biochemistry of steroid hormones
1/15
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
16 Terms
classification of steroid hormones
corticosteroids (typically made in the adrenal cortex)
glucocorticoids: cortisol - regulates metabolism, mood, blood pressure, immunity, pain sensation
mineralocorticoids: aldosterone - electrolyte and fluid balance, blood volume
sex steroids (typically made in the gonads or placenta)
androgens: testosterone - male reproductive development
estrogens: female secondary sexual characteristics, regulation of the menstrual cycles
progestogens: regulation ovulation, maintains pregnancy
steroid hormone synthesis overview
sites of synthesis
adrenal cortex: produces corticosteroids and androgens
ovaries: secrete estrogens and progesterone
testes: primarily produce androgens
similar biochemical pathways are shared across adrenal cortex, ovaries and testes
tissue specific enzymes: located in mitochondria and ER
steroid hormones are lipid soluble and freely permeable to cell membranes so they are not stores within cells
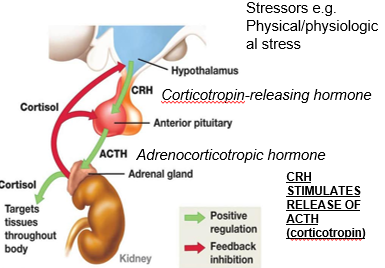
regulation of adrenal gland hormones
hypothalamic hypophysiotropic hormones: CRH stimulates ACTH release from the anterior pituitary, which regulates adrenal hormone production
feedback by target gland hormones: cortisol provides negative feedback to the hypothalamus and pituitary, maintaining hormonal balance
steroid hormones are derived from cholesterol
steroid hormones: derived from cholesterol, syhtesized in the liver
structure: unique lipid structure
four linked hydrocarbon rings
hydrocarbon tail
hydroxyl group
amphipathic molecule (hydrophilic and hydrophobic)
steroid hormone synthesis key steps
cholesterol modifications
shortening the hydrocarbon tail
hydroxylation of steroid nucleus: addition of OH group modifies the 4 ring structure to produce functional hormones
key enzymes
cytochrome P450 oxidases: require NADPH and oxygen. located in ER and mitochondria of adrenal glands, ovaries and testes
step 1: steroid sythesis
StAR: steroidogenic acute regulatory protein controls the uptake of cholesterol into the mitochondria
cholesterol is converted to pregnenolone by the cholesterol side chain cleavage
catalyzed by the enzyme, cytochrome P450 side chain cleavage (also called desmolase or CYP11A1)
this is a rate limiting step. NADPH and oxygen are required, occurs in adrenal, ovary and testis
progesterone is synthesized from pregnenolone
converts the 3 hydroxyl group (OH) to a 3 keto group
enzymes:
3 beta -OH dehydrogenase
5,4 delta isomerase
cortisol is synthesized from progesterone
progesterone → 17-hydroxyprogesterone
enzymes: 17 alpha hydroxylase (CYP17A1)
17 hydroxyprogesterone → 11 deoxy cortisol
enzymes: 21 alpha hydroxylase (CYP21A2)
11 deoxy cortisol → cortisol
enzyme: 11 beta hydroxylase (CYP11B1)
glucocorticoid synthesis (cortisol)
cholesterol → pregnenolone by CYP11A1 (cholesterol desmolase)
pregnenolone → 17 hydroxyprogesterone by CYP17A1 (17 alpha hydroxylase)
17 hydroxyprogesterone → cortisol by CYP21A2 (21 alpha hydroxylase) and CYP11B1 (11 alpha hydroxylase)
functions of cortisol:
metabolism: increases blood glucose via gluconeogenesis
immune response: suppresses inflammation
stress response: helps the body manage stress
aldosterone is synthesized from progesterone
progesterone → 11 deoxycorticosterone
enzyme: 21 alpha hydroxylase
11 deoxycorticosterone → corticosterone
enzyme: 11 beta hydroxylase
corticosterone → aldosterone
enzymes: 18 hydroxylase, 18 hydroxy dehydrogenase (aldosterone synthase)
mineralocorticoid synthesis (aldosterone)
Cholesterol → Pregnenolone by CYP11A1 (Cholesterol Desmolase).
Pregnenolone → Progesterone by 3β-HSD (3β-Hydroxysteroid Dehydrogenase).
Progesterone → 11-Deoxycorticosterone by CYP21A2 (21α-Hydroxylase).
11-Deoxycorticosterone → Aldosterone by CYP11B2 (Aldosterone Synthase).
functions of aldosterone
salt and water balance: promotes sodium reabsorption in kidneys
blood pressure regulation: increases blood volume and pressure
examples of steroids cellular response
cortisol: enhances glucogenesis, suppresses immune response
aldosterone: increases sodium reabsorption in kidneys
testosterone: promotes muscle growth and male characteristics
estradiol: regulates menstrual cycle and reproductive tissues
glucocorticoid deficiency
condition: Addison’s disease
causes: insufficient cortisol production
symptoms: fatigue, low blood pressure, weight loss, hyperpigmentation of the skin
mineralocorticoid deficiency
condition: hypoaldosteronism
causes: insufficient aldosterone production
symptoms: dehydration, low blood sodium levels (hyponatremia), high potassium levels (hyperkalemia), hypotension (low blood pressure)
disorders of adrenal gland insufficiencies
autosomal recessive disorders of cortisol biosynthesis
failure to secrete cortisol - loss of negative feedback to HPA axis
depending on the specific enzyme step involved there may be distinct symptoms and lab findings
classification:
3 beta dehydrogenase deficiency
17 alpha hydroxylase
21 hydroxylase deficiency
11 beta hydroxylase deficiency
congenital adrenal hyperplasia (CAH)
inherited autosomal recessive disorders
mutations in the genes encoding enzymes in mineralocorticoids, glucocorticoids or sex steroids synthesis
enlarged adrenal glands
results in reduced levels of cortisol or aldosterone with overproduction of androgen