PNB 2275 - Exam 4 (Renal Phsyiology I)
1/48
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
49 Terms
Draw out the basic anatomy of the kidney
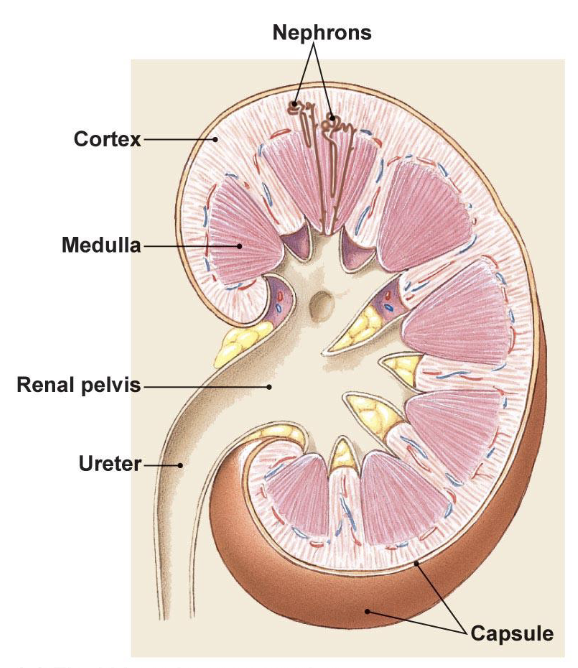
minor calyces
drain pyramids at papillae
major calyces
receives urine and drain to the renal pelvis
What are the two types of nephrons?
Cortical
Juxtamedullary
cortical nephron abundance and function, and location
85%; reabsorption with peritubular capillaries
Outer cortex of kidney (makes sense since it’s closer to surface to reabsorb)
juxtamedullary nephron abundance and function, and location
15%; concentrate urine via vasa recta and peritubular capillaries
Inner Coretex near medulla
LONG loop of Henle
Draw out the Bowman Capsule anatomy, and what molecules and flow of plasma/molecules
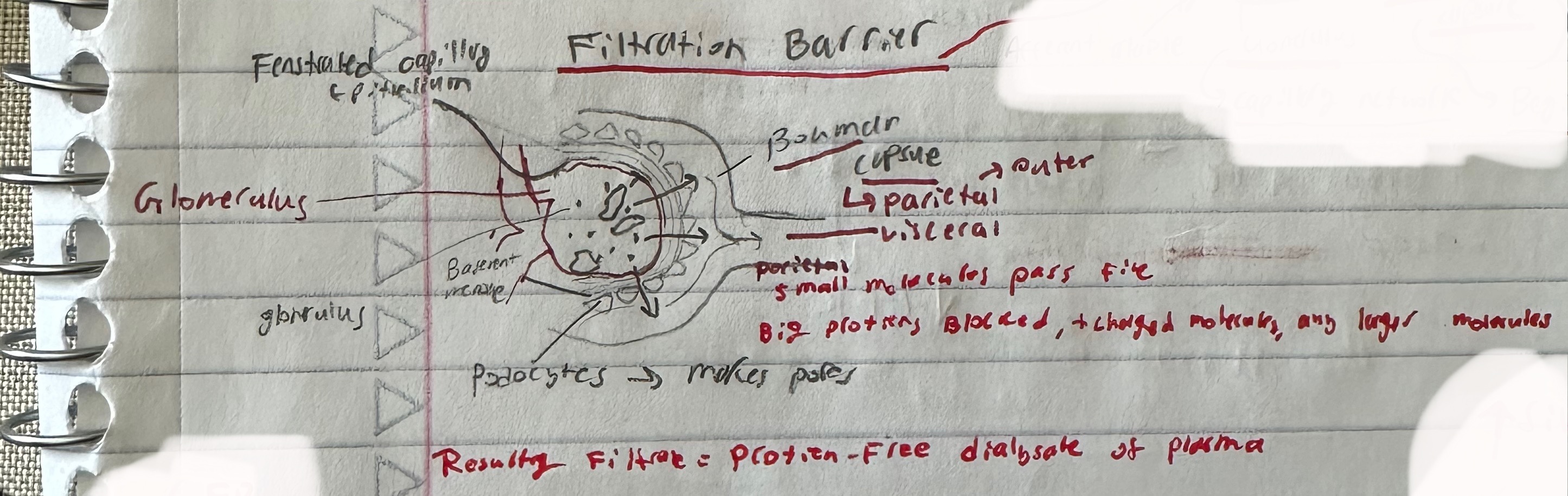
parietal epithelium of Bowman Capsul
squished flat cells
visceral epithelium of Bowman Capsule
podocytes; create pores for leakage
What does the efferent arteriole become
carries blood not filtered out from the glomerulus and becomes the peritubular capillaries
macula densa cell location and function
DCT; osmoreceptors detect Na change and pressure change
granular/juxtaglomerular cells location and function
surround arteriole, mostly afferent. Modified smooth muscle that secretes renin
Mesangial cells location and function
between capillaries; provide support and have contractile function to regulate GFR
function of renal corpuscle
filtration
three structures in corpuscle that support filtration
fenestrated capillaries, basement membrane, podocyte pores
why is the pressure so high in glomerulus compared to normal capillary bed?
Gromerulus: 55 mmHg v.
Normal Capillary Bed: 34 mmHg
Gromerulus → INC Width of afferant arteriole than efferent (creates a pressure gradient).
Gromerulus “punches into” the Bowman Capsule
Where in the nephron does only filtration ocurr?
Gromerulus to Bowman Capsule
where in the nephron does reabsorption occur? (the peritubular capillaries reabsorbing stuff FROM the nephron)
Proximal Convoluted Tubule, Loop of Henle, Distal Convoluted Tubule, Collecting Duct
Mostly in PCT and LOH
Where in the nephron does secretion occur? (the peritubular capillaries secreting stuff INTO the nephron)
Proximal Convoluted Tubule, Distal Convoluted Tubule, Collecting Duct
equation for excretion
Excretion = Filtration - Reabsorption + Secretion
E = F - R + S
Every
Facial
Rains
Semen
product after filtration
plasma that is protein and cell free
what happens when excretion is less than filtration (E < F)?
NET REABSORPTION
ex: Filtration rate of substance X = 100 mg/min
Excretion rate of X = 40 mg/min
➡ That means 60 mg/min was reabsorbed
→ Net reabsorption = yes
what happens when excretion is more than filtration (E > F)
there is net secretion'
Filtered load of PAH = 10 mg/min, Excreted amount of PAH = 50 mg/min
Excretion = Filtration – Reabsorption + Secretion
Assuming no reabsorption (true for PAH):
50 mg/min = 10 mg/min + Secretion
➡ Secretion = 40 mg/min
What is GFR?
Glomerular Filtration Rate
amount of plasma filtered from the glomeruli into the Bowman's space per unit time (mL/min)
How much of the blood volume enters the renal tubule and how much is reabsorbed here?
20% enters, and 19% is reabsorbed, meaning less than 1% of total blood volume is excreted
How much plasma is filtered per day
125 mL/min
180L (filter plasma 60 times)
What three pressures that drive GFR
hydrostatic (55 mmHg), fluid (-15 mmHg), and osmotic (-10 mmHg)
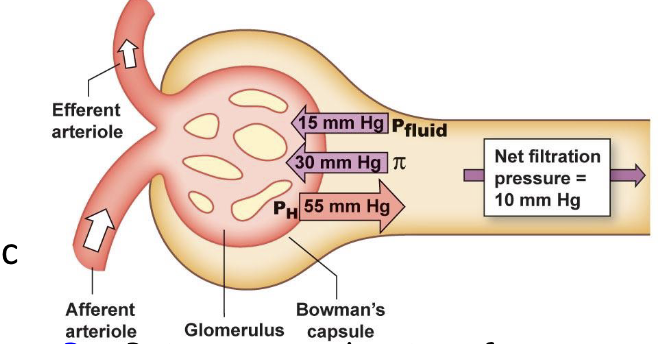
How is Net glomerular filtration rate claculated?
Net = PH - PBS(fluid) - π
How is GFR calculated?
GFR = Kf(PH - PBS(fluid) - π)
What increases Filtration?
INC Hydrostatic Pressure of Glomerulus,
DEC Fluid Pressure & DEC colloid Osmotic Pressure
What decreases Filtration?
INC Fluid pressure (Bowman hydrostatic pressure), INC colloid osmotic pressure
DEC Hydrostatic pressure of Glomerulus
Kf, what cells regulate it
coefficient relating to capillary space and permeability; regulated by mesangial cells (contractile)
what 3 factors influence hydrostatic pressure?
arteriole pressure, buffered w/ autogregulation
afferent arteriole resistance
Efferent arteriole resistance
How does constriction of Afferent Arteriole affect GFR? Dilation?
Constrict → INC resistance → DEC hydrostatic Pressure → DEC Glomerular BP (b/c of less hydrostatic pressure) → Dec Flow → DEC GFR (need pressure from hydrostatic to flow)
Dilate → Dec resistance → INC hydrostatic pressure → Inc glomerular BP (b/c of more hydrostatic pressure) → Inc Flow → INC GFR (more hydrostatic pressure, more flow)
How does constriction of Efferent Arteriole affect GFR? Dilation?
Constrict → Inc Resistance → DEC FLOW out of glomerulus (causing a build-up of fluid) → INC Glomeralr blood pressure → INC GFR
Dialate → Dec Resistance → INC Flow out of glomerulus (more open to allow more flow) → DEc Glomerular BP → DEC GFR
What happens when the Afferent and Efferent arterioles are both constricted at the same time? Both dialated at same time?
BOTH Constrict → Changes in Pressures cancel out BUT → Dec GFR (bc of less overall renal blood flow)
BOTH Dialate → Changes in pressures cancel out BUT → INC GFR (bc more renal blood flow)
three mechanisms of autoregulation of GFR
Myogenic Response (blood itself)
tubuloglomerular feedback loop (Juxtaglomerular Apparatus)
renin-angiotensin II system (Hormones + Autonomic NS)
What does myogenic response act on?
afferent arteriole
myogenic response mechanism
increase Renal (systemic) BP, stretch receptors release calcium for vasoconstriction of afferent arteriole, DEC PH of Glomerulus → DEC GFR
What type of control does tubuloglomerular feedback use? What does it do?
Paracrine Control
Overall DECREASES GFR
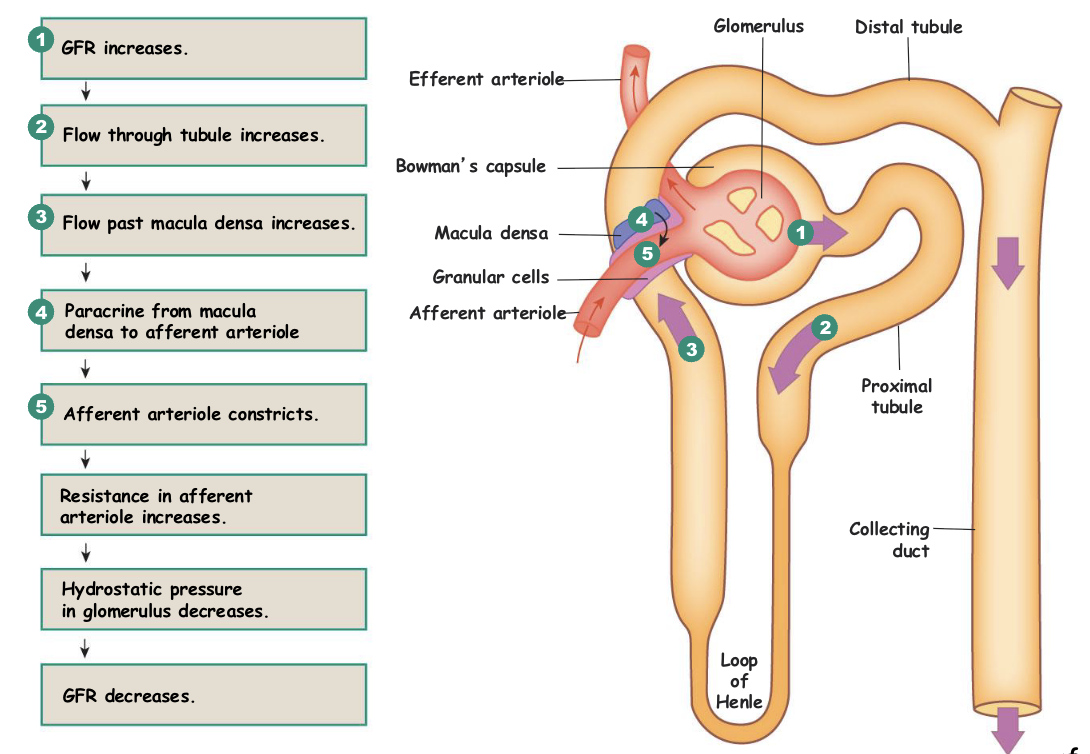
What two signals trigger the Tubuloglomerular Feedback?
INC in GFR
INC in NaCl
tubuloglomerular feedback loop acts on what?
juxtamedullary apparatus
what two paracrines do macula densa cells release and what do they function in?
adenosine (vasoconstriction), NO (vasodilation)
tubuloglomerular feedback loop mechanism
increase BP → increase GFR/flow → increase Na in the DCT → macula densa cell detection of the increased flow → paracrine release for vasoconstriction of afferent arteriole → increase resistance of Afferent Arteriole → decrease in PH of Glomerulus → DEC GFR
Decrease in BP triggers the kidney to release _______ which cleaves ________ released by the liver into ________
renin; angiotensinogen; angiotensin I
angiotensin converting enzyme location and function
lung epithelium; convert angiotensin I to II
angiotensin II impacts
vasoconstriction, thirst, ADH and aldosterone release (increase BP and BV)
What three things stimulate renin release?
decrease BP, sympathetic innervation, drop in osmolarity of tubular fluid due to macula densa causing vasoconstriction of afferent arteriole decreasing GFR
What does ANP do?
Dialates Afferent Arteriole → INC GFR
INHIBITS Renin Secretion
Promotes Na+ loss (INC excretion)