PHS 3105 - Ch 14 (NO Cranial Nerves)
1/55
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Chapter 14 - The Brain and Cranial Nerves (In depth Cranial Nerves Knowt in a different flashcard set)
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
56 Terms
Adult Brain
__% of body’s nervous tissue
Average weight: __ kg (__ lb)
“Typical” volume: __ mL
Volume range: __ to __ mL
97% of body’s nervous tissue
Average weight: 1.4 kg (3 lb)
“Typical” volume: 1200 mL
Volume range: 750 to 1200 mL
Brains of males are about 10% larger than those of females
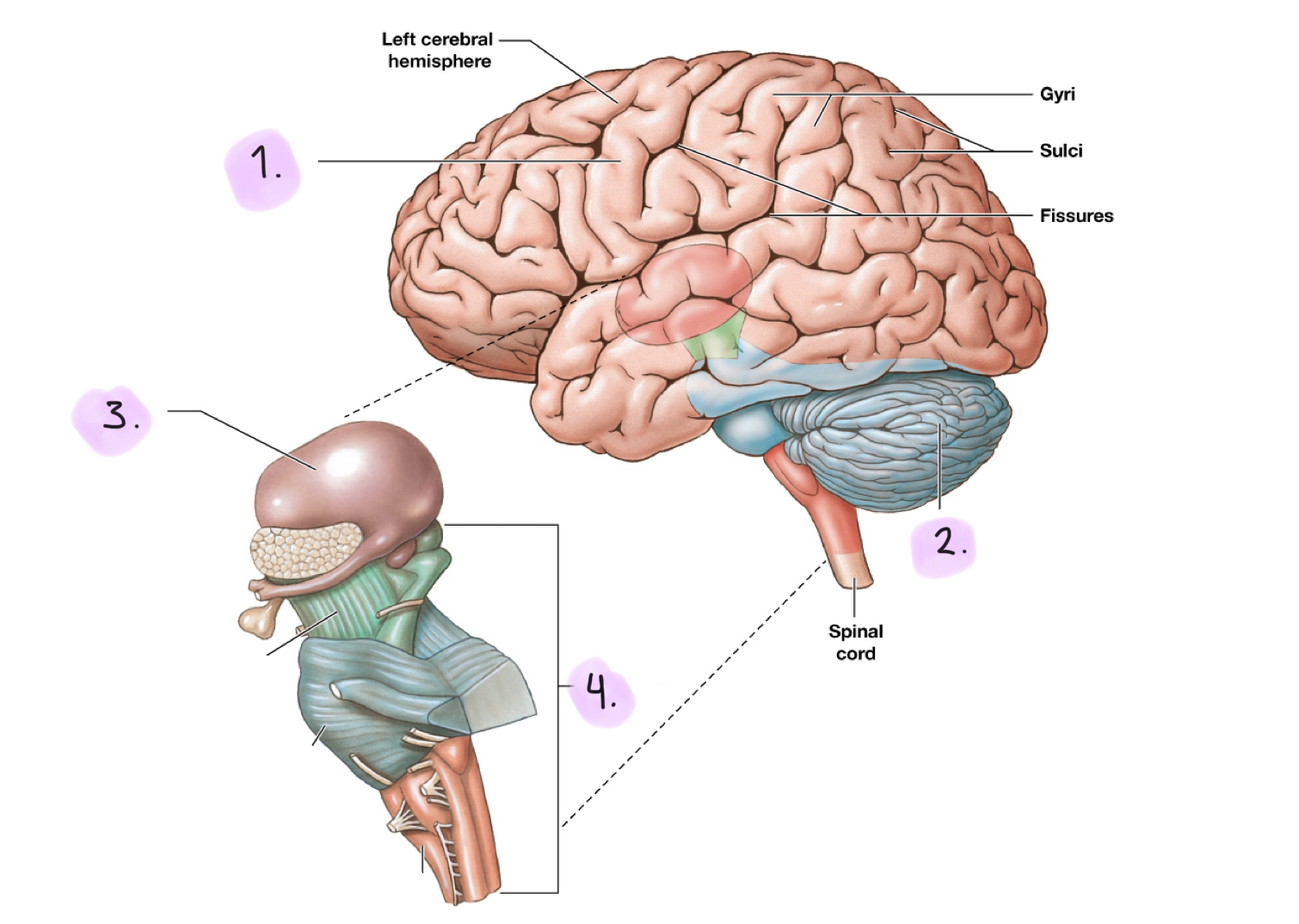
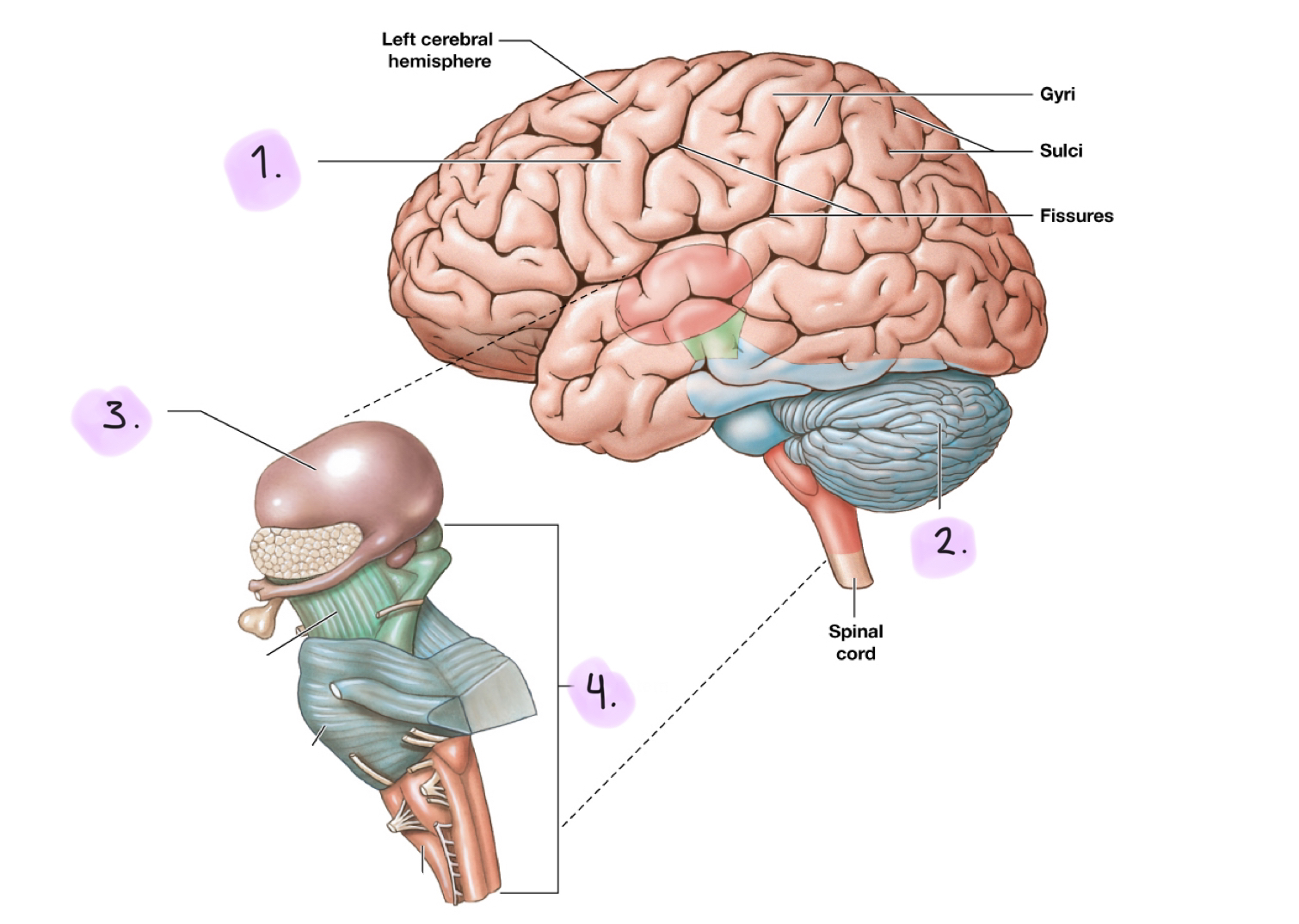
Regions of the brain
__
__
__
__
Cerebrum
Cerebellum
Diencephalon
Brainstem
Red nucleus (midbrain)
Recieves input from the cerebrum and cerebellum and issues subconsious motor commands.
Cerebellum: Balance
Walking and talking subconsiously
Substantia nigra (midbrain)
Produces dopamine (pleasure) that inhibits activity of the basal nuclei of cerebrum.
Affected by Parkinson’s disease
Cerebrum
Largest part of adult brain
Controls sensation and complex movement
Controls higher mental functions such as conscious thoughts, intellect, memory, etc.
Divided into left and right cerebral hemispheres
Cerebral cortex: Highly folded superficial layer of gray matter
Gyri, sulcus, fissures
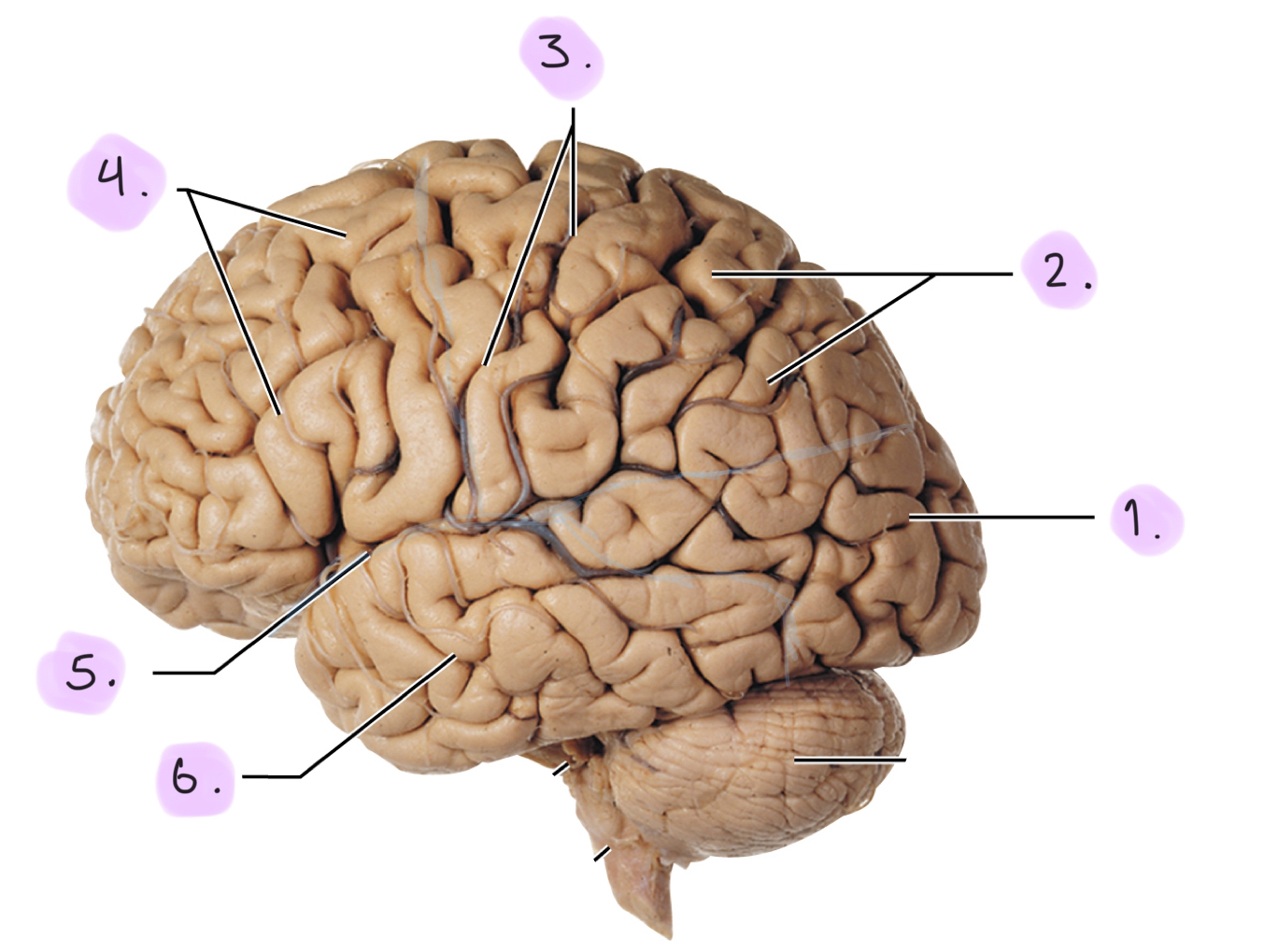
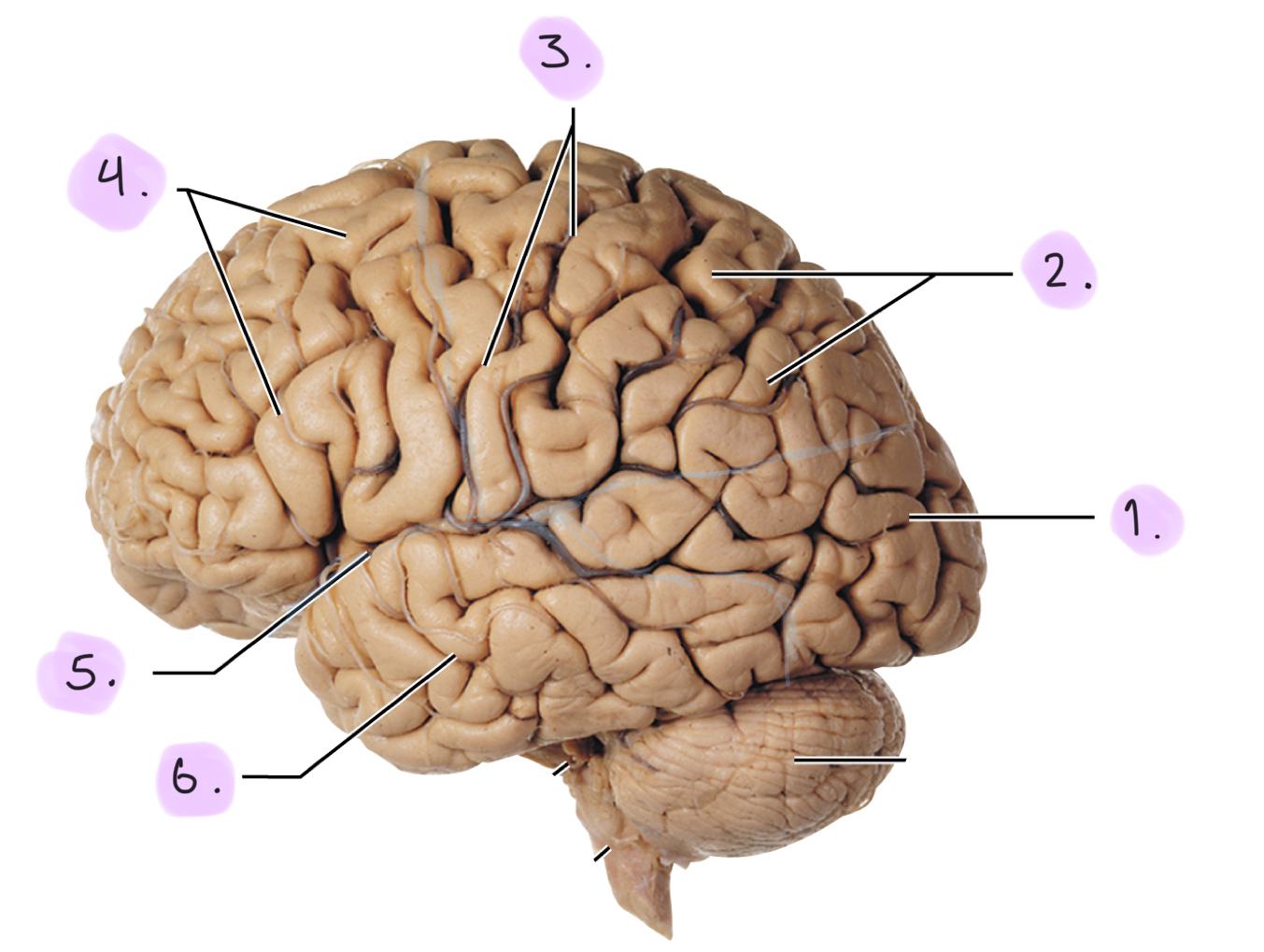
Structure of the cerebrum (lobes + sulci)
__
__
__
__
__
__
Occipital lobe
Parietal lobe
Central sulcus: Divides parietal lobe from frontal lobe
Frontal lobe
Lateral sulcus: Divides frontal lobe from temporal lobe
Temporal lobe
Not listed: Parieto-occipital sulcus: Divides parietal lobe from occipital lobe
Gyri (cerebrum)
Rounded elevations that increase the surface area
Sulci (cerebrum)
Shallow depressions between gyri
☆ Sulci, sulk, sinking/depressions
Fissures (cerebrum)
Deeper grooves
Cerebellum
Maintain balance and equilibrium of body. conscious and subconscious movements; and perception (coordinates)
Second-largest part of brain
Automatic processing and coordinating center (multitask)
Two hemispheres
Covered by gray matter (cerebellar cortex)
Cerebellar cortex & cerebellar nuclei control body movement
Split by vermis
Cerebellar peduncles
Cerebellar peduncles (+ 3 peduncles)
Tracts that link the cerebellum to other brain structures
Superior cerebellar peduncles: link to midbrain, diencephalon and cerebrum
Middle cerebellar peduncles: link to the pons
Inferior cerebellar peduncles: link to the medulla oblongata and spinal cord
Ataxia (cerebellum)
Disturbance in musclar coordination caused by damage from trauma or stroke
Alcohol intoxication can cause temporary ataxia
Diencephalon
Integrates sensory information with motor commands at the subconscious level
Contains:
Epithalamus
Thalamus
Hypothalamus
Lateral geniculate body: Receives visual information, sends to visual centers
Medial geniculate body: Receives auditory information, sends to auditory centers
Epithalamus (diencephalon)
Roof of diencephalon, superior to third ventricle
Anterior: Choroid plexus of the lateral ventricles
Posterior: Pineal gland secretes melatonin which regulates day-night cycles (circadian-rhythm) and reproductive function
Thalamus (diencephalon)
Relays and processes sensory information
Anterior: Limbic system controls emotion
Medial: Provides emotional awareness and understanding. Connects hypothalamus to cerebrum
Ventral: Sensory information about touch,(motor) pressure, pain, temperature, and proprioception to cerebral cortex
Hypothalamus (diencephalon)
Controls emotion, autonomic functions, hormone production, and visceral regulation
Infundibulum: Narrow stalk that connects the hypothalamus to the pituitary gland
Secretes ADH (supra-optic nucleus) and oxytocin (periventricular nucleus)
Regulates body temperature (pre-optic area)
Emotional and behavioral drives:
Feeding center: sensation of hunger
Thirst center: sensation of thirst
Satiety center: regulates food intake
Drives: unfocused “impressions” originating in the hypothalamus
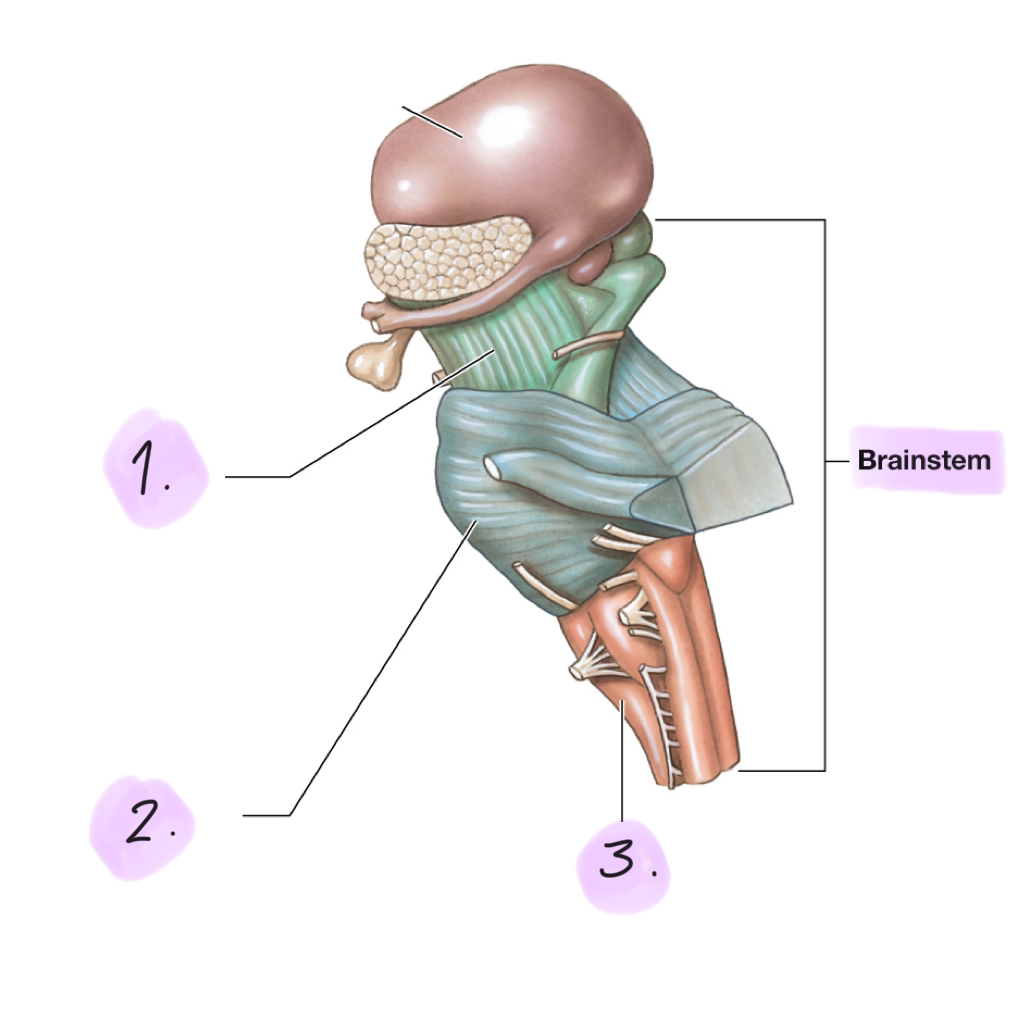
Brainstem
__
__
__
Processes and relays information between the spinal cord and the cerebrum and cerebellum.
Includes:
Midbrain
Pons
Medulla oblongata
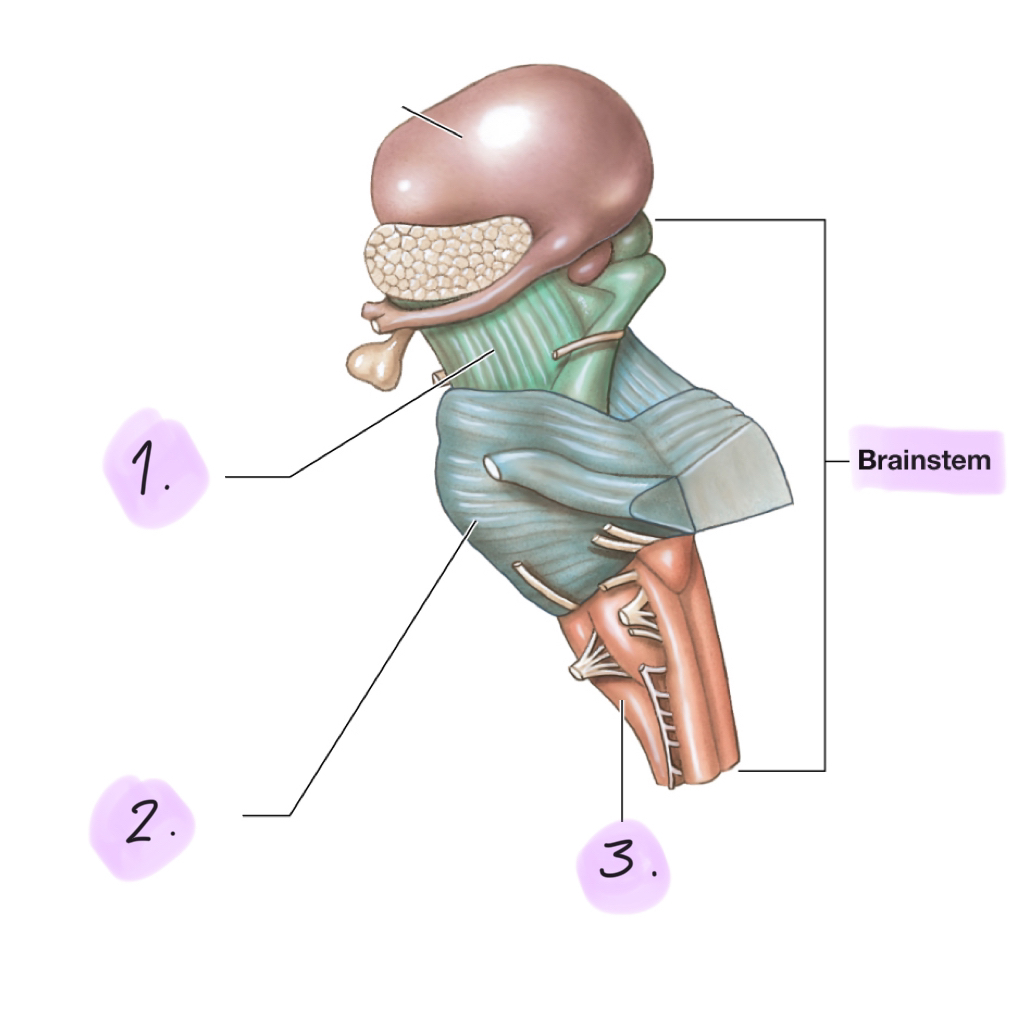
Midbrain (brainstem)
Processes visual and auditory information and associated reflexes and helps maintain consciousness
Superior colliculi: Process visual sensations and reflexes in response to visual stimuli
Inferior colliculi: Process auditory sensations and reflexes in response to auditory stimuli
☆ Eyes are slightly superior to ears, visual is superior.
Pons (brainstem)
Contains tracts (collections of CNS axons), relay centers, and nuclei involved in somatic and visceral motor control
Transverse Connects the cerebellum to the brainstem
Ascending tract: Sensory
Descending tract: Motor
Medulla oblongata (brainstem)
Relays sensory information to the thalamus and contains centers that regulate autonomic functions, such as heart rate, breathing, and blood pressure.
Cardiovascular centers: Adjust heart rate, peripheral blood flow, and reflex activity
Connects the brain to the spinal cord
Inferior portion has a narrow central canal
Ventricles (4 Ventricles)
Chambers in the brain lined with ependymal cells
Two lateral ventricles: One in each hemisphere, separated by medial partition
Third ventricle: In the diencephalon. Communicates with lateral ventricles via an interventricular foramen
Fourth ventricle: Extends into the medulla oblongata. Joins central canal of spinal cord.
Connects with third ventricle via a narrow canal in midbrain called cerebral aqueduct
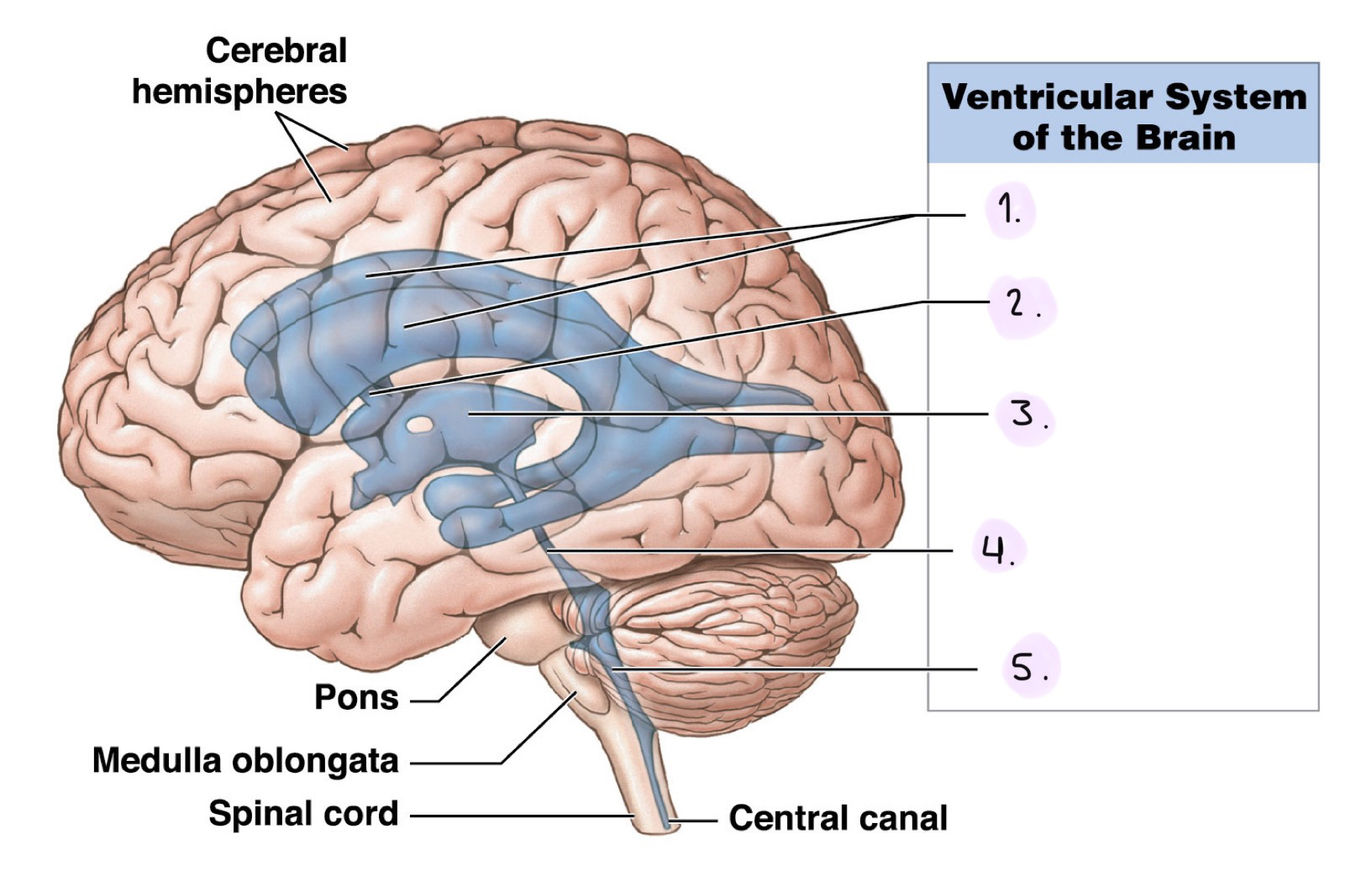
Label the Ventricular System (Lateral View)
__
__
__
__
__
Lateral ventricles
Interventricular foramen
Third ventricle
Cerebral aqueduct
Fourth ventricle
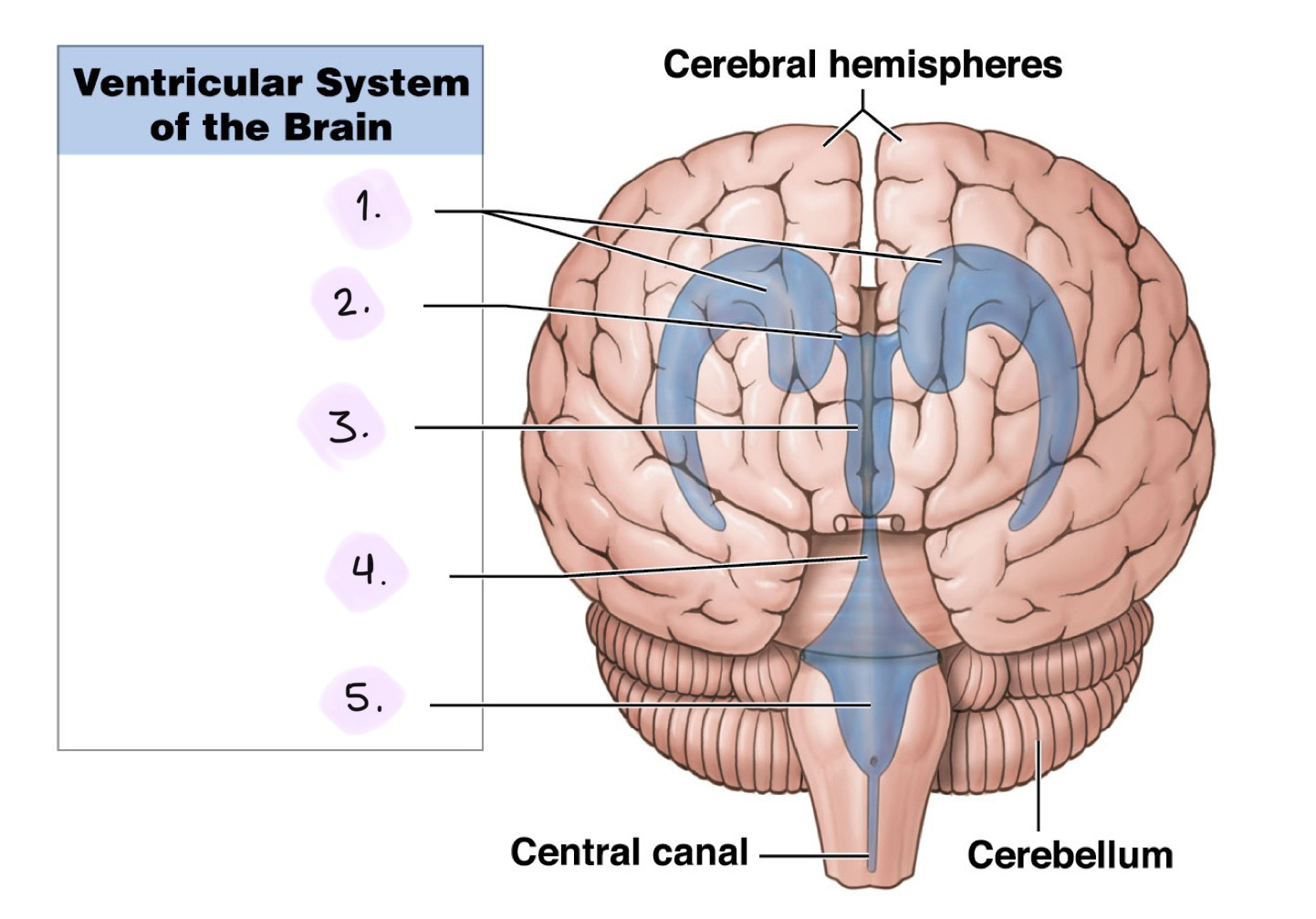
Label the Ventricular System (Anterior View)
__
__
__
__
__
Lateral ventricles
Interventricular foramen
Third ventricle
Cerebral aqueduct
Fourth ventricle
How is the brain protected
Physical (3) and Biochemical (1)
Physical protection
Bones of the skull
Cranial meninges
Cerebrospinal fluid
Biochemical protection
Blood brain barrier
Cranial meninges (three layers)
Dura mater
Arachnoid mater
Pia mater
Continuous with the spinal meninges
Dura mater (cranial meninges)
Outermost meningeal layer
Outer fibrous layer (periosteal cranial dura)
Fuest to the periosteum of cranial bones
Inner fibrous layer (meningeal cranial dura)
Dura folds: Extensions of he meningeal cranial dura into the cranial cavity that stablize and support the brain
Dural venous sinuses: Large veins located within the dural folds. Drains head of used blood
☆ Dura, durable, outermost layer
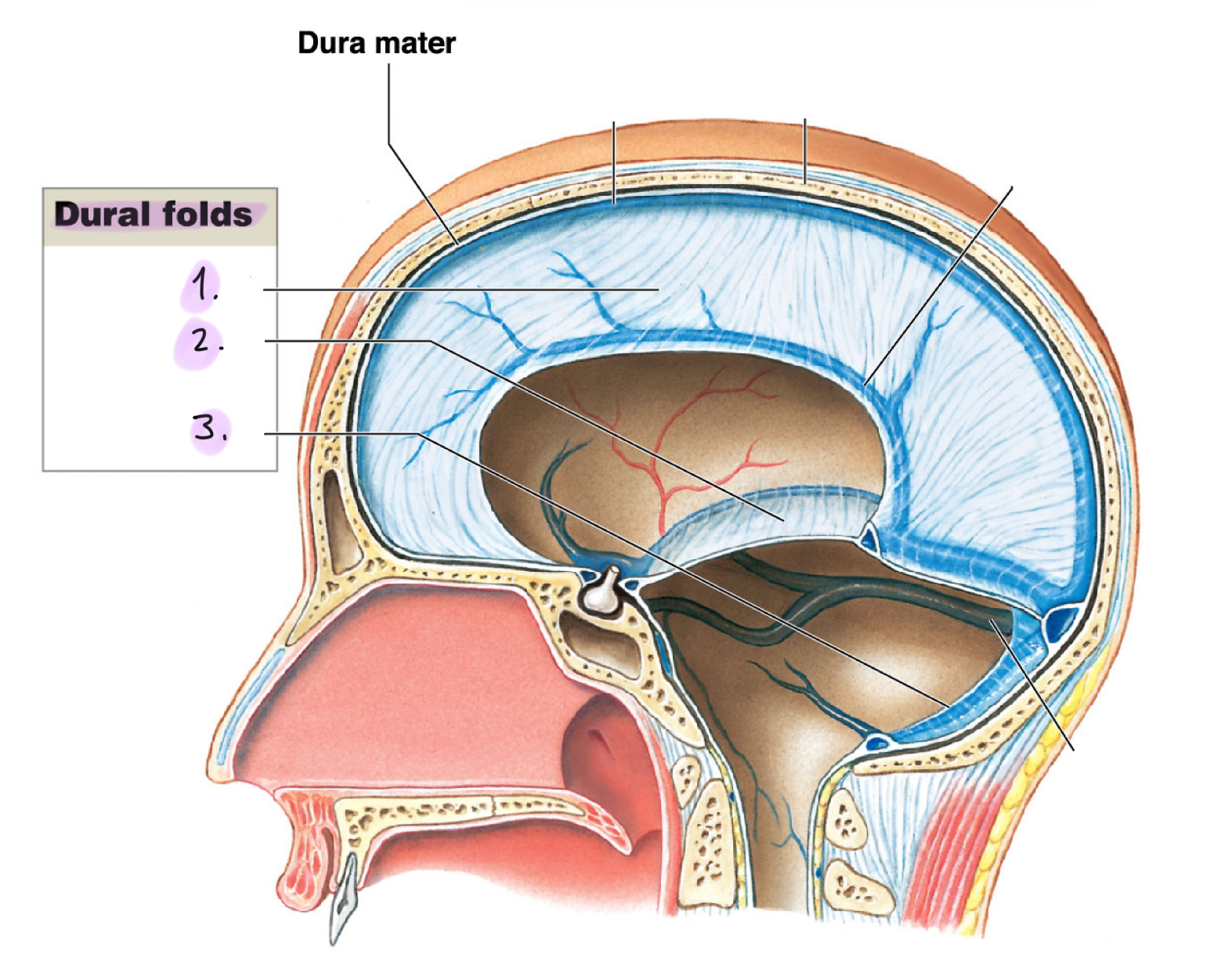
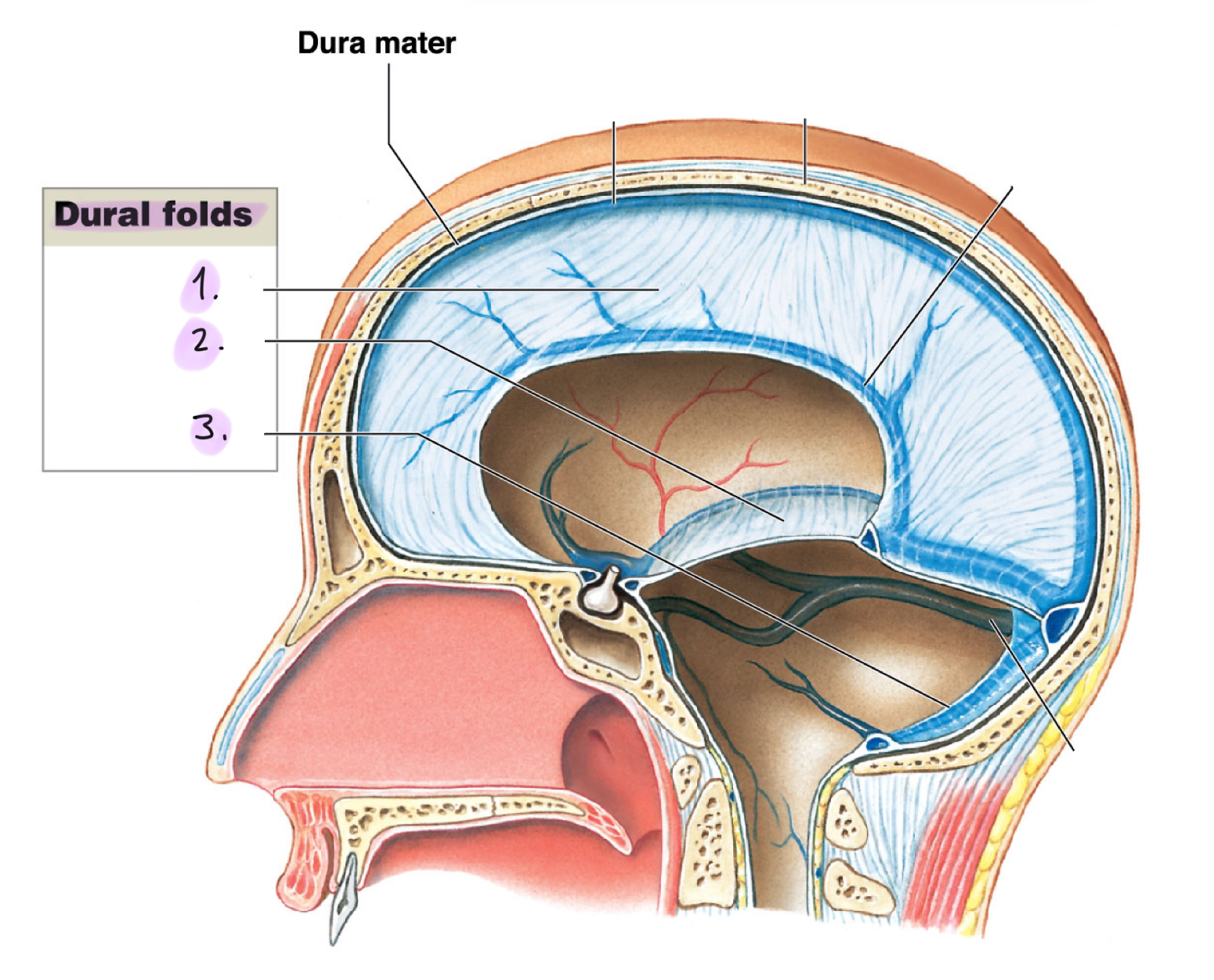
Dura folds (dura mater)
__
__
__
Dural folds drain cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) and holds the brain in position to protect from damage.
Falx cerebri: Projects between the cerebral hemispheres. Contains the superior sagittal sinus and the inferior sagittal sinus
Tentorium cerebelli: Separates cerebrum from cerebellum. Contains transverse sinus
Flax cerebelli: Divides the cerebellar hemispheres below tentorium cerebelli
Arachnoid mater (cranial meninges)
Middle meningeal layer that resembles a spider web
Attaches to the dura mater
Subdural space: Narrow gap between dura mater and arachnoid mater that forms as a result of trauma or disease
Subarachnoid space: Lies between the arachnoid mater and pia mater
Pia mater (cranial meninges)
Innermost meningeal layer which attaches to the surface of the brain
Anchored by astrocytes (form blood brain barrier)
Cerebrospinal fluid (CSF)
Surrounds all exposed surfaces of the CNS
Supports the brain: the brain floats in CSF inside the cranium
Cushions brain and spinal cord
Transports nutrients, chemical messengers, and wastes
CSF cushions brain against sudden jolts and makes it buoyant
Formation of CSF
Choroid plexus: Area in ventricles that secretes (produces) CSF and removes waste from CSF
Specialized ependymal cells
Circulation of CSF
Circulates from choroid plexus → ventricles → central canal (of spinal cord) → materials diffuse → subarachnoid space → fourth ventricle → circulates subarachnoid space → nutrients brought in, waste products taken out.
Cranial trauma
Head injury resulting from impact with an object
Epidural hemorrhage
Blood is forced between the dura mater and the skul; pressure distorts the brain tissue
Subdural hemorrhage
Bleeding beween the dura mater and the arachnoid mater; less pressure, but still can damage the brain tissue
More space, takes longer for pressure to build up, less pressure
Blood supply to the brain
Internal carotid arteries and vertebral arteries deliver nurients and oxygen to the brain
Blood removed from the dural venous by the internal jugular veins
Cerebrovascular diseases
Disorders that interfere with blood supply to the brain
Cerebovascular accident (CVA) / Stroke
Two types:
__
__
☆ Most frequent artery that strokes: __
Stops blood flow to a portion of the brain. Affected neurons begin to die within minutes
Hemorrhagic
Obstructive
☆ Middle meningeal artery
Hemmorrhagic (CVA)
Quicker onset and severe symptoms
☆ Like a burst of a tire; blood is going to shoot out very suddenly
Obstructive (CVA)
Blockage, blood clot; blood can’t get from one spot to another spot.
Blood-brain barrier (BBB)
A bunch of interconnected capillary epithelial cells tightly wound together that isolates CNS from general circulation and protects the brain.
Astrocytes regulate chemical control in the BBB so not everything can penetrate the brain.
Antibiotics to/for the brain:
Need to be lipophilic (fat-type) antibiotic and injected directly
Only lipid-soluble compounds can diffuse through BBB. Ex/ Oxygen, CO2, ammonia, steroids, prostaglandins, small alcohols
Break in blood-brain barrier
Around pituitary gland, directly behind your nose.
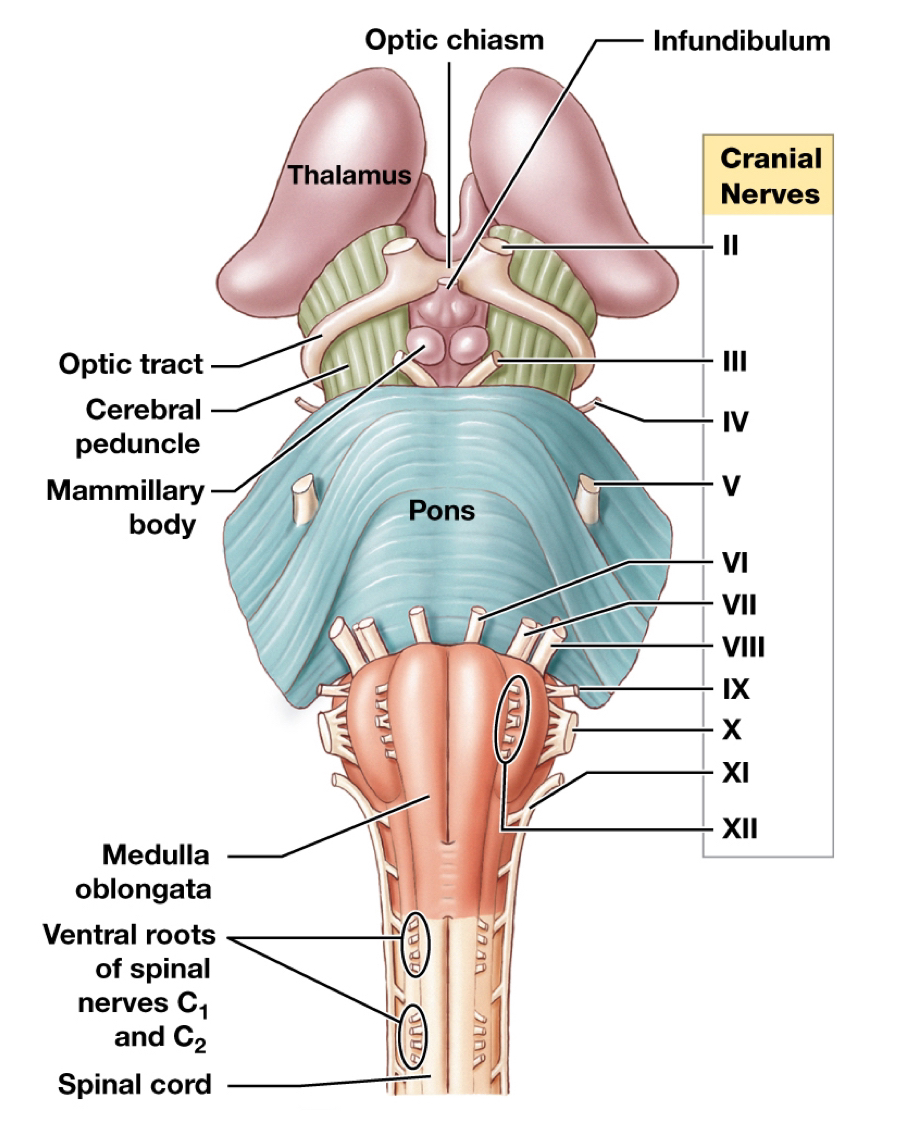
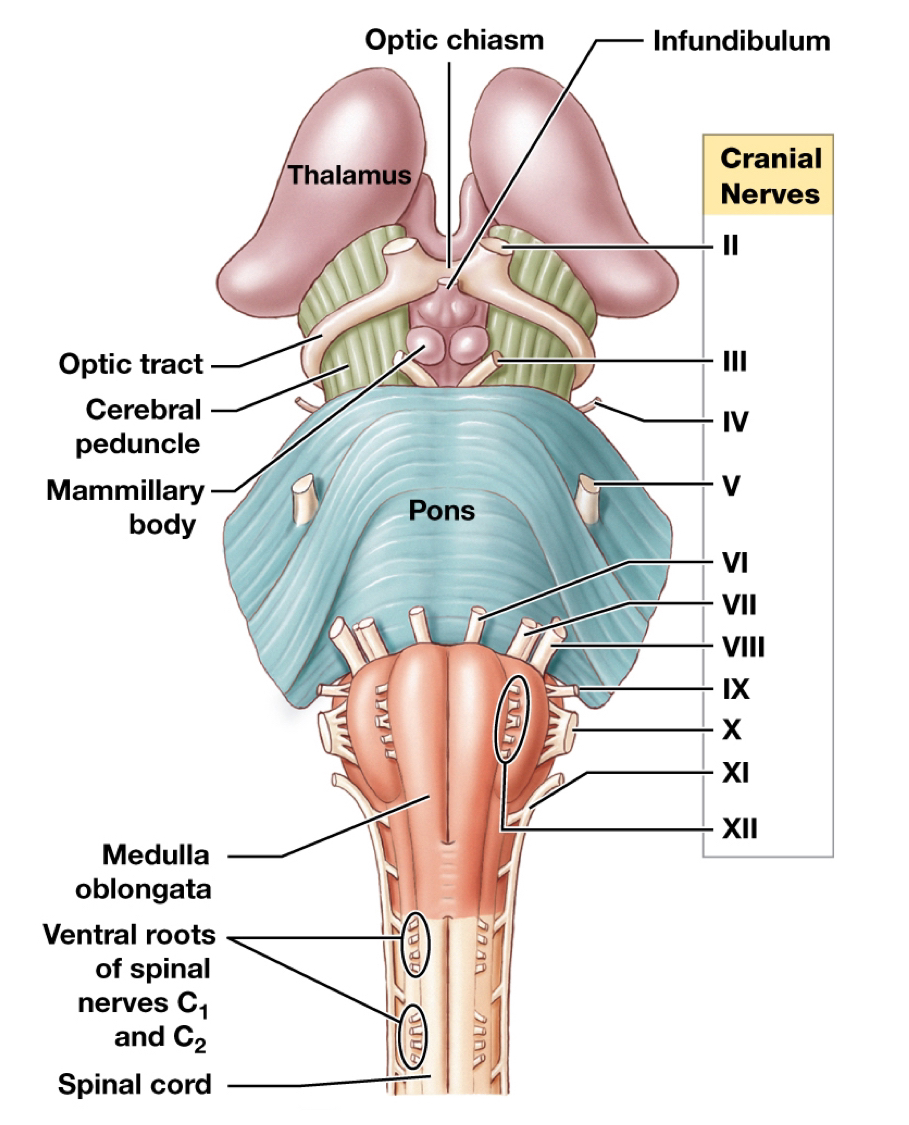
Label the cranial nerves
I: __
Pons:
II: __
III: __
IV: __
V: __
VI: __
VII: __
Between:
VIII: __
Medulla Oblongata:
IX: __
X: __
XI: __
XII: __
I: Olfactory bulb
Pons:
II: Optic nerve
III: Ocularmotor nerve
IV: Trochlear nerve
V: Trigeminal nerve
VI: Abducens nerve
VII: Facial nerve
Between:
VIII: Vestibucochlear nerve
Medulla Oblongata:
IX: Glossopharyngeal nerve
X: Vagus nerve
XI: Accessory nerve
XII: Hypoglossal nerve
Gracile nucleus and Cuneate nucleus
Pass somatic sensory information to the thalamus.
Somatic sensory: Muscles
Solitary nuclei
Receive visceral sensory information, integrate it, and relay it to autonomic centers.
Visceral sensory: Internal organs
Inferior olivary complex
Relays information to the cerebral cortex about somatic motor commands
Cerebral cortex: Brain
Limbic system
Establishes emotional states. Links conscious functions of the cerebral cortex with the autonomic functions of the brainstem. Memory storage and retrieval.
Limbic lobe
Hippocampus: long-term memory
Amygdaloid body (amygdala): sensory and emotional response
Fornix
Hypothalamus
Fornix (limbic system)
Tract of white matter that connects hippocampus with the hypothalamus.
Anterior nuclei of the thalamus
Primary motor cortex (cerebrum)
Controls voluntary skeletal muscles via somatic motor neurons. Found in precentral gyrus in the frontal lobe
Pyramidal cells: neurons of primary motor cortex
Primary somatosensory cortex (cerebrum)
Receives somatosensory information for touch, pressure, pain, vibration, and temperature. Found in postcentral gyrus of parietal lobe
Special sensory cortices (cerebrum)
Visual cortex: Visual, Occipital lobe
Auditory cortex: Auditory, Temporal lobe
Olfactory cortex: Smell, Temporal lobe
Gustatory cortex: Taste, Insula (middle of brain)
Wernicke’s area (Cerebrum)
Responsible for language comprehension. Back of temporal lobe.
Coordinates visual and auditory memories
Patients are not aware of their problem. Words these patients using are not real words.
☆ Wernike’s, w, words
Broca’s area (cerebrum)
Motor speech area, responsible for speech production. Front of brain (left cerebral hemisphere)
Regulates patterns of breathing and vocalization
Damage results in:
Aphasia: inability to speak or read
Dyslexia: inability to comprehend or use written words
☆ Broca’s, b, broken speech
Hemispheric lateralization
Left cerebral hemisphere: __
Right cerebral hemisphere: __
Left cerebral hemisphere
Reading, writing, and math
Speech and language
Decision making
Right cerebral hemisphere
Analyzes sensory information: touch, smell, sight, taste
Recognition of faces and voice inflection
Electrocephalogram (EEG)
Pet scan or MRI
Alpha waves: Healthy, awake adults at rest with eyes closed
Beta waves: Intense concentration or mentally stressed adults. High-frequency
Theta waves: Children or intensely frustrated adults; may indicate brain disorder
Delta waves: Asleep infants or awake adults with brain damage. Low-frequency
Seizure
A temporal cerebral disorder accompanied changes in the pattern of electrical activity in the brain and by uncontrolled movements and unusual sensations.
☆ SA node - AV node (Heart: lub-dub) Signal stays in AV node for 0.003 miliseconds