AP AFAM Unit 1: Origins of the African Diaspora
1/311
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
312 Terms
Black Campus Movement (1965-1972)
A movement where hundreds of thousands of Black students and supporters protested at over 1,000 colleges nationwide for greater opportunities to study Black history and support for Black students.
Birthplace of Humanity
A term referring to Africa as the ancestral home of African Americans and the origin of humanity.
Misleading Notions
Incorrect perceptions about Africa, such as viewing it as a primitive continent without history.
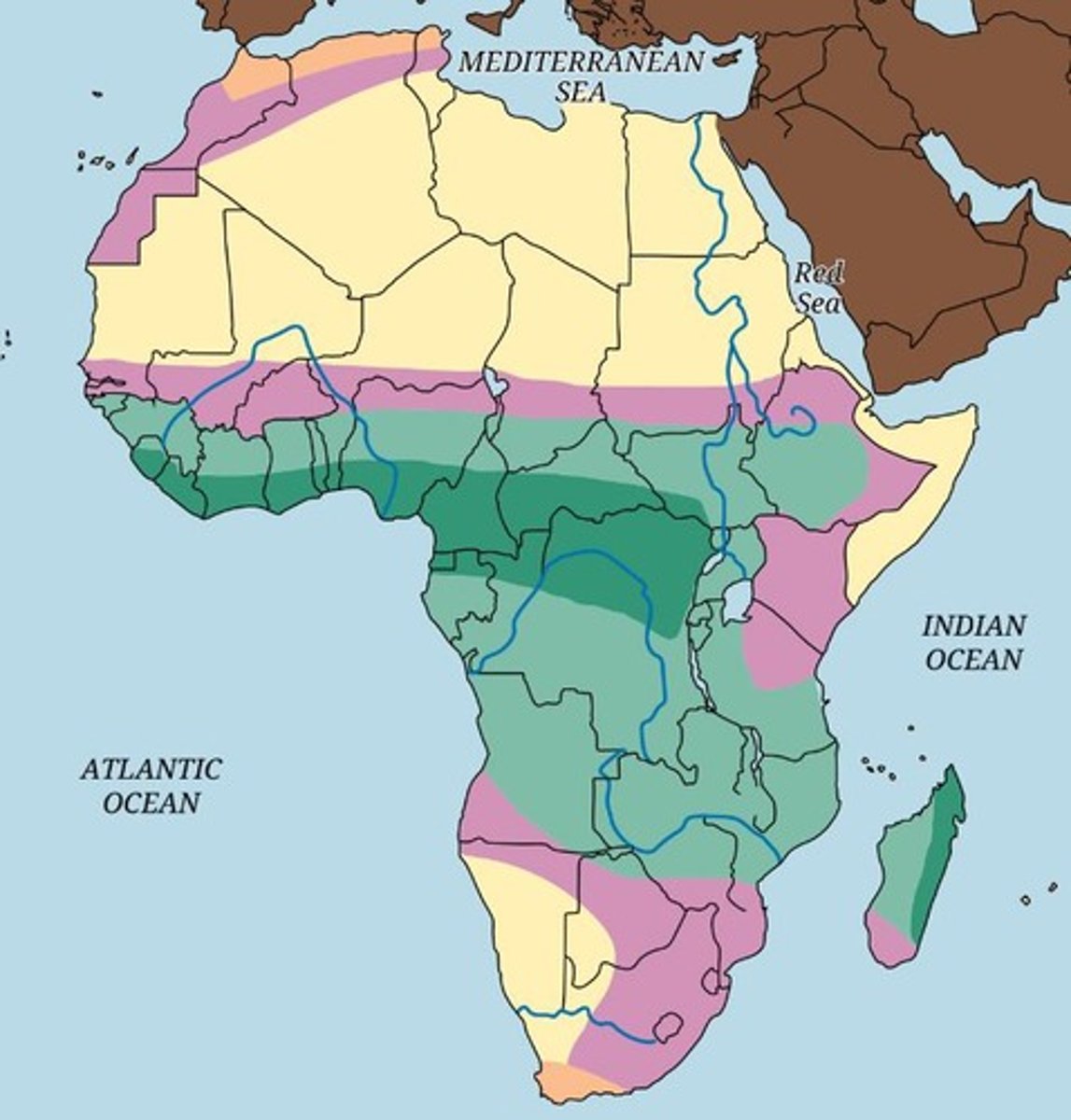
Geographic Features of Africa
Africa is the second-largest continent with five primary climate zones: desert, semiarid, savanna grasslands, tropical rainforests, and Mediterranean.
Major Rivers of Africa
Five major rivers include the Niger River, Congo River, Zambezi River, Orange River, and Nile River.
Impact of Africa's Varied Landscapes
The diverse landscapes influenced settlement and trade patterns, supporting the emergence of early societies.
Population Centers in Africa
Emerged in the Sahel and savanna grasslands due to major water routes, fertile land for agriculture, and trade connections.
Climate Variations in Africa
Different climates facilitated diverse trade opportunities, with nomadic herders in desert areas trading salt.
Perceptions of Africa
Shifted from viewing it as a primitive continent to recognizing it as the homeland of powerful societies with significant contributions.
Contributions of Early African Societies
Developments in arts, architecture, technology, politics, religion, and music that inform African American experiences.
Emergence of African American Studies
Grew from Black artistic, intellectual, and political movements into a formalized field of study.
Contemporary Black Freedom Struggles
Understanding of current movements for Black rights within and beyond academic study.
Support for Black Students
Demand for greater support for Black students, faculty, and administrators during the Black Campus Movement.
African Diaspora
Communities of people of African descent living outside Africa, influenced by historical migrations and connections.
Atlantic Slave Trade
A historical period that disrupted African societies and contributed to the African diaspora.
Fertile Land in Africa
Supported the expansion of agriculture and domestication of animals, contributing to population centers.
Nomadic Herders
People in desert and semiarid areas who move in search of food and water, often trading salt.
Cultural Regions of Africa
Diverse areas within Africa that developed unique societies and trade patterns due to geographical features.
Historical Contributions of Africa
Recognition of Africa's role in global history through its societies and innovations.
African Societies
Diverse and complex societies that were globally connected before the Atlantic slave trade.
Variations in climate
Facilitated diverse opportunities for trade in Africa.
Nomadic herders
Often moved in search of food and water, and some traded salt.
Sahel
A region where people traded livestock.
Savannas
Regions where people cultivated grain crops.
Tropical rainforests
Regions where people grew kola trees and yams and traded gold.
Domestication
The process of adapting wild plants and animals for human use.
Nomadic
Describing a lifestyle characterized by moving from place to place rather than settling permanently.
Kola trees and yams
Crops grown in tropical rainforests that were traded.
Geographically diverse
Referring to the variety of physical landscapes and climates in a region.
Climate zones
Regions classified by their climate characteristics.
Sahara
The largest hot desert in the world, located in North Africa.
Savanna grasslands
Ecosystems characterized by open spaces and scattered trees, suitable for grazing.
Niger River
A major river in West Africa that has historically supported trade and agriculture.
Congo River
A major river in Central Africa, significant for trade and transportation.
Nile River
The longest river in the world, crucial for the development of ancient Egyptian civilization.

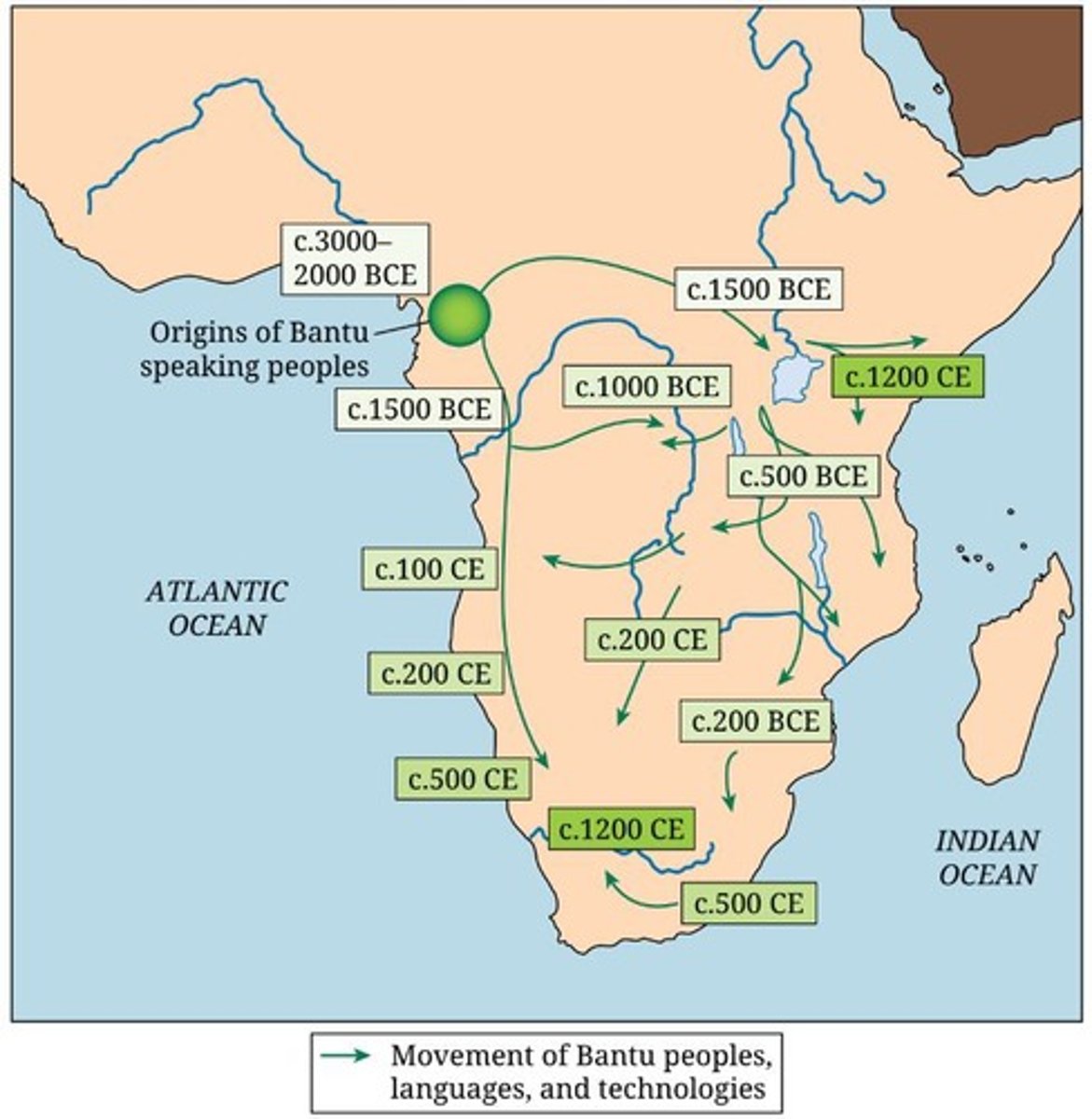
Bantu expansion
A series of migrations throughout Africa from 1500 BCE to 500 CE triggered by population growth.
Technological innovations
Developments in tools and weapons that contributed to population growth.
Agricultural innovations
Advancements in farming practices, including cultivating bananas, yams, and cereals.
Bantu linguistic family
A group of hundreds of languages spoken by Bantu-speaking peoples across Africa.
African ethnolinguistic diversity
The wide variety of ethnic groups and languages found in Africa.
Population growth W & C Africans
The increase in the number of people in West and Central Africa due to various factors.
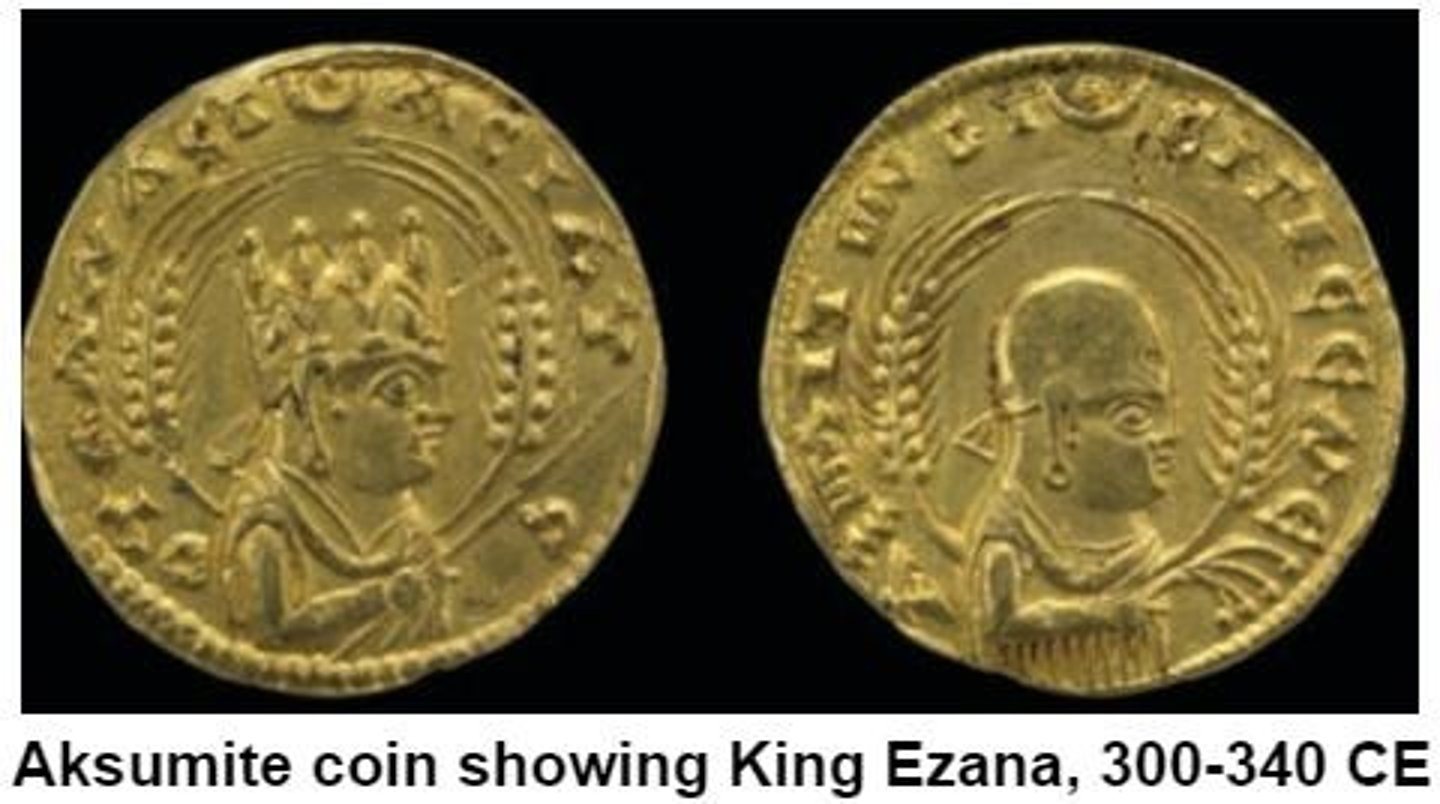
Aksumite Empire
An ancient empire in eastern Africa that emerged around 100 BCE and was connected to major trade networks.

Ge'ez
The script developed by the Aksumite Empire, still used in the Ethiopian Orthodox Church.
Nok society
One of the earliest iron-working societies in West Africa, known for terracotta sculptures and pottery.

King Ezana
The leader under whom Aksum became the first African society to adopt Christianity.
African ethnolinguistic
Refers to the various ethnic groups and languages of Africa.
King Ezana
The ruler of the Aksumite Empire who adopted Christianity.
Ge'ez
An ancient South Semitic language that is the liturgical language of the Ethiopian Orthodox Church.
Nok
An ancient civilization in Nigeria known for its terracotta sculptures.
terracotta sculptures
Clay sculptures that were created by the Nok civilization.
most ancient complex society
Refers to the earliest advanced societies with structured governance and culture.
diversity
The variety of different ethnic groups and cultures within Africa.
First Christian African society
Refers to the Ethiopian Orthodox Church as the first Christian society in Africa.
countered racist stereotypes
Challenged the misconceptions about Africans lacking government or culture.
complex societies
Societies with advanced political structures and cultural practices.
Nubia
An ancient region located along the Nile, known for its powerful kingdoms.
25th dynasty of Black Pharaohs
A dynasty in ancient Egypt that was ruled by Nubian kings.
Aksumite Empire
An ancient empire located in present-day Ethiopia and Eritrea, known for its trade and cultural achievements.
maritime trade
Trade conducted over the sea, significant for connecting different regions.
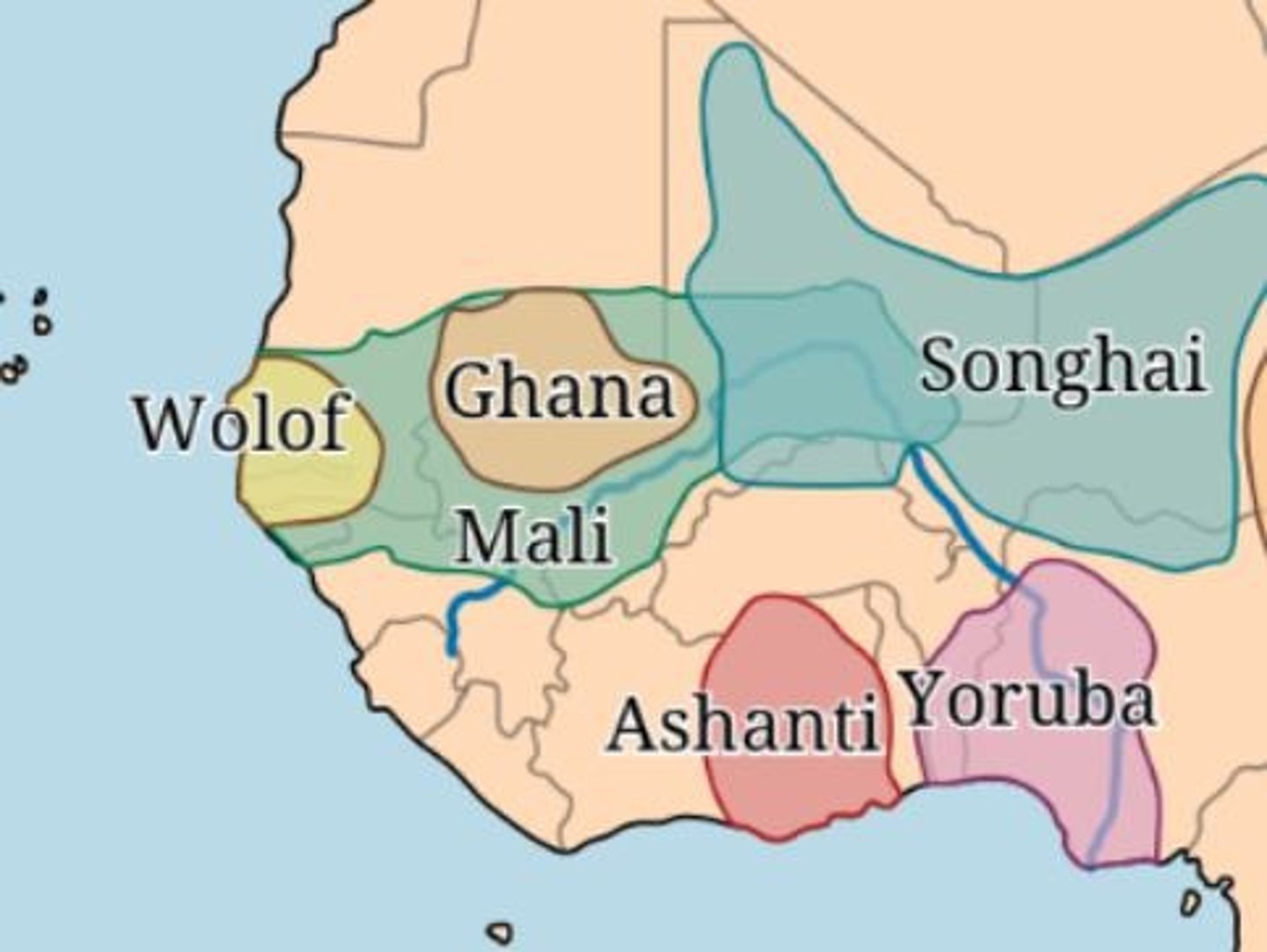
Sudanic empires
The empires of Ghana, Mali, and Songhai that flourished in West Africa.
Ghana Empire
An ancient empire in West Africa that thrived from the 7th to the 13th century.
Mali Empire
An empire that flourished from the 13th to the 17th century, known for its wealth and cultural achievements.
Songhai Empire
The last and largest of the Sudanic empires, flourishing from the 15th to the 16th century.
gold mines
Natural deposits of gold that were crucial to the wealth of the Sudanic empires.
nexus of trade routes
The central point where multiple trade routes converge, facilitating commerce.
Trade, learning, cultural exchange
The interactions that occurred through trade, leading to the sharing of knowledge and culture.
North African Horses
Horses bred in North Africa that were valued for their strength and speed.
Trans-Saharan commerce
Trade that occurred across the Sahara Desert, connecting North Africa with sub-Saharan regions.
Islam
A major world religion that spread throughout West Africa during the time of the Sudanic empires.
Mansa Musa
The wealthy ruler of the Mali Empire known for his pilgrimage to Mecca in 1324.

Hajj in 1324
The religious pilgrimage to Mecca undertaken by Mansa Musa, which showcased his wealth.
Trade route shift = diminishing wealth
The transition from trans-Saharan to Atlantic trade routes that reduced the wealth of the Songhai Empire.
Purchased steel weapons
Acquisition of advanced weaponry that enhanced the military power of the Mali Empire.
centers of learning
Institutions in West African empires that promoted education and scholarship.
Timbuktu
A city in Mali known for its historical significance as a center of trade and learning.

Griots
Prestigious historians, storytellers, and musicians who maintained and shared a community's history, traditions, and cultural practices.
Female Griots
African women who preserved knowledge of a community's births, deaths, and marriages in their stories.
Mali's book trade and universities
Centers of learning and commerce in Mali that contributed to the spread of knowledge.
Timbuktu
A historical city in Mali known for its role as a center of trade and education.
Oshe Shango
A ceremonial wand among the Yoruba in Nigeria, core to dances honoring the orisha Shango.
Shango
The orisha of thunder, fire, and lightning, and a deified ancestor—a monarch of the Oyo kingdom.
Veneration of ancestors
The practice of honoring past ancestors, considered significant for guidance in decision-making.
Divination
Asking a priest or spiritual leader to predict the future through supernatural means.
Healing practices
Traditional understanding of illness connected to a person's relations with God, ancestors, and the universe.
Collective singing and dancing
A spiritual practice that has survived in African diasporic religions, often blended with Islam and Christianity.
Voodoo
A syncretic faith practiced in Haiti, blending African spiritual practices with Christianity.
Vodun
Another term for Voodoo, specifically in Haiti.
Regla de Ocha-Ifa
A syncretic faith in Cuba, once known as santería, blending African and Christian practices.
Candomblé
A syncretic faith in Brazil that combines African spiritual practices with Christianity.
Islamic influence in Mali and Songhai
The adoption of Islam by leaders in these regions through trans-Saharan trade.
Christianity in Kongo
The introduction of Christianity to Kongo by Portuguese sailors.
Syncretic practices
The blending of aspects of introduced faiths with indigenous spiritual beliefs and cosmologies.
African diasporic religions
Religions that emerged from the blending of African spiritual practices with other faiths in the Americas.
Sonni Ali
A leader of the Songhai Empire who embraced Islam while honoring ancient traditions.
Babalawo
A spiritual leader in Yoruba culture believed to predict the future by reading patterns in palm nuts.
Impact on American Christianity
The influence of West African practices on mainstream Christianity in American colonies.
Collective singing in American churches
A practice that became common in conservative American Protestant churches, influenced by West African traditions.
divination
West African spirituality in modern cosmologies
syncretic religious practice
blended practices such as Vodun, Regla de Ocha-Ifa, and Candomblé
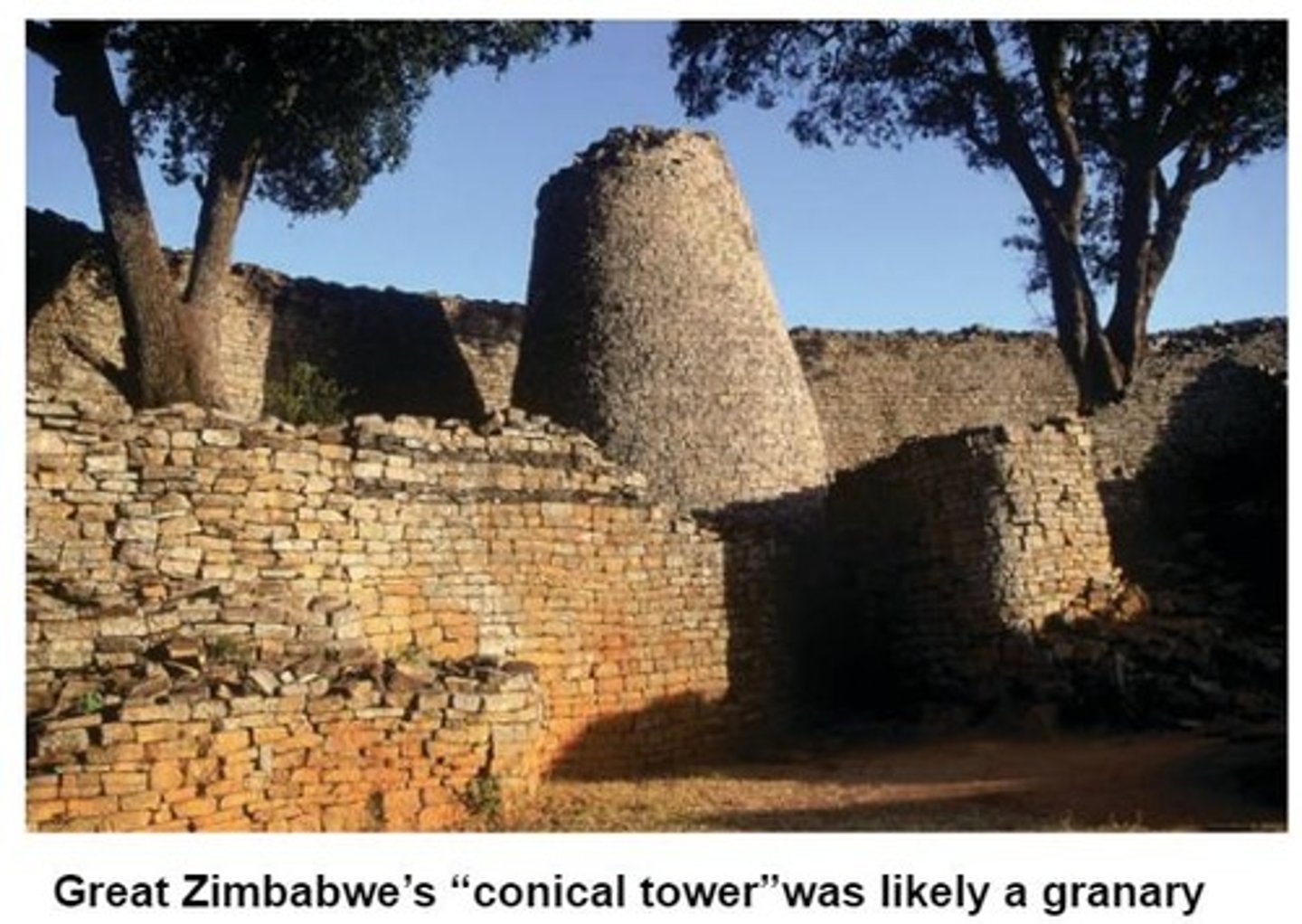
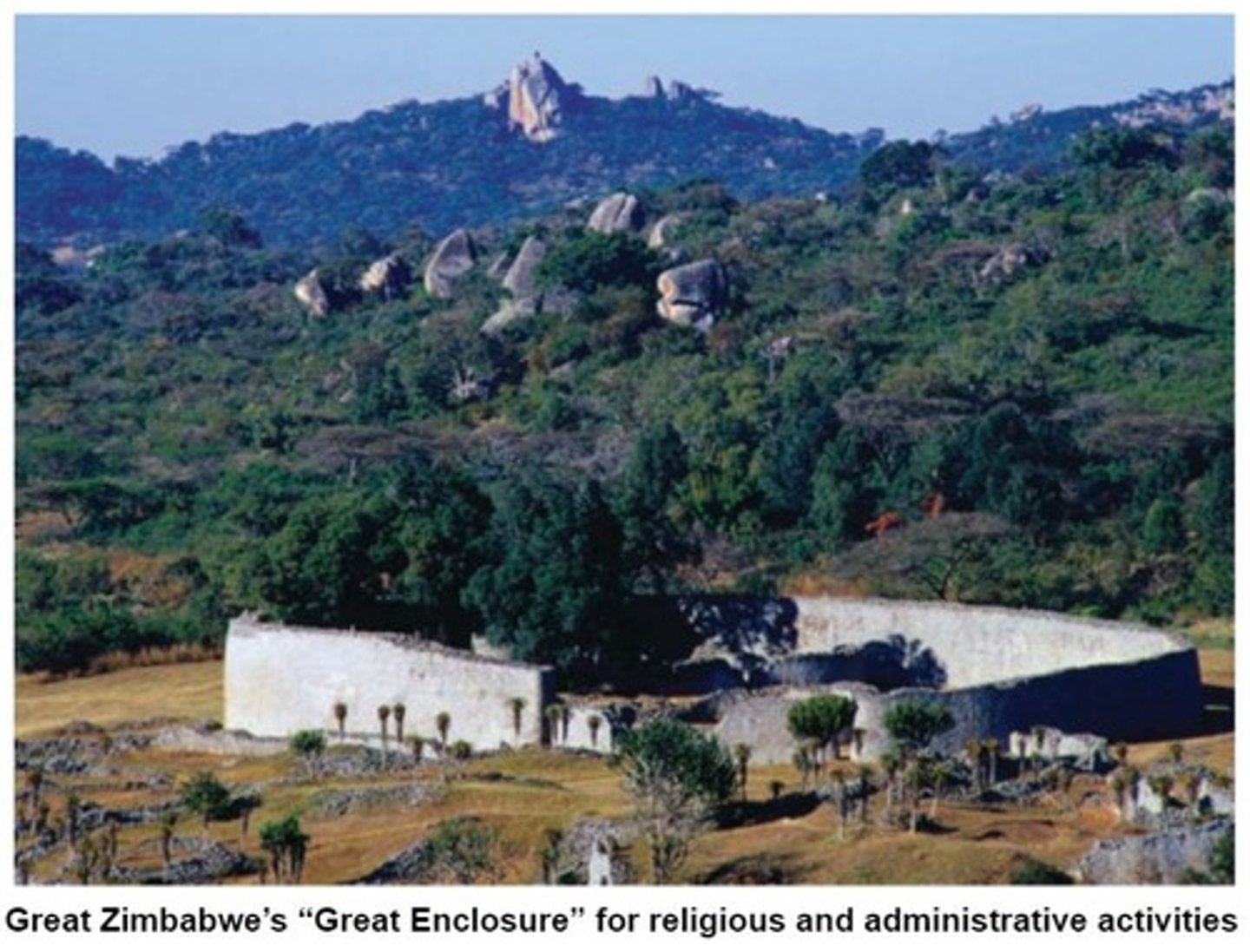
Great Zimbabwe
The Kingdom of Zimbabwe and its capital city, flourishing from the 12th to the 15th century