb, uses DC voltage
OLED is thinner and lighter; more flexible and mobile
OLED doesn’t require glass. Can be incredibly small, one diode per pixel.
OLED has the best black levels (high contrast)
OLED has very accurate color representation
no backlight; organic compound provides the light
If an LCD monitor on a laptop is having minor issues, such as intermittent lines on the screen, what might be going on?
The display cable might need to be reconnected or replaced
intermittent lines, flickers, or brief glitches usually points to a problem in the signal path rather than the panel instantly failing
If an LCD monitor on a laptop is having complete display failures, what could we suggest is going on?
If it’s not a damaged screen, it could be an issue with either the inverter or backlight.
Damaged Inverter/backlight
Does the inverter run at high voltage and possibly at high temperatures? Is it prone to failure?
If the inverter fails will an external monitor still work properly?
How can you verify that it is an inverter or backlight problem?
If the display cable that connects the LCD to the motherboard were loose or disconnected will anything show up on the screen?
If the video adapter fails will anything show up on the screen?
yes, it does run at high voltage/temperatures and is prone to failure
yes, an external monitor will still work
shine a flashlight at the screen, if you see the OS then it is likely a damaged inverter or backlight. Do this in a dark room.
No
No
What does the inverter do?
How many connectors does the inverter have?
What do you need to do when replacing an inverter?
The inverter powers the LCD’s CCFL (cold cathode fluorescent lamp) bulb, which requires AC power, so it converts DC to AC power.
inverter has two connectors, high voltage connection that leads to the power source and one for a cable that connects to the display
to replace inverter turn off the laptop and take out the battery, then take off these two connectors. Hold circuit boards by the edges, trying not to touch any circuits or chips
What are some signs that the backlight is starting to wear out/going bad?
dimmer screen
reddish/pinkish hue to the screen
a loss of color
Do LED and OLED screens suffer as many failures as CCFL based LCDs?
No, they don’t suffer as many failures as LCDs. LED and OLEDs don’t need an inverter or a lamp, so less points of failure.
What is another name for Digitizer?
What does a digitizer do?
Also known as a touchscreen.
A digitizer is a screen that allows for tapping or writing on the screen. Can use your finger or a stylus (a writing tool) if the device allows. It converts tapped or written impulses (analog) on the screen into instructions (digital) for the operating system to follow
Magnetic Disk characteristics
Traditional spinning drive platters with read/write arm with head to store data to the disk
2.5 form factors (3.5 inch for desktop) or 1.8 inch
generally less expensive
SSD (solid-state drive) characteristics
no moving parts, all memory
silent, fast access time, less latency
2.5 inch or 1.8 inch form factors
generally uses NAND based flash memory
generally more expensive
M.2
Is M.2 a form factor or a protocol?
Is M.2 a smaller form factor?
Does M.2 form factor still require SATA cables?
What drives does M.2 form factor support? Which is faster and why?
Are M.2 drives easy to replace?
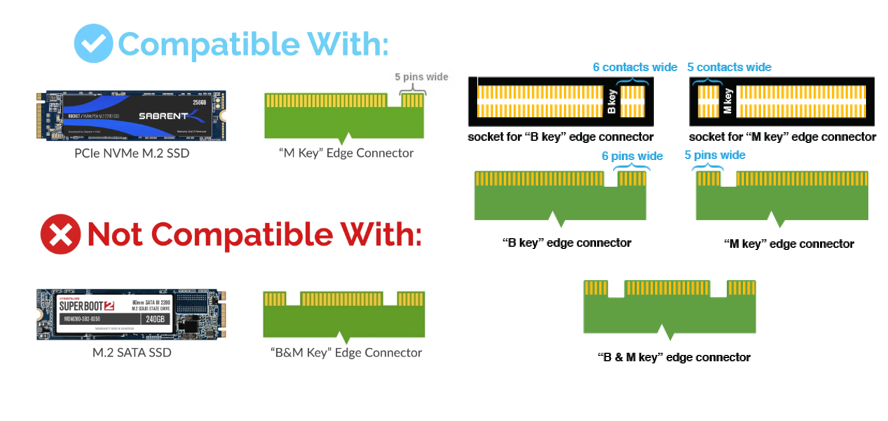
M.2 is a form factor, not a protocol
A smaller form factor
no SATA data or power cables required
M.2 supports M.2 SATA SSDs and M.2 NVMe. NVMe is faster because it doesn’t use the SATA interface, which is limited to transfer rates of 6Gb/s or 600MB/s. Since SSDs are capable of transferring data at a higher rate NVMe uses a new interface, PCIe, which has higher transfer speeds. PCIe 3.0: 32Gb/s or 4GB/s
PCIe 4.0: 64Gb/s or 8GB/s
easy to install and replace, only one screw
Hybrid drive characteristics
uses both HDD and SSD
M.2 Physical size, connectors, and logical interfaces
M.2 based cards have up to 67 pins and might use the 2230 standard (22x30 mm) or the 1216 standard (12×16 mm), among others
Webcam and Microphone
Do webcams support video capture?
Do webcams usually have a built in microphone?
Do webcams sometimes required specialized drivers and software?
Can webcams be a security concern?
How do you disable a webcam and microphone?
Are built in microphones usually good for non-casual use?
Support video capture
Many have built in camera and microphone on the display
Sometimes require specialized drivers and software
Webcams can be a security concern and so can microphones because they can get hacked
Most laptops have a function keys that disable both if not it can also be disabled in the OS
Most built in microphones are not good for non-casual use and will require an external USB microphone.
Wi-Fi Antenna
Wi-Fi Antenna are used to connect to what type of network?
In laptops what type of interfaces do Wi-Fi cards use?
For internal Wi-Fi cards usually how many wire end connectors does it have?
Do Wi-Fi antenna cards have their own mac address?
If they have their own mac address, how do you look it up from the command line or Power Shell?
used to connect to a wireless local area network (WLAN)
Wi-Fi cards use either M.2 card or (1 screw) a Mini PCI Express Card (2 screws)
when we say M.2 and PCIe, we are referring to the physical edge connector and electrical interface
Most internal Wi-Fi cards have two wire end contacts, one for Wi-Fi and one for Bluetooth
Wi-Fi antennas have their own unique identifier called, MAC address (MAC ID). It’s printed on a sticker on the antenna and also programmed into the ROM and is a 45-bit number described using hexadecimal numbering.
In windows you can type ipconfig/all in Command prompt and PowerShell to get the MAC address for the wireless Wi-Fi card (in macOS or Linux you can use ip a or ifconfig)
What is the difference between M.2, mini PCIe, and PCIe?
What are the Mini PCIe Physical size’s, connectors, and logical interfaces:
Full Height Mini PCIe: 30×50.95 mm and uses a 52 pin edge connector
Half-Height Mini PCIe (common for Laptop Wi-Fi card): 30mmx26.8 mm and 52 pin edge connector
PCIe Physical size, connectors, and logical interfaces
USB
What does USB stand for?
can USB be used for both charging and data transfers?
What type of USB connector do newer android devices use?
What type of USB connector did older android devices use?
Name two connectors that iOS-based devices use
universal serial bus
yes, USB can be used for both charging and data transfers
newer android devices use USB C
older android devices used Micro-USB
iOS devices use both USB C and Lightning

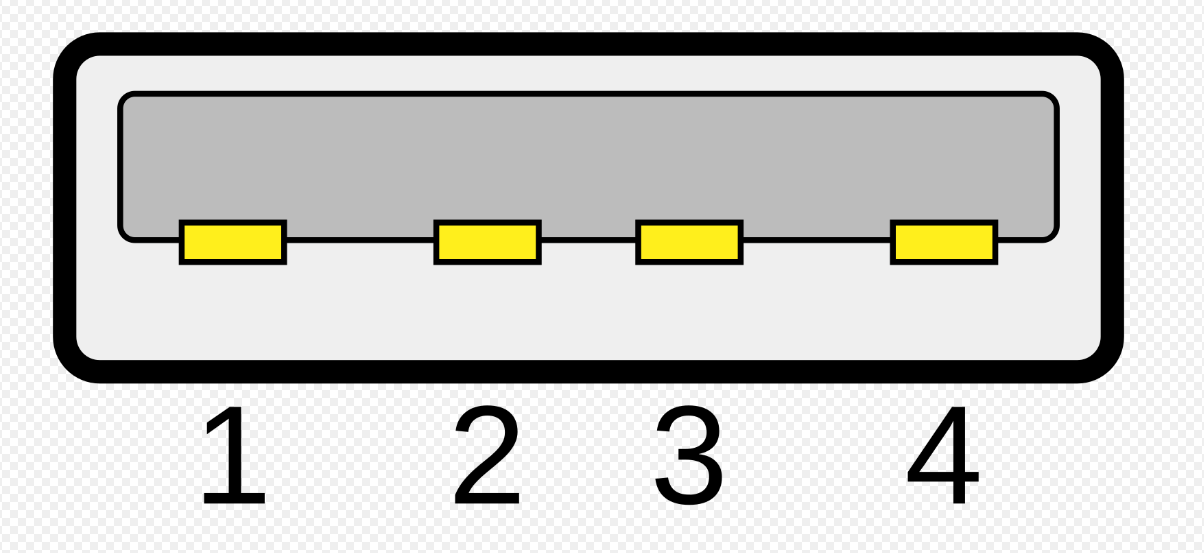
What USB type is this?
USB Type A: 1.1 - 2.0

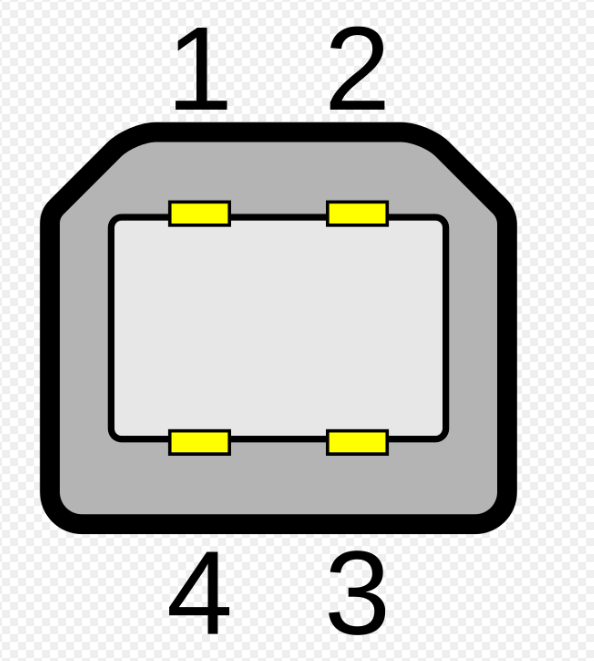
What USB type is this?
USB Type B: 1.1 - 2.0

What USB type is this?
How many pins does it have?
Does this type of connector support other USB standards? If so which?
Can this type of connector transmit different types of signals? If so which?
USB Type C
has 24 pins and is double sided
supports USB 2.0, USB 3.x (3.1 or 3.2), and USB 4
can transmit video (Display port, HDMI), Thunderbolt, and power

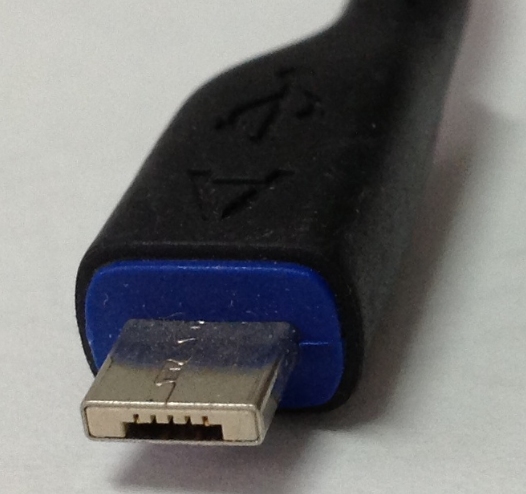
What USB type is this?
USB Mini A: 1.1 - 2.0
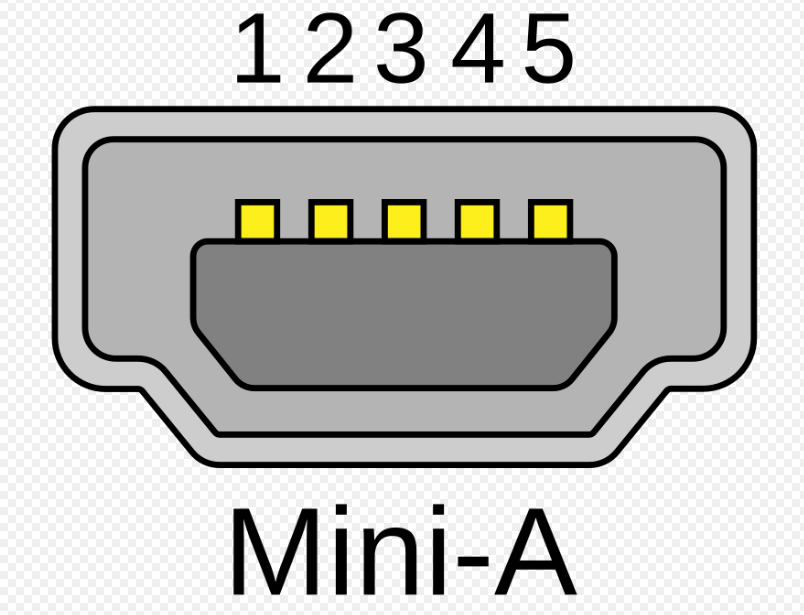

What USB type is this?
USB Micro A: 1.1 - 2.0
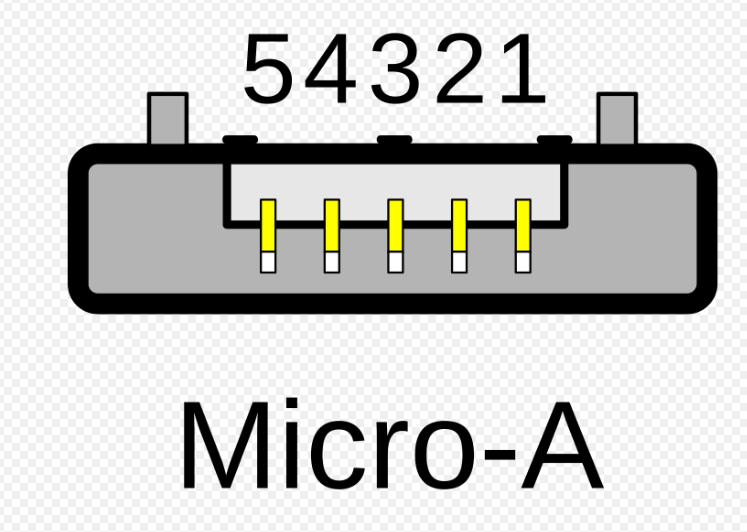

What USB type is this?
USB Mini B 1.1 - 2.0
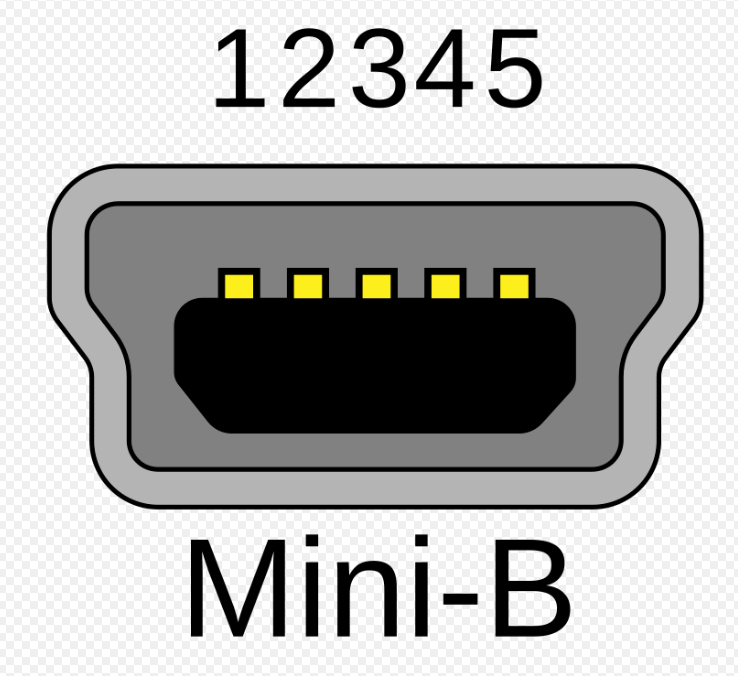
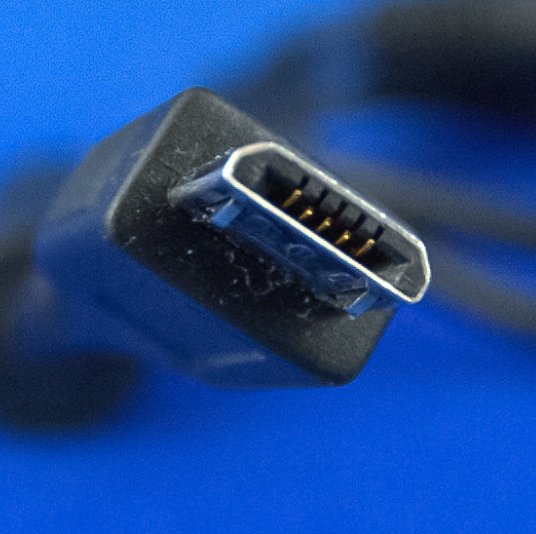
What USB type is this?
USB Micro B: 1.1 - 2.0
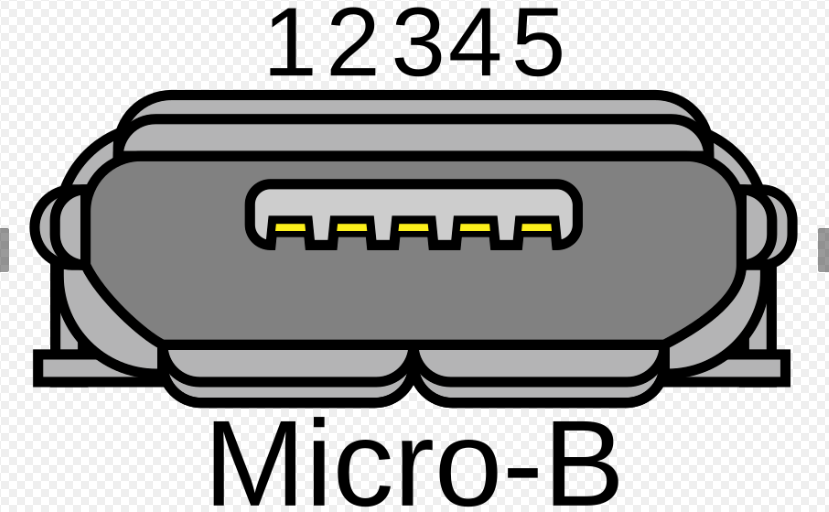

What USB type is this?
USB 3.0 Micro B Super Speed
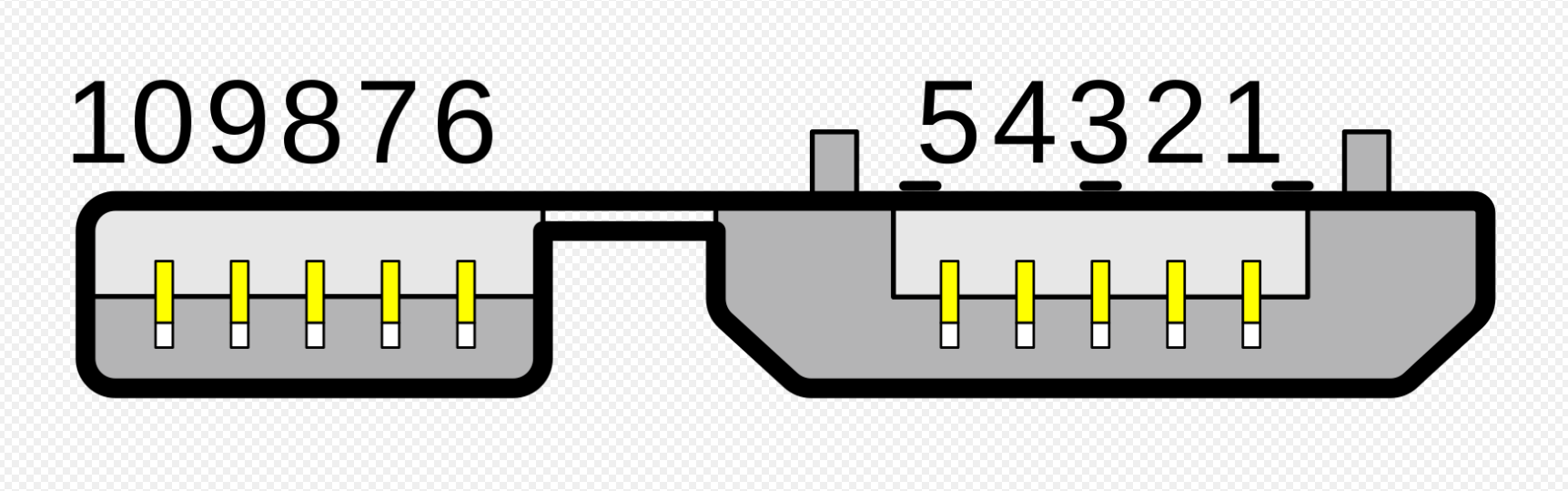
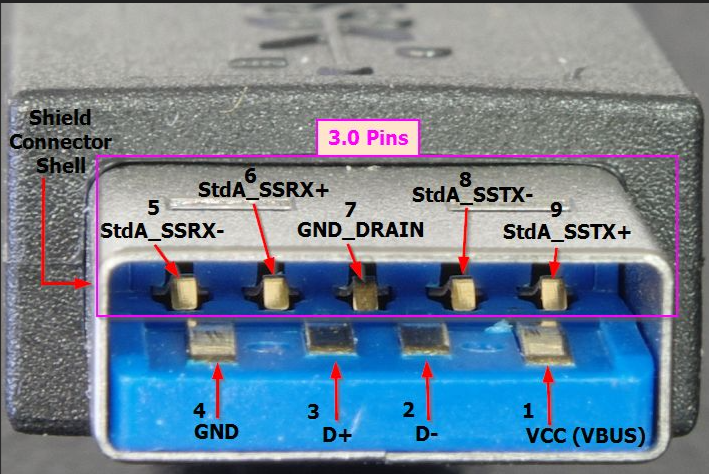
What USB type is this?
USB 3.0 Type A Super Speed
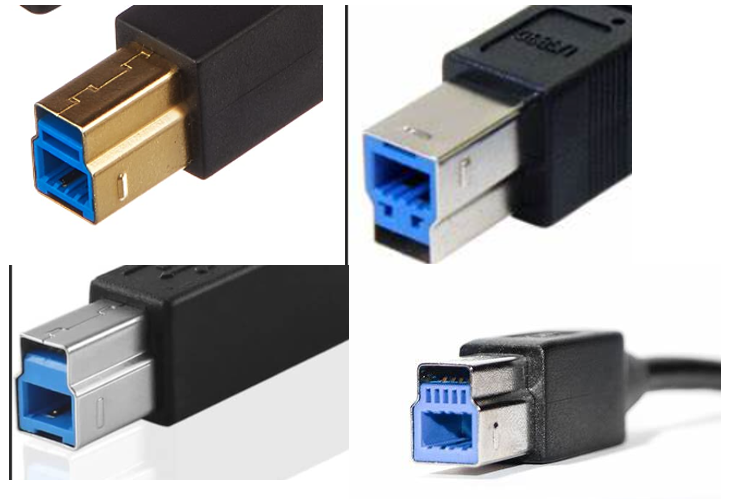
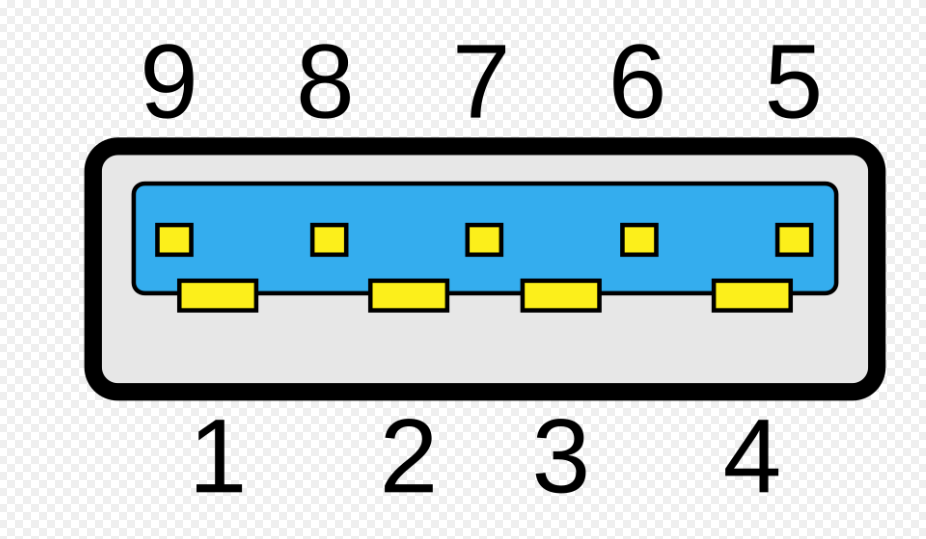

What USB type is this?
USB 3.0 Type B Super Speed
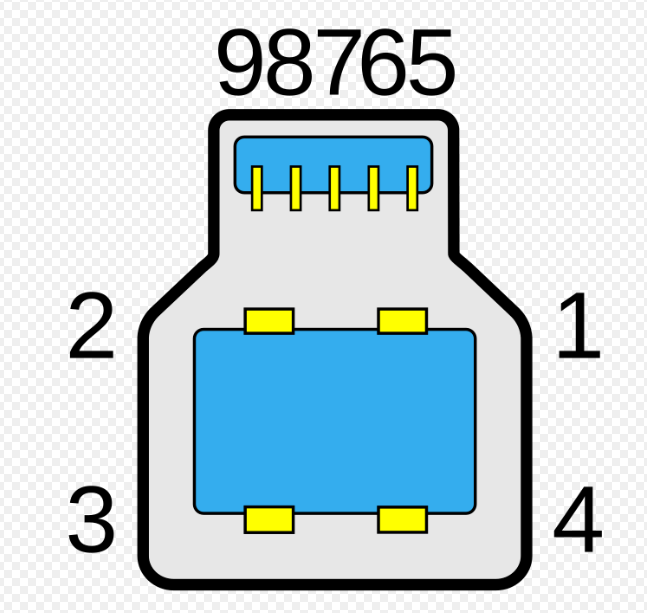

What type of connector is this?
DB-9 (or DE-9)
before the DE-9, the DB-25 (for RS-232 serial communication) connector was already well known so when the DE-9 was introduced with fewer pins many still used the DB prefix instead of the correct DE prefix.
both have a D shaped shell
DB has a larger shell compared to DE connectors
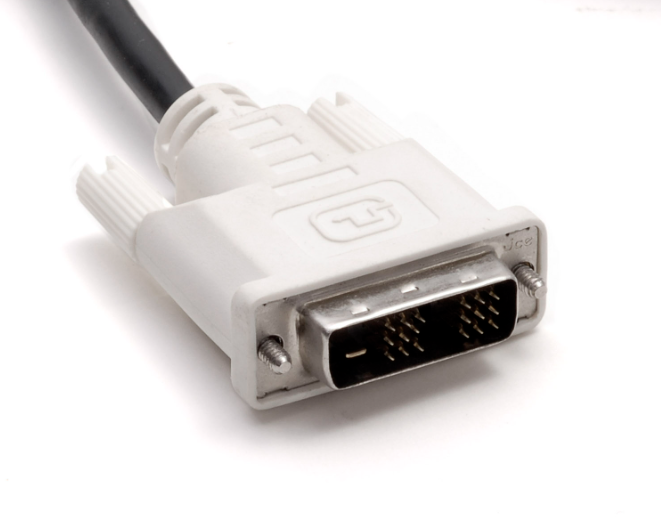

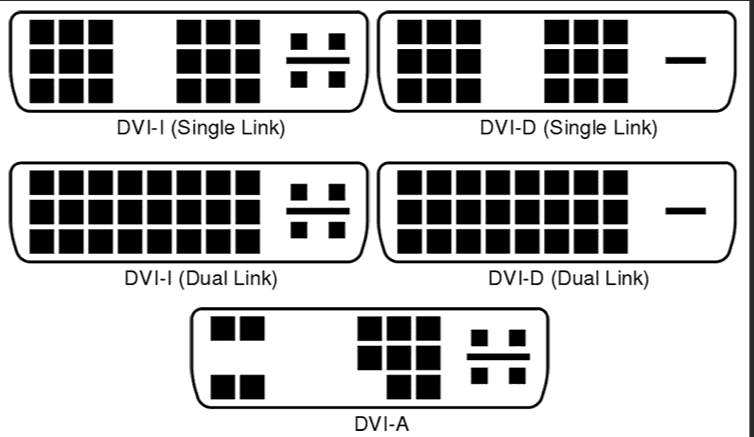
What type of connector is this?
DVI
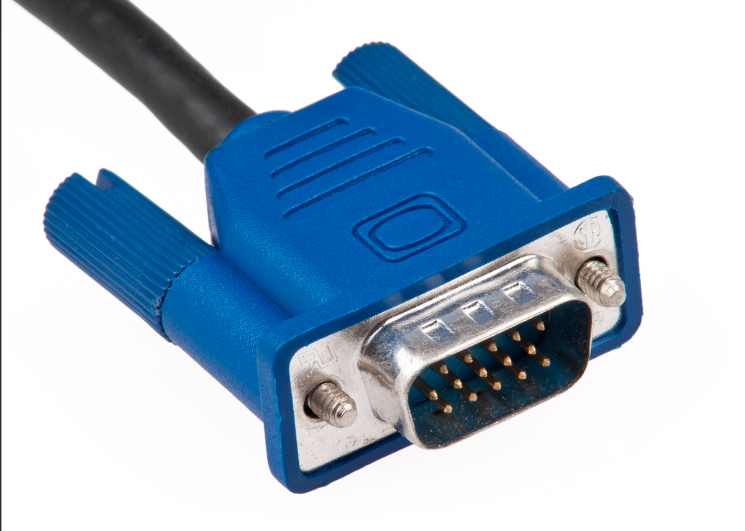

What type of connector is this?
VGA
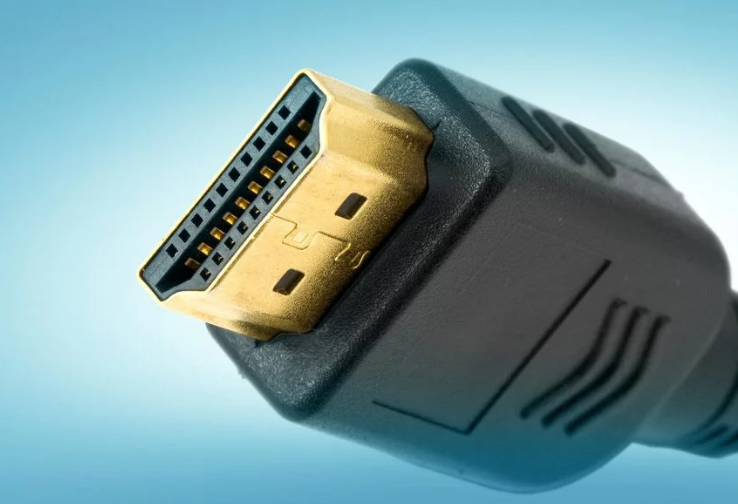


What type of connector is this?
HDMI
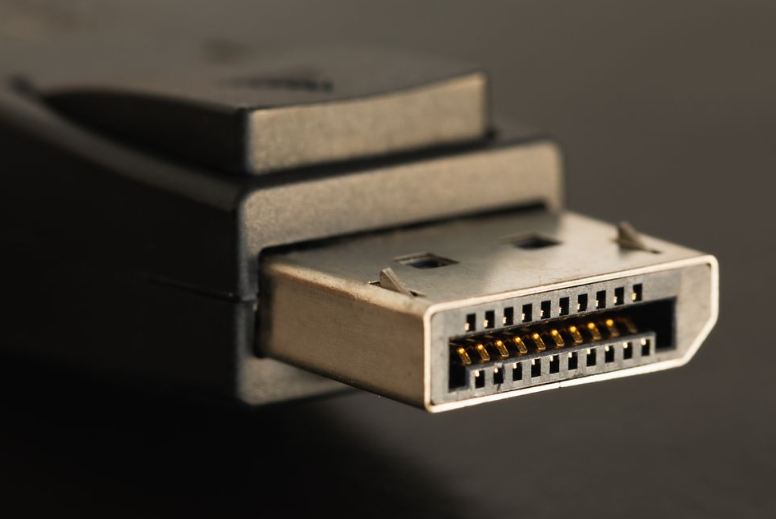


What type of connector is this?
Display Port
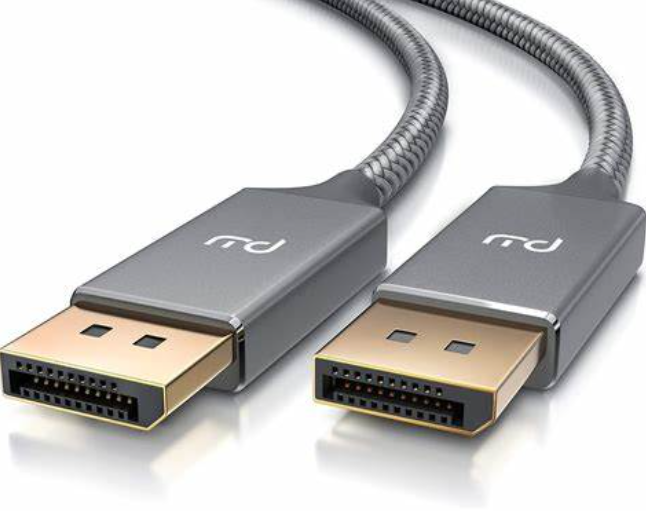
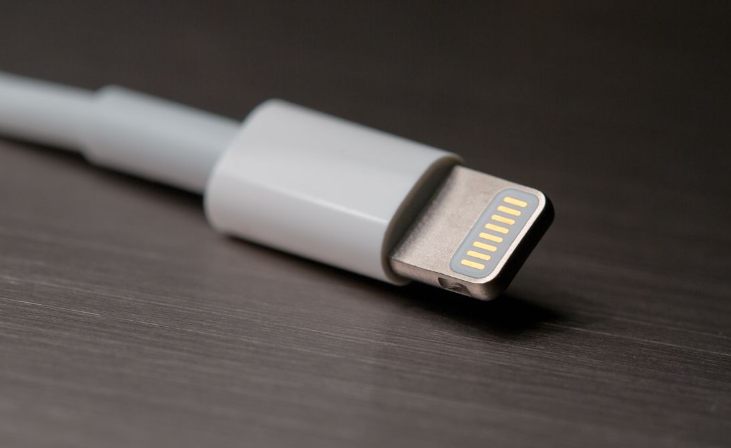


What type of connector is this?
Is it proprietary?
How many pins does it have?
What are some advantages that it has over micro USB?
Lightning
yes, apple proprietary technology
has 8 pins for digital signals
Advantages over Micro-USB
higher power output for phones and tablets (faster charging)
can be inserted either way(came before USB-C)
simple design

What type of connector is this?
Thunderbolt
Tethering
What is tethering?
What are the different way to allow tethering?
Tethering is the process of sharing a device’s internet connection with other devices
using a smartphone or tablet as a mobile hot spot to provide internet access to other devices like laptops, tablets, or other phones
Wi-Fi hotspot, USB tethering, Bluetooth Tethering
What’s the difference between a mobile hotspot and phone hotspot?
A mobile hotspot is a stand alone device hat works the same as a phone’s hotspot but can do a lot more.
some come with security features like firewalls and guest networks
newer 5G hot spots have up-to-date Wi-Fi standards that make it easier o support more devices simultaneously
connects 32 or more devices, depending on hotspot
better radios and antennas
needs a hotspot data plan
no unlimited data plans

Touch Pens
allows for note taking, signatures
precise selection
easier to see the screen (hand isn’t in the way)
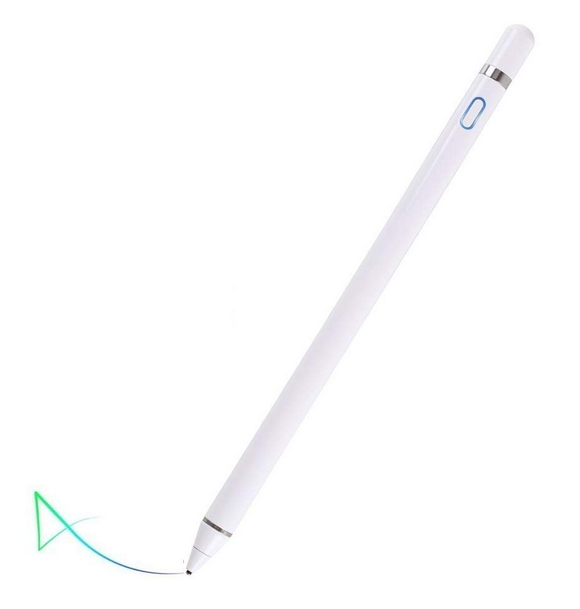

Active Stylus
digital stylus
more advanced writing tool
communicates directly to the device
pressure sensitive for some, programmable buttons, palm rejection for some, etc.
must be compatible with the tablet
example: iPad uses apple pencil

Drawing Pad
uses an active stylus with an external digitizer
very precise input
third-party device
support across many operating systems

Track Pad
replaces the mouse
External options are available
on laptops you can disable the track pad


Docking Stations
connects either by physical docking or cable-based docking (USB-C or Thunderbolt)
physical docking will require an external keyboard and mouse
cable-based docking stations usually support more laptop models
can recharge laptop battery
adds additional functionality
extends existing laptop interface


Port Replicator
replicates existing laptop ports
typically do not provide power
fewer features than docking stations
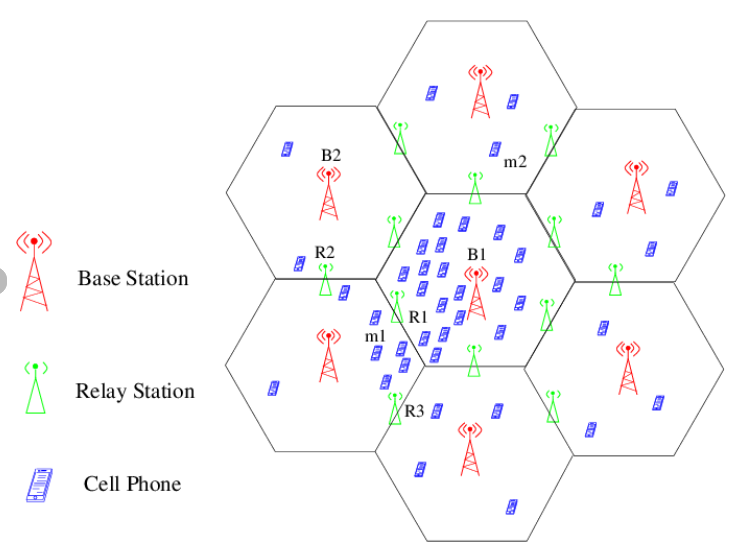
Cellular Networks
Cellular Networks are communication networks that are divided into small geographical areas called cells, each of which is served by a cell tower (base station)
2G Networks
what standards did 2G support?
what different services did 2G support?
what were the data speeds of 2G?
Supported GSM and CDMA
Services of 2G:
Introduced digital voice transmission replacing analog
sms (short message service)
mms (multimedia messaging service)
basic mobile internet access through GPRS (general packet radio service) and later EDGE (Enhanced Data rates for GSM Evolution)
Ranged between 56 Kbps (GPRS) and 384 Kbps (EDGE)
GSM
What is GSM?
What types of communication does GSM support?
Which carriers use GSM?
Which network generations does GSM support?
Is GSM still used today? If they aren’t then what replaced them?
What type of technology did GSM use?
Did CDMA use soft or hard handoff?
GSM stands for Global System for Mobile Communications, it’s a standard for digital cellular networks
GSM supports voice calls, SMS (short message service), MMS (multimedia messaging service), and data transmission.
The main carriers that use GSM are T-Mobile, AT&T.
There are a few more less known carriers like Pine Cellular, Indigo Wireless, TerreStar and more
GSM supports 2G and 3G networks
GSM is no longer used today, AT&T and T-Mobile have already shutdown 3G GSM/UMTS in 2022. AT&T has already shut down 2G GSM and T-Mobile has greatly reduced its coverage and quality. They’ve mostly been faced out in favor of 4G LTE and 5G
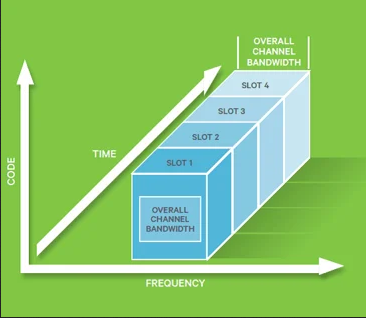
GSM used Time Division Multiple Access (TDMA) and Frequency Division Multiple Access (FDMA).
TDMA: Multiple users share the same frequency channel by dividing the signal into time slots. Each user is assigned a specific time slot in which they can send or receive data.
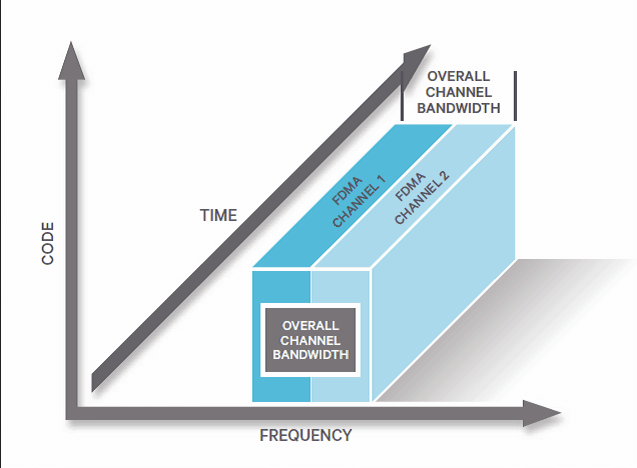
FDMA: divides the available frequency spectrum into smaller channels. Each call or data session is assigned a specific frequency channel, ensuring that users in the same cell don’t interfere with one another
Introduced SIM cards (subscriber identity modules) to store subscriber information, which users could switch between devices
hard handoff: phone disconnects from one cell tower before connecting to another during movement
CDMA
What is CDMA?
What types of communication does CDMA support?
Which carriers use CDMA?
Which network generations does CDMA support?
Is CDMA still used today? If they aren’t then what replaced them?
What type of technology did CDMA use?
Did CDMA use soft or hard handoff?
CDMA stands for Code Division Multiple Access, it’s a standard for digital cellular networks
CDMA supports voice calls, SMS (short message service), MMS (multimedia messaging service), and data transmission.
Carriers that supported CDMA were Sprint, Boost, and Verizon
CDMA supported 2G and 3G
CDMA is no longer widely used today, it’s mostly been faced out in favor of 4G LTE and 5G
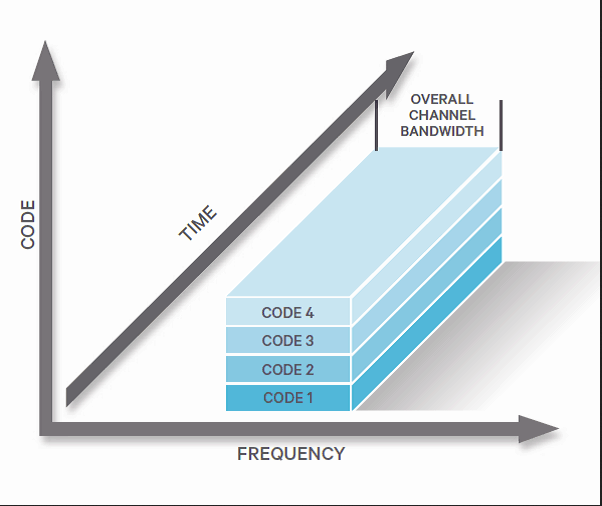
CDMA uses Code Division Multiple Access (CDMA)
allows multiple users to share the frequency channel at the same time by assigning a unique code to each call or data session, users occupy the entire available bandwidth simultaneously
traditionally did not use SIM cards but newer CDMA networks began to use them
Soft handoff: phone communicate with multiple towers simultaneously for smoother transitions between cells
3G Technology
what standards did 3G support?
what different services did 3G support?
what were the data speeds of 3G?
3G supported GSM and CDMA standards
Services of 3G:
digital voice transmission
sms (short message service)
mms (multimedia messaging service)
enhanced data services over 2G
higher internet access
multimedia streaming
video calls
between 384 Kbps and 42 Mbps, depending on the network type and technology (HSPA+ provided the highest data rates for 3G)
4G and LTE
What is 4G, LTE, and LTE-Advanced?
what standards/technologies does 4G support?
what are the main differences between 4G and 2G-3G?
what are the data speeds of 4G?
4G refers to the fourth generation of mobile network technology. The International Telecommunication Union (ITU) set the standards for 4G under the IMT-Advanced guidelines. LTE is the specific technology that was developed to enable 4G services and meet the ITUs IMT-Advanced guidelines for 4G. Early LTE technology did not fully meet the guidelines until LTE Advanced came out.
4G uses the LTE standard
4G has a few main difference from previous generations
unlike 2G-3G, 4G is entirely IP based (voice and data use packet-switching)
uses a new standard, LTE
Focused on data services rather than voice, although VoLTE (Voice over LTE) later provided a way to handle voice calls over LTE networks
4G LTE Advanced uses MIMO (Multiple Input Multiple Output), more antennas to increase data throughput
Peak download speeds of up to 1 Gbps and upload speeds of up to 500 Mbps
5G
What standards/technologies does 5G support?
what are the main differences between 5G and 4G?
what are the data speeds of 5G?
5G along with a few other technologies extends the use of Massive MIMO (multiple-Input Multiple-Output)with many more antennas to support higher data throughput and multiple users
There are a few main differences between 5G and 4G
Uses higher frequency bands (above 24 GHz) for ultra-fast speeds but with limited range
Uses lower frequencies below 6 GHz for broader coverage and better penetration
Much faster than 4G and less latency
5G: Theoretical average speeds of up to 10 Gbps, though typical speeds range from 100 Mbps to several Gbps.
IoT
PRL
Preferred Roaming List
a database used by CDMA based mobile phones to prioritize and manage which cellular towers or networks a phone should connect to when outside of its home network, especially when roaming, for the most efficient or cost-effective networks available.
PRL updates are sent by the carrier to keep the list of preferred roaming partners current, usually over the air but for in cases might need to be done manually
Hot Spot
Bluetooth Pairing
GPS
MDM
MDM configurations
Microsoft 365
iCloud
Synchronizing Data
What is S/MIME?
Why aren’t 4G or 5G standards compatible across all carriers?
4G or 5G standards aren’t compatible across carriers because different carriers use different radio channels, one carrier’s model of a phone may not include channels used by other carriers
Also because other carriers will not permit other carrier’s devices to be used on their networks.
Which had more global support GSM or CDMA?
GSM
What is MIMO technology?
Multiple-input multiple-output: a wireless network that allows the transmitting and receiving of more than one data signal simultaneously over the same radio channel.
Massive MIMO is a MIMO system with an especially high number of antennas.
What are the three main coverage layers of 5G?
Coverage Layer: Low-Band 5G
Frequency: Sub-2GHz (low)
higher frequency means longer wavelength
Capacity: Low (slower speeds, less bandwidth, limited simultaneous connections, congestion)
Propagation: High (long distance, goes around obstacles better, penetrates walls, trees, buildings easier, coverage is wide.)
Capacity Layer (Mid-Band 5G)
Frequency: 2 GHz- 7 GHz (medium)
Capacity: Medium
good mix of coverage and speed
speed is 150 Mbps - 1 Gbps
Propagation: Medium
covers neighborhoods well
includes the C-band (3.7-3.98 GHz) highly used in cities
High Capacity Layer (High Band/mmWave 5)
Frequency: 24 GHz and up (high)
Capacity: Very High
very fast! 1-3 Gbps
Propagation: Very Low
can’t penetrate walls
need to be near source to get signal