Dermatology - Equine
1/62
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
63 Terms
Chorioptes equi
Equine feather mites
Will have pruritis of distal limbs
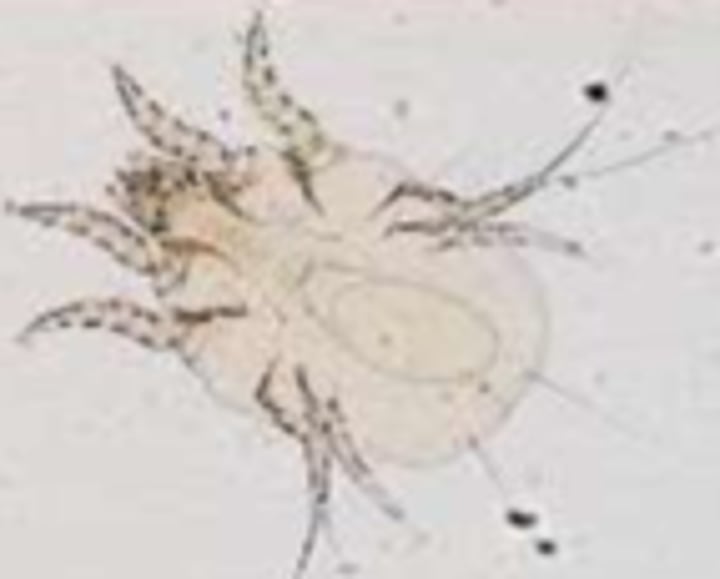

Treatment of chorioptes
Clip feathers
Treat all horses
Disinfect stable and equipment
Doramectin Injection
Trombiculi autumnalis
Very severe pruritis with biting and stamping of legs.
May also have lesions on the head.
Treatment of trombiculi autumnalis
Pyrethrin or fipronil spray.
Remove straw bedding
Avoid infected pastures
Clip feathers and disinfect equipment.
Psoroptes equi
Lesions on the head, tail and inside of ears.
Psoroptes equi treatment
If otitis - doramectin
Otherwise pyrethrin spray or lime sulphur solution
Lice
Lesions on the mane, base of tail and trunk.
Highly contagious
Treatment of lice
Permethrin pour-on
Selenium sulphide shampoo.
Oxyuris equi
Lesions on the tail and perineum only.
Treatment - ivermectin or pyrantel.
Sweet Itch
Culicoides hypersensitivity.
Type IV HS reaction.
Lesions on the mane, rump, tail base, pinna and neck.
More common in native and Scandinavian breeds.
Diagnosis of Sweet itch
Intradermal testing
Treatment of sweet itch
Improve ventilation
Stable horses over night
Fly repellent
Fly rugs
Pour-on permethrin can be used.
Diagnosis of ectoparasites
Coat brushing and skin scrapes.
Common causes of pruritis
· Ectoparasites
· Bacteria/Fungal infection
· Hypersensitivity reactions - insect-bite, food allergy, contact allergy, atopic dermatitis.
· Drug reactions - TMPS, MLs, Vaccines etc.
Food Allergy
· Lesions mainly on face, neck and trunk.
Type I HS
· May have angioedema and urticaria.
· Common allergens - alfalfa, barley, bran, clover, feed additives + supplements
Contact Dermatitis
Type IV HS
· Lesions around areas in contact with tack, rugs etc.
· Also areas in contact with pasture or bedding (such as mouth or ventrum)
· Leads to erythema, oedema, alopecia and lichenification.
Urticaria
· Immunological reaction against allergens in contact with the skin or inhaled/ingested.
· Pathogenesis
· Contact with a stimulus leads to histamine release and increased vascular permeability.
· This results in angioedema and oedematous papules ang plaques.
Treatment of urticaria
Treatment
· Identify trigger
· Wash skin
· Steroids, Cetirizine + Omega 3 fatty acids.
Causes of ulcerative lesions
Viral
· EHV-3- mainly on vulva, perineum, prepuce and penis.
· Transmitted during mating.
· Vesicular Stomatitis
Neoplasia - SCC
Pressure Sores
Summer Sores - Habronemiasis
Rain Scald
Dermatophilus congolensis
Causes infection when there is skin damage and moisture
Often associated with poor conditions or immunity.
Zoospores remain viable in crusts.
Lesions on the rump, dorsum, face, neck and pastern.
Management of Dermatophilus lesions
· Wash tack and equipment
· Prevent horses staying wet
· Maintain good hygiene
· Avoid sunlight in affected areas as it increases irritation.
Treatment of Dermatophilus lesions
· Antiseptic - chlorhexidine or povidone-iodine
· K-permanganate
· Dry skin thoroughly after washing.
Onchocerca
· Microfilaria parasite - adults live in the nuchal ligament.
· Lesions - alopecic flat crusts on the head, neck and ventrum.
· Treatment - MLs (may have permanent leukoderma.)
·
Pemphigus
Type II HS due to antibodies against epidermal cells.
P Foliaceous
Will have scaling and diffuse crusting
P Vulgaris/Bullous
Will see ulceration of the mucocutaneous junctions.
Ringworm
Caused by dermatophytes - mainly trichophyton equinuum.
Leads to scaly lesions with circular areas of alopecia on the head, neck, thorax and girth.
Treatment of Dermatophytosis
Correct underlying immune suppression
Allow lesions to have exposure to sunlight
Antiseptic and anto-fungal solution (such as miconazole)
Mud Fever
Pedal/Pastern Dermatitis
Mainly caused by Dermatophilus congolensis (or Staph aureus)
Infection occurs after damage to the skin from trauma, mites, moisture, UV light etc.
Chronic Proliferative Lymphoedema
Occurs in heavy draft horses.
· Due to a dysfunction of elastin in distal lymphatic vessels.
· Will have lower limb oedema, skin hyperplasia, hyperkeratosis, lichenification, fissures and nodules.
Vitiligo
· Depigmentation commonly in grey horses (Andalusians and Arabs)
· Mainly seen around the eyes and lips.
Alopecia Areata
· Auto-immune disease leading to non-pruritic thinning of mane and tale and areas of alopecia
· Diagnosis - biopsy and histopathology (exclamation shape hair bulb)
Cause of sarcoids.
· Possibly associated with BPV and flies act as vectors.
· Also transmission through direct contact with affected horses and cattle.
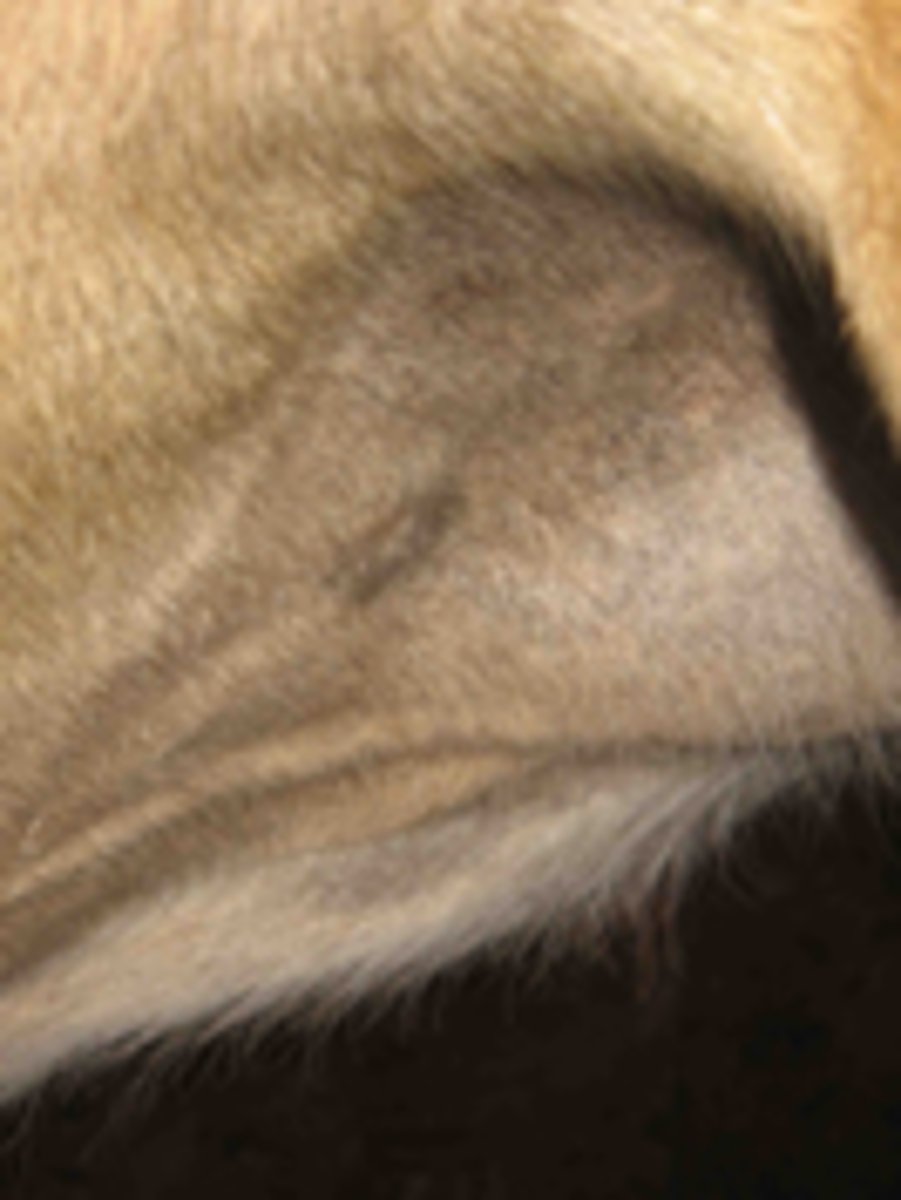
Occult Sarcoid
Flat, grey, hairless (may become mildly hyperkeratotic)
Superficial and usually mild.
Commonly on face, neck and groin.

Verrucose Sarcoid
Rough and hyperkeratotic.
Wart-appearance
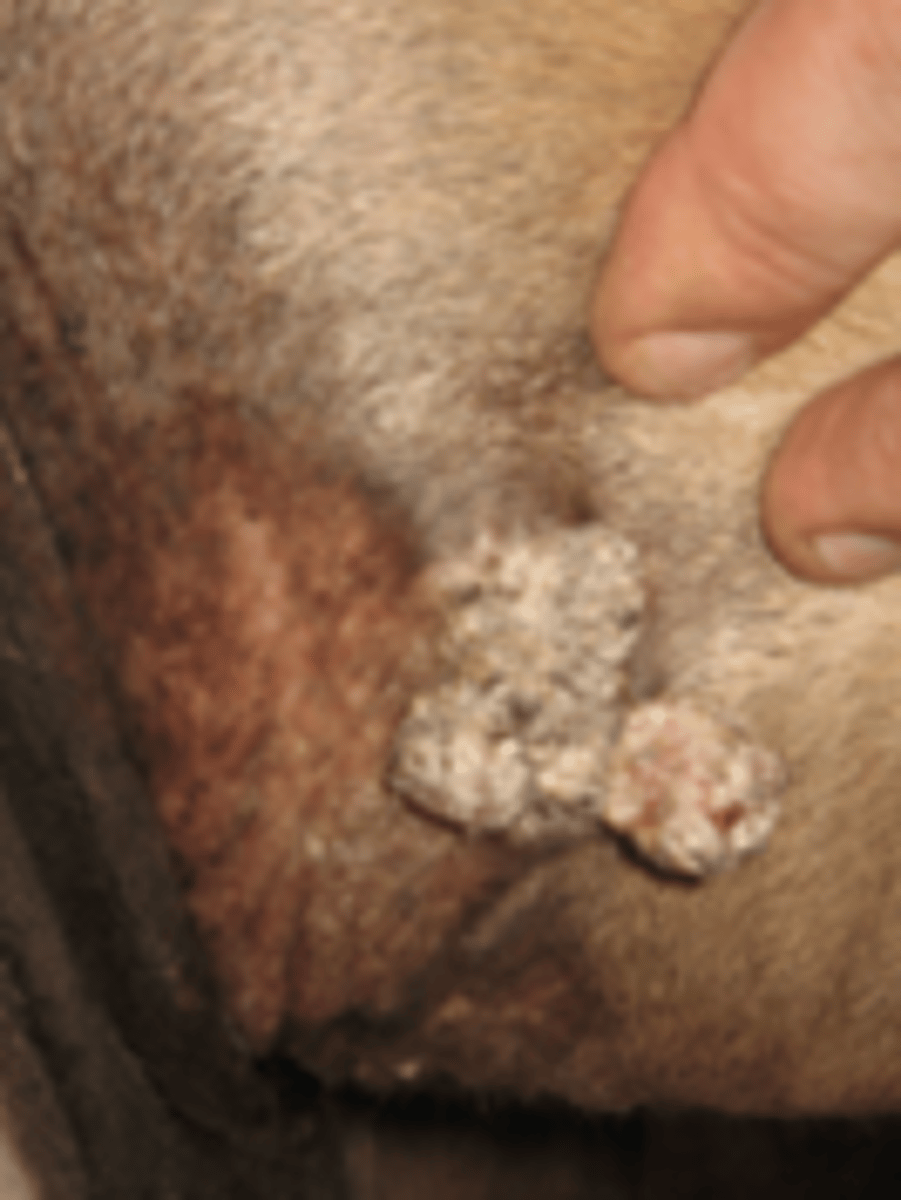
Nodular Sarcoid
Discrete, solid nodules under thin and shiny skin.
Type A - confined to SC tissue
Type B - involvement of overlying skin.
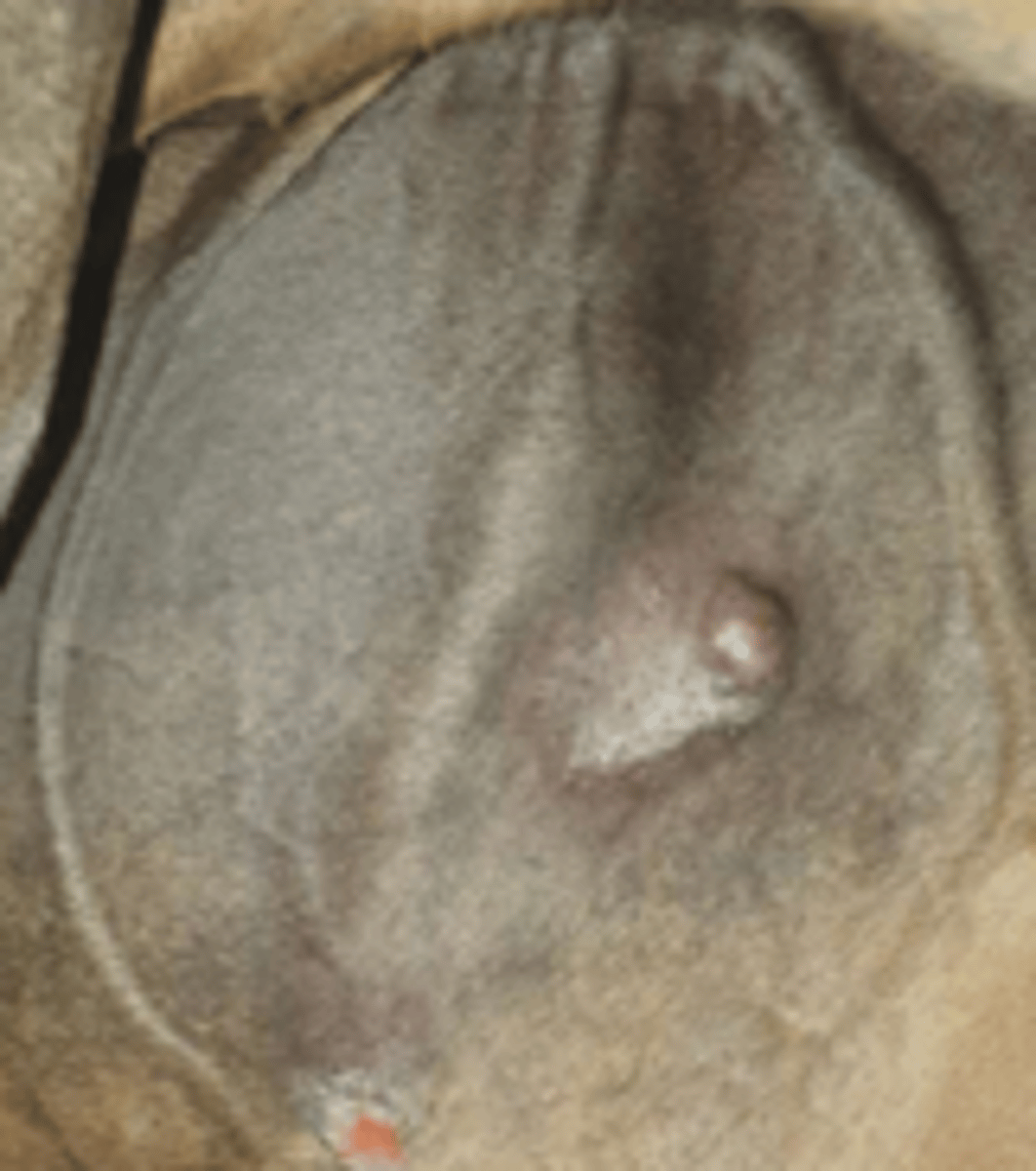
Fibroblast Sarcoid
Fleshy masses which appear erupted, pink and ulcerated.
Can be invasive
Type I - pedunculated with a small base under the skin.
Type II - wide base and diffuse margins.
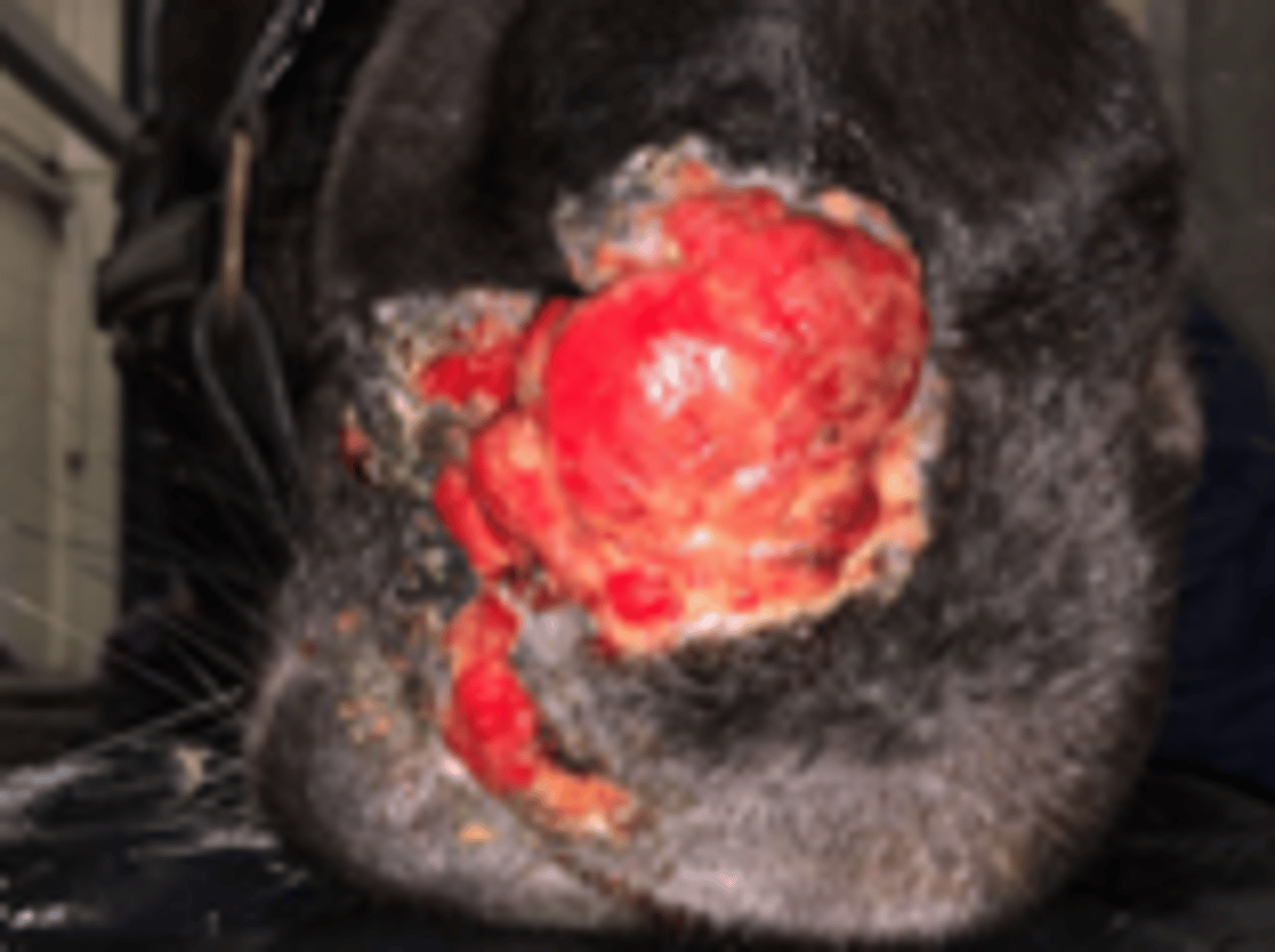
Malevolent Sarcoid
Aggressive, rare form of sarcoid that spreads through the skin and along lymph vessels
Usually occur after trauma or failed treatment.
Sarcoid Treatment
Surgical excision
Laser excision
Topical treatment
Intralesional treatment
Electrochemotherapy
Vaccination
Topical treatment of sarcoids
5-fluorouracil, Mitomycin C and AW5 Cream
Requires multiple applications
Only used for low mass burdens
Intralesional therapy for sarcoids
Mitomycin C, Stelfonta and Cis/Carboplatin
Injected directly in the mass
Electrochemotherapy
Uses electric field pulses to increase cell membrane permeability and improve response to chemotherapy - often around the eyes.
Sarcoid Vaccination
Autologous nitrogen-deactivated vaccine
Melanomas
· Commonly found in grey horses (higher incidence in lighter grey)
o Due to a gene mutation causing changes in melanocyte behaviour.
o Incidence also increases with age.
· Often in the perineum, tail, parotid region, lips, or eyes.
Melanocytic naevi
Single, discrete nodule
Dermal melanoma
Small nodule in deeper dermis
Dermal melanomatosis
Large melanomas commonly around the perineum
Malignant melanoma
Rare and very invasive. Commonly around the tail.
Often no longer pigmented.
Treatment of melanomas
Surgical removal
Vaccination may prevent formation and spread.
Squamous Cell Carcinoma
· Commonly found at found at mucocutaneous junctions such as the urogenital region and eye (mainly third eyelid).
SCC Risk Factors
· More common in geldings (smegma is carcinogenic and as geldings do not erect their penis, it is not regularly cleaned)
· UV radiation (sun) also increases risk.
· EcPV2 (Equine Papilloma Virus) virus.
Treatment of SCC
Surgical (may require phallectomy)
Lesions on the mane, tail and ventral line
Sweet itch
Lesions on the tail base
Oxyuris equi, insect-bite hypersensitivity, Lice (+ trunk)
Lesions on the chest, neck and face
Dermatophytosis
Lesions on the back, rump and face
Rain scald
Lesions on the trunk, neck and head
Atopy or lice
Lesions on the back and girth
Contact dermatitis.
Fungal culture medium
Saboureau's dextrose sugar.
Type I HS
IgE mediated and involves histamine release by mast cells.
· Allergy
Insect bite hypersensitivity.
Type II HS
IgG mediated and associated with complement and antibody binding.
- Pemphigus complex
Type III HS
Immune complex deposition and neutrophil activation
- Vasculitis
- Purpura haemorrhagica
- Lupus
Type IV HS
T-cell mediated (often granuloma formation with recruitment of mono-nuclear cells (monocytes and tissue macrophages))
- Insect bites
- Drug reactions