Organic Synthesis
1/26
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
27 Terms
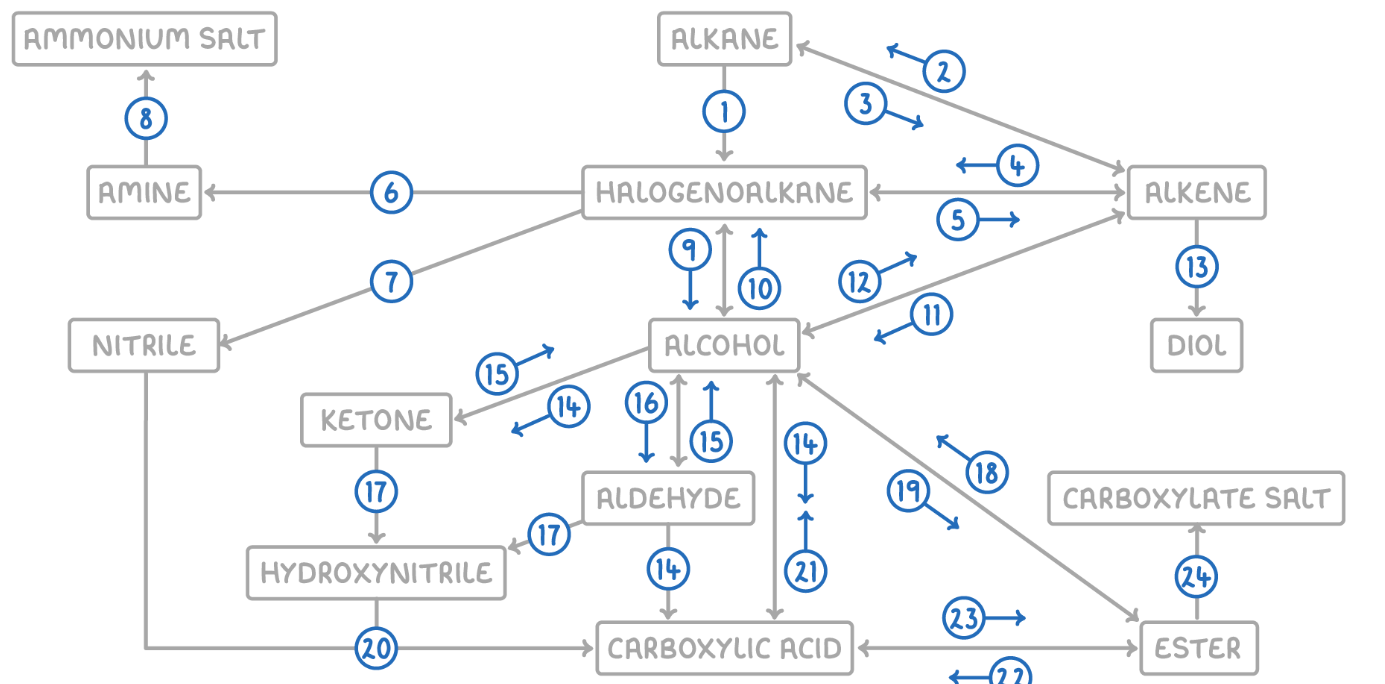
Alkane to Halogenoalkane
Reaction Type: Free Radical Substitution
Reagents & Conditions: Halogen in the presence of UV light.
Explanation: The UV light breaks the halogen bond (initiation) to create radicals, which then substitute hydrogen atoms on the alkane chain.
Alkene to Alkane
Reaction Type: Electrophilic Addition (Hydrogenation)
Reagents & Conditions: Hydrogen gas (H2) with a Nickel catalyst at 150°C.
Explanation: Used to turn unsaturated fats into saturated fats (margarine production).
Alkane to Alkene
Reaction Type: Cracking (Thermal or Catalytic)
Reagents & Conditions: High temperature (Thermal) or High temperature with a zeolite catalyst (Catalytic).
Explanation: Breaking long-chain alkanes into shorter, more useful alkanes and alkenes.
Alkene to Halogenoalkane
Reaction Type: Electrophilic Addition
Reagents & Conditions: Hydrogen halide (HCl, HBr) at room temperature.
Explanation: The double bond opens up to accept the hydrogen and the halogen.
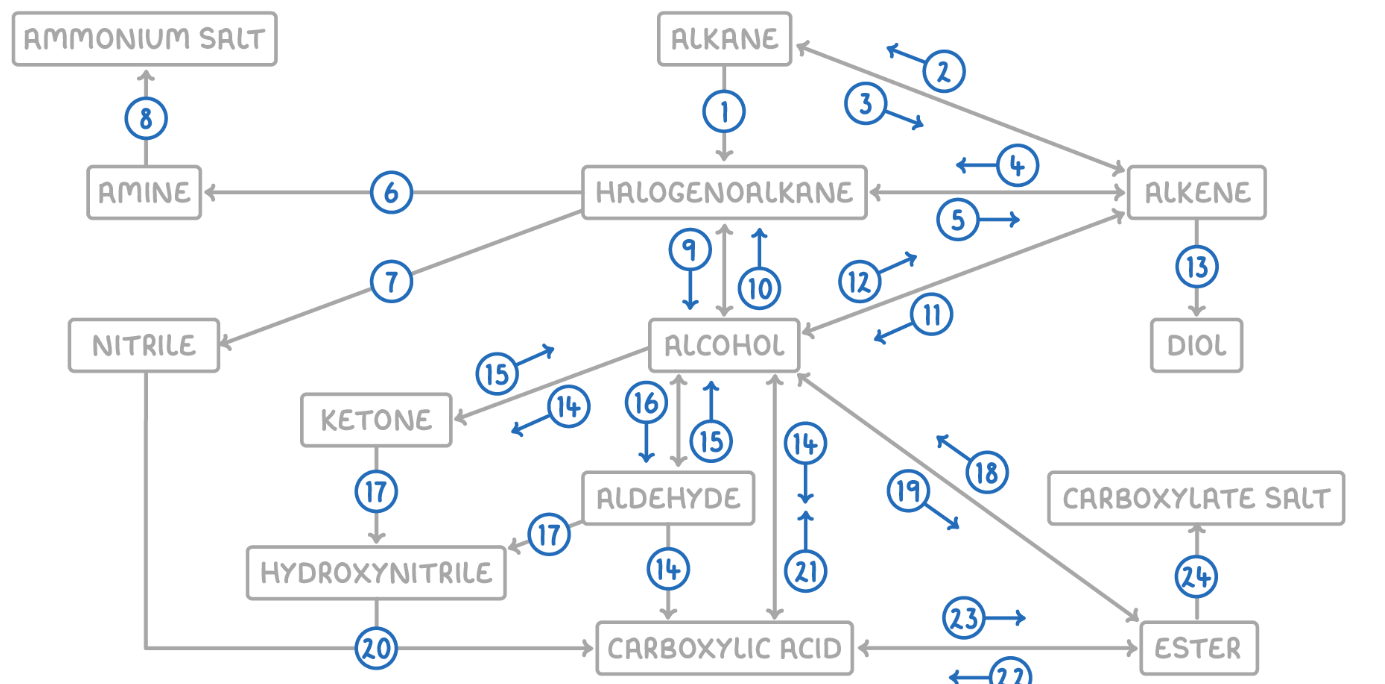
Halogenoalkane to Alkene
Reaction Type: Elimination
Reagents & Conditions: Ethanolic KOH or NaOH, heated under reflux.
Note: It is crucial that the solvent is ethanol, not water.
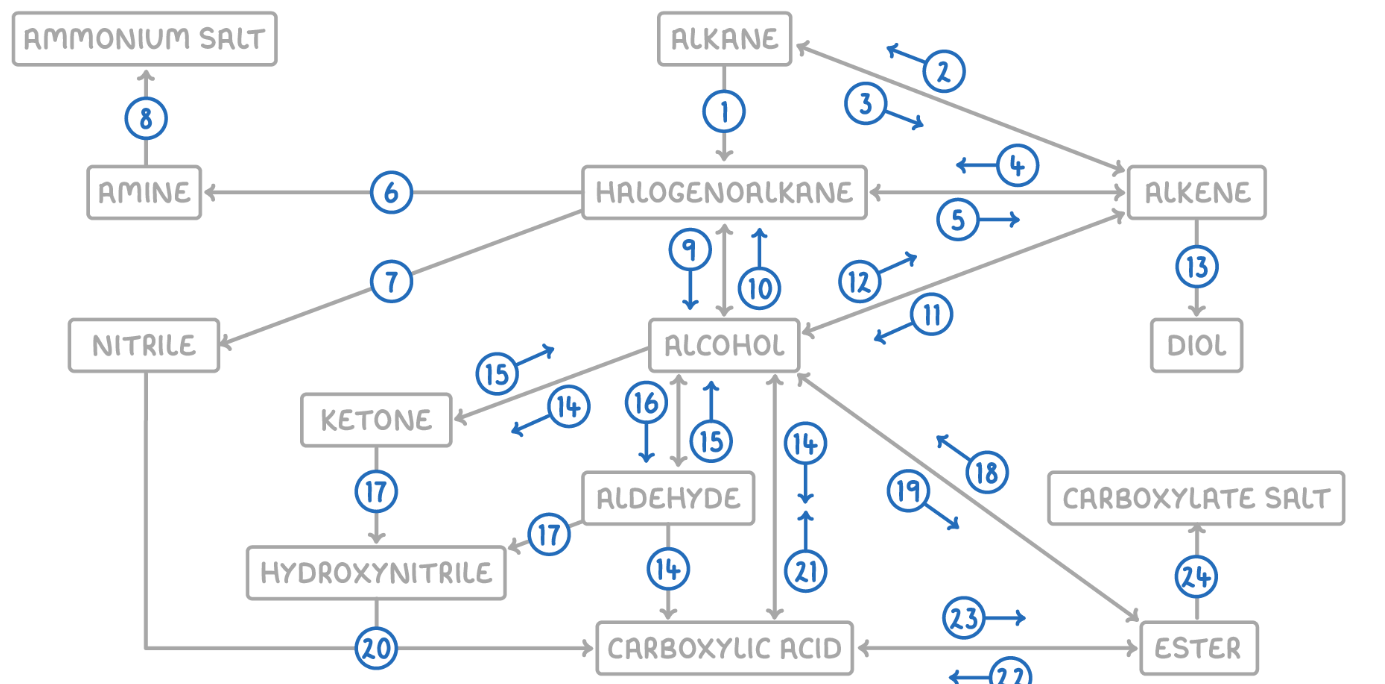
Halogenoalkane to Amine
Reaction Type: Nucleophilic Substitution
Reagents & Conditions: Excess ethanolic ammonia (NH3), heated in a sealed tube/under pressure.
Explanation: Excess ammonia is used to prevent further substitution into secondary/tertiary amines.
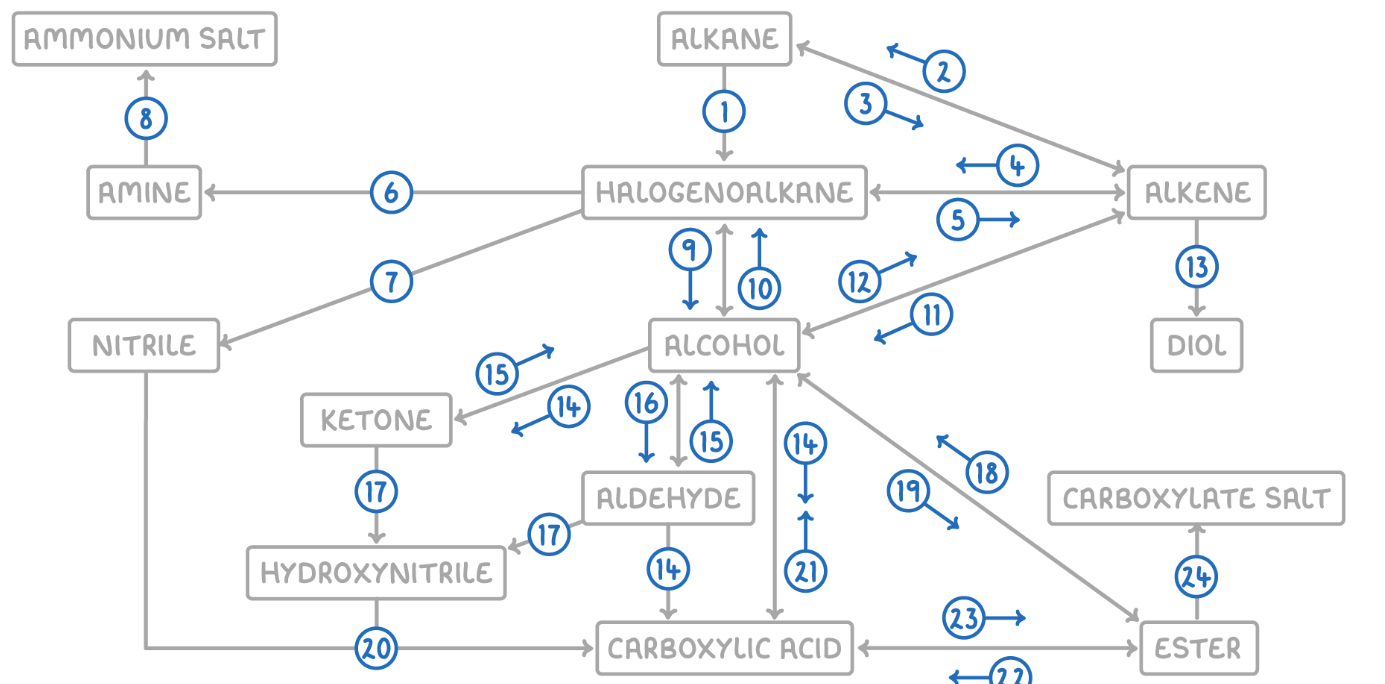
Halogenoalkane to Nitrile
Reaction Type: Nucleophilic Substitution
Reagents & Conditions: Potassium cyanide (KCN) or Sodium cyanide (NaCN) in ethanol, heated under reflux.
Significance: This reaction increases the length of the carbon chain by one carbon atom.
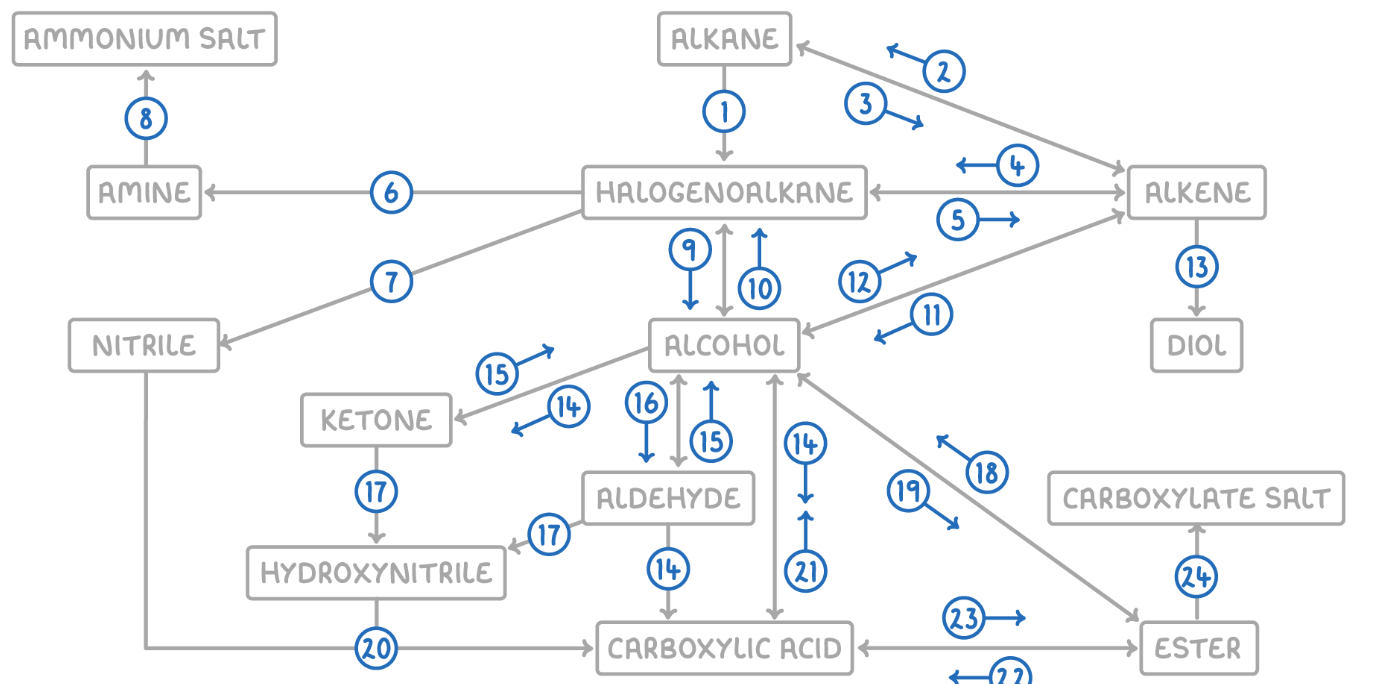
Amine to Ammonium Salt
Reaction Type: Neutralization (Acid-Base)
Reagents & Conditions: Dilute acid (e.g. HCl).
Explanation: The lone pair on the nitrogen accepts a proton (H+) to form a positive ion.
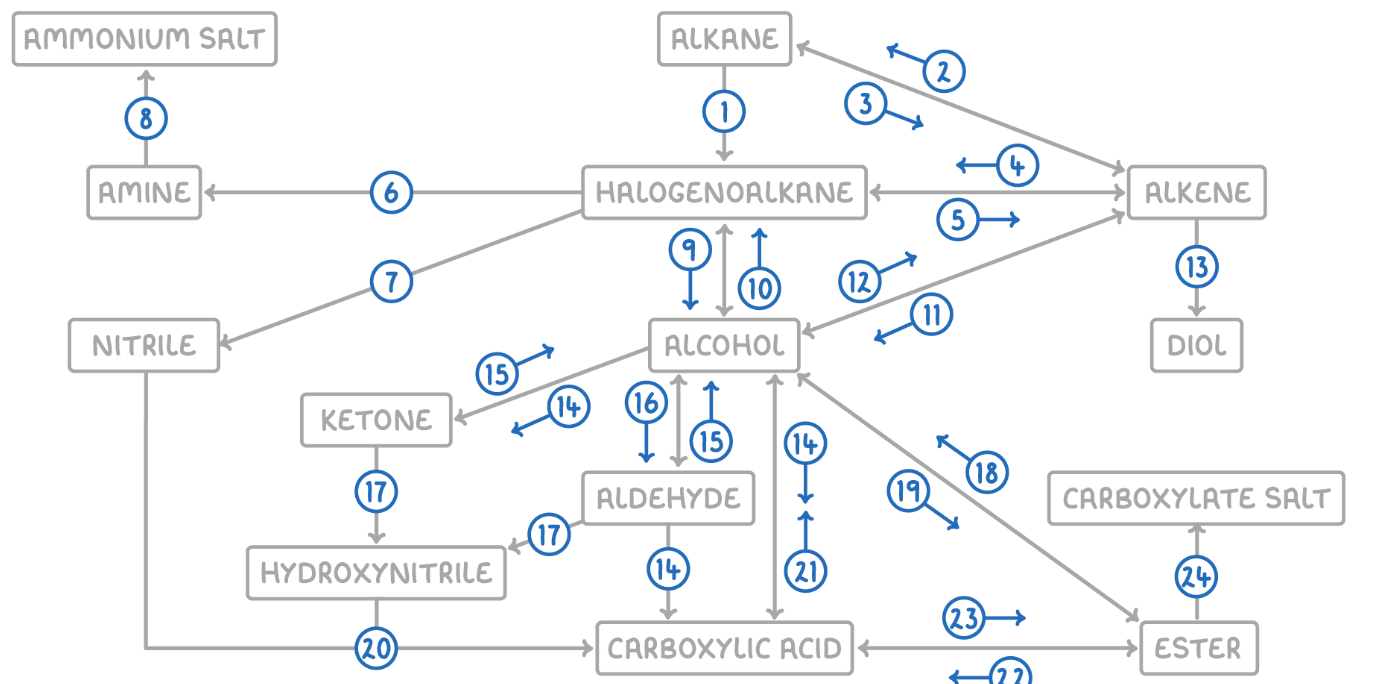
Halogenoalkane to Alcohol
Reaction Type: Nucleophilic Substitution (Hydrolysis)
Reagents & Conditions: Aqueous NaOH or KOH, heated under reflux.
Note: Here water (aqueous) is the solvent, contrasting with reaction 5 (ethanolic).
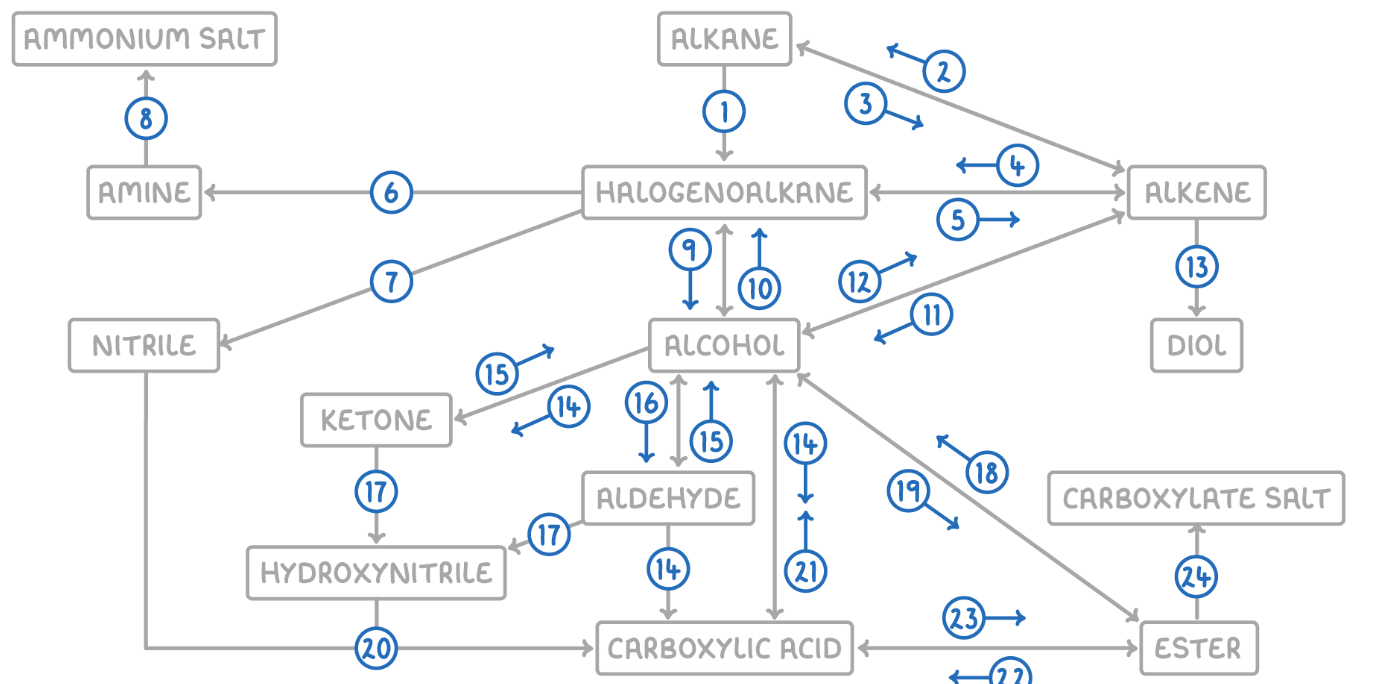
Alcohol to Halogenoalkane
Reaction Type: Nucleophilic Substitution
Reagents & Conditions:
For Chloroalkanes: PCl5 (room temp) or conc HCl.
For Bromoalkanes: KBr + 50% conc H2SO4.
For Iodoalkanes: PI3 (made in situ from red phosphorus + iodine).
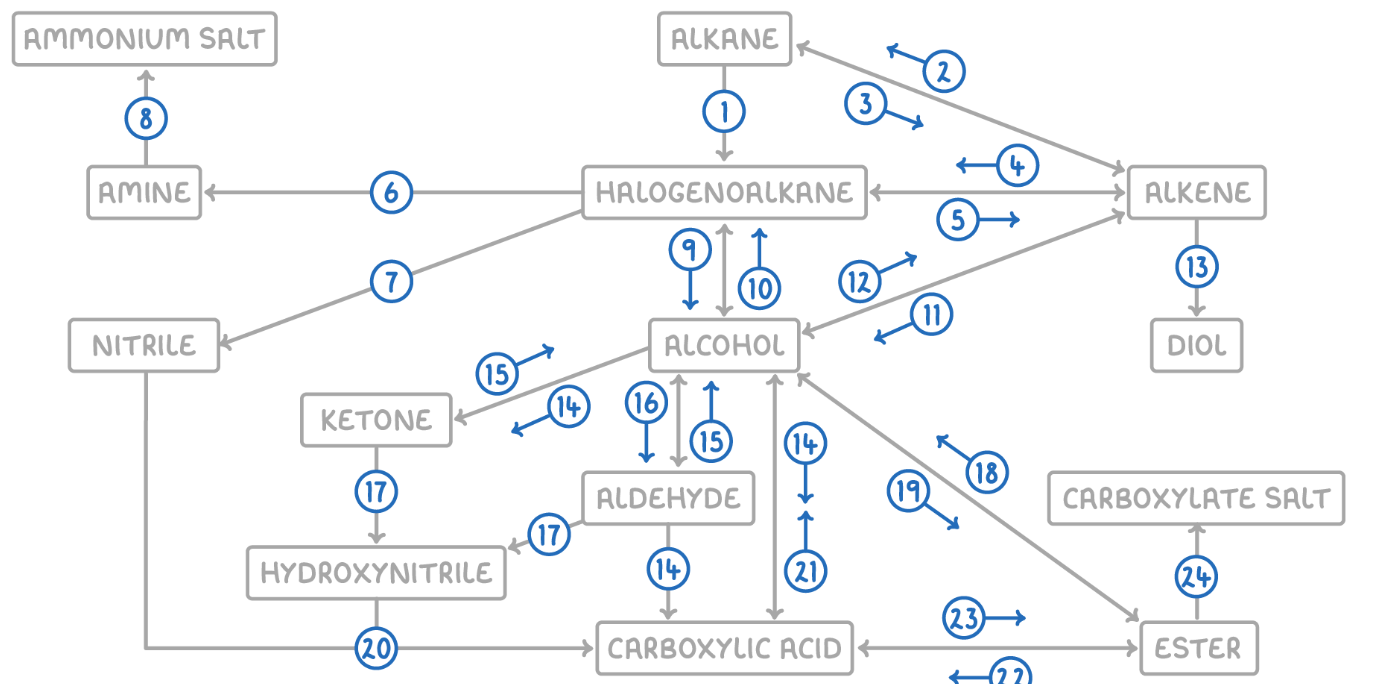
Alcohol to Alkene
Reaction Type: Elimination (Dehydration)
Reagents & Conditions: Concentrated H2SO4 or H3PO4, heated to approx 170°C.
Explanation: Removes a water molecule from the alcohol.
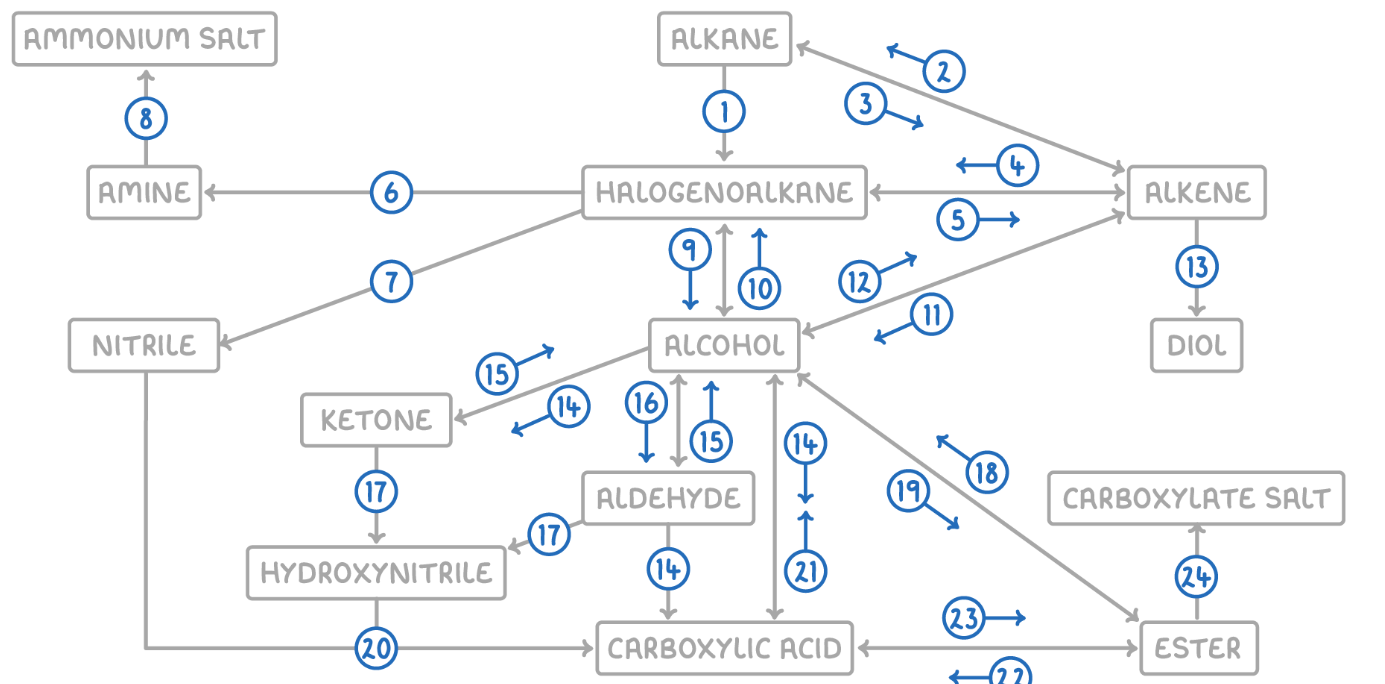
Alkene to Alcohol
Reaction Type: Electrophilic Addition (Hydration)
Reagents & Conditions: Steam (H2O) with H3PO4 catalyst, 300°C, 60 atm (Industrial process).
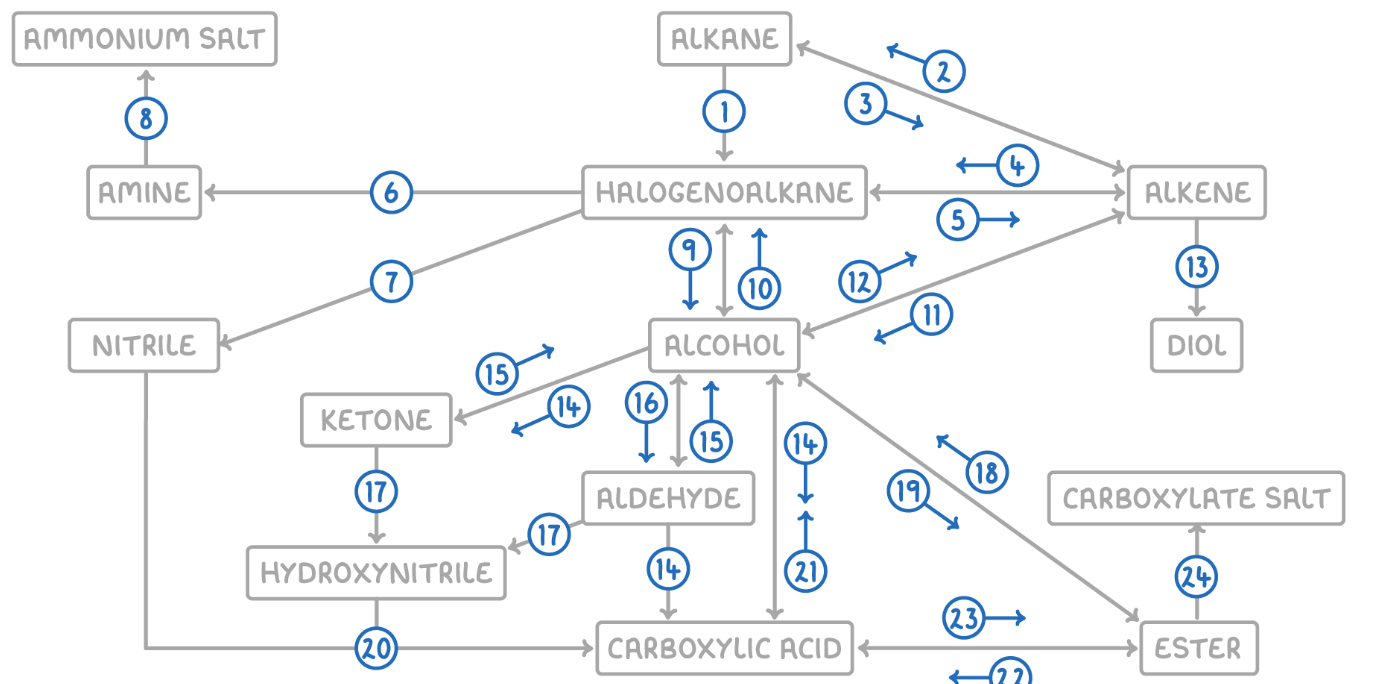
Alkene to Diol
Reaction Type: Oxidation
Reagents & Conditions: Acidified Potassium Manganate(VII) (KMnO4), cold and dilute.
Observation: The purple solution turns colourless (manganese gets reduced).
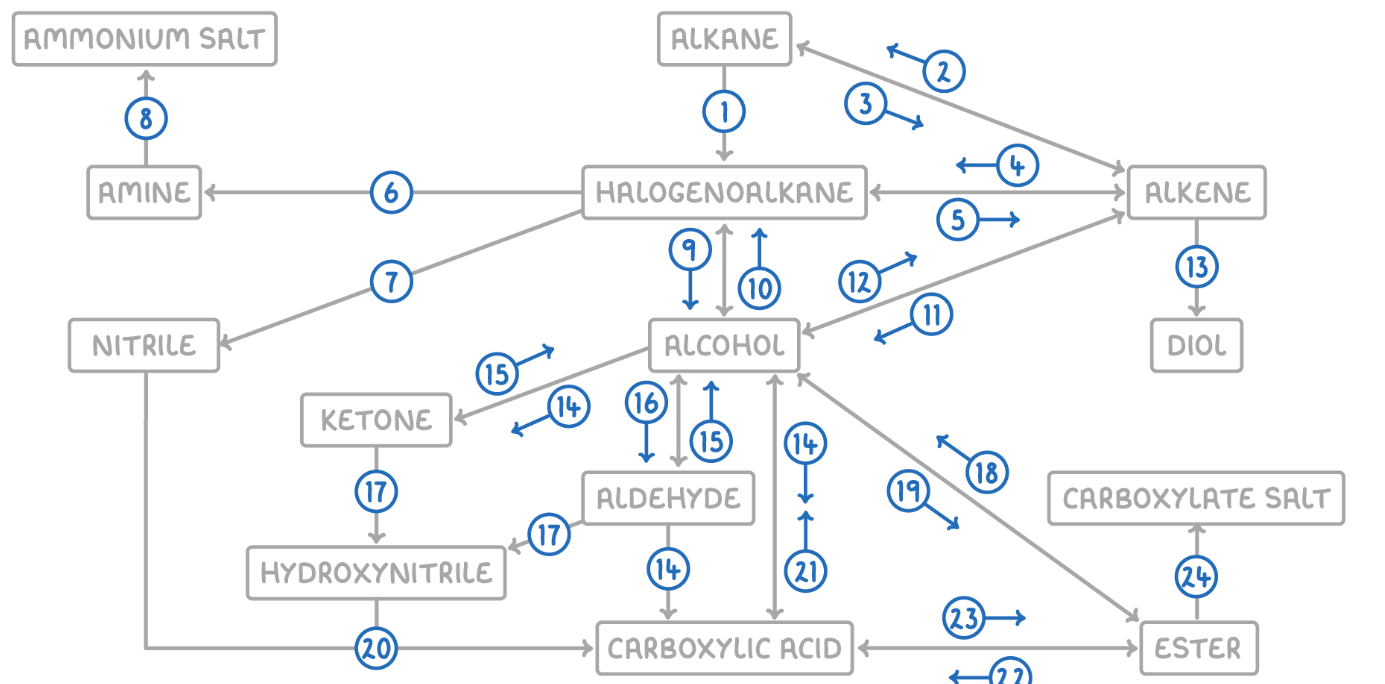
Aldehyde to Carboxylic Acid
Reaction Type: Oxidation
Reagents & Conditions: Acidified Potassium Dichromate (K2Cr2O7), heated under reflux. (Aldehyde)
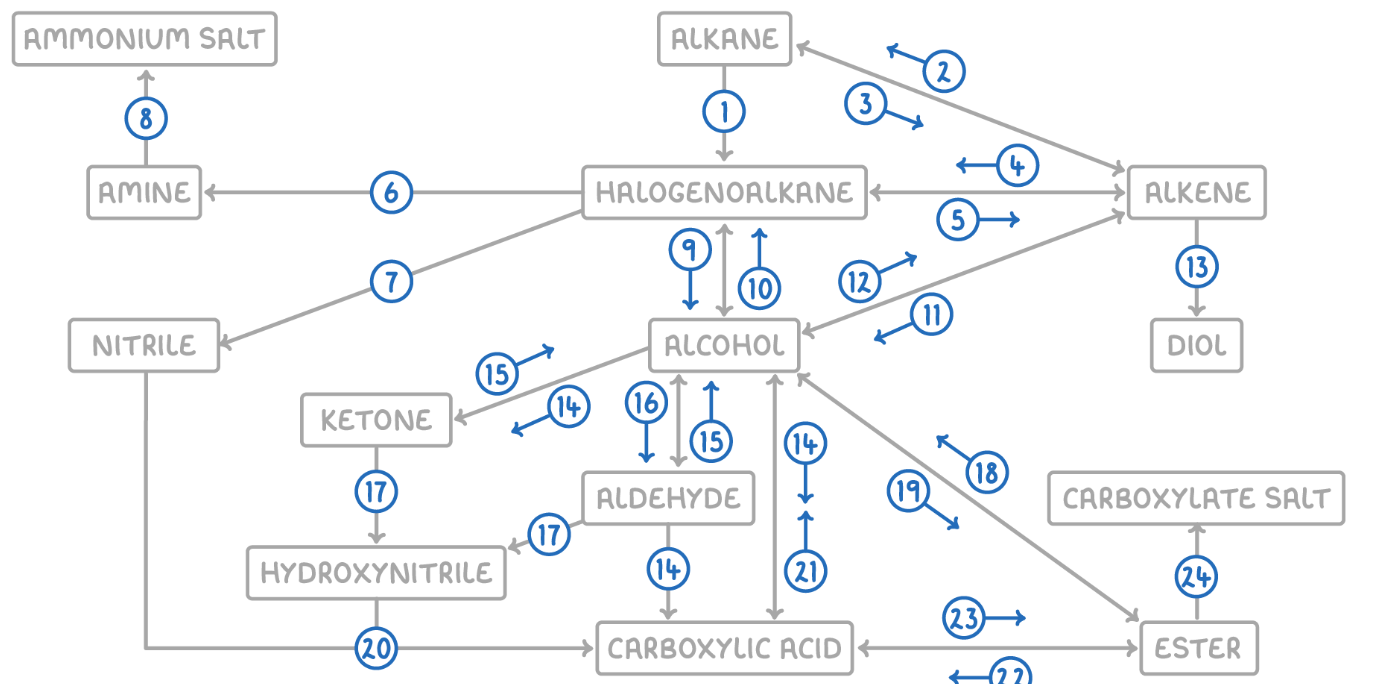
Alcohol (Primary) to Carboxylic Acids
Reaction Type: Oxidation
Reagents & Conditions: Excess Acidified Potassium Dichromate (K2Cr2O7), heated under reflux.
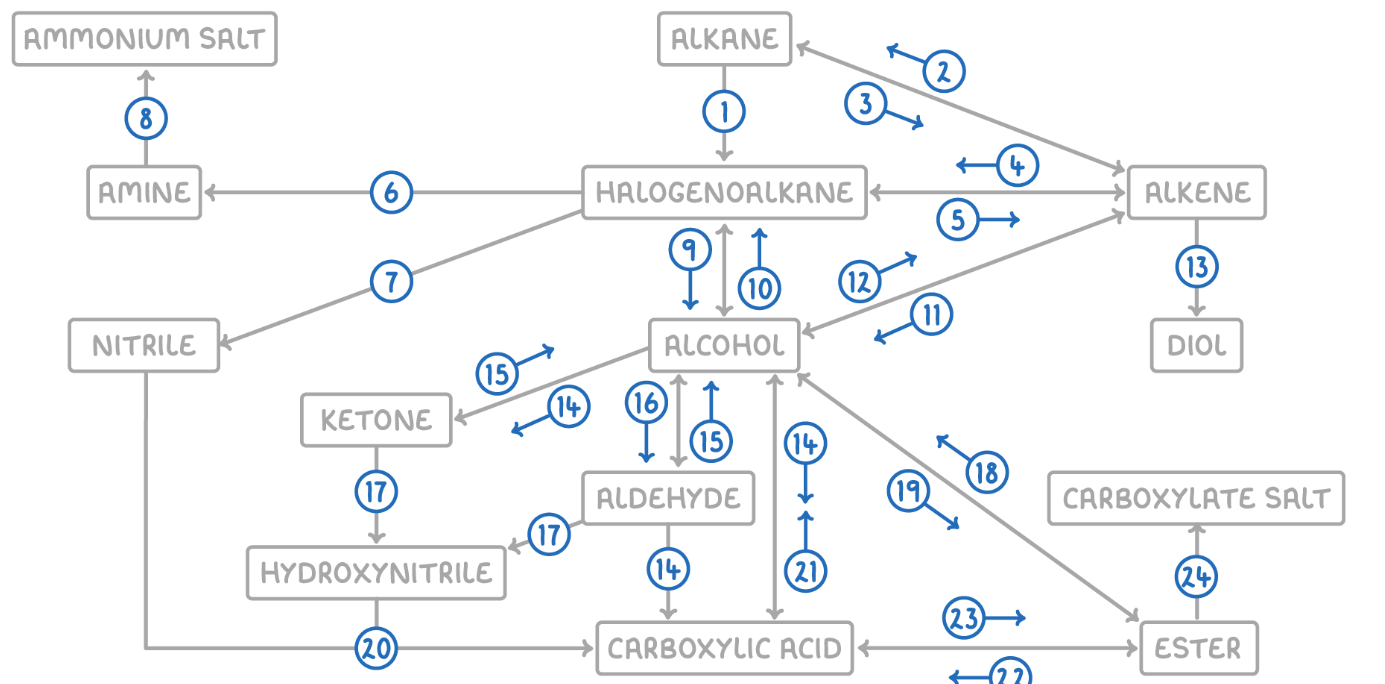
Ketone to Alcohol (Secondary)
Reaction Type: Reduction (to Secondary)
Reagents & Conditions: Warm with aqueous NaBH4 (Sodium Borohydride).
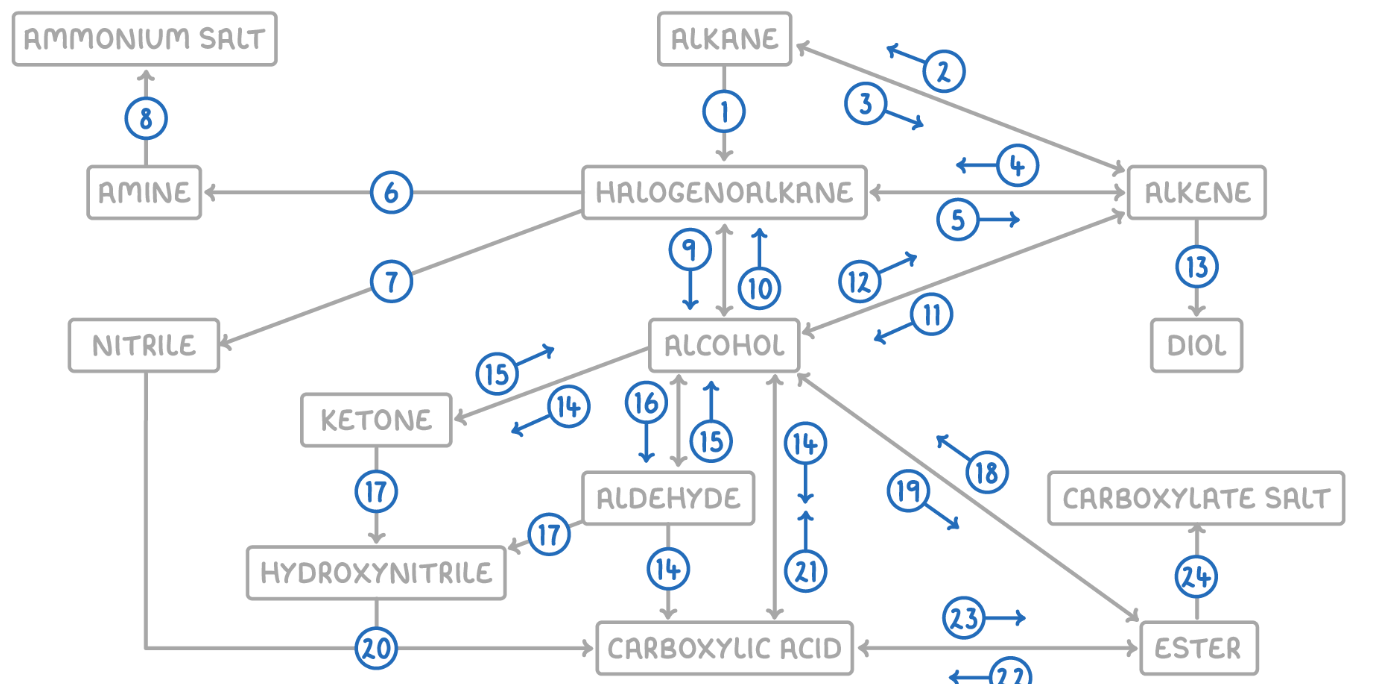
Alcohol (Secondary) to Ketone
Reaction Type: Oxidation
Reagents & Conditions: Acidified Potassium Dichromate (K2Cr2O7), heated under reflux.
Aldehyde to Alcohol (Primary)
Reaction Type: Reduction (to Primary)
Reagents & Conditions: Warm with aqueous NaBH4.
Alcohol (Primary) to Aldehyde
Reaction Type: Partial Oxidation
Reagents & Conditions: Acidified Potassium Dichromate (K2Cr2O7), gently heated and distilled immediately.
Explanation: Distillation removes the aldehyde before it can oxidize further into a carboxylic acid.
Aldehyde/Ketone to Hydroxynitrile
Reaction Type: Nucleophilic Addition
Reagents & Conditions: NaCN (Sodium Cyanide) and dilute H2SO4.
Explanation: This reaction extends the carbon chain.
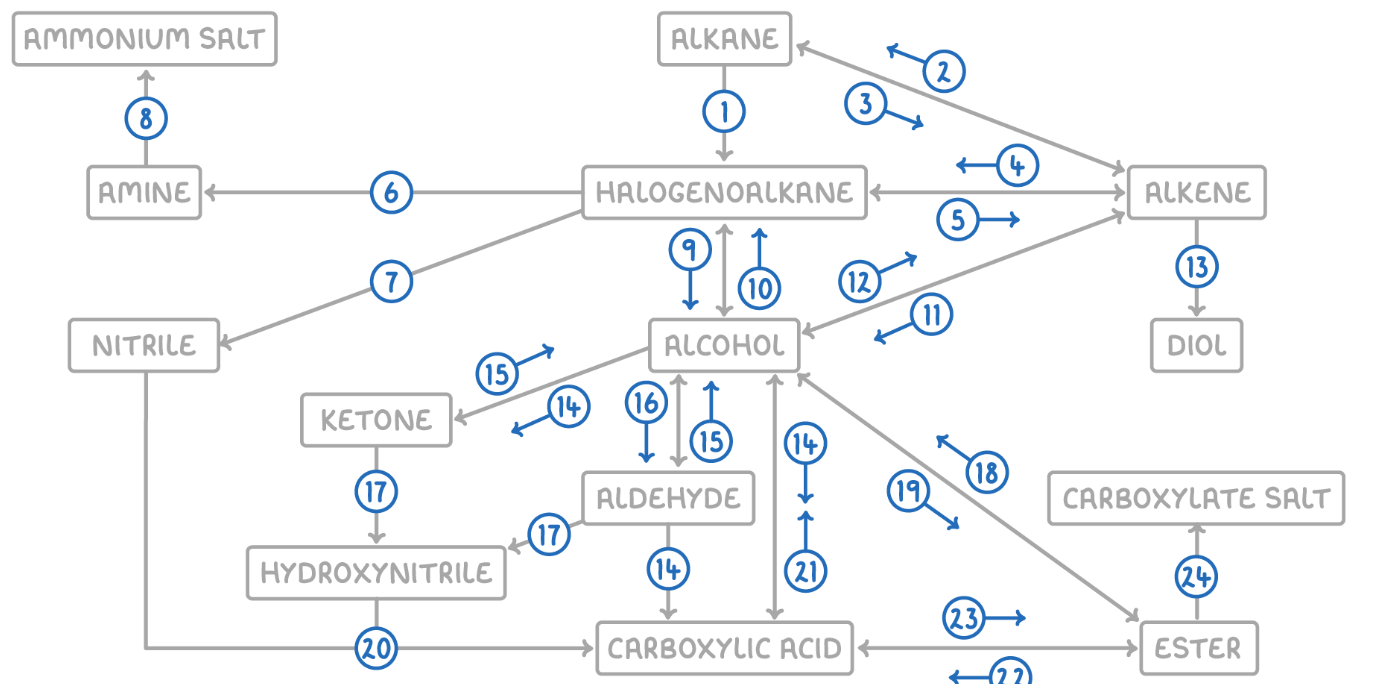
Hydroxynitrile (or Nitrile) to Carboxylic Acid
Reaction Type: Hydrolysis
Reagents & Conditions: Dilute acid (HCl or H2SO4), heated under reflux.
Explanation: The -CN group is converted into a -COOH group.
Carboxylic Acid to Alcohol
Reaction Type: Reduction
Reagents & Conditions: LiAlH4 (Lithium Aluminium Hydride) in dry ether.
Note: This is a strong reducing agent capable of reducing the acid directly to a primary alcohol.
Alcohol to Ester
Reaction Type: Esterification (Condensation)
Reagents & Conditions: Carboxylic acid + concentrated H2SO4 catalyst, heated.
Ester to Alcohol
Reaction Type: Hydrolysis (Acidic or Alkaline)
Reagents & Conditions: Dilute acid or alkali, heated.
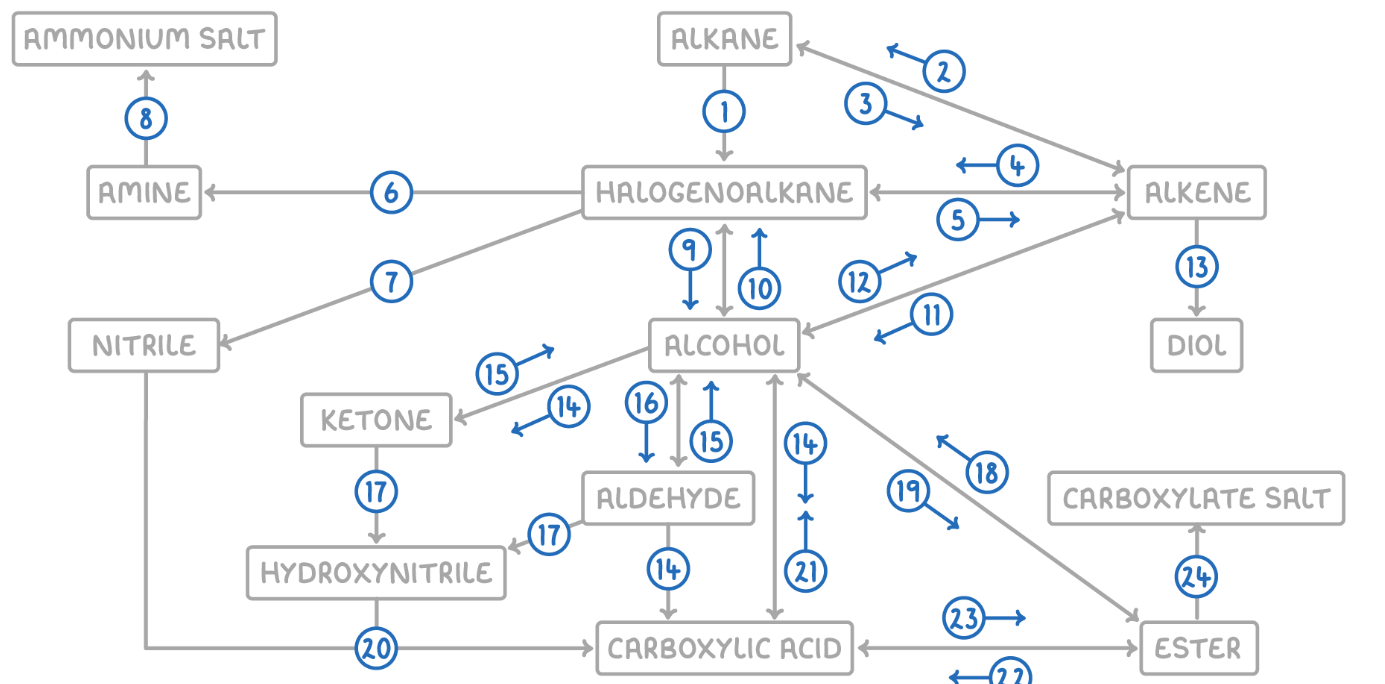
Ester to Carboxylic Acid
Reaction Type: Acid Hydrolysis
Reagents & Conditions: Dilute acid (HCl), heated under reflux.
Product: Produces the carboxylic acid and an alcohol. This reaction is reversible.
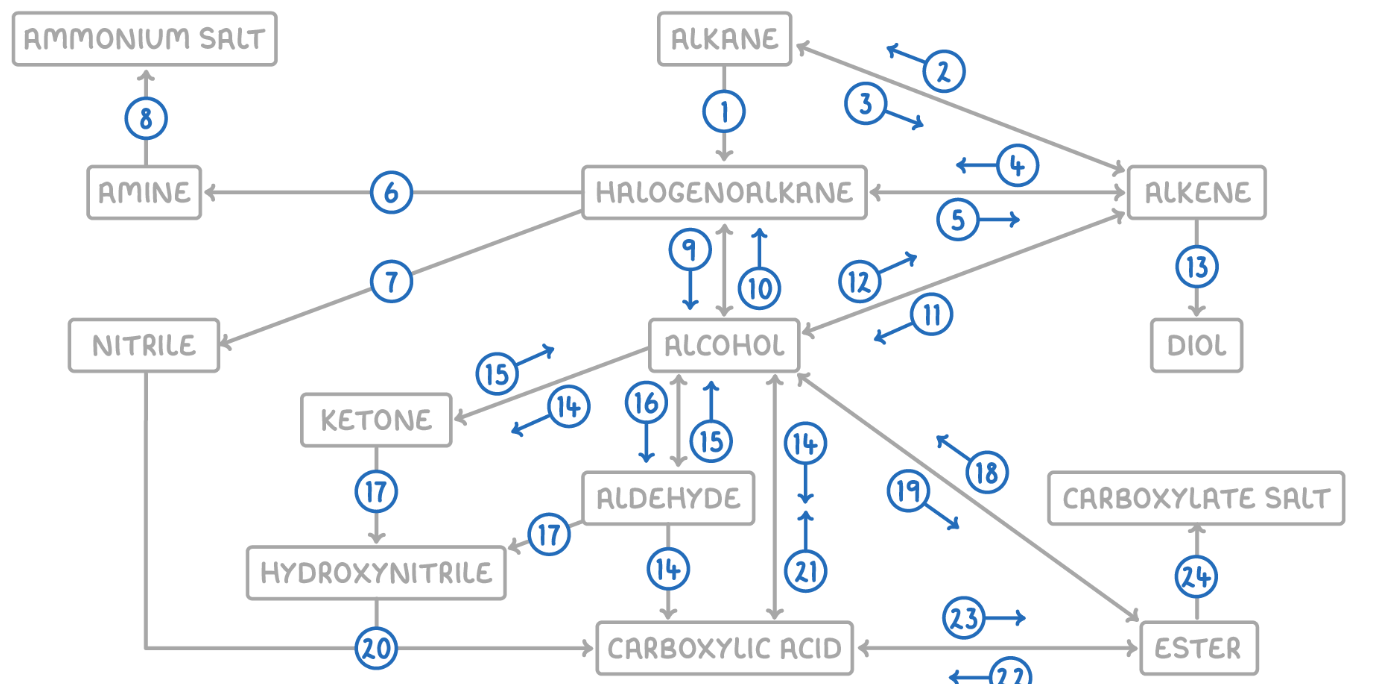
Carboxylic Acid to Ester
Reaction Type: Esterification
Reagents & Conditions: Alcohol + concentrated H2SO4 catalyst, heated.
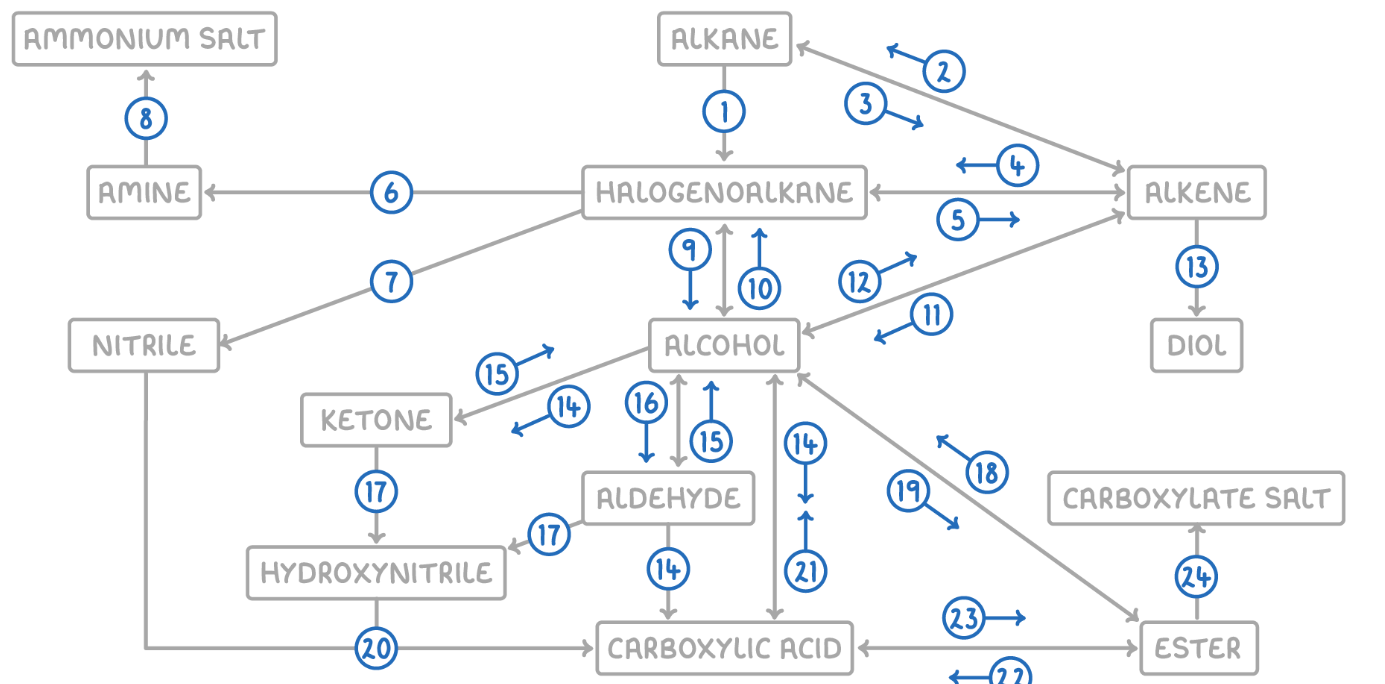
Ester to Carboxylate
Reaction Type: Alkaline Hydrolysis (Saponification)
Reagents & Conditions: Aqueous NaOH or KOH, heated under reflux.
Product: Produces the carboxylate salt (e.g., Sodium Ethanoate) and an alcohol. This reaction is irreversible and has a high yield.