3C- Support Oxygenation and Ventilation
1/66
Earn XP
Description and Tags
TMC: 15 questions
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
67 Terms
Low to moderate oxygen concentrations (FIO2s between 0.21 and 0.50) are generally effective in treating hypoxemia caused by which of the following?
Low alveolar PO2
Diffusion defect
Moderate V/Q imbalance
1 and 2
1 and 3
2 and 3
1, 2 and 3
1, 2, and 3
When hypoxemia is caused by a reduced alveolar PO2, a diffusion defect, or a moderately low V/Q ratio, normal levels of arterial oxygenation can be achieved by simple oxygen therapy techniques, usually with an FIO2 < 0.50. Low to moderate O2 concentrations are not effective in treating hypoxemia due to physiologic shunting ('refractory hypoxemia'). Treatment of hypoxemia due to physiologic shunting requires application of continuous distending pressure (PEEP or CPAP) to open collapsed alveoli and maintain their inflation.
An 84-kg (185-lb) 6-ft 1-in (185-cm) male is receiving mechanical ventilation by a volume-controlled ventilator in the assist/control mode on the following settings and corresponding ABGs:
Mandatory rate: 10/min
VT: 750 mL
FIO2: 0.6
PEEP: 5 cmH2O
pH 7.33
PaCO2 47 mmHg
PO2 78 mmHg
HCO3- 23 mEq/L
BE -1 mEq/L
Which of the following represents the most appropriate action?
add deadspace
decrease rate
increase PEEP
increase VT
increase VT
A patient with asthma receiving volume-controlled ventilation has the following arterial blood results on the settings below:
Mode Assist/control
Mandatory rate 14
VT 600 mL
FIO2 40%
PEEP 5 cm H2O
I:E 1:2
pH 7.48
PaCO2 32 torr
PaO2 81 torr
HCO3- 24 mEq/L
BE 0 mEq/L
Which of the following changes is most appropriate?
increase inspiratory flow
increase rate to 16
add 50-100 mL of deadspace
decrease rate to 10
add 50-100 mL of deadspace
This patient is over ventilating as manifested by low CO2. CO2 may be raised by decreasing mandatory rate, decreasing tidal volume, or adding deadspace. Because CO2 is only barely off of target adding 50-100 mL of dead space is most appropriate. While decreasing rate is a step in the right direction it is likely that decreasing the rate by 4 is too significant.
A tandem aerosol device is used
to deliver sufficient flowrates through large-volume nebulizers.
for patients requiring FIO2 of 0.50 or greater.
whenever the flowrate is set to 15 L/min or above.
on patients with croup
to deliver sufficient flowrates through large-volume nebulizers.
A tandem aerosol device is used when only one device is incapable of producing enough total gas flow to meet or exceed the patient's inspiratory demand.
The primary goal of O2 therapy is to:
decrease the work of breathing
decrease myocardial workload
improve tissue perfusion
correct arterial hypoxemia
correct arterial hypoxemia
If a sudden tension pneumothorax is experienced on a volume-cycled mechanically ventilated patient, the respiratory therapist should expect an increase in
cardiac index
A-aDO2
static compliance
RAW
A-aDO2
A-aDO2 will increase with a pneumothorax because delivered oxygen will have less functional surface area in the pulomnary capllary membranes to diffuse into the ciculatory system. The air trapped in the pleural space pushes against the lung, limiting the lung's ability to expand and utilize all areas of the lung parynchema. The large "A" referes to the Alveolar oxygen tension, while the small "a" refers to arterial oxygen tension in the blood.
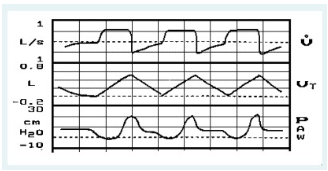
You observe the following graphics display on a patient receiving volume controlled A/C ventilation. The most significant problem is:
a leak in the patient-ventilator system
inadequate inspiratory flow setting
improper sensitivity setting
presence of auto-PEEP/air-trapping
inadequate inspiratory flow setting
A febrile patient is receiving non-invasive positive pressure ventilation with an IPAP of 26 and an EPAP of 10 cmH2O. The following uncorrected blood gas data on these settings is available:
pH 7.32
PaCO2 48 mm Hg
PaO2 80 mm Hg
HCO3- 24 mEq/L
BE 0 mEq/L
Which of the following change is most appropriate?
decrease EPAP
increase IPAP and EPAP
increase IPAP
maintain settings
increase IPAP
Directing a cool oxygen mixture to an infant in an oxyhood can result in which of the following?
increased peripheral perfusion
decreased metabolic rate
increased oxygen consumption
decreased convective heat loss
increased oxygen consumption
A patient develops air trapping/auto-PEEP during positive pressure ventilation. This will tend to increase
baseline airway pressure
patient-ventilator synchrony
pulmonary blood flow
work of breathing
work of breathing
Air trapping/auto-PEEP increases alveolar pressures, thereby impeding pulmonary blood flow, increasing pulmonary vascular resistance and increasing the possibility of pulmonary barotrauma. Auto-PEEP also can cause thoracic distention and flattening of the diaphragm, which can increase the work of breathing. Last, auto-PEEP can result in patient-ventilator dyssynchrony in patient-triggered modes of mechanical ventilation. Auto-PEEP generally does not alter baseline airway pressure. This is why some refer to it a 'occult' PEEP
Which of the following monitoring/alarm systems is mandatory for acutely ill patients receiving noninvasive positive pressure ventilation?
disconnect alarm
volume monitor
inversed I:E ratio
high FIO2 alarm
disconnect alarm
A patient who is hemodynamically unstable experiences a drop in cardiac output from 5.1 L/min to 3.2 L/min immediately following an increase in PEEP from 20 cmH2O to 25 cm H2O. FIO2 is currently at 0.70. The respiratory therapist should first do which of the following?
Increase FIO2 to 1.0
Increase FIO2 to 0.8
Decrease PEEP to 20 cmH2O
Discontinue PEEP
Decrease PEEP to 20 cmH2O
When a patient is receiving high levels of PEEP, the hemodynamic stability of the patient should be monitored. In this case, an increase in PEEP resulted in a decrease in cardiac output to a level that is below normal. Normal cardiac output is 4 to 8 L/min. When this happens, it is paramount that the PEEP level be decreased to its prior setting. Beyond this, to address the patient's hypoxemia, FIO2 should be increased, even if it has to be increased above 60%.
While preparing to administer a metered-dose inhaler (MDI) to a patient with COPD, the respiratory therapist notices the patient becomes unconscious and markedly cyanotic. Which of the following should the therapist immediately do?
place on a nonrebreathing mask
deliver several puffs of the MDI
page the physician
begin chest compressions
place on a nonrebreathing mask
A patient with COPD is receiving oxygen therapy at 2 L/min by nasal cannula. During a routine check, the respiratory therapist finds the patient unresponsive. The ECG waveform on the monitor is consistent with ventricular tachycardia. The therapist should immediately
Perform cardioversion
Place the patient on a nonrebreathing oxygen mask and check for a pulse
Begin chest compressions
Defibrillate at 360 joules with synchronization set to ON
Place the patient on a nonrebreathing oxygen mask and check for a pulse
An 18-hour-old, 29-week gestational age neonate is being maintained on a ventilator with an FIO2 of 0.5. The neonatologist believes that the patient has respiratory distress syndrome (RDS). The following blood gas results are obtained from an umbilical artery sample:
pH 7.35; PaCO2: 37 torr; PaO2: 49 torr; HCO3: 25 mEq/L
Based on this information, what should the respiratory therapist recommend?
Get a chest radiograph film to look for a pneumothorax
Get an ABG sample from a radial artery
Give 100% O2 in an O2 hood.
Start 5 cm H2O PEEP.
Start 5 cm H2O PEEP.
100% O2 may help to improve oxygenation. However, the patient should remain on the ventilator since an oxygen hood does not support breathing. PEEP should improve the PaO2 level since it will increase the functional residual capacity (FRC). It is indicated on the basis of low O2 and normal CO2 levels.
A patient receiving mechanical ventilation is experiencing an increase in autoPEEP. Which of the following should the respiratory therapist increase to lower autoPEEP?
mandatory rate
PEEP
flow rate
pressure support
flow rate
A 50 kg (110 lb) patient requires mechanical ventilation. Which of the following tidal volumes should be selected INITIALLY?
400 mL
800 mL
200 mL
600 mL
400 mL
With the exception of ARDS/IRDS patients, tidal volumes of about 8 mL/kg are suitable. In this instance, a tidal volume in the range of 400 mL (8 mL/kg x 50 kg) would be acceptable.
Blood gas results for a patient receiving mechanical ventilation with an FIO2 1.0 and PEEP of 25 cm H2O are as follows:
pH 7.37
PaCO2 43 torr
PaO2 110 torr
HCO3- 24 mEq/L
BE -1 mEq/L
The respiratory therapist should recommend
performance of an optimal PEEP study
administration of potassium chloride (KCL)
decrease in FIO2
decrease in PEEP
decrease in FIO2
Arterial blood gas results reveal adequate ventilation but over oxygenation. To correct this either PEEP or FIO2 may be decreased. When oxygen percentage is greater than 60%, FIO2 should be decreased first to below 60%. Then, PEEP may be decreased.
The development of AutoPEEP is mostly likely caused by which of the following:
insufficient inspiratory flow rate
excessive expiratory time
mechanical sighs
excessive inspiratory flow rate
insufficient inspiratory flow rate
A patient with in the emergency room is tolerating NPPV with 40% oxygen by mask to prevent full mechanical ventilation. IPAP is 22 cmH2O and an EPAP is 10 cmH2O. The following blood gas data is available:
pH 7.31
PaCO2 50 mm Hg
PaO2 129 mm Hg
HCO3- 26 mEq/L
BE +20 mEq/L
Which of the following changes is most appropriate?
decrease EPAP
intubate and place on a volume-cycled ventilator
increase IPAP
decrease FIO2 and increase IPAP
decrease EPAP
This patient has two problems - elevated CO2 (under ventilation) and over oxygenation. Under ventilation may be corrected by increasing the distance between inspiratory pressure and expiratory pressure. Over oxygenation may be addressed by decreasing expiratory pressure alone. In this case, decreasing expiratory pressure will also increase the distance between the inspiratory and expiratory pressures, thereby increasing ventilation. Therefore, the best option is to decrease EPAP only.
While caring for a patient receiving volume-controlled ventilation you note a sudden drop in the peak inspiratory pressure. Causes of this change could include which of the following?
Tension pneumothorax
Burst ET tube cuff
Exhalation valve leak
1 and 2
1 and 3
2 and 3
1, 2 and 3
2 and 3
During volume-controlled ventilation, there are three basic reasons for a fall in peak inspiratory pressure: (1) a decrease in either the volume or flow setting; (2) patient-ventilator system leaks, such as an ET tube cuff leak or a malfunctioning exhalation valve; and (3).decreased patient impedance, i.e., decreased airway resistance or increased lung/thorax compliance. A tension pneumothorax would decrease lung compliance and thus increase peak inspiratory pressures.
Arterial blood gases on a patient in the cardiac intensive care unit are as follows:
pH 7.31
PaCO2 50 mmHg
PaO2 81 mmHg
HCO3- 24 mEq/L
BE 0 mEq/L
Which of the following is an appropriate action?
increase minute ventilation
administer sodium bicarbonate
decrease FIO2
increase FIO2
increase minute ventilation
A 46-year-old male patient, weighing 176 lb (80 kg), is receiving mechanical ventilatory support. The patient is being weaned from the ventilator over the last several hours. Current ventilator settings are: SIMV, rate 4, VT 550 mL, FIO2 0.40, PEEP 5 cm H2O. An assessment of the patient reveals the following:
MIP -32 cm H2O
VC 1.1 L
VT(spontaneous) 300 mL
RR 16/min
pH 7.35
PaCO2 45 torr
PaO2 80 torr
HCO3- 26 mEq/L
BE 0 mEq/L
The respiratory therapist should recommend
discontinuing mechanical ventilatory support
continuing current therapy and monitor
reducing mandatory rate to 2
placing the patient back on full ventilatory support
placing the patient back on full ventilatory support
To determine if the patient is ready to wean we must examine the MIP, VC, and tidal volume as well as other ventilatory and clinical parameters. Minimum tidal volume is 5 mL per kilogram. This patient weighs 80 kg which means the appropriate minimum spontaneous tidal volume must be at least 400 mL. This patient has a tidal volume of 300 mL, indicating that lack of readiness to wean from the ventilator. All other parameters appear appropriate. Even if only one parameter is not appropriate, the patient should not be weaned from the ventilator.
Which of the following patients would benefit most from an inverse I:E ratio ventilation?
kyphoscoliosis
ARDS
COPD
chronic bronchitis
ARDS
A 3-year-old child is receiving oxygen therapy by an aerosol tent after being admitted for laryngotracheobronchitis. The respiratory therapist notices large fluctuations in FIO2 inside the canopy. The therapist should
close the upper opening in the tent
increase oxygen flow rate
switch to an oxyhood
increase aerosol output
increase oxygen flow rate
A 75-kg (165-lb) male is receiving mechanical ventilation by a volume-controlled ventilator in the assist/control mode on the following settings:
Mandatory rate 16
VT 500 mL
FIO2 0.5
PEEP 5 cm H2O
Arterial blood gas results:
pH 7.29
PaCO2 51 mm Hg
PO2 68 mm Hg
HCO3- 25 mEq/L
BE +1 mEq/L
Which of the following represents the most appropriate action?
increase FIO2 to 0.6
increase tidal volume to 650 mL
increase PEEP to 8 cmH2O
increase rate to 18
increase rate to 18
Arterial blood gases show the patient is not ventilating and is under oxygenating. Because ventilation should be corrected first it is appropriate to either increase the tidal volume or increase the rate. In this case the PaCO2 is off by more than 4 mmHg and therefore should be addressed only with an increase in rate.
Which of the following will result in an increase in mean airway pressure for a patient receiving volume-controlled ventilation?
decrease in mandatory rate
increase inspiratory flow rate
decreased I:E ratio
increase in tidal volume
increase in tidal volume
Mean airway pressure increases most significantly with an increase in mandatory rate on a ventilator. The second most significant cause of increased mean airway pressure is an increase in tidal volume. Increasing inspiratory flow rate, decreasing mandatory rate, and decreasing inspiratory time will all cause a decrease in mean airway pressure.
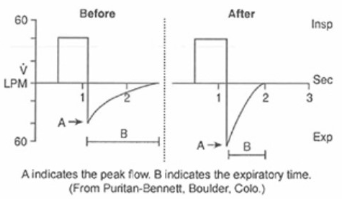
A 20-year-old asthma patient is receiving mechanical ventilation on a microprocessor-type ventilator. The following graphics are noted before and after the patient is given 0.5 mL of aerosolized levalbuterol (Xopenex). How should the results be interpreted?
The patient has normal airway resistance
The medication dose is ineffective.
Suctioning is needed
The patient's bronchospasm has decreased.
The patient's bronchospasm has decreased.
A 65-kg (143-lb), 5-ft, 5-in male patient with pneumonia is receiving mechanical ventilator support by a Servo adult ventilator on the following settings with corresponding arterial blood gas values:
Mode Assist/control
Mandatory rate 14/min
VT 450 mL
FIO2 0.6
PEEP 5 cmH2O
pH 7.35
PaCO2 45 mmHg
PaO2 74 mmHg
HCO3- 24 mEq/L
BE 0 mEq/L
Which of the following actions is most appropriate?
increase PEEP
increase rate
increase tidal volume
increase FIO2
increase PEEP
True control mode ventilation (patient not able to trigger breaths or breathe spontaneously) is indicated in which of the following situations?
hypercapnic respiratory failure
hypoventilation syndrome
management of tetanus seizures
ventilator weaning
management of tetanus seizures
An 89-kg (196-lb), 175-cm (5-ft 9-in) male patient has received mechanical ventilatory support for the past 7 days. He has the following data after a one-hour trial on t-piece at FIO2 0.40:
pH 7.35
PaCO2 45 torr
PaO2 90 torr
HCO3- 25 mEq/L
RR 28
Tidal volume 400 mL
Extubate and place on Bi-Level therapy at FIO2 0.40.
Discontinue mechanical ventilation.
Reduce FIO2 to 0.40.
Continue the weaning trial.
Continue the weaning trial.
The patient's clinical data and weaning parameters are all within acceptable ranges, therefore weaning should continue.
A doctor orders a changeover to CPAP for a patient receiving bi-level positive airway pressure (BiPAP) via a device with separate IPAP and EPAP controls. To effect this change you would:
set EPAP = 0 cm H2O
set IPAP greater than EPAP
set IPAP less than EPAP
set IPAP equal to EPAP
set IPAP equal to EPAP
To provide CPAP on a bi-level positive airway pressure (BiPAP) device, you could either set the unit to the CPAP mode or set the unit to the BiPAP/spontaneous breath mode with IPAP equal to EPAP.
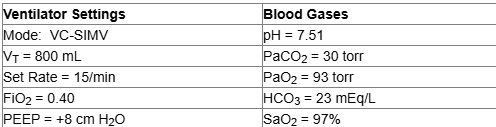
A patient who weighs 85 kg (187 lb) is receiving volume controlled SIMV after open-heart surgery. Ventilator settings and blood gases are below. Based on these data, you should:
add mechanical deadspace
reduce the set (machine) rate
decrease the PEEP to 5 cm H2O
increase the set tidal volume
reduce the set (machine) rate
The low PaCO2 and high pH with normal HCO3 reveal acute respiratory alkalosis/hyperventilation. Since the set SIMV (mandatory) rate is high, it should be reduced. This will lower the total minute ventilation, raise the PaCO2 and lower the pH back toward normal. In general, mechanical deadspace is contraindicated in modes that allow spontaneous breathing such as SIMV.
A patient is receiving non-invasive positive pressure ventilation with an IPAP of 28 and an EPAP of 12 cmH2O. The following blood gas data on these settings is available:
pH 7.37
PaCO2 42 mm Hg
PaO2 72 mm Hg
HCO3- 24 mEq/L
BE 0 mEq/L
Which of the following change is most appropriate?
decrease IPAP and EPAP
decrease EPAP
increase IPAP
increase IPAP and EPAP
increase IPAP and EPAP
This patient shows adequate ventilation but mild hypoxemia. To correct hypoxemia, expiratory pressure should be increased. However, increasing expiratory pressure alone will decrease the distance between the inspiratory and expiratory pressures and will inadvertently decrease ventilation. This is not desirable because CO2 is already appropriate. To prevent a change in ventilation IPAP must be increased by the same degree that EPAP is increased.
A patient is undergoing a full cardiopulmonary arrest. The patient is intubated and is being monitored with an infrared capnographic device. PetCO2 data is showing 3%. Which of the following is most appropriate?
recalibrate the capnometer
increase alveolar ventilation
obtain PaCO2 by a Douglas bag
clean the infrared device
increase alveolar ventilation
An end-tidal CO2 of only 3% is low. This indicates poor ventilation. In looking at the answers the best one is poor alveolar perfusion. A clean infrared device does not relate and the calibration of the capnograph is not pertinent.
A 70-kg (154-lb) female patient with myasthenia gravis is receiving mechanical ventilation by a volume-controlled ventilator in the assist/control mode on the following settings:
Mandatory rate 10/min
VT 600 mL
FIO2 0.5
ABG:
pH 7.47
PaCO2 33 mmHg
PO2 81 mmHg
HCO3- 23 mEq/L
BE -1 mEq/L
Which of the following represents the most appropriate action?
decrease rate to 8
increase rate to 12
add 50 mL of deadspace
decrease VT to 500 mL
add 50 mL of deadspace
To adjust patient oxygenation during high-frequency oscillation ventilation (HFOV), you manipulate which of the following settings:
oscillation frequency
mean pressure (Pmean)
% inspiratory time
amplitude/power
mean pressure (Pmean)
The main determinant of oxygenation during HFOV is the mean airway pressure (Pmean). In general, the higher Pmean, the larger the FRC and the better the oxygenation for a given FIO2.
Which of the following is accurate regarding time-cycled, pressure-limited mechanical ventilation?
I-time varies with peak inspiratory pressure
Tidal volume remains constant as flow rate changes
I-time is constant, regardless of flowrate.
Tidal volume will decrease as I-time is increased
I-time is constant, regardless of flowrate.
I-time is directly controlled in time-cycle, pressure-limited mechanical ventilation. It then remains constant and is not affected by flow rate or peak inspiratory pressure. Adjustments made to flow in this mode of mechanical ventilation will result in changes to the delivered tidal volume. If I-time is changed, the delivered tidal volume will also change in a directly proportional manner.
A patient with bilateral pneumonia is receiving pressure-controlled ventilation with the following arterial blood results on the settings below:
Mode PCV
Mandatory rate 22
PIP 25 cm H20
FIO2 0.65
PEEP 15 cm H2O
pH 7.29
PaCO2 51 torr
PaO2 65 torr
HCO3- 26 mEq/L
BE +2 mEq/L
Which of the following should be increased?
FIO2
PIP
Rate
PEEP
PIP
This event is demonstrating hypoventilation as manifested by a high PaCO2. On a time-cycled ventilator the most appropriate control to adjust in order to decrease CO2 is the peak inspiratory pressure (PIP).
Which of the following is true regarding the assist/control (A/C) mode ventilation?
A/C does not provide full ventilatory support
A/C avoids patient-ventilator asynchrony
A/C decreases the occurrence of auto-PEEP
A/C can result in hyperventilation
A/C can result in hyperventilation
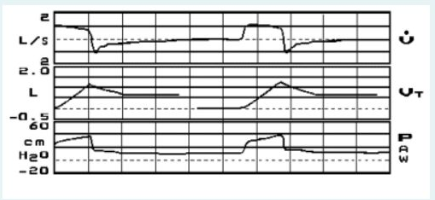
You observe the following graphics display on a patient receiving volume controlled ventilation. The most significant problem is:
presence of auto-PEEP/air-trapping
improper sensitivity setting
A leak in the patient-ventilator system
inadequate inspiratory flow setting
A leak in the patient-ventilator system
The respiratory therapist notes refractory hypoxemia in a patient breathing with a nonrebreathing mask. The therapist should do which of the following to improve oxygenation?
Partial rebreathing mask
Switch to a nasal cannula
CPAP
IPPB
CPAP
The main treatment for refractory hypoxemia, which is often associated with ARDS, is positive airway pressure. If the patient is receiving mechanical ventilatory support, this is called PEEP. Without ventilatory support this is called CPAP.
At least what percent improvement would you want to see in the P/F ratio after implementing a recruitment maneuver to consider it successful?
5%
15%
20%
0%
20%
Which of the following ventilator alarm/indicator systems would indicate inadequate flow for a patient receiving volume control A/C ventilation?
low tidal volume
high pressure limit
I:E ratio
low PEEP/CPAP
I:E ratio
On many ventilators, an I:E ratio alarm/indicator system is activated when the inspiratory time exceeds the expiratory time. The most common cause for this event during volume control ventilation is inadequate inspiratory flow, which can be rectified simply by increasing the flow.
Which of the following conditions is an NOT an indication for the use of PEEP?
pulmonary edema
pulmonary shunting
atelectasis
pulmonary embolism
pulmonary embolism
A disadvantages of using a self-inflating resuscitator on an infant is that:
pressure-release valves make over-inflation of the lungs less likely.
maximum FIO2 of 1.0 is difficult to maintain.
use more commonly results in gastric insufflation.
it is difficult to assess the seal between the mask and face.
it is difficult to assess the seal between the mask and face.
Even after extensive adjustments and coaching, a patient receiving noninvasive positive pressure ventilation (NPPV) via a nasal mask has excessive mouth leakage. Which of the following would you initially try to resolve this problem?
nasal pillows
lip seal
oronasal mask
chin strap
chin strap
You need to deliver the highest possible FIO2 to a 67 year-old male patient with pulmonary edema breathing at a rate of 35/min. Which of the following oxygen delivery systems would be most appropriate?
nasal cannula at the flush setting
partial rebreathing mask at 12-15 L/min
aerosol mask with nebulizer set to 100%
non-rebreathing mask at 12-15 L/min
non-rebreathing mask at 12-15 L/min
A patient with pulmonary edema is coughing up large quantities of pink, frothy sputum. ABG values while breathing 30% oxygen are as follows:
pH 7.42: PaCO2 28 torr; PaO2 45 torr; HCO3 21 mEq/L
What would be the best treatment?
IPPB with compressed air
Mask CPAP at 5 cm water with 40% O2
50% O2 and postural drainage therapy
Start intrapulmonary percussive ventilation.
Mask CPAP at 5 cm water with 40% O2
An 18-hour-old, 29-week gestational age neonate is being maintained on a ventilator with an FIO2 of 0.5. The neonatologist believes that the patient has respiratory distress syndrome (RDS). The following blood gas results are obtained from an umbilical artery sample:
pH 7.35; PaCO2: 37 torr; PaO2: 49 torr; HCO3: 25 mEq/L
Based on this information, what should the respiratory therapist recommend?
Get an ABG sample from a radial artery
Get a chest radiograph film to look for a pneumothorax
Give 100% O2 in an O2 hood.
Start 5 cm H2O PEEP.
Start 5 cm H2O PEEP.
A pediatric patient with status asthmaticus is receiving volume control A/C ventilation. You observe on the ventilator's graphics screen that the expiratory flow fails to drop to zero before the next machine breath. What could you do to correct the situation?
decrease the expiratory time
increase the set VT
switch to pressure control
decrease the respiratory rate
decrease the respiratory rate
The fact that the patient's expiratory flow fails to reach zero before the next machine breath indicates the presence of air-trapping or auto-PEEP. Assuming that the patient is not suffering from bronchospasm (in which case a bronchodilator treatment should be given), the best way to minimize auto-PEEP is to assure an adequate expiratory time. You can do this by: 1) decreasing the inspiratory time (higher flow), 2) increasing the expiratory time, or 3) decreasing the set rate. Unless accompanied by an increase in expiratory time, switching to the pressure control mode will not correct this problem. And without a change in flow, increasing the VT will increase the inspiratory time and I:E ratio, thus potentially worsening the problem.
In assessing a patient receiving volume controlled A/C ventilation, you note that the I:E warning light is flashing and that the I:E ratio is 1:0.7. Which of the following actions would you take to correct this problem?
increasing the inspiratory flow
obtaining an arterial blood gas
activating the I:E limit system
increasing the preset breathing rate
increasing the inspiratory flow
For most adults, an I:E ratio of 1:2 or 1:3 is desirable. A high I:E ratio (> 1:1.5) indicates that inspiration is too long relative to exhalation. In this case, one should check and adjust the inspiratory flow provided by the ventilator (increasing the flow decreases the inspiratory time).
Which of the following conditions is an indication for the use of PEEP?
tension pneumothorax
pulmonary embolism
pulmonary edema
asthma
pulmonary edema
PEEP (positive end-expiratory pressure) can help overcome the shunting and hypoxemia common in both cardiogenic and noncardiogenic pulmonary edema. In cardiogenic pulmonary edema, PEEP can help decrease venous return and thus decreases pulmonary blood flows and pressures. In noncardiogenic pulmonary edema (e.g., ARDS), PEEP opens collapsed alveoli and improves the V/Q ratio.
An adult patient in the Emergency Department has the following blood gases on a simple O2 mask @ 8 L/min: pH=7.19; PaCO2=68 torr; HCO3=25 mEq/L; PaO2= 85 torr. The attending physician orders intubation and ventilatory support. Which of the following modes of support would you consider appropriate for this patient?
VC-A/C, rate = 12/min
VC-SIMV, rate = 12/min
Demand flow CPAP @ 10 cm H2O
1 and 3
1, 2 and 3
2 and 3
1, and 2
1, and 2
A patient is weaning from mechanical ventilation on the following ventilator settings:
Mode SIMV
Mandatory rate 6/min
Total rate 30/min
VT (set) 500 mL
VT (exhaled) 220 mL
FIO2 0.40
PEEP 5 cmH2O
Pressure support 6 cmH2O
Arterial blood gas results show:
pH 7.34
PaCO2 46 torr
PaO2 80 torr
HCO3- 24 mEq/L
BE -2 mEq/L
The respiratory therapist should recommend
Switching to assist/control mode of ventilation
Increasing the set tidal volume
Increasing pressure support
Increasing PEEP to 10 cm H2O
Increasing pressure support
This patient is obviously weaning from the ventilator, as manifested by the SIMV mode and a mandatory rate of 6. However, an excessive total rate of ventilation, 30 per minute, and markedly reduced spontaneous tidal volumes are indications that the patient is experiencing an increase in labor of breathing. The best solution is to assist the patient in taking larger tidal volumes. This can best be done by administering or increasing pressure support. Pressure support will increase spontaneous tidal volume size, decrease total respiratory rate, and decrease the overall work of breathing.
A mechanically ventilated patient is improving and the physician wants to begin weaning procedures. Originally, she was receiving VC-A/C. She has now been placed on pressure support ventilation at 10 cm H2O. At first, the patient seemed comfortable on PSV. But, after 45 minutes she complained of breathing difficulty. What should the respiratory therapist INITIALLY recommend?
Increase the pressure support level to 15 cm H2O
Add 5 cm H2O of positive end-expiratory pressure
Put her back on the VC-A/C mode
Give diazepam (Valium) for anxiety.
Increase the pressure support level to 15 cm H2O
An oxygen-dependent COPD patient is brought to the emergency room on 4 L/min oxygen by nasal cannula. From the paramedic documentation it is observed that respiratory rate has changed from 30 to 18 bpm. Heart rate has decreased from 120 to 90. Saturation is 92% and the patient's color has also improved. The therapist should do which of the following?
maintain current therapy
switch to a partial rebreathing mask
decrease flow to 1 lpm
discontinue oxygen therapy
decrease flow to 1 lpm
A 75-kg (165-lb) male is receiving mechanical ventilation by a volume-controlled ventilator in the assist/control mode on the following settings:
Mandatory rate 12/min
VT 500 mL
FIO2 0.6
PEEP 8 cm H2O
Arterial blood gas results:
pH 7.30
PaCO2 52 mm Hg
PO2 65 mm Hg
HCO3- 27 mEq/L
BE +3 mEq/L
Which of the following represents the most appropriate action?
increase tidal volume to 600 mL
increase PEEP to 10 cmH2O
increase rate to 14
increase FIO2 to 1.0
increase rate to 14
Arterial blood gases show the patient is not ventilating and is under oxygenating. Because ventilation should be corrected first it is appropriate to either increase the tidal volume or increase the rate. In this case the PaCO2 is off by more than 4 mmHg and therefore should be addressed only with an increase in rate.
You are asked to assist in turning an adult ICU patient receiving continuous ventilatory support via an endotracheal tube. Which of the following is your responsibility during this procedure?
prevent accidental extubation
prevent accidental removal of epigastric tube
prevent disconnection of the Foley catheter
prevent disconnection of vascular lines
prevent accidental extubation
To adjust the CPAP level generated by a simple water column, you would:
vary the depth of expiratory line under water
increase the flow through the CPAP circuit
vary the depth of inspiratory line under water
decrease the flow through the CPAP circuit
vary the depth of expiratory line under water
When a dual-limb breathing circuit is used to provide continuous flow CPAP, the expiratory limb is connected to a separate PEEP/CPAP valve, such as an underwater column or spring-loaded disk. With a water column PEEP/CPAP valve, you simply immerse the expiratory limb of the circuit under water. The PEEP/CPAP level is adjusted by varying how far you immerse the tube under water, with each centimeter equal to 1 cm H2O PEEP/CPAP.
A 52-year old, 75 kg (165 lb) male with a history of Guillain-Barre Syndrome is receiving full ventilatory support with a volume-controlled ventilator at the following settings:
Mode A/C
FIO2 0.60
Rate 14
VT 550 mL
PEEP 5 cm H2O
Arterial blood gas analysis reveals the following:
pH 7.23
PaCO2 58 torr
PaO2 69 torr
HCO3- 26 mEq/L
BE +1 mEq/L
Which of the following actions should the respiratory therapist take first?
Increase the mandatory rate
Increase tidal volume to 600 mL
Increase PEEP to 10 cmH2O
Switch to SIMV and add pressure support
Increase the mandatory rate
Arterial blood gases reveal that the patient is under ventilating and under oxygenating. Because of ventilation should be corrected before oxygenation, the high CO2 must be addressed first. CO2 may be lowered by increasing mandatory rate or increasing tidal volume. CO2 may also be lowered by removing dead space but that is not an option that is offered here. Because CO2 is out of range by more than 4 mmHg the most appropriate option is to increase mandatory rate.
A motorcycle accident victim keeps removing a 28% Venturi mask, complaining that the device causes his beard to itch and is 'noisy.' His SpO2 is 92%. What action should you take?
change to a 24% Venturi mask
change to a simple mask at 2 L/min
change to a nasal cannula at 2 L/min
change to a nasal cannula at 4 L/min
change to a nasal cannula at 2 L/min
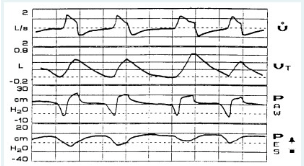
You observe the following graphics display on a patient receiving pressure control A/C ventilation. The most significant problem is:
a leak in the patient-ventilator system
inadequate inspiratory flow setting
improper sensitivity setting
presence of auto-PEEP/air-trapping
improper sensitivity setting
The primary problem apparent in this graphic is the large drop (over -10 cm H2O) in airway pressure (Paw) occurring BEFORE inspiration begins. This indicates an improper sensitivity setting. The significance of this problem is further evident in the bottom tracing of esophageal pressure, where large swings in pressure indicate increased work of breathing.
A patient is receiving non-invasive positive pressure ventilation by mask with an IPAP of 15 cmH2O and an EPAP of 5 cmH2O. Corresponding blood gas data is as follows:
pH 7.29
PaCO2 51 mm Hg
PaO2 82 mm Hg
HCO3- 23 mEq/L
BE -1 mEq/L
Which adjustment is most appropriate?
decrease EPAP
increase IPAP
increase EPAP
increase both EPAP and IPAP
increase IPAP
An 84-kg (185-lb) 6-ft 1-in (185-cm) male is receiving mechanical ventilation by a volume-controlled ventilator in the assist/control mode on the following settings and corresponding ABGs:
Mandatory rate 10/min
VT 750 mL
FIO2 0.6
PEEP 5 cmH2O
pH 7.33
PaCO2 47 mmHg
PO2 78 mmHg
HCO3- 23 mEq/L
BE -1 mEq/L
Which of the following represents the most appropriate action?
decrease rate
add deadspace
increase PEEP
increase VT
increase VT
In this problem the CO2 is slightly high. One may reduce CO2 by doing one of three things - increasing rate, increasing tidal volume, or removing dead space. Among the options listed increasing tidal volume is the most appropriate, primarily because the other options are definitely incorrect. Decreasing rate would increase CO2, which is a move in the wrong direction. Adding dead space would do the same. Increasing PEEP relates to oxygenation which is a slight problem but ventilation should be addressed first.
You are about to initiate volume control ventilation for a 7 year-old girl with cerebral palsy. She weighs 18.5 kg (40 lb). Which of the following is an appropriate tidal volume to use in this child?
150 mL
350 mL
50 mL
250 mL
150 mL
In general, tidal volumes during volume control ventilation should be set in the 6 to 10 mL/kg, with 8 mL/kg a good starting point for most adult and pediatric patients. In this case, 8 mL/kg equates to about a 150 mL tidal volume (8 x 18.5 = 148). Note that was the patient to have acute hypoxemic respiratory failure and meet the ALI/ARDS protocol requirements, you would aim for a lower tidal volume, in the 4 to 6 mL/kg range.
An asthmatic patient is experiencing a gradual increase in bronchoconstriction over time. What ventilator graphic would best demonstrate this scenario?
pressure/volume loop
pressure/volume curve
pressure/time curve
flow/volume loop
pressure/time curve
A patient who is experiencing gradual bronchoconstriction would demonstrate a steady increase in peak pressures in the lung due to increased airway resistance. Therefore the best graphic would be one that includes pressure. The reason that a pressure/time curve is correct is because the scenario suggests that the observation is being made "over time".