Empires of East Asia
0.0(0)
Card Sorting
1/35
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Chinese, Mongolian, and Japanese Empires
Last updated 2:24 AM on 2/14/23
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
36 Terms
1
New cards

Tang Taizong
Chinese emperor (r. 627-649) who founded the Tang dynasty (618-907).
2
New cards

Civil Service Exam
In China, it was an exam based on Confucian teachings that was used to select people for various government service jobs in the bureaucracy.
3
New cards
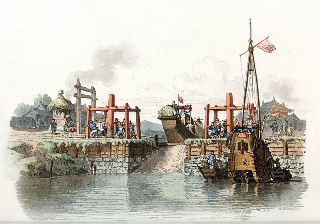
Grand Canal
A canal linking northern and southern China
4
New cards
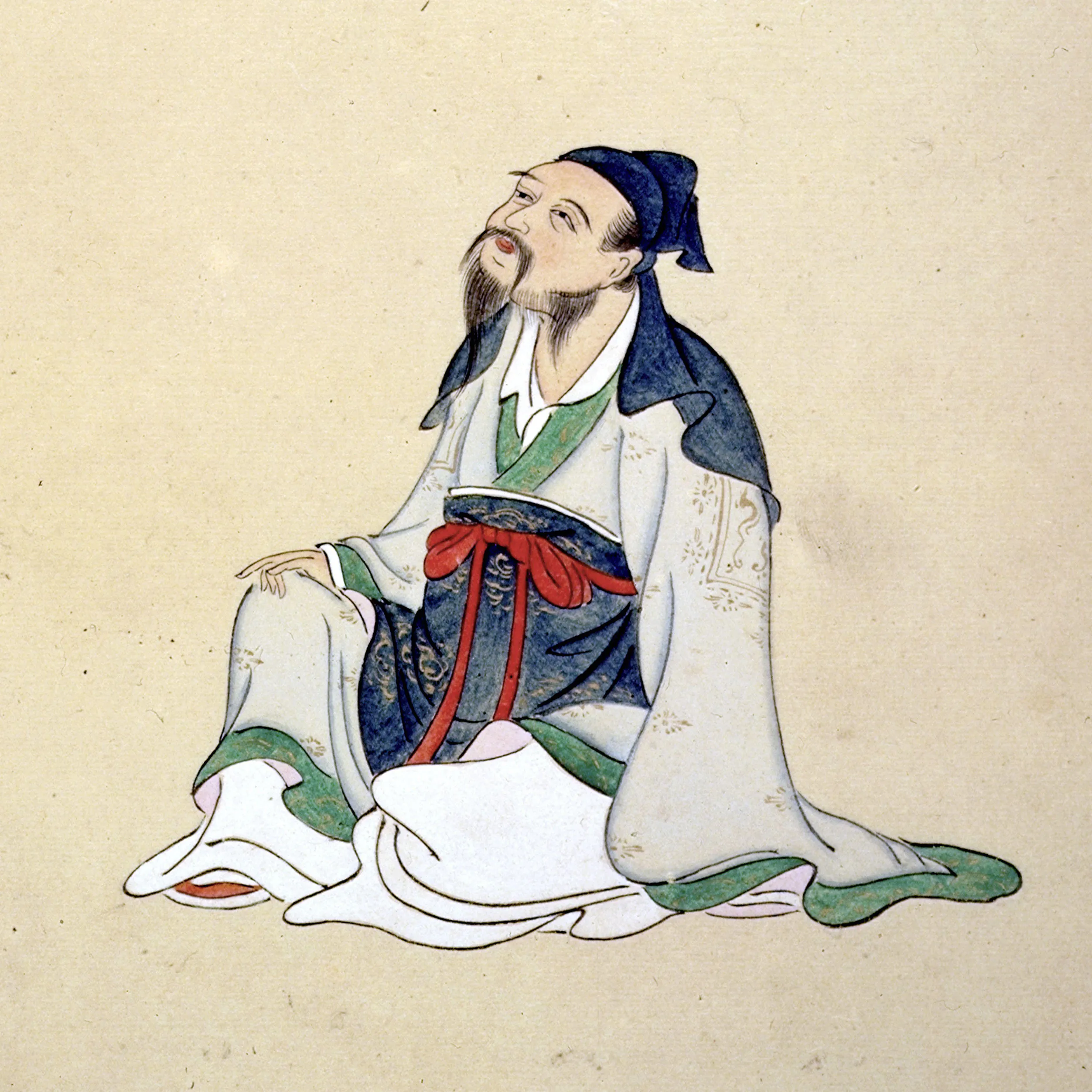

Li Bo
Most famous poet of the Tang era; blended images of the mundane world with philosophical musings.
5
New cards
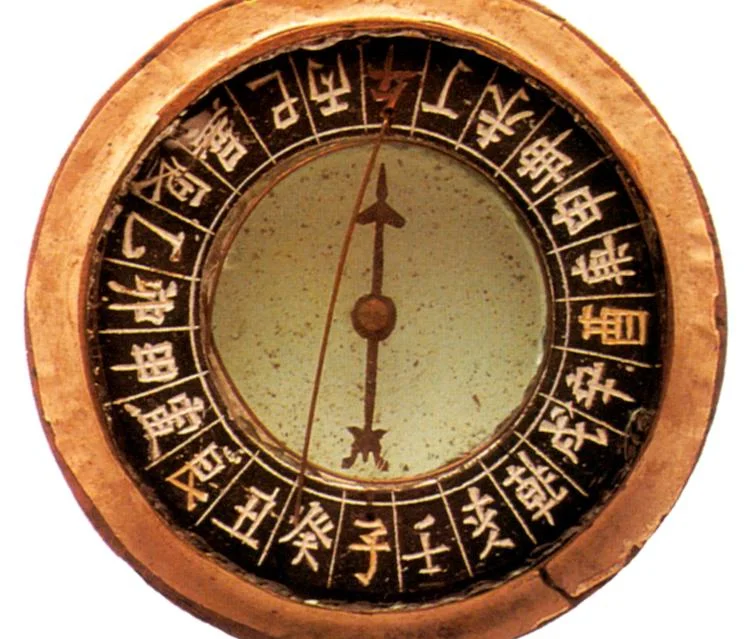
Song Dynasty Achievements & Inventions
Growing urban areas, gunpowder & guns, Chinese exports of porcelain, tea and silk, paper money, magnetic compass, rudder
6
New cards

Foot Binding
Chinese practice of tightly wrapping girls' feet to keep them small, begun in the Tang dynasty; an emphasis on small size and delicacy was central to views of female beauty.
7
New cards
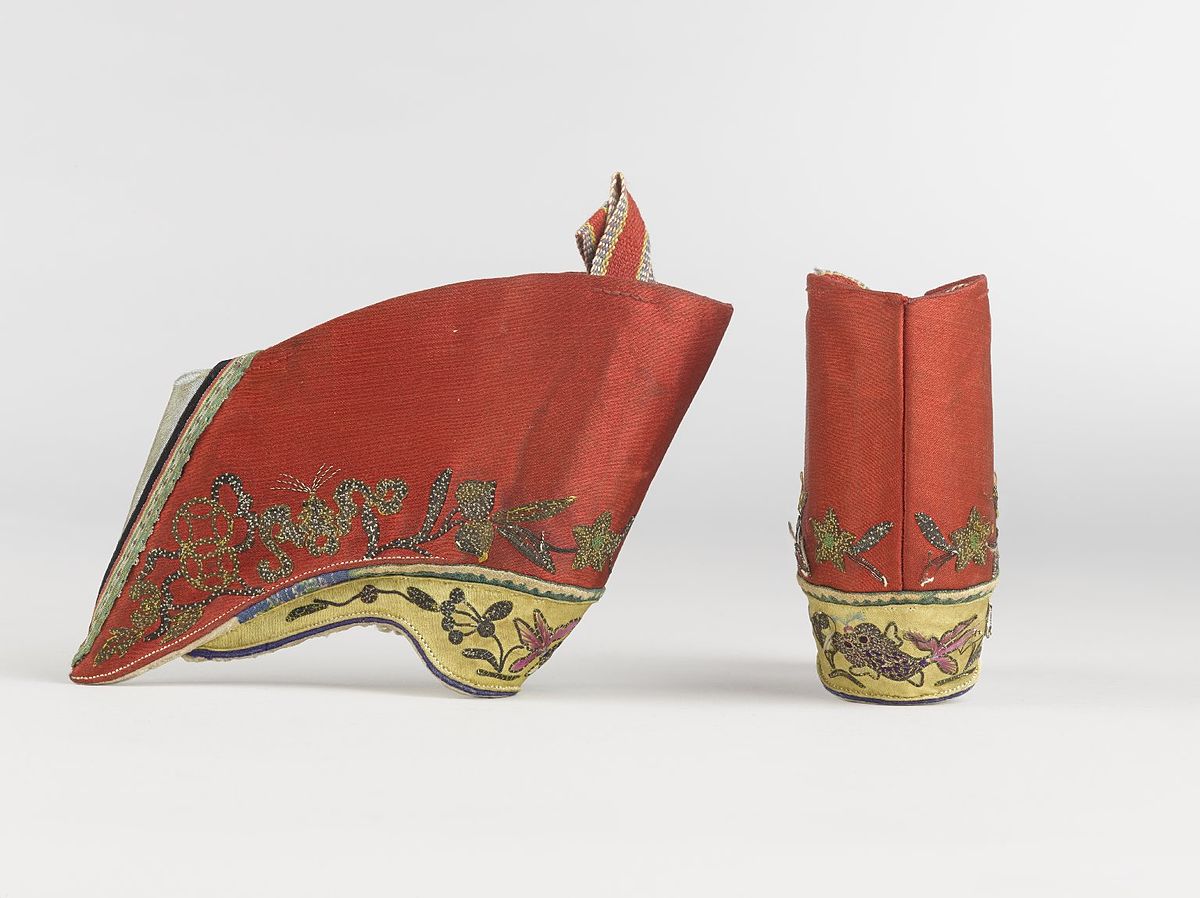

Lotus Shoes
Embroidered silk shoes that held the bound feet
8
New cards

Ghengis Khan (Chinggis Khan)
Also known as Temujin; he united the Mongol tribes into an unstoppable fighting force; created largest single land empire in history.
9
New cards
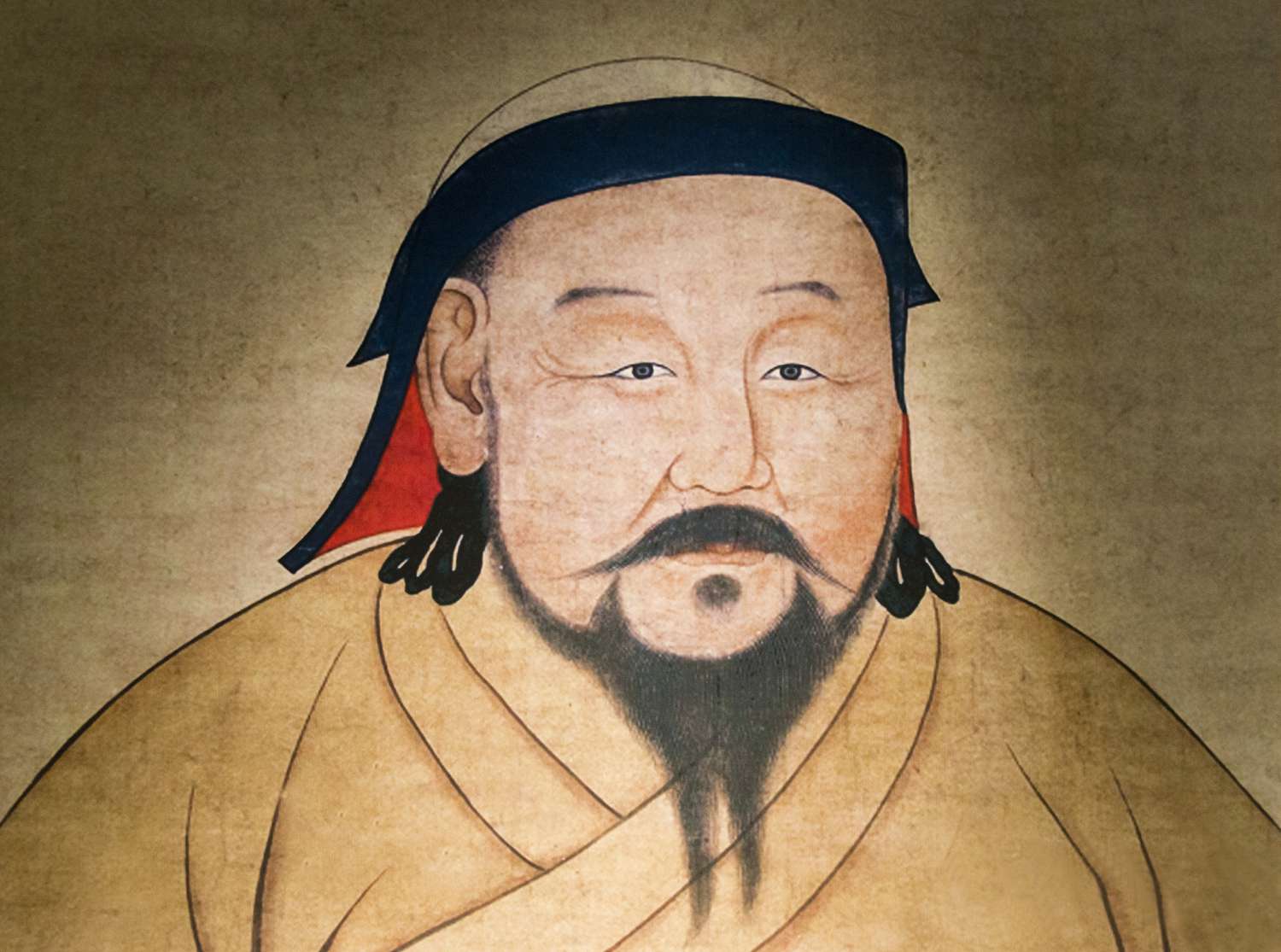

Khan
A Mongol ruler
10
New cards
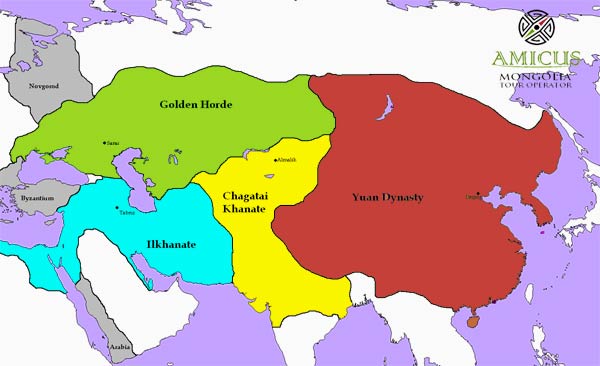
Khanate
One of several separate territories into which Genghis Khan's empire was split, each under the rule of one of his sons
11
New cards
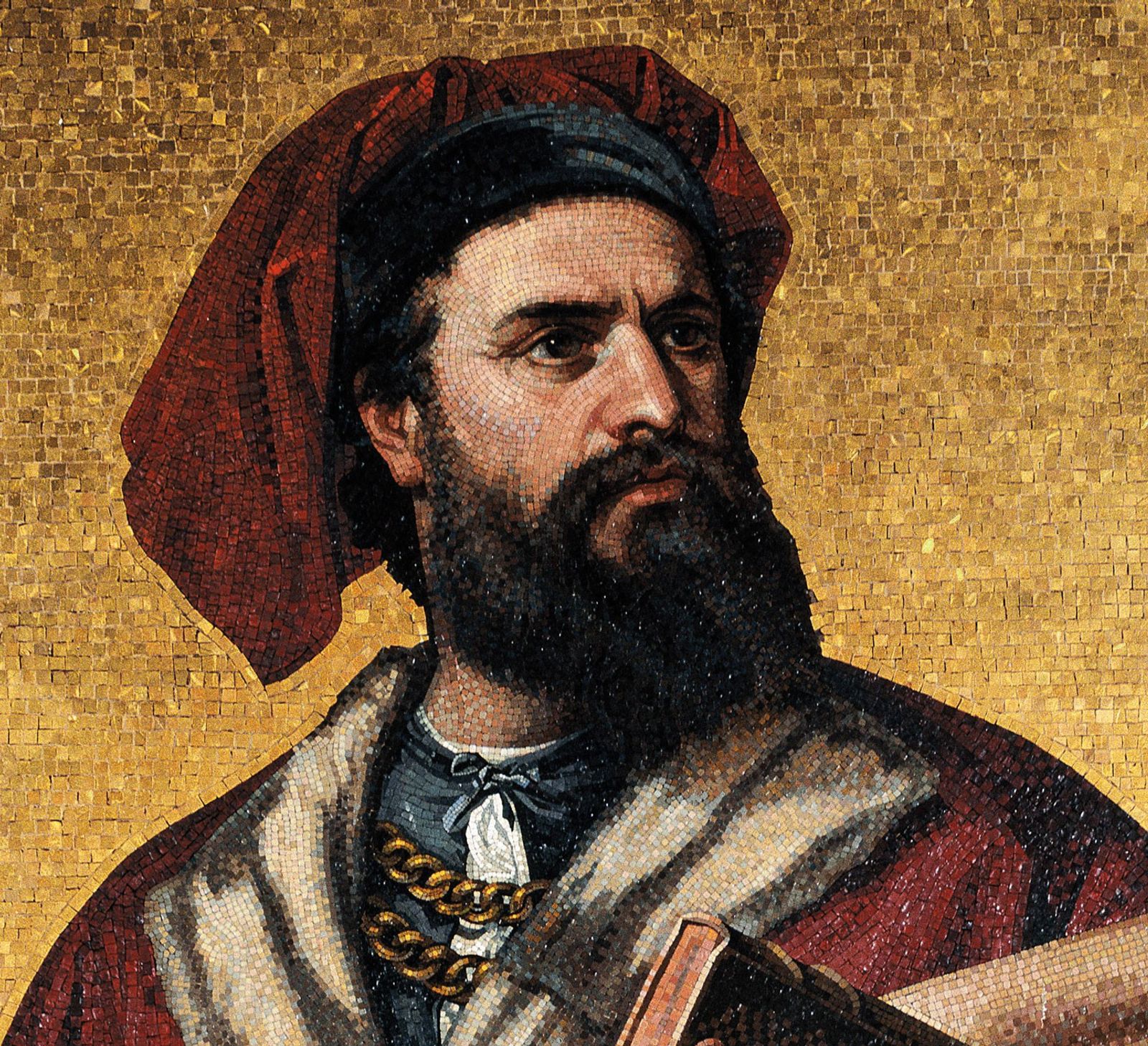

Marco Polo
Venetian merchant and traveler. His accounts of his travels to China offered Europeans a firsthand view of Asian lands and stimulated interest in Asian trade.
12
New cards

The Travels of Marco Polo
Marco Polo's book explaining his travels to Asia. This book inspired people to travel to Asia, which led to the discovery of America
13
New cards

Pax Mongolica
The period of approximately 150 years of relative peace and stability created by the Mongol Empire.
14
New cards
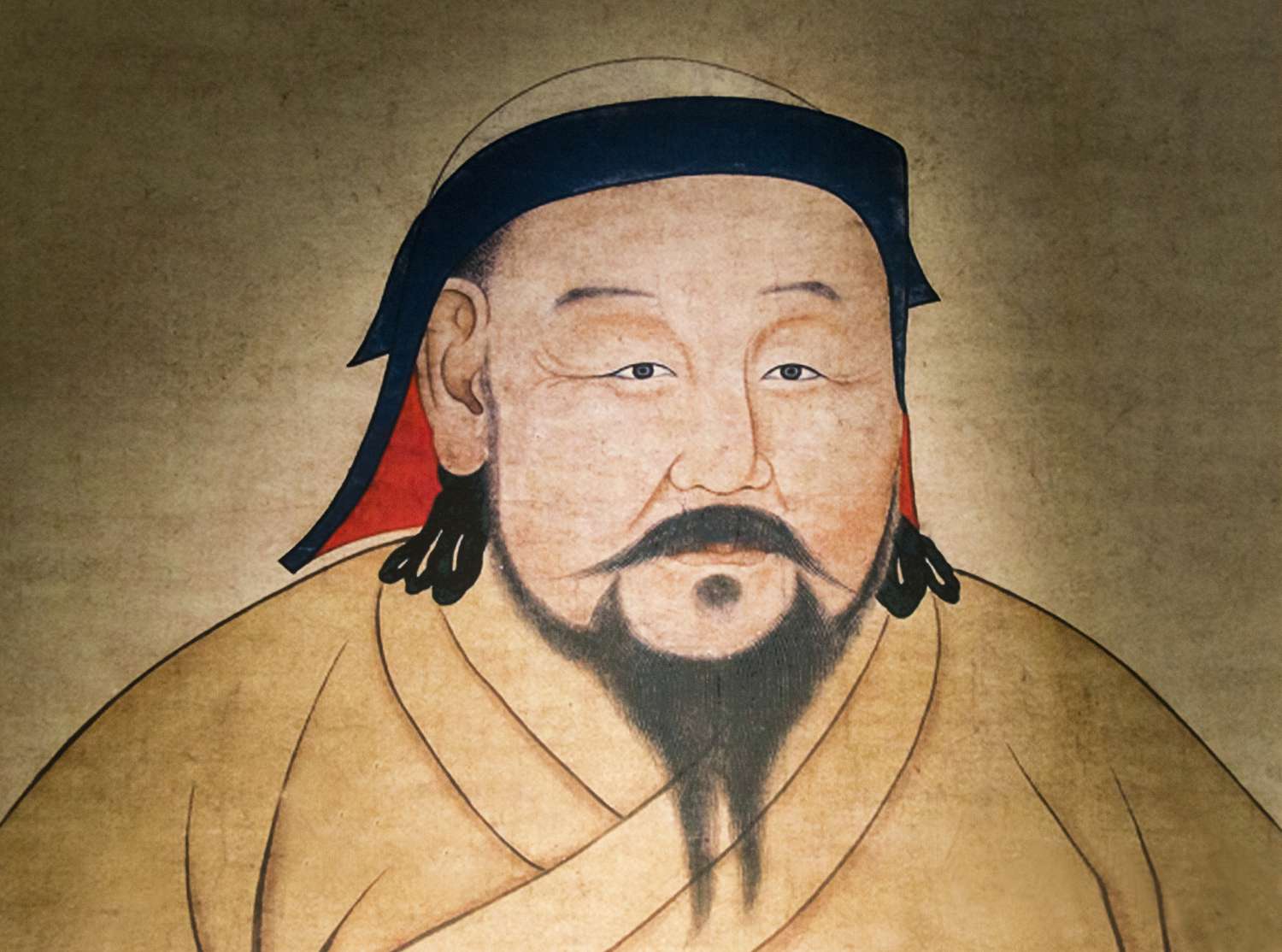

Kublai Khan
Mongolian emperor of China and grandson of Genghis Khan who completed his grandfather's conquest of China
15
New cards
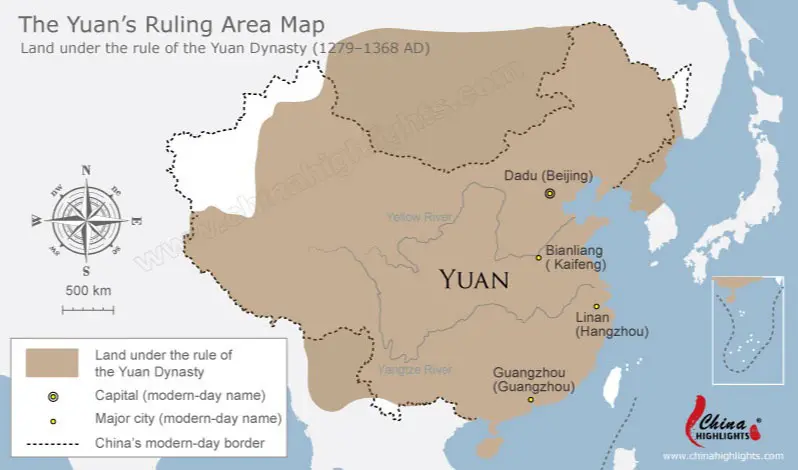
Yuan Dynasty
Dynasty in China set up by the Mongols under the leadership of Kublai Khan, replaced the Song (1279-1368)
16
New cards

Pastoralists
Nomads who kept herds of livestock on which they depended for most of their food
17
New cards
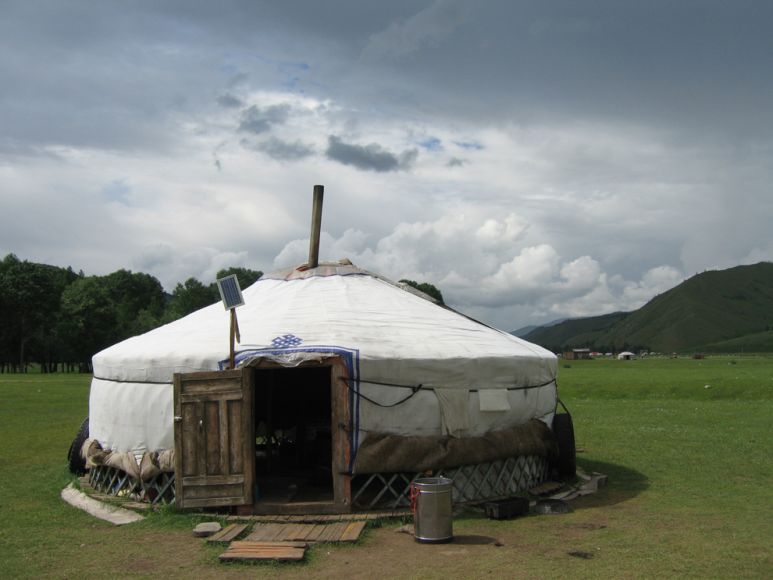

Yurt
A tent used by nomadic people in Mongolia
18
New cards

Kamikaze Winds
Winds which kept Japan from being invaded by the Mongols
19
New cards

Yamato Clan
Only family to hold the title of emperor in Japanese history
20
New cards

Rising sun
Symbol of the Yamato Clan
21
New cards
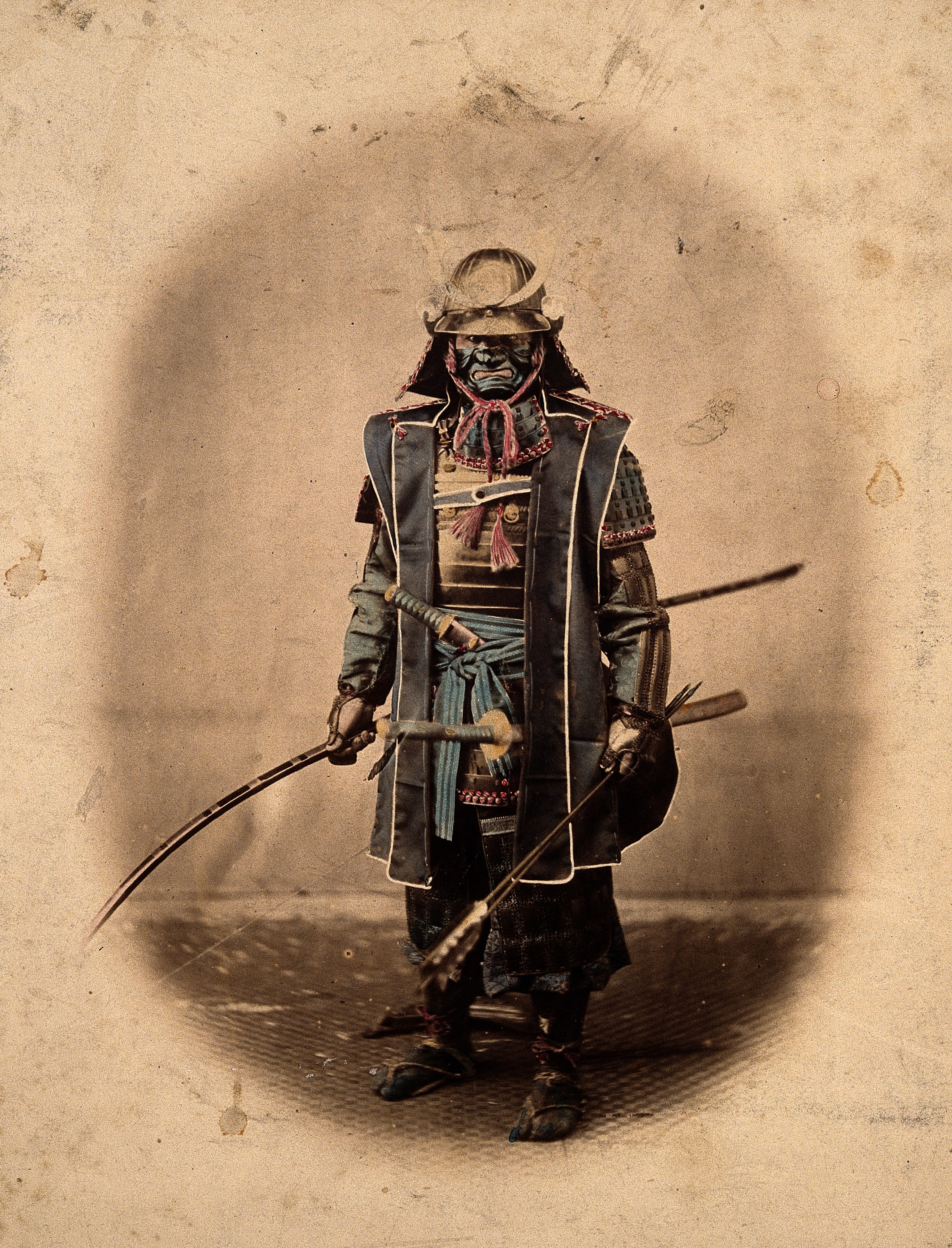

Samurai
Class of warriors in feudal Japan who pledged loyalty to a noble in return for land.
22
New cards

Daimyo
A Japanese feudal lord who commanded a private army of samurai
23
New cards
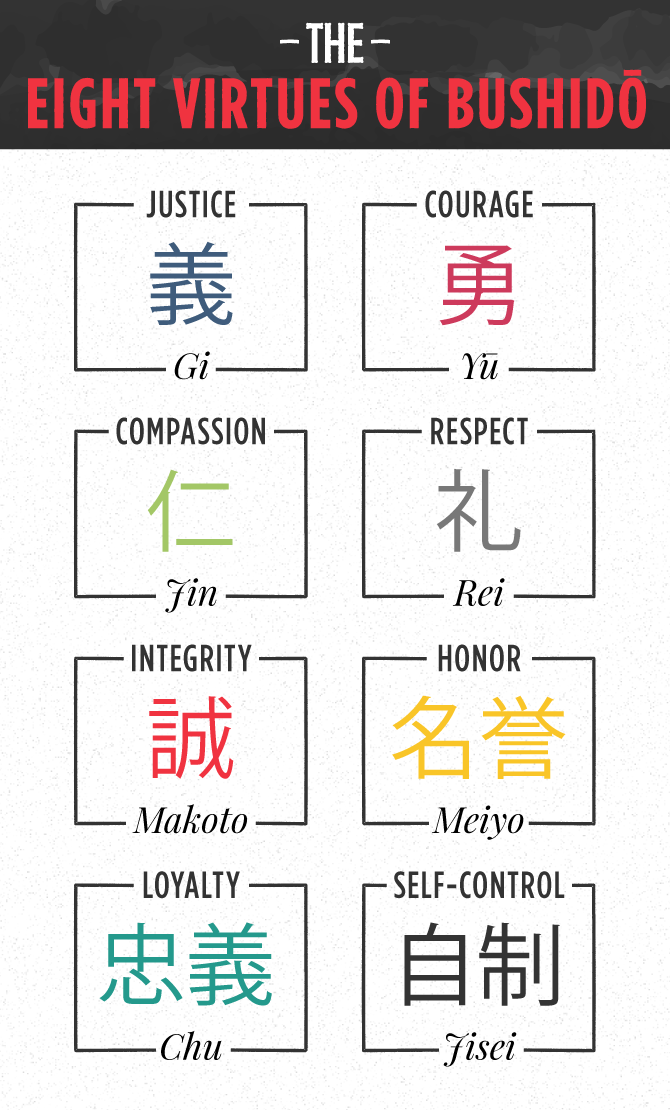
Bushido
The Feudal Japanese code of honor among the warrior class.
24
New cards

Zen Buddhism
A Buddhist sect that emphasizes enlightenment through meditation and stresses simplicity and discipline
25
New cards

Tokugawa Shogunate
Japanese ruling dynasty that strove to isolate it from foreign influences
26
New cards

Feudalism in Japan
System in Japan in which land is given to Daimyo and Samurai in exchange for military service
27
New cards
Heian Period
The era in Japanese history from A.D. 794-1185, arts and writing flourished during this time
28
New cards

Kabuki Theater
A form of Japanese theater developed in the seventeenth century that features colorful scenery and costumes and an exaggerated style of acting
29
New cards

Haiku
A Japanese form of poetry, consisting of three unrhymed lines of five, seven, and five syllables
30
New cards
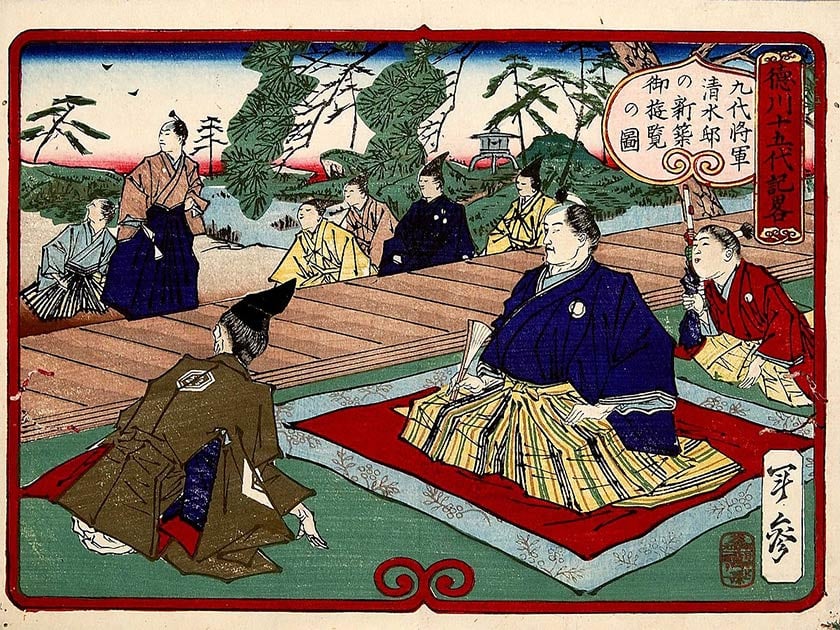

Shogunate
The Japanese system of centralized government under a shogun, who exercised actual power while the emperor was reduced to a figurehead.
31
New cards
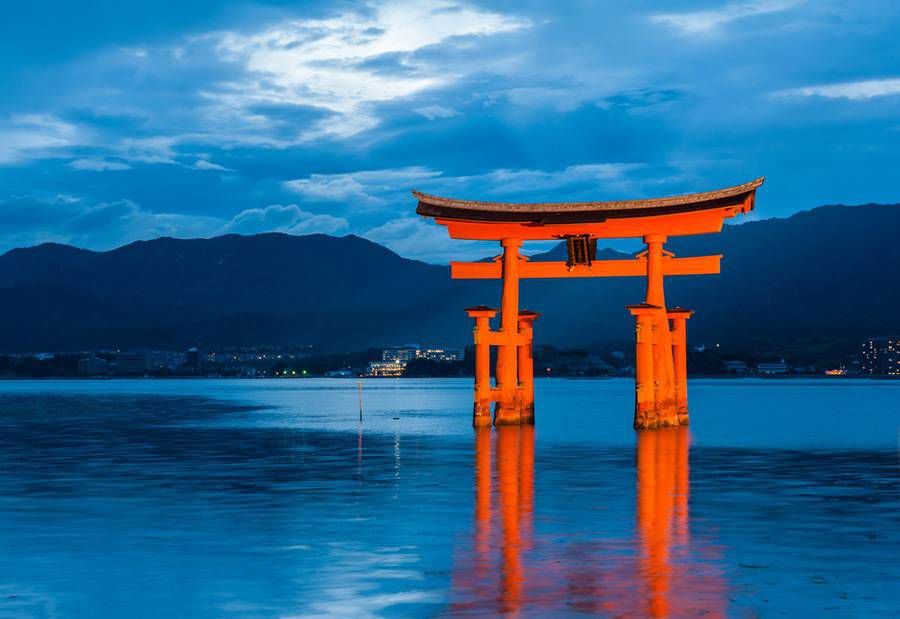

Torii
The gateway of a Shinto shrine
32
New cards

Shogun
A general who ruled Japan in the emperor's name
33
New cards
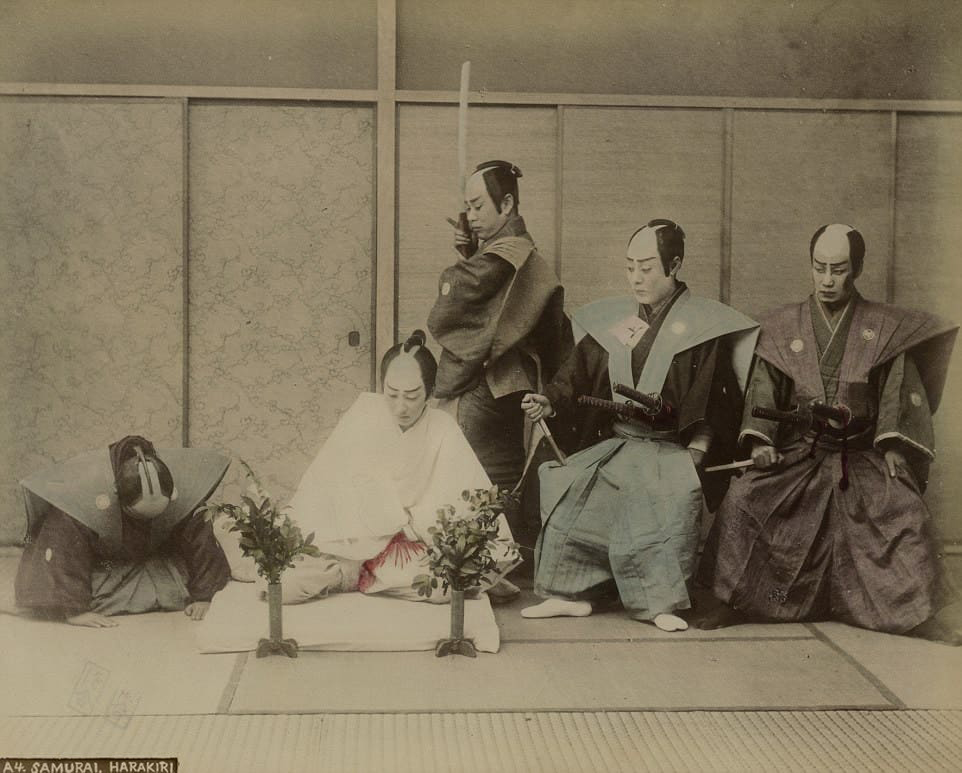

Sepukku
Ritual suicide in Japan; commonly known in West as harakiri; demonstrated courage and a means to restore family honor.
34
New cards
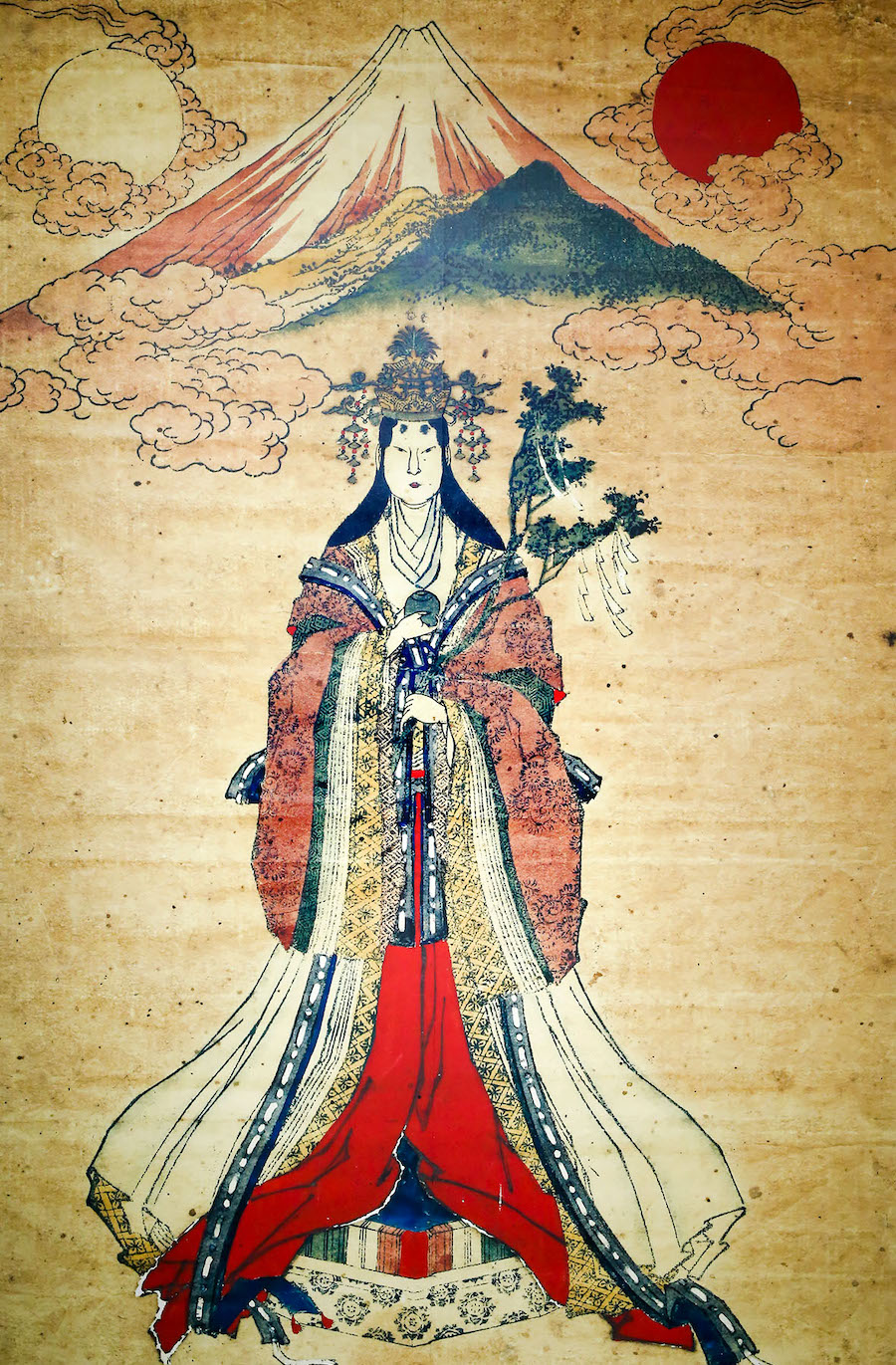

Kami
A divine being in the Shinto religion.
35
New cards
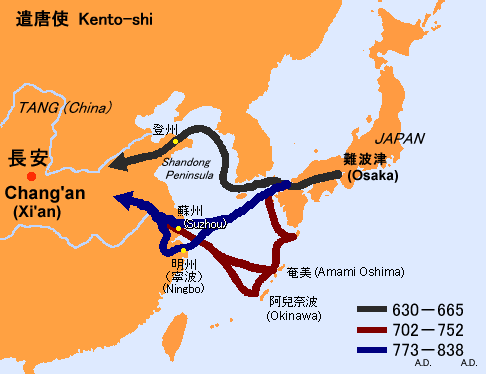
Selective Cultural Borrowing (Japan)
Choose specific elements of Chinese culture to adopt (ex. Zen/ Chan Buddhism and students were sent to schools in China)
36
New cards

Geography of Japan
Archipelago, lots of natural harbors, mountainous, lacks natural resources