Week 1 - Membrane Structure and Function L 2 and L3
1/47
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
48 Terms
What are the primary functions of cell membranes?
They define boundaries of cells and organelles
Serve as permeability barriers
Sites for specific proteins and functions.
How do membrane proteins contribute to cell function?
1.They regulate transport of solutes
Detect and transmit signals
Mediate cell adhesion and communication.
What is the Endosymbiotic Theory?
It proposes that mitochondria and chloroplasts originated from aerobic and photosynthetic bacteria, respectively, that were ingested by anaerobic bacteria.
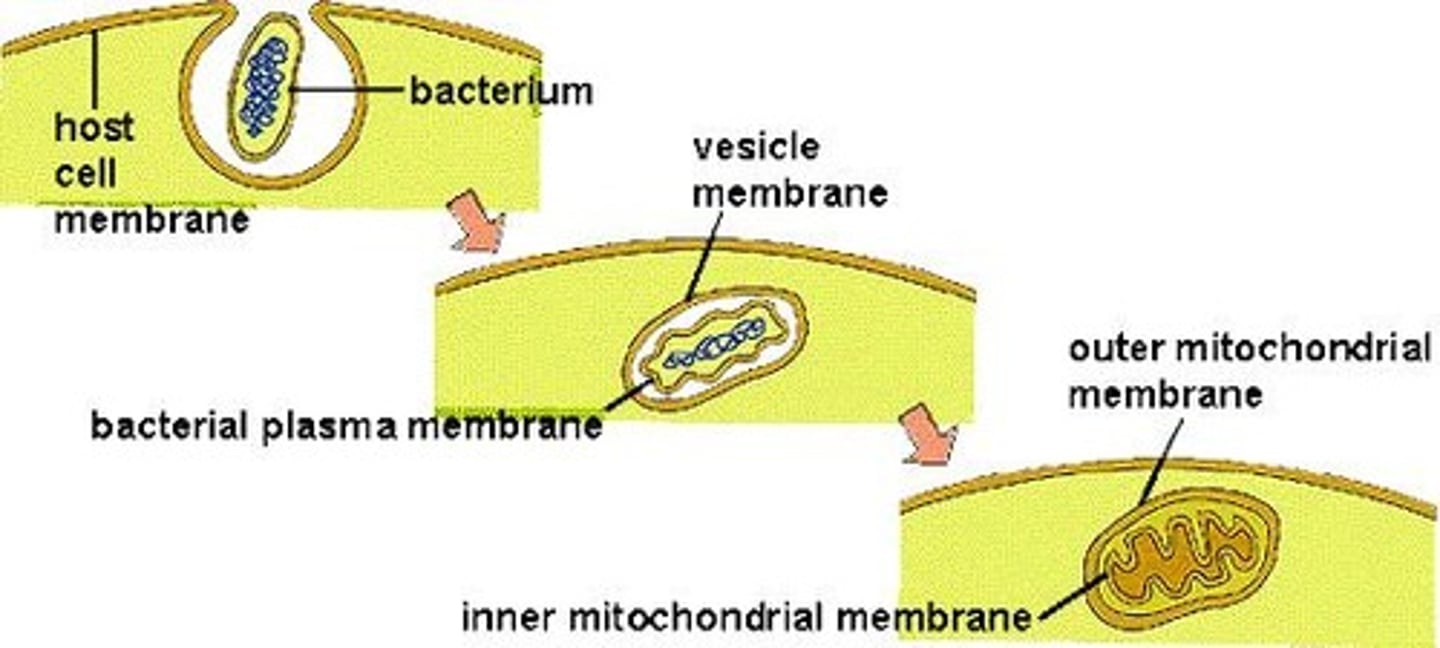
Who first postulated the Endosymbiotic Theory?
Lynn Margulis in 1967.
What is the Fluid Mosaic Model of membrane structure?
It describes membranes as mosaics of different proteins embedded in a phospholipid bilayer, allowing for mobility and dynamic structures.

What did Davson and Danielli propose about membrane structure in 1954?
They suggested a protein-layered phospholipid bilayer with protein-lined membrane pores.
What are the two types of proteins found in the Fluid Mosaic Model?
Integral proteins and peripheral proteins.
What are the major classes of lipids found in membranes?
Phospholipids, glycolipids, and sterols.
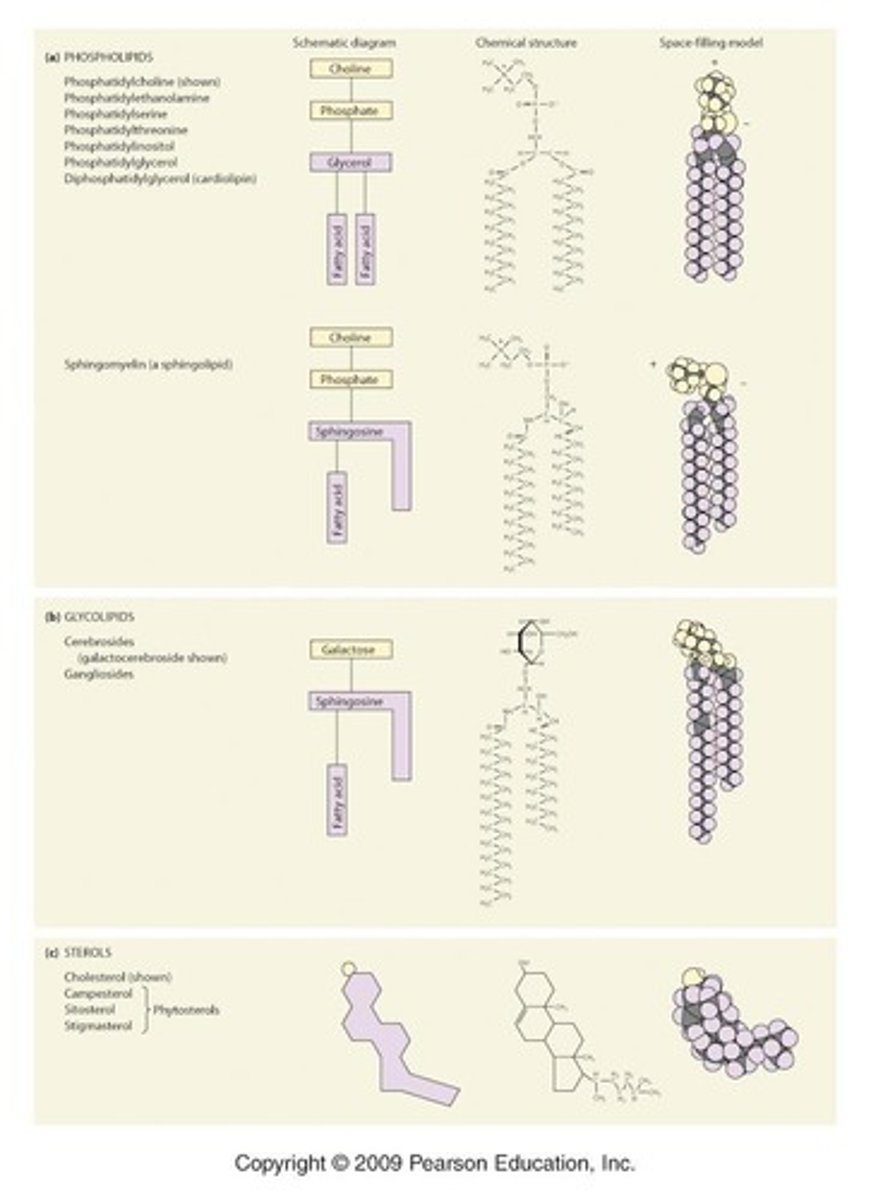
Membrane Lipids
Phosphates, sphingoglycolipids, fatty acid chainsand cholesterol
What is the role of cholesterol in the plasma membrane?
Cholesterol maintains membrane integrity
Pevents excessive fluidity
Helps to immobilize the outer surface.
What is the difference between sterols and hopanoids?
Sterols are not found in prokaryotic membranes; hopanoids are hydrophobic molecules with a short hydrophilic side chain like sterols.
What is transverse diffusion in membrane lipids?
It is the thermodynamically unfavorable movement of phospholipids from one layer of the bilayer to another, catalyzed by flipases.
Why is membrane fluidity important?
It prevents rigid structures
Allows interactions
Essential for cellular processes like movement, growth, secretion
What is the transition temperature (Tm) in relation to membranes?
Tm is the temperature at which a membrane 'freezes' when cooled and 'melts' when warmed, affecting membrane function.
How does cholesterol affect membrane fluidity at low temperatures?
Cholesterol prevents fatty acids from packing tightly, thus reducing the tendency to freeze.
Membrane enriched in unsaturated or saturated fatty acids
Unsaturated- More fluid at lower Tm
Saturated - Less fluid at higher Tm
What paradoxical effect does cholesterol have on membrane fluidity at high temperatures?
At high temperatures, cholesterol makes membranes less fluid.
What role do enzymes play in maintaining membrane fluidity?
They remodel membranes to make cells cold resistant by desaturating bonds and reshuffling fatty acid chains.
What is the role of desaturases in membrane function?
Desaturases influence membrane low-temperature tolerance by introducing double bonds in fatty acids.
What is the primary state in which membranes function properly?
Fluid State
What technique is used to measure lipid mobility within membranes?
Fluorescence Recovery after Photobleaching (FRAP)
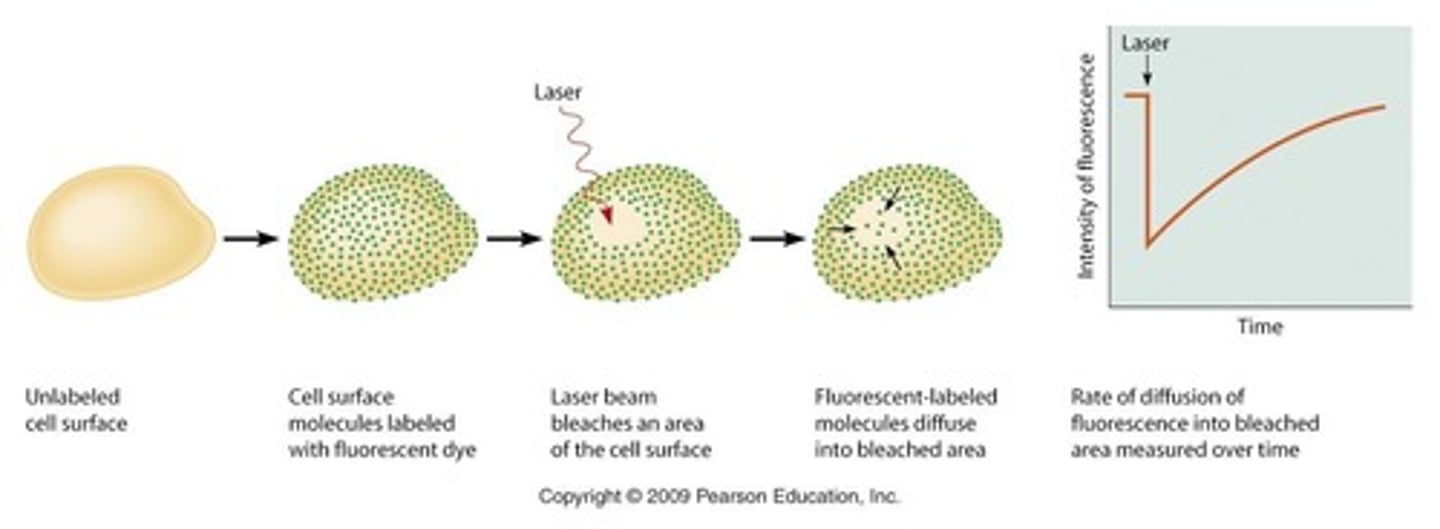
What are the main classes of membrane proteins?
Integral, Peripheral, and Lipid-anchored membrane proteins.
Where is the evidence of the mosaic of proteins?
Freeze-fracture microscopy
What are the characteristics of integral membrane proteins?
They penetrate the phospholipid bilayer
Have amphipathic properties
Contain transmembrane domains
What defines singlepass integral membrane proteins?
They have one transmembrane domain with carboxyl and amino termini extending out opposite sides of the membrane.
What defines multipass integral membrane proteins?
They have multiple transmembrane domains, with termini that can be on opposite or the same side of the membrane.
What are peripheral membrane proteins?
Membrane-associated proteins that lack hydrophobic regions and are attracted to the membrane by electrostatic forces and hydrogen bonding.
They are endoplasmic.
What is the role of lipid-anchored membrane proteins?
They are covalently bound to one of the bilayer surfaces and can include receptors, enzymes, and signaling proteins.
What is GPI-anchored protein?
A type of lipid-anchored protein that is linked to glycosylphosphatidylinositol on the external face of the membrane.
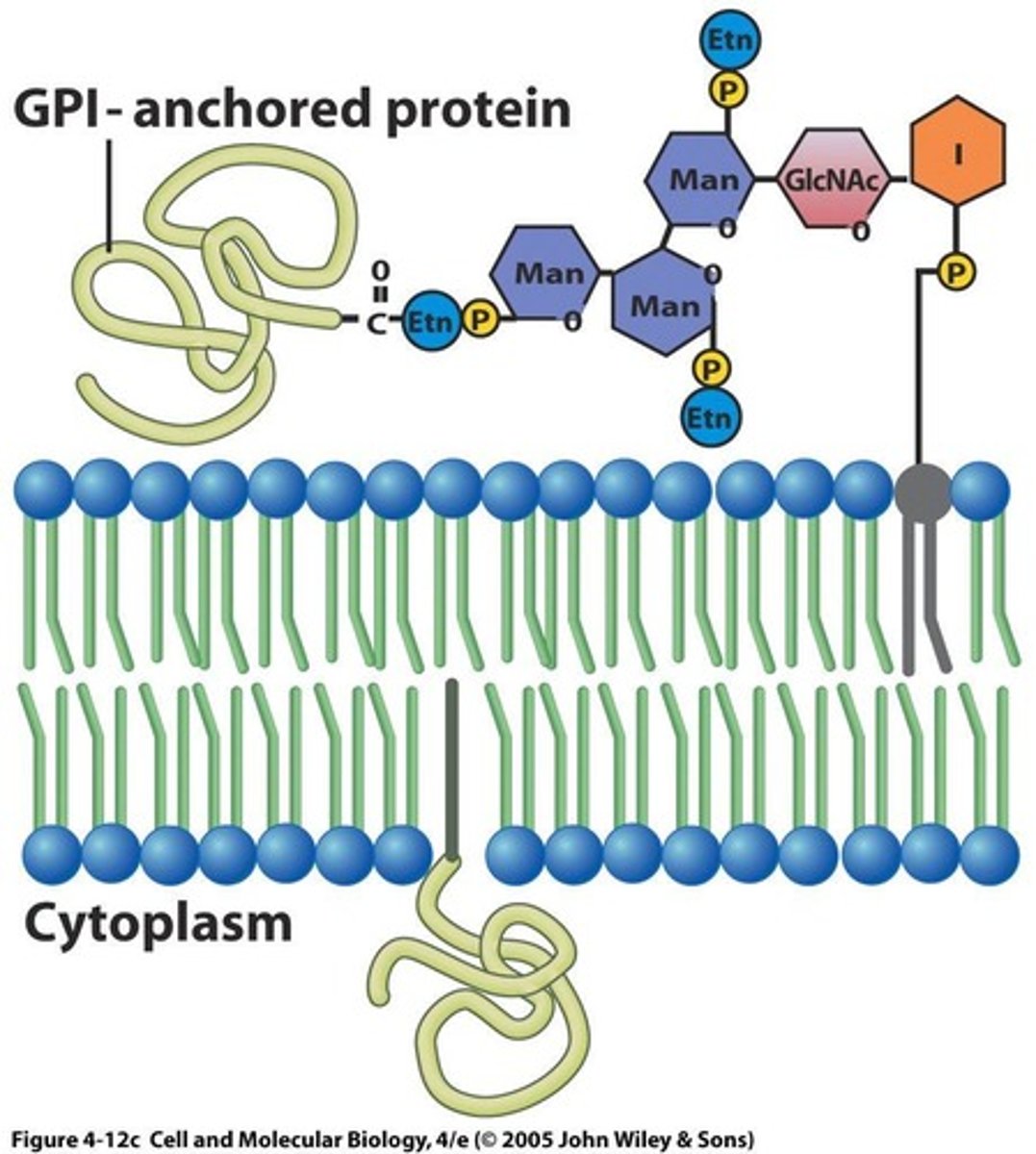
How does membrane protein orientation affect function?
Asymmetrical distribution allows different processes or reactions to occur on each side of the membrane. It is maintained by the lack of transmembrane movement of the proteins.
What is the significance of glycosylation in membrane proteins?
Affects cell adhesion
Migration
Infection processes
intracellular signaling.
What are the two types of glycosylation enzymes?
N-linked and O-linked glycosylation.
What is the composition of carbohydrates in membranes?
They account for 2-10% of membrane weight, primarily linked to proteins as glycoproteins.
What is the structure of glycoproteins?
They have short branched oligosaccharides, typically containing about 15 sugars per chain.
How do blood types relate to membrane glycoproteins?
Blood types A, B, AB, and O are determined by the presence of specific antigens on the surface of red blood cells.
N-linked glycosylation
-Attachment of carbohydrate to nitrogen atom of asparagine side chain
- Biosynthesis in Endoplasmic Reticulum and Golgi
Apparatus
O-linked glycosylation
Involves addition of the oligosaccharide to the oxygen atom on the hydroxyl group of certain serine or threonine residues.
What is the case study example used to illustrate membrane structure?
Human erythrocytes (red blood cells) are used due to their availability and structural features.
What happens to red blood cells in a hypotonic solution?
They take up water, swell, and undergo hemolysis, leading to the release of cell contents.
What are the most abundant integral proteins in red blood cells?
Glycophorin A and Band 3 Protein.
What is the function of Band 3 protein in red blood cells?
It serves as a channel for the passive exchange of anions like HCO3- and Cl-.
What role does Glycophorin A play in red blood cells?
It carries a large number of negative charges that prevent red blood cells from clumping.
What is the function of peripheral proteins in red blood cells?
They are located on the internal surface and help determine the biconcave shape of the cells.
What is the structure of spectrin?
It is an elongated fibrous protein composed of α and β subunits that form a flexible elastic tetramer.
What is the significance of the spectrin-actin network in red blood cells?
It provides strength, elasticity, and pliability, allowing the cells to withstand shearing forces.
What condition results from a deficiency in GPI synthesis?
Paroxysmal nocturnal hemoglobinuria, which makes red blood cells susceptible to lysis.
What is the impact of membrane protein asymmetry?
It influences the function of membrane proteins, allowing for different reactions on either side of the membrane.
What can occur when there are problems with the Spectrim-Actin Network?
Hemolytic anaemias; fragile abnormal shaped RBC
are due to mutations that alter the structure and
function of ankyrin or spectrin