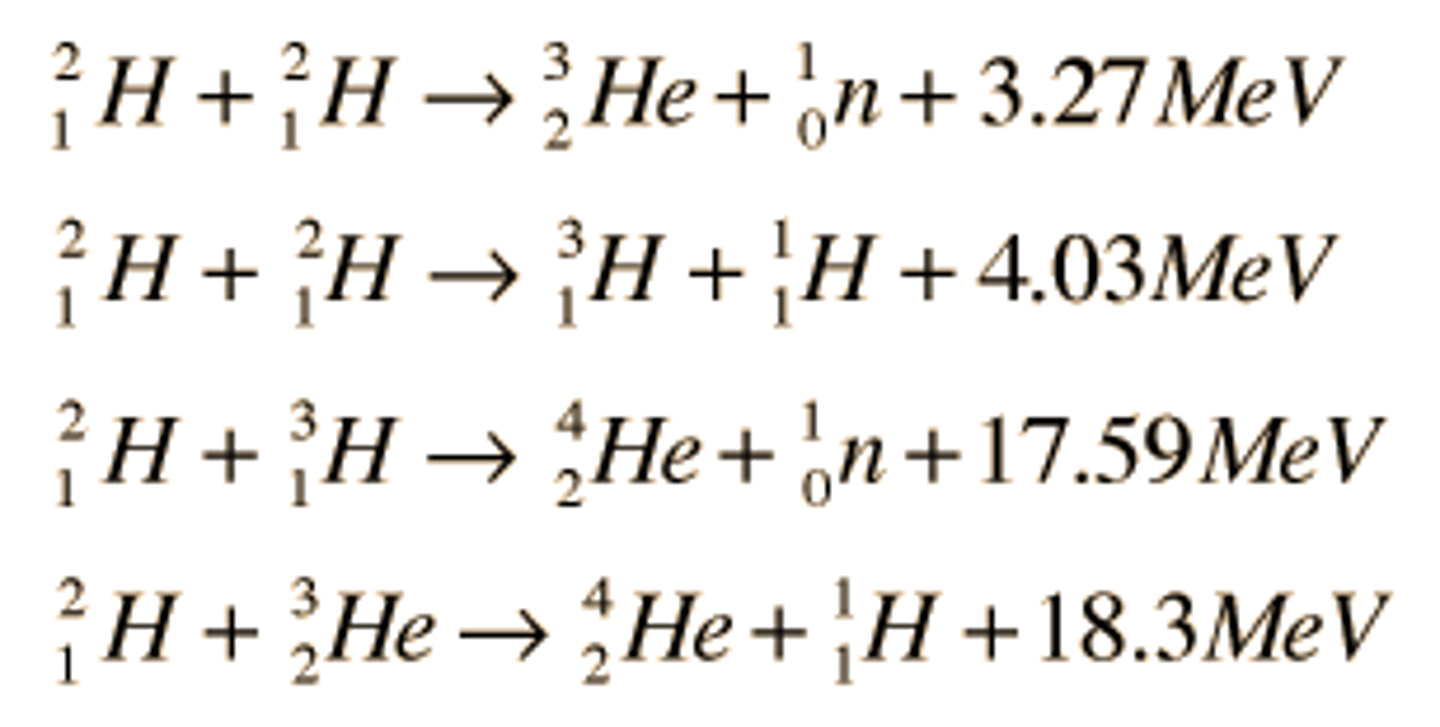Test Review Part I (Conceptual & Half Life Problems Solving)
1/38
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
39 Terms
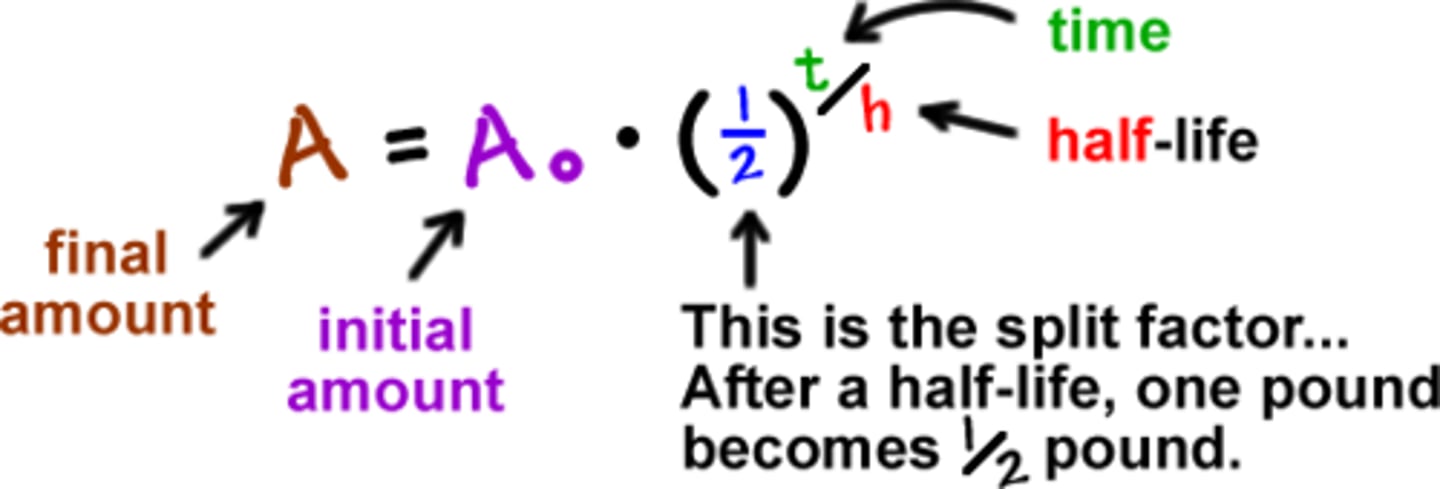
half life equation
What is the Q value?
+Q = Dissinegration Energy -Q = Means there is a threshold energy value
What is a + Q & - Q value indicate?
+ means reaction is spontaneous - means reaction needs energy to occur
Theorized existence and discovered: Neutron
Theorized existence Rutherford ii. Discovered Chadwick
Theorized existence and discovered: electron
i. Theorized existence Stoney ii. Discovered J.J. Thompson
Theorized existence and discovered: proton
i. Theorized existence Prout ii. Discovered Rutherford
Theorized existence and discovered: positron
i. Theorized existence Dirac ii. Discovered Carl Anderson
Developed rudimentary fusion and Fully developed fusion process
Mark Oliphant Fusion light H isotopes, Bethe
Who discovered fission?
Otto Hahn ,
Fritz Strassman
Who fully developed the fission process?
Lise Meitner, Otto Frisch
Who constructed 1st reactor fission?
Fermi
Who discovered transmutation?
Ernest Rutherford & Fredrick Soddy Th → Rd
Who discovered and developed Geiger tube for measuring radiation (two scientists)?
Geiger and Muller
General equation and describe positron emission (decay)
(example) p → n + β+ + ν
A proton in the nucleus is changed to a neutron and a positron is given off for the atom and the element changes to one with one less as its atomic number. The atom has approximately the same mass.
General equation and describe electron capture
p + e- → n + ν
A proton in the nucleus captures an electron and creates a neutron. The element changes to one with one less as its atomic number. The atom has the same mass.
General equation and describe gamma ray emission (decay)
X → X + γ
An element releases a gamma ray of zero mass and zero charge.
General equation and describe beta particle emission (decay)
n → p + β- + ν
A neutron in the nucleus is changed to a proton and a beta particle is given off for the atom and the element changes to one with one more as its atomic number. The atom has approximately the same mass.
fusion
Nuclear reaction where multiple atoms combine to make a single atom. (ex. Sun)
fission
Nuclear reaction where atoms split to make new atoms. (ex. Nuclear reactor)
Neutrino i. Theorized existence ii. Discovered
Pauli, Reines & Cowan
Anti-neutrino i. Theorized existence ii. Discovered
Pauli, Reines & Cowan
nuclear reaction symbol proton
1 p
1
nuclear reaction symbol neutron
1n
0
nuclear reaction symbol electron
0 e
- 1
nuclear reaction symbol beta particle
0 β
- 1
nuclear reaction symbol positron
0 β
+1
element symbol
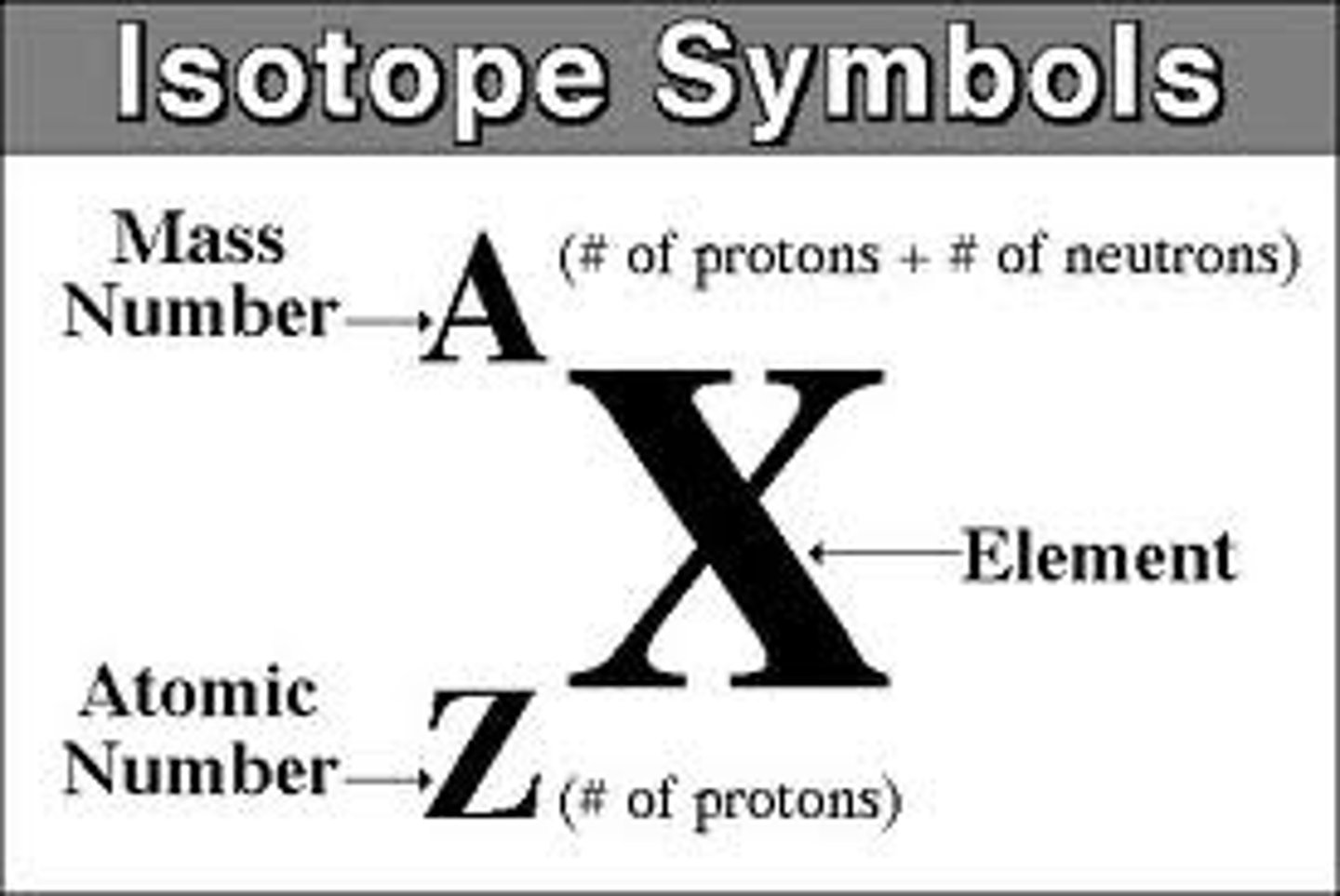
APE MAN
Atomic # = #protons = #electrons
Mass# = Atomic# + #neutrons
isotope
An atom that has the same number of protons but varying numbers of neutrons.
An element is defined by what particle in the nucleus?
protons
Low energy nuclear reactions have a conservation of Nucleons (describe or give an example of how works)?
Nucleons (protons + neutrons) must balance on each side of the nuclear reaction (they must be equal)
Low energy nuclear reactions have a conservation of charge (describe or give an example of how works)?
Total charge must balance on each side of the nuclear reaction (they must be equal). For positron emission that requires that the electron balance be accounted for carefully when calculating ΔE = Δm c^2.
Low energy nuclear reactions have a conservation of momentum (describe or give an example of how works)?
Momentum must balance on each side of the equation (they must be equal). For beta decay if a beta particle or positron a massless neutrino and antineutrino are needed to balance the momentums or spins respectively.
Low energy nuclear reactions have a conservation of mass and energy (describe or give an example of how works)?
If mass is converted to energy or energy is converted to mass during the nuclear reaction neither is balanced individually but together a balance of Energy and Mass is maintained ΔE = Δm c^2
alpha decay
4He emitted
2
beta decay
0e-1 + 0v0 emitted
positron emission
0e+1 + 0v0 emitted
gamma decay
energy released, no atomic number or weight change
fusion reactions examples and include what elements
1H1, 2H1, 3H1, 4He2