bone tumors
1/27
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
28 Terms
bone tumors: general features
primary tumors: rare tumors that are outnumbered by metastases & hematopoietic tumors
most bone neoplasm develops during the first several decades of life & have a propensity for the long bones of the extremities
tumors may be asymptomatic or present with pain or slow-growing mass
risks of tumors increased by chronic injury & inflammation
osteoma
bosselated, round sessile tumors that project from the subperiosteal or endosteal surface of cortex
composed of woven & lamellar bone
slow growing
clinical presentation
solitary & detected in middle age
related/associated disease
Gardner syndrome
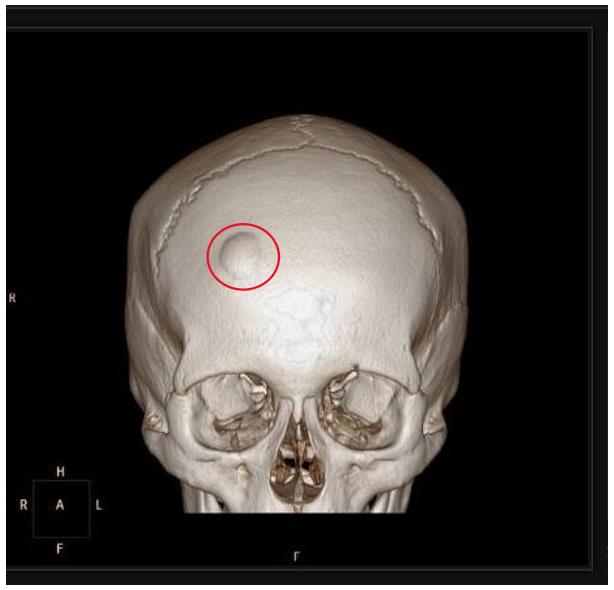
Gardner syndrome
a condition characterized by multiple osteomas
osteoid osteoma
benign, small (< 2.0 cm) lesions that usually involves the tibia & femur (long bones)
nidus of osteoid & connective tissue (woven bone) surrounded by a dense sclerotic bone shell
nidus RADIOLUCENT on X-ray
clinical presentation
occur in male teenagers & young adults
pain @ night (cause by prostaglandin E2) that is relieved by aspirin
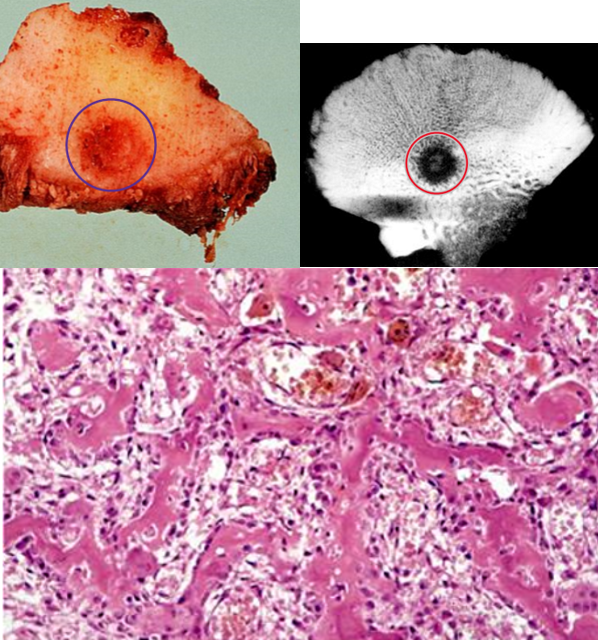
osteoblastoma
larger lesions than osteoid osteomas (> 2 cm) that involve the posterior spine
clinical presentation
back pain
dull pain UNRESPONSIVE to salicylates
does NOT induce a marked bony reaction
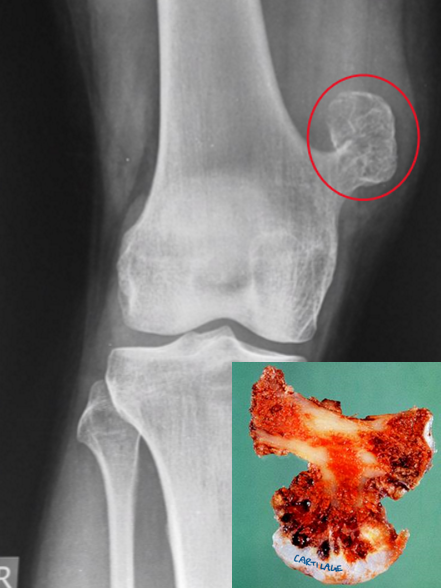
osteochondroma
benign outgrowth (exostosis) of bone with a cartilage cap
develop only in bones of endochondral origin & arise from the metaphysis near the growth plate of long tubular bones → especially near the knee
grossly seen as mushroom-shaped outgrowths
only bone portion seen on X-ray
risk factors
MEN affected more than women
late adolescence & early adulthood
may be associated with an increased risk of malignancy (5 - 20% of hereditary type)
chondroma
benign tumor of hyaline cartilage
results from the failure of ossification
RADIOLUCENT on X-ray
NO PAIN
examples
enchondroma
Ollier disease
Maffucci syndrome
enchondroma
benign tumor of hyaline cartilage that arise with in the medullary cavity
usually < 3.0 cm in size
NO PAIN
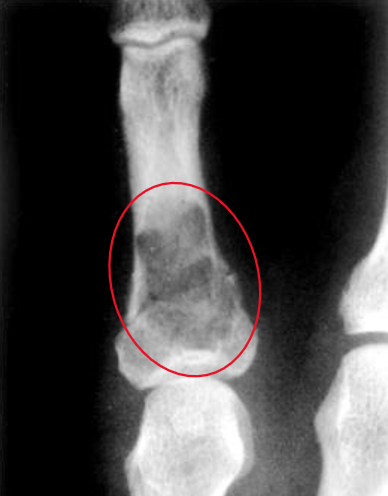
Ollier disease
enchondromatosis - benign, multiple growths of cartilage (enchondromas)
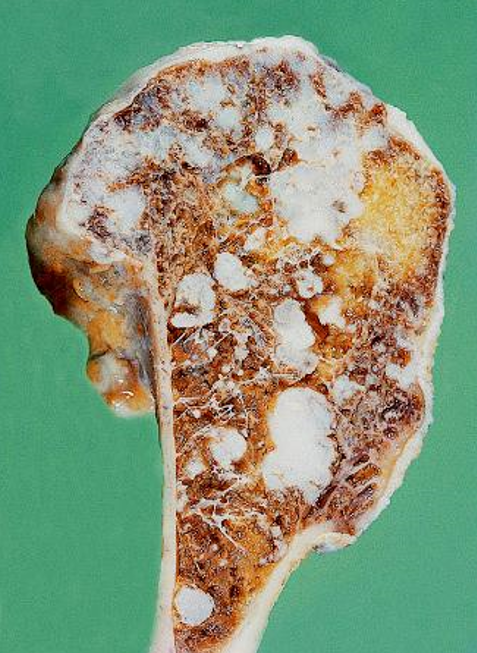
Maffucci syndrome
multiple enchondromas associated with soft tissue hemangiomas (benign lesions of blood vessels)
increased risk of malignancy, including ovarian carcinomas & gliomas
fibrous dysplasia
localized area of disordered maturation of woven bone with fibrous tissue (fibroblasts)
may be polyostotic or monostotic
curvilinear bony spicules shaped like Chinese figure surrounded by fibroblasts seen on biopsy
manifestations results from a somatic gain-of-function mutation during development in GNAS1 (gene that is also mutated in pituitary adenomas)
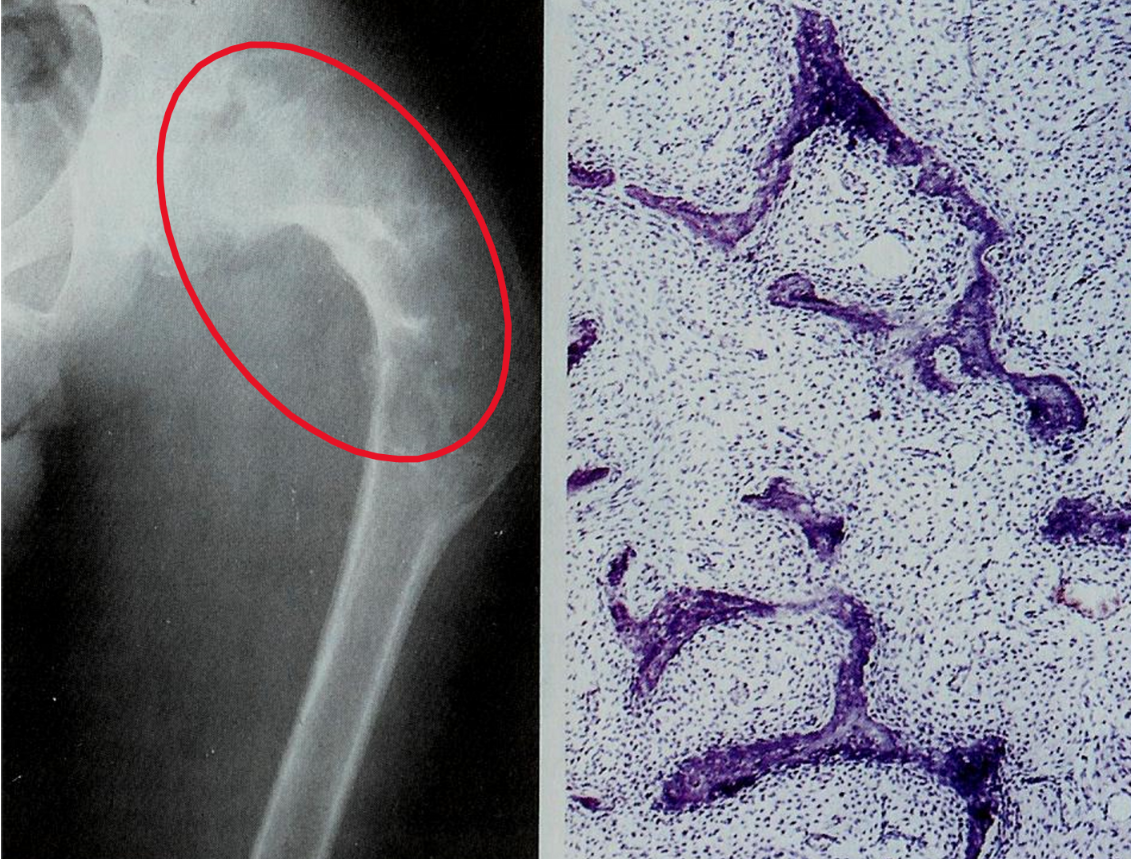
fibrous dysplasia - monostotic
localized area of disordered maturation of woven bone with fibrous tissue that involves the femur, tibia, ribs, humerus, etc.
frequently asymptomatic
occurs equally in boys & girls
fibrous dysplasia - polyostotic
localized area of disordered maturation of woven bone with fibrous tissue that involves the femur, skull, tibia, ribs, humerus, ribs, fibula, radius, ulna, mandible, & vertebrae
may progress to crippling deformities & fractures
manifests @ a slightly earlier age
occurs equally in boys & girls
McCune-Albright syndrome
a condition characterized by polyostotic fibrous dysplasia in females
precocious puberty & café au lait spots on the skin
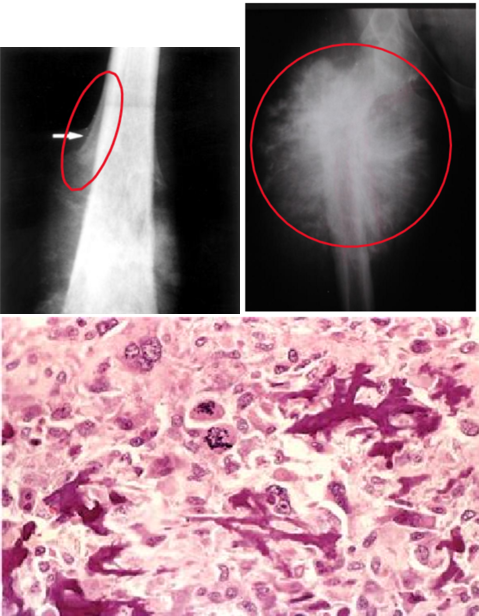
osteosarcoma
most common primary bone cancer arises in the metaphyseal cancellous bone & lifts the periosteum → Codman triangle on X-ray & sunburst also seen X-ray
mainly affects young males around knee area (distal femur or proximal tibia) presenting with pain & progressive swelling
seen in older males with predisposing factors: Paget disease, bone infarcts, & prior radiation (secondary type)
associated with
RB gene - retinoblastomas (white reflex in eyes)
TP53 - Li-Fraumeni syndrome
INK4a, MDM2, CDK4
clinical presentations
large bulky tumors that often contains areas of hemorrhage & cystic degeneration
tumor cells: very in size & shape (pleomorphic) & frequently have large hyperchromatic nuclei
osteoblastic type can produce bone
treatments
chemotherapy followed by surgery
with treatment: 5-year disease-free survival rate 60 - 70%
< 20% 5-year survival rate with overt metastasis or recurrent disease
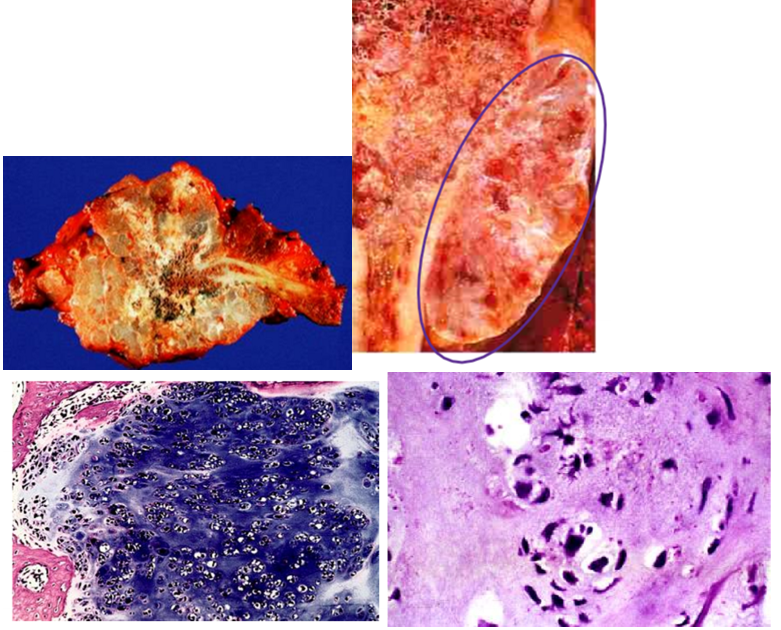
chondrosarcoma
second most common malignant matrix-producing tumor of bone that commonly arise in the central (intramedullary) portions of the axial skeleton, including the pelvis, shoulder & ribs
15% may arise from enchondroma or osteochondroma (secondary type)
clinical presentations
occurs in males age 40 years or older
large, bulky tumors made up of nodules of gray-while, somewhat translucent glistening tissue
tumor cells: vary in degree of cellularity, cytologic atypia, & mitotic activity
treatment
wide surgical excision
5-year survival rate: grade 1 tumors (80 - 90%) vs grade 3 tumors (43%)
grade > stage
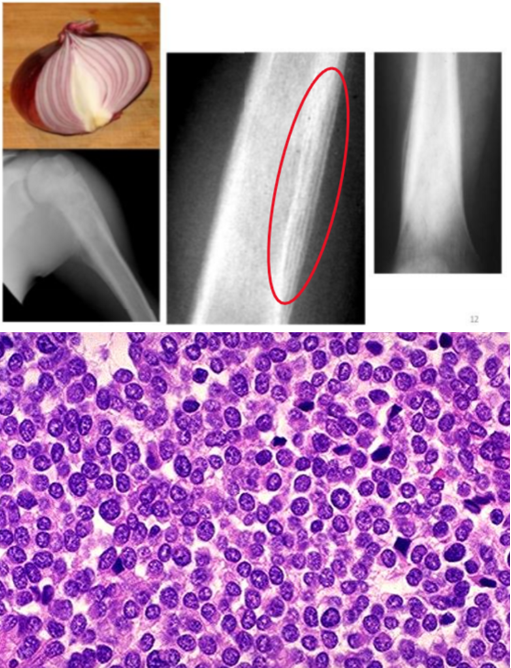
Ewing sarcoma
the second most common group of bone sarcomas in children that usually arise in the diaphysis or long tubular bones, especially the femur & the flat bones of the pelvis
primitive neuroectodermal tumor (PNET) associated with t(11;22)
rapidly growing & arises in the medullary cavity extending to the cortex, periosteum, & soft tissue
clinical presentation
typically occurs between ages 10 - 15
produces “onion skin layering“ on x-ray
composed of sheets of uniform small, round cells with scant cytoplasm
presents as painful enlarging masses & the affected site is frequently tender, warm, & swollen
may have systematic findings, including fever, elevated sedimentation rate, anemia, & leukocytosis which mimic infection (osteomyelitis)
treatment
neoadjuvant chemotherapy followed by surgical excision with or without irradiation
5-year survival rate 75% with aggressive therapy
scenario → give antibiotics & no improvement
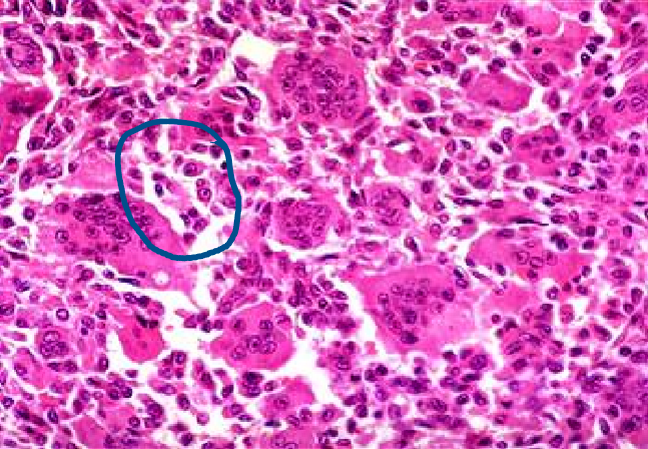
giant cell tumor
uncommon benign but locally aggressive tumor that frequently arises around the knee (distal femur & proximal tibia)
clinical presentations
usually arises in individuals in their 20s - 40s
soap bubble appearance on X-ray
large, red-brown tumors that frequently undergo cystic degeneration
mostly composed of uniform oval mononuclear cells and numerous osteoclast-type giant cells with 100 or more nuclei
neoplastic cells consist of proliferating mononuclear cells, not giant cells
treatment
curettage, but 40% to 60% of cases recur locally
metastatic disease
most common form of skeletal malignancy, with 75% of cases in adults originating from cancers of the prostate, breast, kidney, and lung
in children, they can originate from neuroblastoma, Wilms tumor, osteosarcoma, Ewing sarcoma, & rhabdomyosarcoma
metastases often involve the axial skeleton, proximal femur, & humerus
purely lytic, purely blastic (e.g. prostate), or a mix of lytic & blastic
fracture
loss of bone integrity due to mechanical injury and/or diminished bone strength
simple fracture
fracture in which the overlying skin is intact
compound fracture
fracture in which the bone communicates with the skin surface
comminuted fracture
fracture in which the bone is fragmented
displaced fracture
fracture in which the ends of the bone at the fracture side are not aligned
fracture healing
soft tissue callus
bony calllus
callus
soft tissue callus
hematoma (immediate), fibroblasts & capillaries
osteoclastic & osteoblastic activity (first week)
bony callus
deposits of subperiosteal trabeculae of woven bone (2 weeks)
enchondral ossification (end of 2nd or 3rd week)
callus
excess of fibrous tissue, cartilage, & woven bone (3 - 6 weeks)