Hematology Ch 13: Lymphoproliferative Disorders & Plasma Cell Disorders
1/21
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
22 Terms
Lymphoproliferative disorders
•Clonal, malignant proliferation of B and T lymphocytes.
•Primarily affects the elderly
•Chronic and progresses slowly.
•Most related to compromised immune systems.
•Diagnosed with flow cytometry and chromosomal analysis.
Leukemia
Clonal malignancy that originates in the bone marrow and is noted in the general circulation.
List the types of lymphoproliferative and plasma cell disorders (7)
•CLL Chronic Lymphocytic Leukemia (B cells)
•Hairy Cell Leukemia (B cells)
•Sezary Syndrome
•Prolymphocytic Leukemia
•Hodgkin's and Non- Hodgkin's lymphoma
•Multiple Myeloma
•Waldenstrom's Macroglobulinemia
CLL Chronic Lymphocytic Leukemia
•Clonal proliferation of B lymphocytes
•Malignant lymphocytes have B cell markers: CD15, 19, 20, 22 and CD5 (usually only found on T cells).
•Small lymphocytes accumulate in the spleen, lymph nodes, and BM and can spill out into peripheral circulation.
-key feature: presence of mature lymphs that are dysfunctional
CLL Chronic Lymphocytic Leukemia Presenting signs and symptoms AND lab findings
Presenting signs/symptoms:
Fatigue, pallor, weight loss, and lymphadenopathy
lab findings
PBS shows small lymphs (90%) and some lymphoblasts
smudge cells may be present
high WBC counts (>100,000)
M:E ratio is 10-20:1
CLL Chronic Lymphocytic Leukemia Immunologic Function and Treatment Options
In 80% an anti apoptosis gene is present, so dysfunctional B cells live on
B cell function is compromised, patients show hypogammaglobinemia and bacterial skin infections
Treatment options:
Irradiation (palliative if lymphadenopathy or splenomegaly)
Drugs
Alkylating agents
Monoclonal antibodies
Allogeneic stem cell transplant
PLL Prolymphocytic Leukemia
Variant of chronic lymphocytic leukemia, rare disorder
Poor prognosis and severe
PBS shows mostly circulating prolymphocytes
Symptoms:
Splenic enlargement
Liver involvement
Escalating white counts.
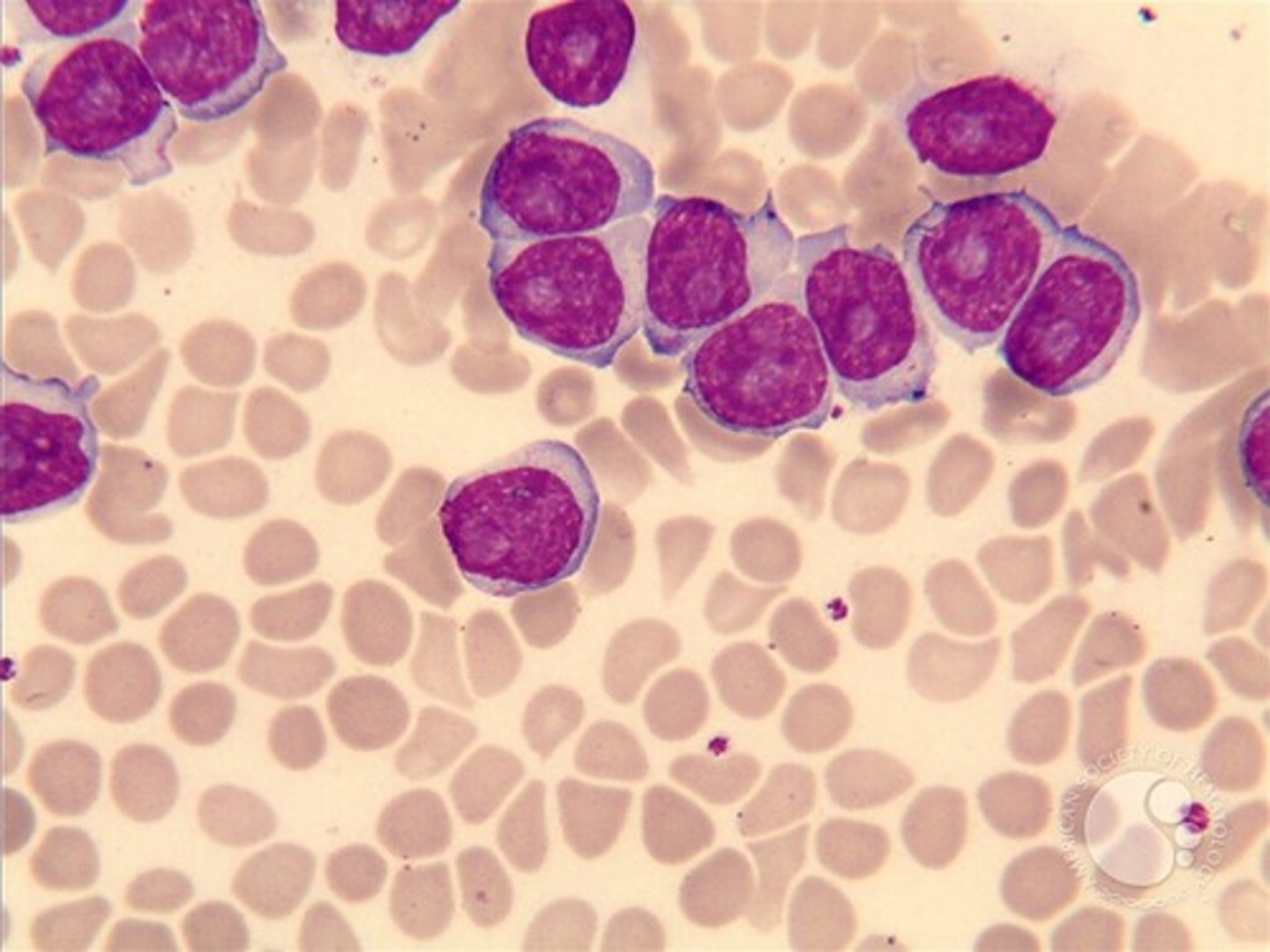
Hairy Cell Leukemia
Rare B cell malignancy.
cells are fragile and mononuclear
Hair-like projections of the cytoplasm.
Spongy appearance of chromatin.
Diagnosis with cytochemical stain tartrate-resistant acid phosphatase (TRAP)
other cells don’t stain with the tartrate
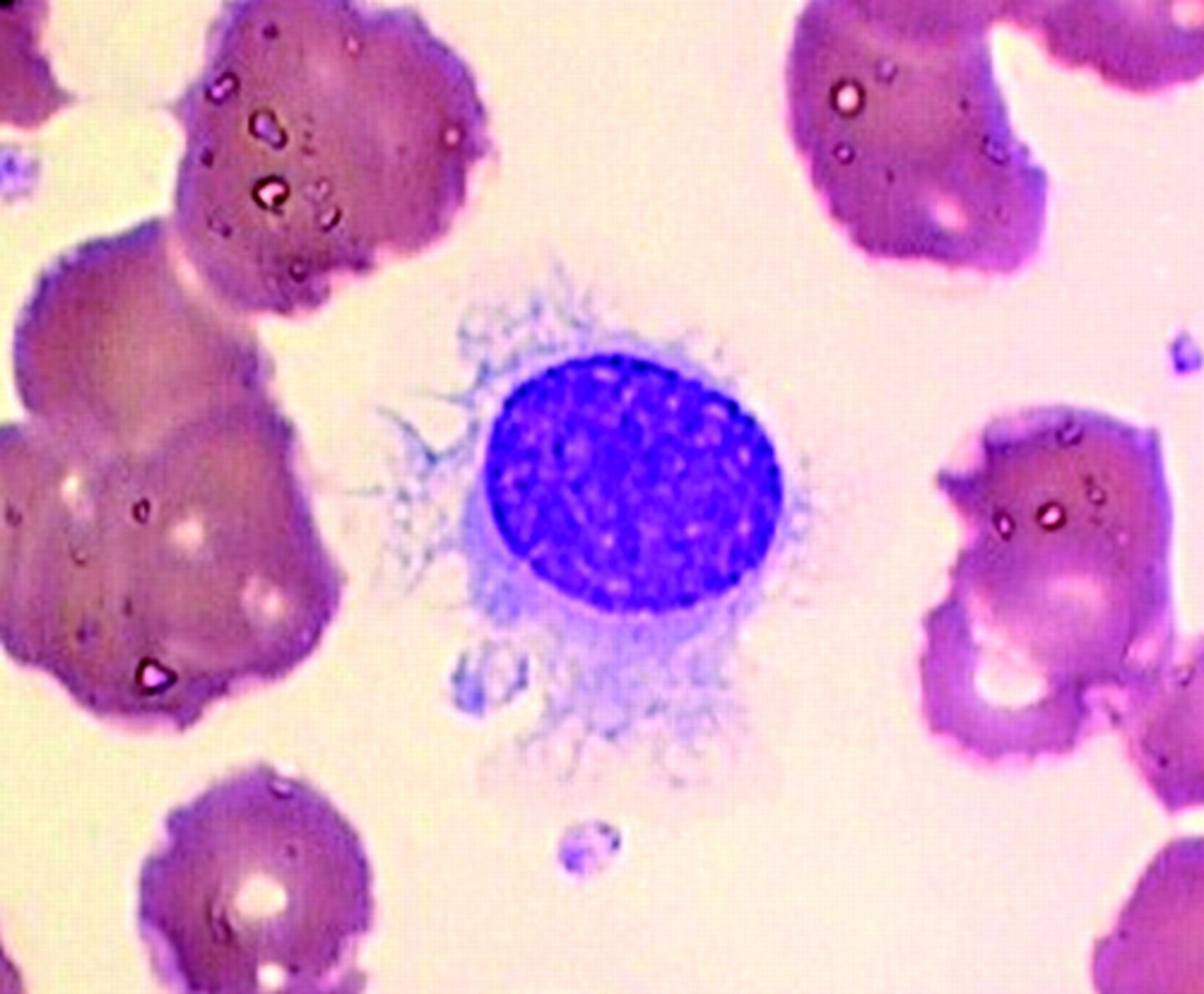
Hairy Cell Leukemia Symptoms and treatment
symptoms
Thrombocytopenia
Pancytopenia
Massive spleen
Abdominal discomfort
Bleeding
Infection
Anemia
Dry tap
BM becomes filled with fibrotic material and marrow cannot be aspirated.
treatment
therapuetic splenectomy
Hodgkin's Lymphoma
One of the most common lymphomas in young males 12-40, also seen in people over 50.
Usually, single cervical lymph node becomes firm to the touch and does not disappear
People exposed to EBV or environmental hazards are at increased risk.
Symptoms of hypermetabolism show:
Low-grade fever and weight loss.
Diagnosis based on lymph node biopsy.
May involve liver, spleen, and bone marrow.
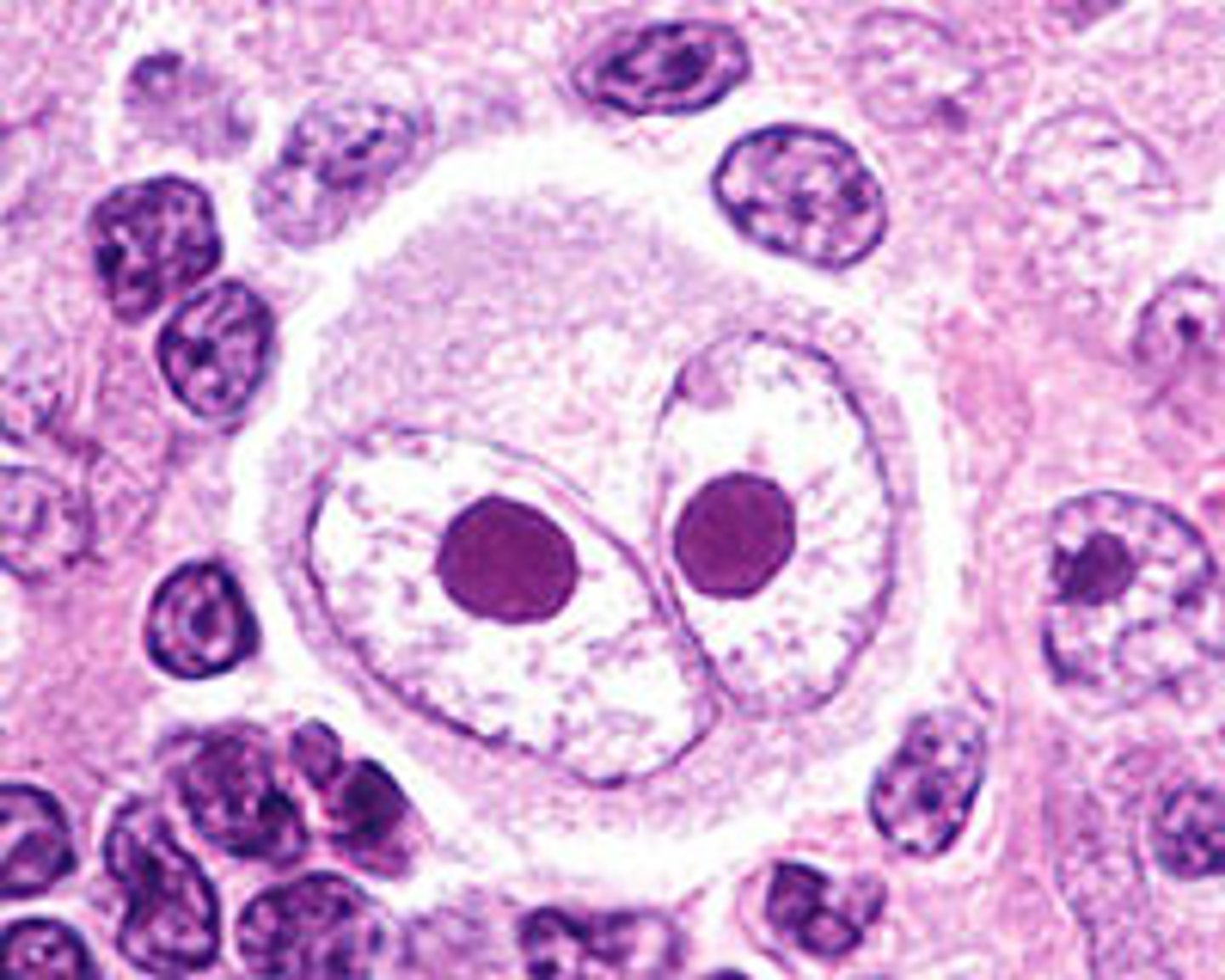
Presence of Reed-Sternberg cell:
Large and multinucleated, resembles "owl's eye"
Non-Hodgkin's Lymphomas
3X more common than Hodgkin's lymphoma.
May present as painless cervical lymph node involvement.
Lymphoma cells may be seen in peripheral smear.
Diagnosis based on histological types of lymphocytic cells.
Treatment includes radiation and chemotherapy
treated with chemo and radiation.
Disease may spread:
Gastrointestinal, respiratory, skin, liver, or spleen
Sezary Syndrome
T-cell lymphoma with cutaneous mycosis fungoides
skin biopsies reveal an infiltration of lymphocytes.
spleen, bone marrow, and lymph nodes may become affected.
sezary cells are present in the PBS
large, convoluted ovoid nucleus
may be mistaken for monocytes
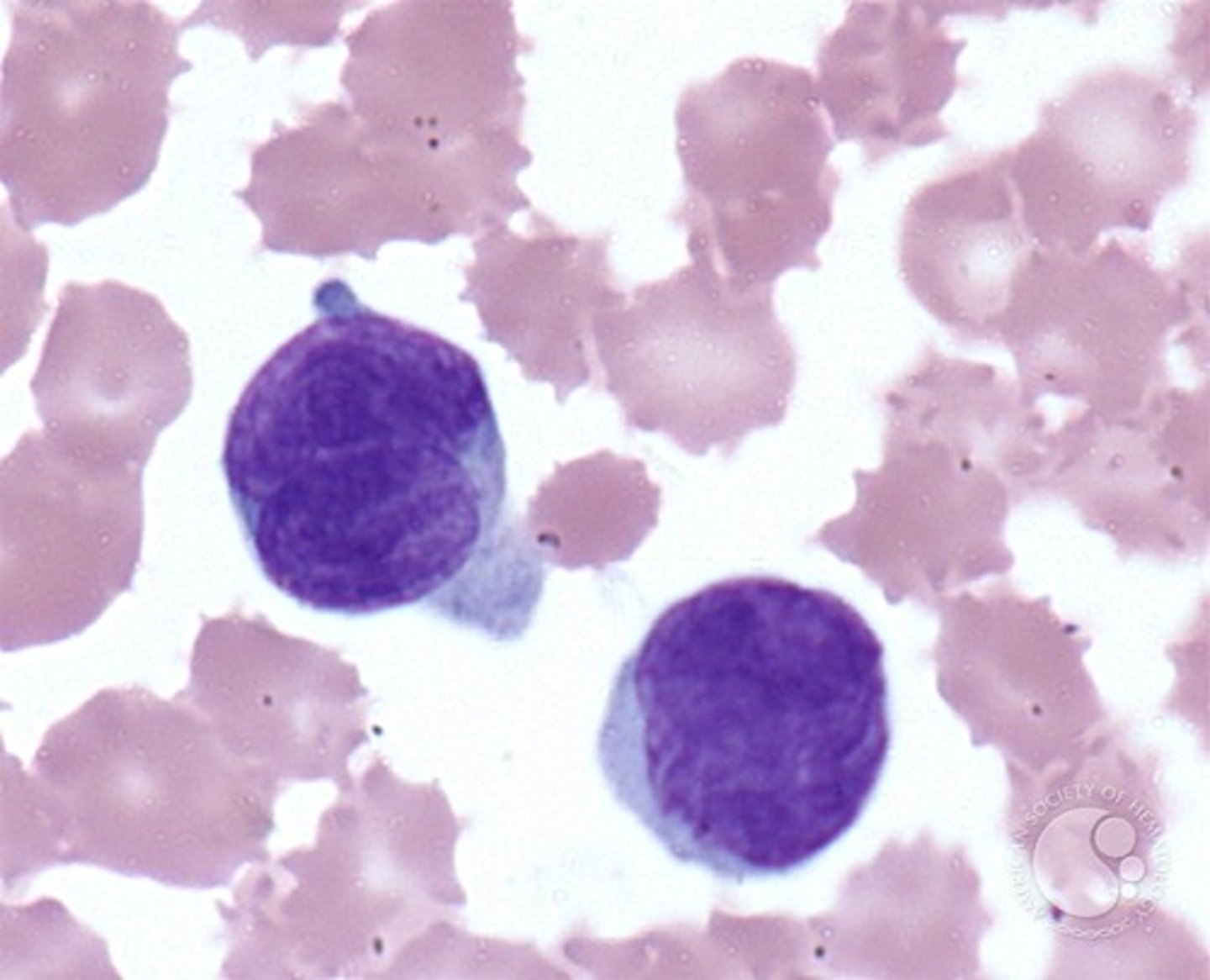
Describe normal plasma cells
evolves from B lymphs and makes immunoglobulins
BM diff shows no more than 5% of these cells
Very rarely seen in peripheral blood.
If seen in periphery, it is in response to infection, inflammation or malignancy
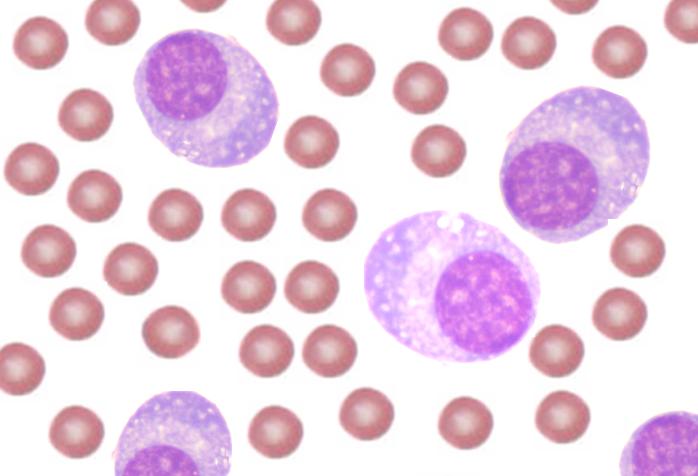
Multiple Myeloma
Disorder of plasma cells
Accumulation of plasma cells in bone marrow and other locations.
monoclonal proliferation of IgG antibodies
excess globulin production causes hyperviscosity of the blood (blurred vision and headaches)
Occurs at older age.
Multiple Myeloma Diagnosis
rouleaux formation in the PBS
nonspecific binding of red cells, caused by RBCs circulating in abnormal proteins
can cause falsely decreased RBC and elevated MCV and MCHC
elevated ESR
Bence Jones proteins are found in the urine
Symptoms of Multiple Myeloma
•Fatigue, due to anemia
•Excessive thirst/urination, due to excess calcium
•Nausea, due to excess calcium
•Bone pain/back and ribs, due to plasma cell acceleration
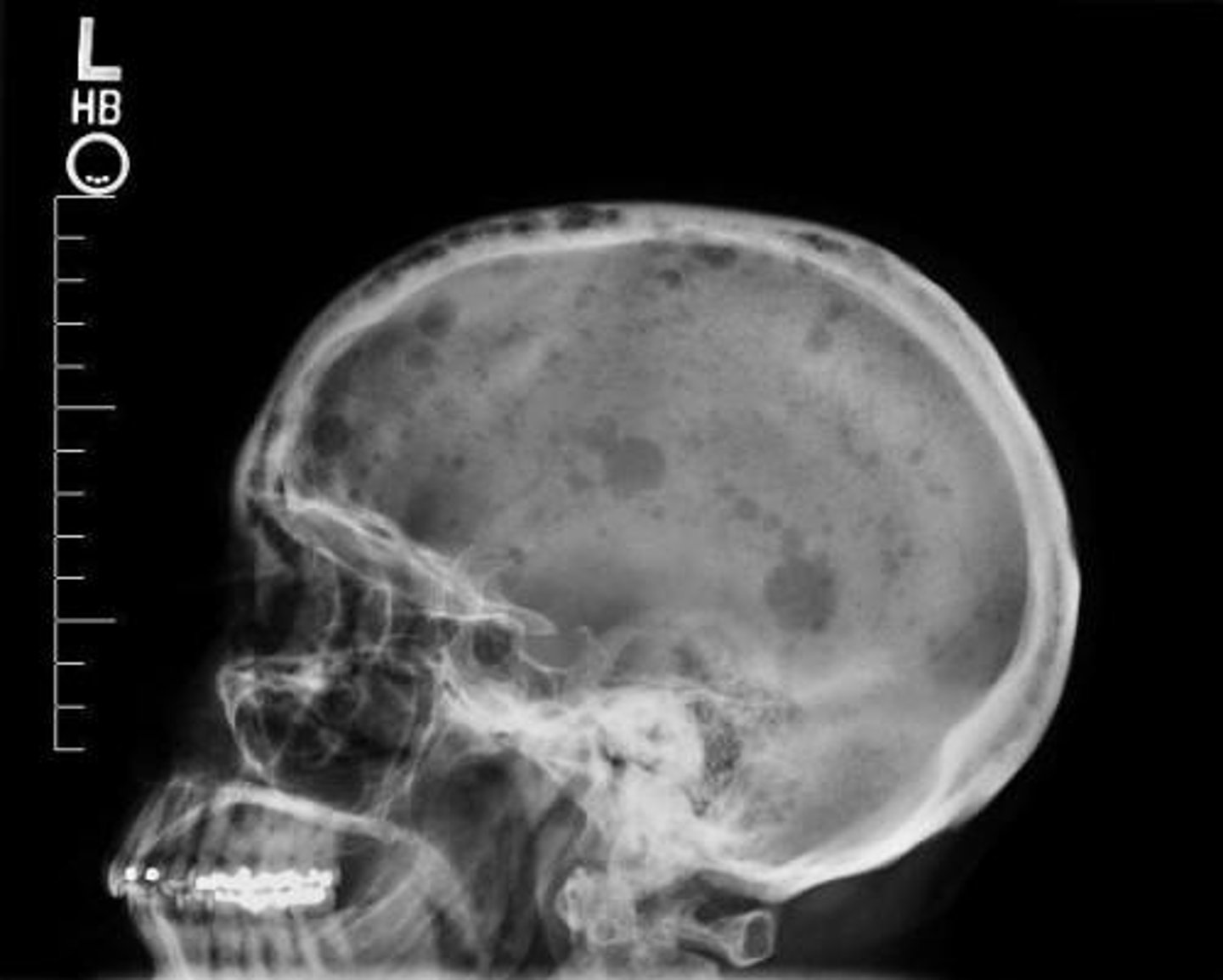
•Bone fractures, due to calcium leaching from bones into circulation. Punched out lesions on X ray.
•Unexpected infections, due to compromised immunity
•Weakness and numbness in the legs, due to vertebrae compression.
Waldenstrom's Macroglobulinemia
•Overproduction of IgM caused by abnormal B lymphocytes.
•Increased IgM interferes with coagulation factors by coating platelets and impeding their function.
•Hyperviscosity syndrome: slow flowing blood may lead to CNS symptoms ex. Vision disturbances, dizziness.
•Peripheral smear may show rouleaux and plasmacytoid lymphocytes.
•Cryoglobulins may be found in some patients
•May lead to Raynaud's phenomenon.
•Causes bleeding.
Waldenstrom's Macroglobulinemia Treatment
•Chemotherapy
•Possible stem cell transplantation
•Plasmapheresis: Blood is removed and separated; then, cells are returned, and offending plasma is discarded.
What is the most common presenting symptom in patients with CLL?
enlarged lymph nodes
What are the peripheral smear indicators of an autoimmune hemolytic anemia in a patient with CLL?
nRBCs and spherocytes
In contrast to other leukemias, which of the following conditions presents with pancytopenia?
hairy cell leukemia (HCL)
What is the most characteristic change seen in the PBS of a patient with multiple myeloma?
rouleaux formation