Aromatic chemistry
1/29
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
30 Terms
Why does benzene have an electron rich area?
Each carbon atom in the benzene ring has a p-orbital containing one electron, the orbitals overlap to form a delocalised system of electrons above and below the ring which is an electron rich area.
Is benzene polar?
No, it is non-polar.
Does benzene react with hydrocarbon solvents or water?
It mixes well with hydrocarbon solvents but will not dissolve in water as it is non polar.
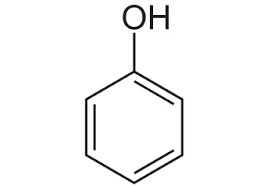
What is the structure of phenol?
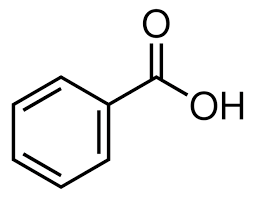
What is the structure of benzoic acid?
What is an arene?
An organic compound containing a ring structure of carbon atoms with delocalized pi electrons.
What is the reactivity of arenes?
Arenes are very stable and rarely destroyed in reactions, the typical reactions of arenes are substitution reactions. This is because the aromatic ring has high electron density and can be attacked by electrophiles.
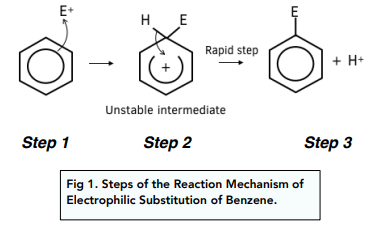
What is the general equation for electrophilic substitution of arenes?
How is the electrophile NO2+ made?
H2S04 + HNO3 → H2NO3 + HSO4- → NO2+ + H2SO4- +H20
conc. sulfuric acid protonates nitric acid
protonated nitric acid loses a water molecule
What is the product of the nitration of benzene?
Nitrobenzene.
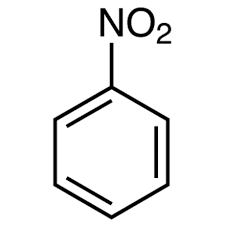
How is phenylamine made from nitrobenzene?
Nitrobenzene is made using nitric acid and sulfuric acid, then it is reduced using tin and hydrochloric acid.
What are phenylamines and other substituted aromatic amines used for?
Starting materials for dyestuffs.
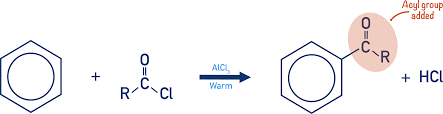
What is Friedel-Crafts acylation?
electrophilic substitution, hydrogen atom is substituted into the benzene ring for an acyl group
heat and AlCl3 catalyst
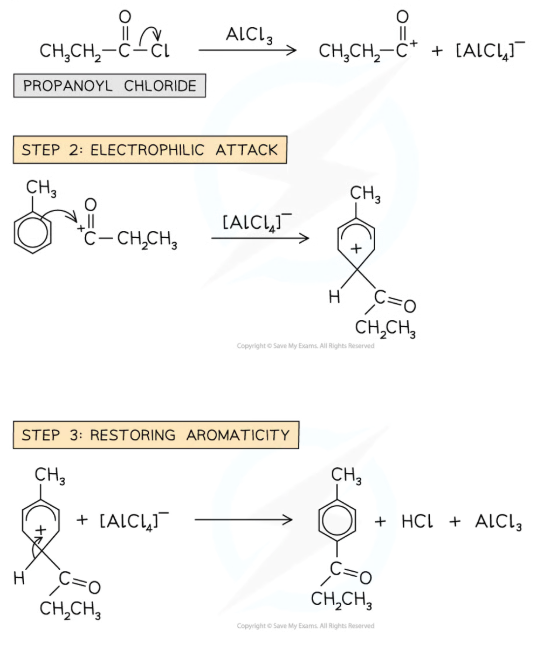
What is the equation for Friedel-Crafts acylation?
Why is benzene more stable than other molecules of similar size?
The outer electron in the p orbital of each carbon atom is delocalised to form the central ring.
What are arenes?
Compounds that contain benzene as a part of their structure, they have high melting points due to the high stability of the delocalised ring, but low boiling points as they are non polar and often cannot dissolve in water.
What reaction mechanism do arenes undergo and why?
Electrophilic substitution due to its area of high electron density making it susceptible to attack to electrophiles.
Why can arenes undergo acylation?
The delocalised electron ring can act as a nucleophile leading to the attack on acyl chlorides. A reactive intermediate must be produced from the acyl chloride and an aluminium chloride catalyst.
What was the IUPAC name of Kekule’s suggested structure of benzene?
cyclohexa-1,3,5-triene
Benzene doesn’t decolourise bromine in an organic solvent, what does this suggest about its structure?
It has no C=C bonds
What are the bond angles in benzene?
120 degrees, it is planar
how are acid anhydrides formed?
water is removed from two carboxylic acids
why do acyl chlorides react violently?
due to their very polar COCl group
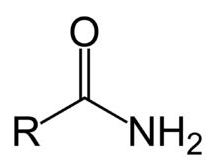
what do amides react to form?
N-substituted amides
why is benzene more stable than cyclohexa-1,3,5-triene?
it has delocalised electrons
what are two similarities and differences in Kekule’s model of benzene and the delocalised model?
p orbitals overlap sideways in both models
pi bond system lies above and below the ring in both models
Kekule has alternating single and double bonds while the delocalised model does not have fixed bonds, rather its electrons in the pi system are delocalized over the entire ring, resulting in all six carbon-carbon bonds having the same length
the delocalised model has electrons delocalised electrons through the pi system, the Kekule model has no delocalised electrons
how can data for the enthalpies of hydrogenation of cyclohexene and benzene be given as evidence to support the delocalised model instead of the Kekule model?
the expected enthalpy of hydrogenation of the kekule model is (3 × -120) -360
the enthalpy of hydrogenation of benzene is 152 less exothermic
increased stability suggests electrons are delocalised
what pieces of evidence support the delocalised model of benzene?
carbon bond lengths lie between c-c and c=c
benzene is less reactive than alkenes
reacts through substitution
what is the equation for the formation of nitrobenzene from benzene and what reagents are need?
C6H6 + HNO3 ➔ C6H5NO2 + H2O
concentrated HNO3 and H2SO4
Wwhat is the equation for the formation of the electrophile for the nitration of benzene?
HNO3 + H2SO4 → NO2- + HSO4- + H2O