PCR Exam_HW
1/56
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
57 Terms
nucleotide composition
phosphate-sugar-base
nucleoside
base and sugar
dNTPs include which 4 things
dATP, dCTP, dGTP, dTTP
purines
A and G
“all gold”
pyrimidines
C and T
non-coding regions
introns
where are STRs seen?
introns
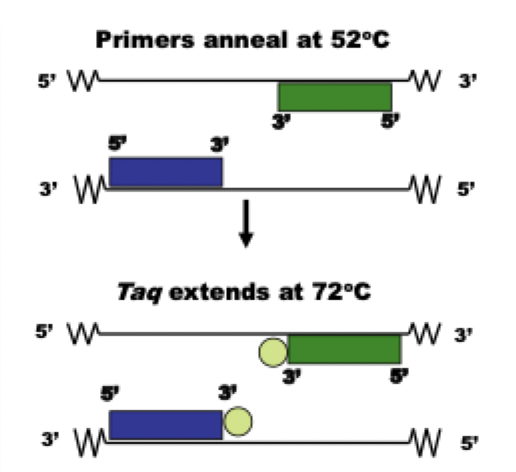
when looking at STR regions, how to design primers?
primers attach on 3’ and build new DNA 5’→3’
when you look at forsenics, what do you focus on?
“who can we not exclude?”
master mix includes what?
nucleotides (limiting reagent), reaction buffer, DNA polymerase (Taq polymerase)
cofactor for Taq
MgCl2
buffer purpose
makes pH stable, keeps DNA negatively charged, conducts electricity
purpose of Taq polymerase
attach to primer, build dNTP, can’t do its job if annealing doesn’t work
where do primers attach?
before STR area of interest
Taq is always at which temp
72°C
which cycles do you actually amplify things?
not until the 3rd cycle. cycles 1 and 2 are when you cut off the extraneous portions
how much DNA is made during PCR? (equation)
2^n
n= number of cycles
what causes DNA to move?
current, DNA charge, DNA size, gel pore size, buffer pH
what causes resolution?
size and charge of DNA
what enzyme causes the DNA structure to unwind and break down?
helicase
the more loci you look at, the greater ____ of ______ you get
power of discrimination
CODIS system
combined DNA Index System, a federally mandated database
looks at the same 13 STRs
technique used to detect DNA with a specific base sequence with a labeled hybridization probe to DNA bands immobilized onto nitrocellulose paper
southern blot
which process is this: hybridization performed on intact chromosomes
FISH (fluorescent in situ hybridization)
rtPCR is more ___ than standard PCR
sensitive
what can cause a PCR assay with no bands on any samples?
too few PCR cycles, malfunctioning PCR temp, stringency too high
purified DNA is indefinitely stable at what temp
-70°C
SNP with misplaced termination codon aka
nonsense variant
what does this describe: a variation in DNA in 1-2% of the population and may/may not affect protein function A
DNA polymorphism
composition of primer in PCR
oligonucleotide complementary to bases downstream of the target
how can a false neg PCR test caused by the presence of an inhibitor of the reaction be detected?
use internal control (amplification control)
what to do when: a PCR analysis of a vaginal sample gives neg result
amp control below cutoff
pos control above cutoff
neg control below cutoff
don’t report results!! repeat sample.
name of PCR product
amplicon
what parameter is used for genotype cell decisions?
cycle number at midpoint of curve
in rtPCR, which value is used to determine target number in specimen?
cycle number where the organism specific fluorescence begins logarithmic rise
in genetic analysis of cancer cells, why is loss of heterozygosity important
homozygosity for the same allele size causes mutation
if stringency is too low, what’s the solution?
increase annealing temp, che ck primer length and specificity, decrease MgCl2 concentration in master mix
primer dimers caused by
complementary primers to each other
adding DNA template to master mix and allowing to stabilize
primer dimers prevented by
keep reagents and PCR plate on ice bath
use hot start on thermocycler
PCR test of neg result in sample, pos control, neg control, and amp control?
neg, pos, neg, pos
after DNA performance with large 1200-1500bp, the bands are close to cathode. how to improve?
decrease % agarose concentration
if 35% of nucleotides are A, predict G
15%
why is it important to perform PCR on DNA from a crime scene?
small amounts of DNA get amplified for analysis
why do forensic labs analyze non-coding DNA and not genes?
DNA is “anonymous” and is <0.5% of human DNA that differs among people. they don’t control any known functions
master mix includes
oligonucleotide primers, 4 deoxynucleotides, reaction buffer (pH, salts, MgCl2),
components of PCR
taq polymerase, template DNA, master mix
why use polymorphic sequences in DNA?
use STRs, they’re unique
PCR 3 steps and temps
denature: 94*C
anneal: 42*C
extension: 72°C
how is temp of each PCR step determined?
if there’s a higher GC ratio, temp is higher at 98°C for denaturation
where do primers attach?
at 3’ end
why does DNA move through agarose gel?
electric current, size, buffer-pH
what factors determine migration of bands?
DNA size, length of DNA
2 techniques for PCR experiments
PCR amplification and gel electrophoresis
what’s needed to visualize DNA?
cellophane sheets, loading dye (ethidium bromide), 100x fast blast, tracing paper or acetate film
STR number of nucleotides and repeats
3-4 nucleotides
2-10 repeatsS
VNTR number of nucleotides
16+
SNP
single base pair polymorphism